
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431 VIKOR Phan Nguyen Ky Phuc September 19, 2024 1 Vikor
The(VIKOR) method was developed for multicriteria optimization of complex systems. It
determines the compromise ranking list, the compromise solution, and the weight stability
intervals for preference stability of the compromise solution obtained with the initial (given) weights.
This method focuses on ranking and selecting from a set of alternatives in the presence of conflicting criteria.
It introduces the multicriteria ranking index based on the particular measure of “closeness” to the “ideal” solution
The procedures of VIKOR can be described as follows.
• Set of alternatives, A • Set of criteria C • Set of weights W
• Set of rating X = {xac∣a ∈ A,c ∈ C} , xac denotes the rating of alternative a corresponding to criteria c
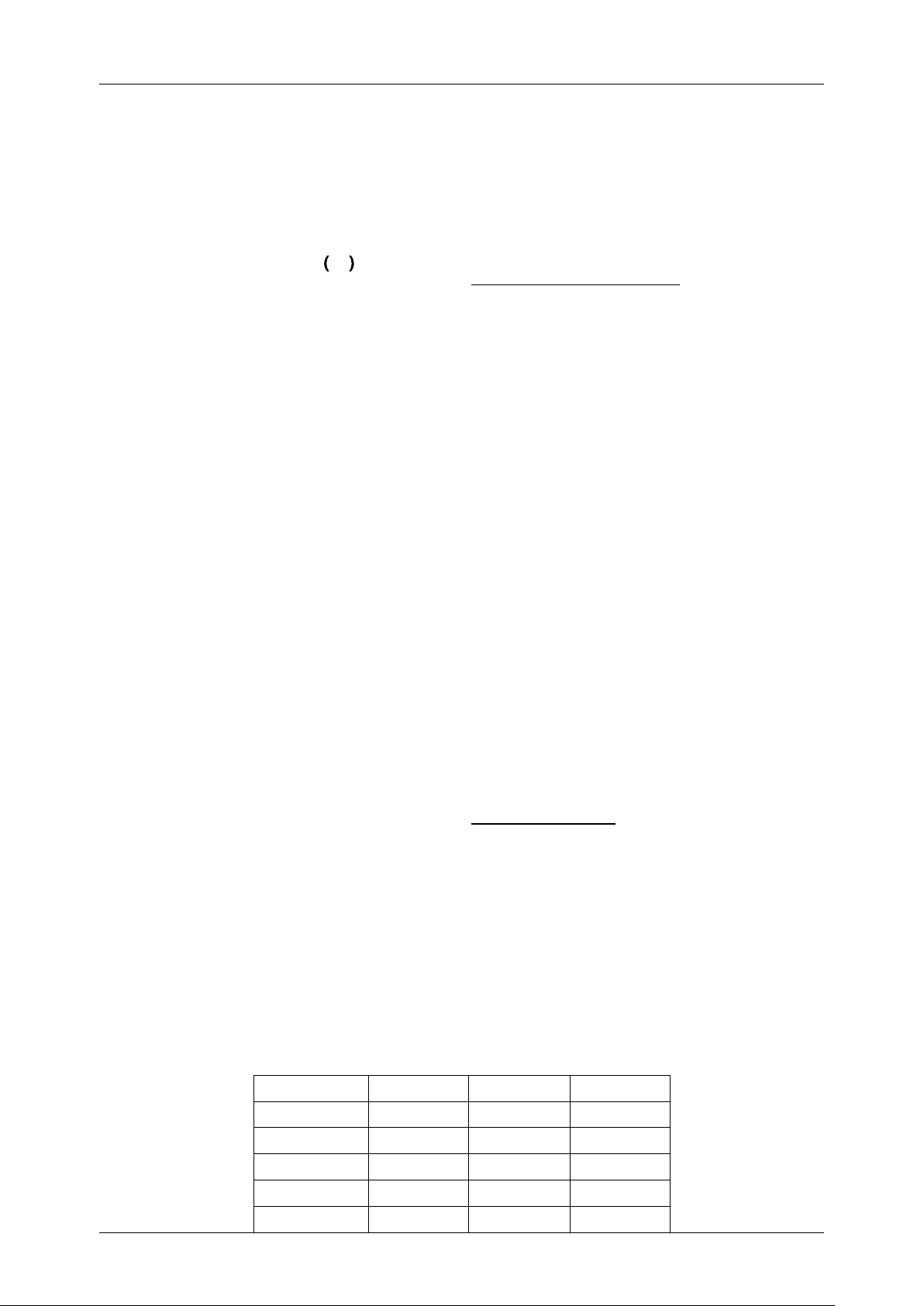
• The information table I = (A,C,X,W) can be represented as shown in Table below
Table 1: Information Table of VIKOR Alternatives C1 C2 ⋯ Cm A1
x11 x12 ⋯ x1m A1
x21 x22 ⋯ x2m ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ An
xn1 xn2 ⋯ xnm W
w1 w2 ⋯ wm 1
Development of the VIKOR method started with the following form of Lp−norm-metric For each column, find: lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
The maximum value of the column i.e., denoting as , The
minimum value of the column, i.e., denoting as
For benefit criteria: larger is better Normalize elements as:
For cost criteria: smaller is better Normalize elements as:
Development of the VIKOR method started with the following form of Lp−norm-metric: Within the VIKOR method, and
are used to formulate ranking measure. −norm Sa = La1
=∑[wc × rac]∀a ∈ A c∈C
Ra = Lk∞−norm = max[wc × rac]∀a ∈ A c
S+ = mina Sa or let S+ = 0 be zero gap, i.e., achieve the aspired level, i.e. minimum regression
S−= maxa Sa or let S−= 1 be the worst level-maximum regression
R+ = mina Ra or let R+ = 0 be zero gap, i.e., achieve the aspired level, i.e. minimum regression
R−= maxa Ra or let R−= 1 be the worst level-maximum regression Compute
when S+ = 0, S− = 1, R+ = 0, and R− = 1. v is introduced as the weight of the strategy of “the majority
of criteria” (or “the maximum group utility”), here v = 0.5.
Qa = v × Sa +(1 − v)× Ra
Rank the alternatives, sorting by the values S, R, and Q, in decreasing order. The results are three ranking lists.
The alternative a1 is the best atternative if it satisfies following conditions 03 MCDM Page 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Ho Chi Minh City International University MCDM
Industrial Systems Engineering Department
Lecturer: Phan Nguyen Ky Phuc
• The alternative a1, which is ranked the best by the measure Q (minimum)
• Satisfy C1 Condition:”Acceptable advantage”: 1
Q a2 − Q(a1) ≥ number of alternatives − 1
where a2 is the alternative with second position in the ranking list by Q;
• Satisfy C2 Condition. ”Acceptable stability in decision making”:
Alternative a1 must also be the best ranked by S or/and R. This compromise solution is
stable within a decision-making process, which could be: ”voting by majority rule”
(when v > 0.5 is needed), ”by consensus” v ≈ 0.5, or ”with vote” (v < 0.5). Here, v is the
weight of the decision-making strategy ”the majority of criteria” (or ”the maximum group utility”).
If one of the conditions is not satisfied, then a set of compromise solutions is proposed, which consists of:
• Alternative a1 and a2 if only condition C2 is not satisfied, or
• Alternative a1,a2,⋯,an if only condition C1 is not satisfied; and an is determined by the
relation Q(an)− Q(a1) < number of alternatives
1 −1 for maximum n (the
positions of these alternatives are ”in closeness”). 1.1 Example
Consider a manager trying to evaluate if a new facility is needed to replace the current
system. Assume three criteria, durability, capability, and reliability, are considered by the
manager and the preferred ratings of each alternative can be expressed as shown in Table
below Then we normalize the result
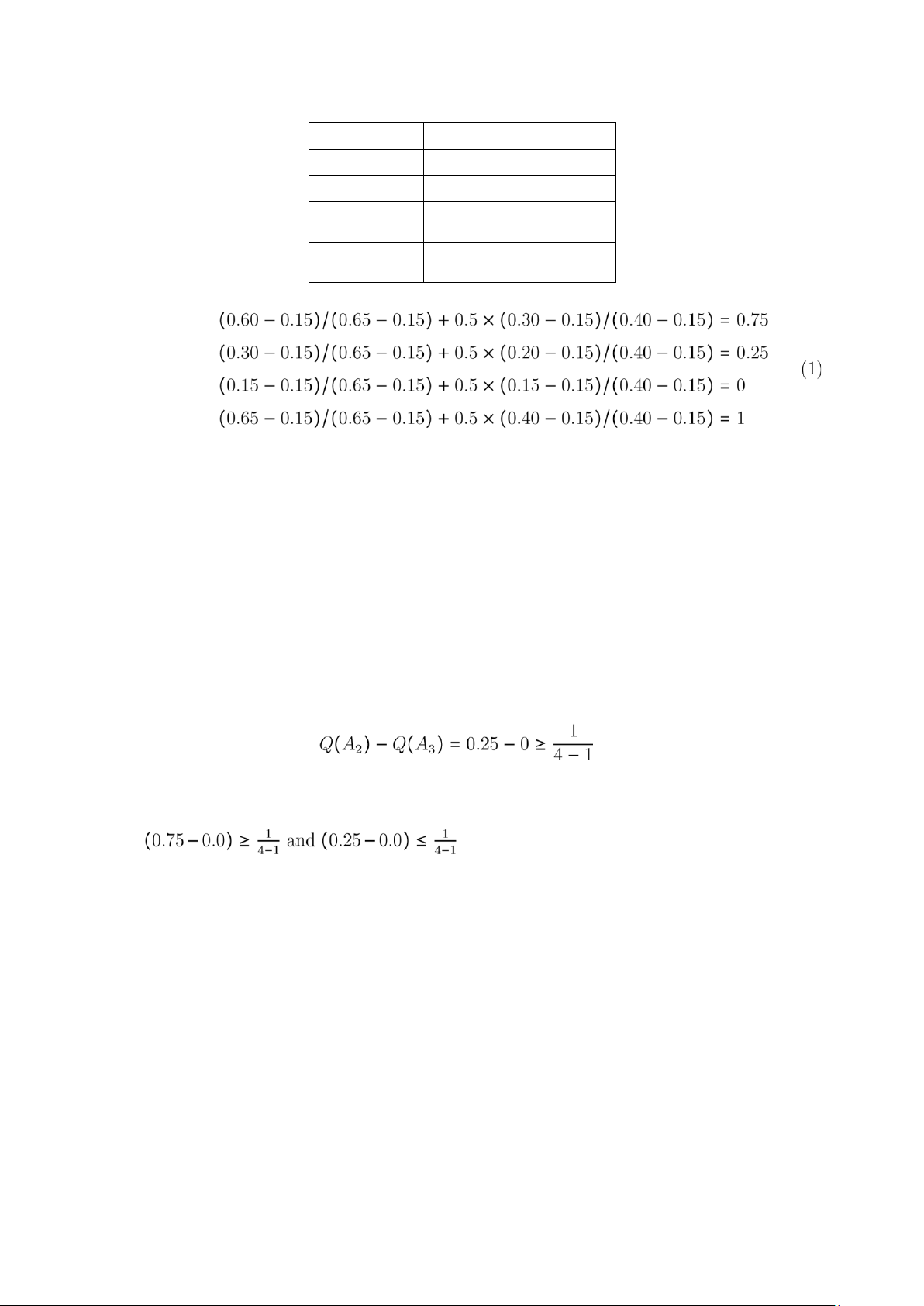
Alternatives Durability Capability Reliability A1 5 8 4 A2 7 6 8 A3 8 8 6 A3 7 4 6 Weights 0.3 0.4 0.3 03 MCDM Page 3 lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Ho Chi Minh City International University MCDM
Industrial Systems Engineering Department
Lecturer: Phan Nguyen Ky Phuc Alternatives Sj Rj A1 0.60 0.3 A2 0.30 0.2 A3 0.15 = S+ 0.15 = R+ A4 0.65 = S− 0.4 = R− From the result of Table Q1 = 0.5 × Q2 = 0.5 × Q3 = 0.5 ×
Q4 = 0.5 ×
Vector Q = [0.75,0.25,0,1]
In case of simple rank, i.e the smaller Q score is the better, the ranking result is
A3 ≻ A2 ≻ A1 ≻ A4
Check dominance based on C1 and C2
C1 condition is checked
C1 condition is NOT satisfied C2 condition Since
, so only 2 alternatives A3 and A2 are selected.