



Preview text:
Control Processes and Systems 1. Managerial Control
Importance of controlling
Types of controls
Internal and external control
2. The Control Process
Establish objectives and standards
Measure actual performance
Compare results with objectives
Take corrective action
3. Control Tools and Techniques
Project management and control Inventory control Breakeven analysis Financial controls Balanced scorecards
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Managerial control Importance of controlling
The process of measuring performance and taking action to ensure desired results
Has a positive and necessary role in the management process
Ensures that the right things happen, in the right way, at the right time
Benefit: Organizational learning (Example: After-action review) TYPES OF CONTROL
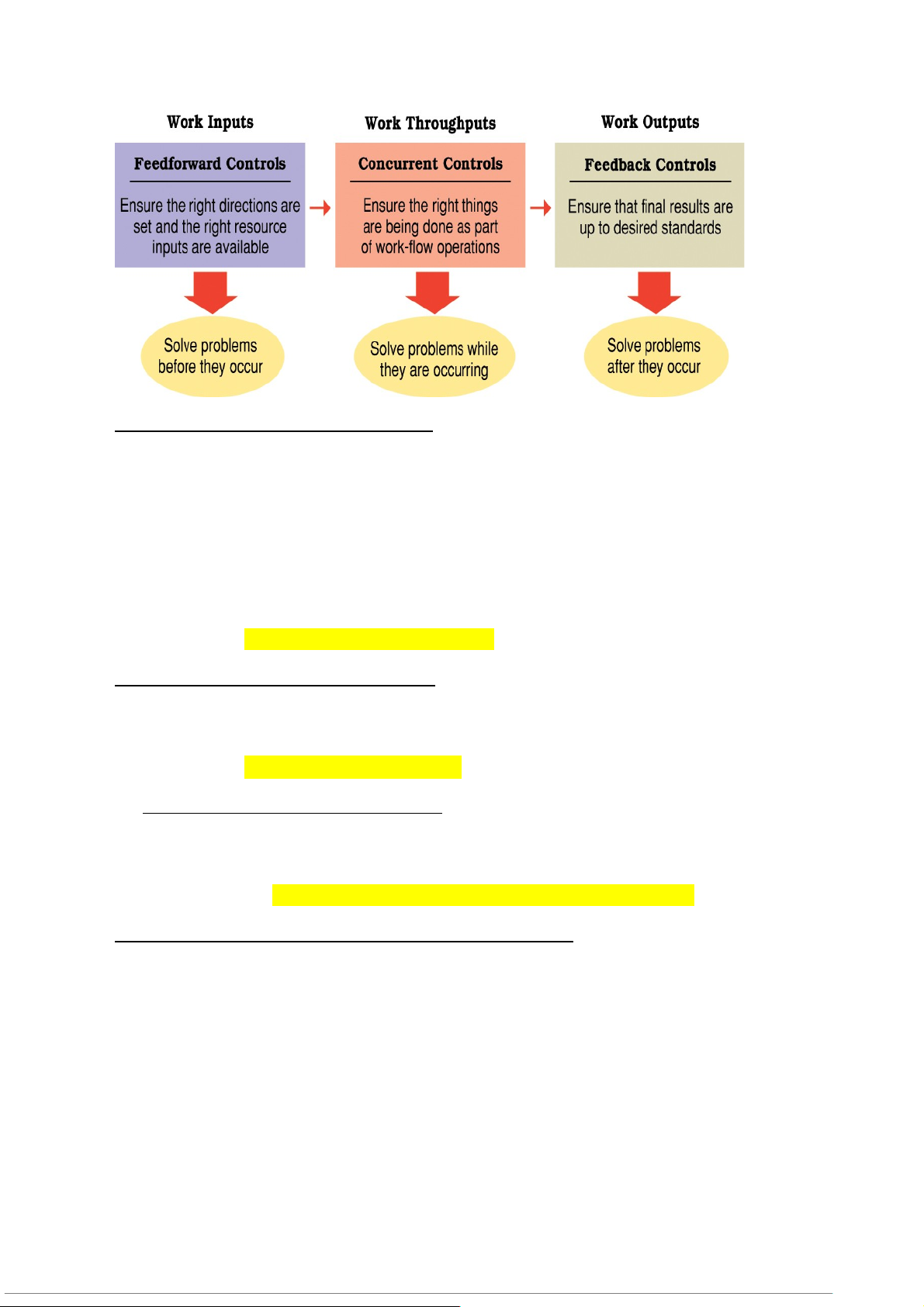
-Feedforward controls (kiểm soát đầu vào)
Employed before a work activity begins Ensures that: Objectives are clear
Proper directions are established Right resources are available
Goal is to solve problems before they occur
-Concurrent controls (kiểm soát đồng thời)
Focus on what happens during work process
Monitor ongoing operations to make sure they are being done according to plan
Goal is to solve problems as they occur - Feedback controls (kiểm soát phản hồi)
Take place after work is completed
Focus on quality of end results
Goal is to solve problems after they occur and prevent future ones
-Internal and external control (kiểm soát nội bộ và bên ngoài)
+ Internal control: Allows motivated individuals and groups to exercise self-discipline in
fulfilling job expectations (cho phép nhân viên tự kỷ luật bản thân để hoàn thành cv)
+ External control: Occurs through personal supervision and the use of formal
administrative systems (sd hệ thống để qly và giám sát)
Ví dụ: Công ty sử dụng KPI để đánh giá nhân viên
CÁC HÌNH THỨC KIỂM SOÁT KHÁC
-Self-control (nv tự kiểm soát)
Internal control that occurs through self-discipline in fulfilling work and personal goals and responsibilities
-Bureaucratic control (kiểm soát quan liêu)
Influences behavior through authority, policies, procedures, job descriptions, budgets, and day-to-day supervision
Ví dụ: Một công ty có quy trình phê duyệt chi phí chặt chẽ để tránh lãng phí.
-Clan control (kiểm soát theo văn hóa dnghiep)
Influences behavior through norms and expectations set by the organizational culture
2. THE CONTROL PROCESS
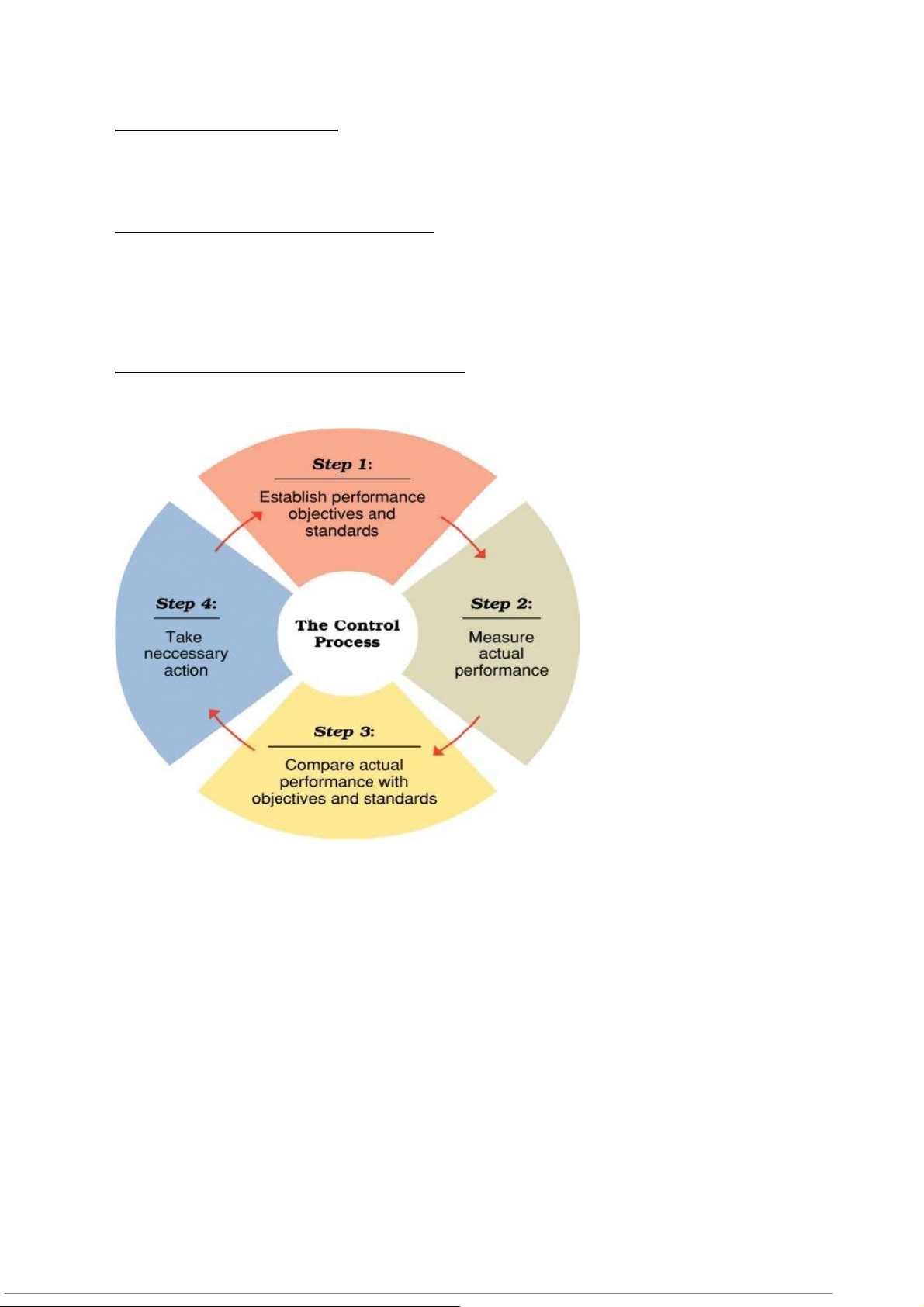
Step 1 — establishing objectives and standards – thiết lập lục tiêu và quy chuẩn -Output standards
Measure performance results in terms of quantity, quality, cost, or time -Input standards
Measure effort in terms of amount of work expended in task performance
Step 2 — measuring actual performance – đo lường hiệu suất thực tế
-Goal is accurate measurement of actual performance results and/or performance efforts
-Must identify significant differences between actual results and original plan
-Effective control requires measurement
Step 3 — comparing results with objectives and standards - So sánh kết quả với mục tiêu và tiêu chuẩn
Công thức đo khoảng cách giữa hiệu suất mong muốn và thực tế
-Need for action = Desired Performance – Actual Performance -Comparison methods: Historical comparison Relative comparison Engineering comparison Ví dụ:
Một cửa hàng bán lẻ so sánh doanh số tháng này với tháng trước. (So sánh lịch sử)
Một công ty công nghệ so sánh tốc độ xử lý đơn hàng của mình với đối thủ. (So sánh tương đối)
Một nhà máy sản xuất so sánh mức tiêu thụ điện thực tế với mức tiêu chuẩn của
ngành. (So sánh kỹ thuật)
Step 4 — taking corrective action – thực hiện điều chỉnh
-Taking action when a discrepancy exists between desired and actual performance
(khi có sự chênh lệch giữa kết quả thực tế và mục tiêu ban đầu.)
-Management by exception (qly theo ngoại lệ)
Giving attention to situations showing the greatest need for action
Types of exceptions (các loại ngoại lệ cần chú ý)
Problem situation -> Khi hiệu suất thực tế thấp hơn mong đợi, cần có biện pháp khắc phục.
Opportunity situation -> Khi hiệu suất thực tế vượt xa mong đợi, có thể
tận dụng để tối ưu hơn nữa.
3. CONTROL TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES
-Project Management - quản lý dự án, cta cần lập kế hoạch, giám sát và kiểm soát các
dự án từ đầu đến cuối
Overall planning, supervision, and control of projects
Projects – unique one-time events that occur within a defined time period
(đặc thù, có thời gian thực hiện xác định.)
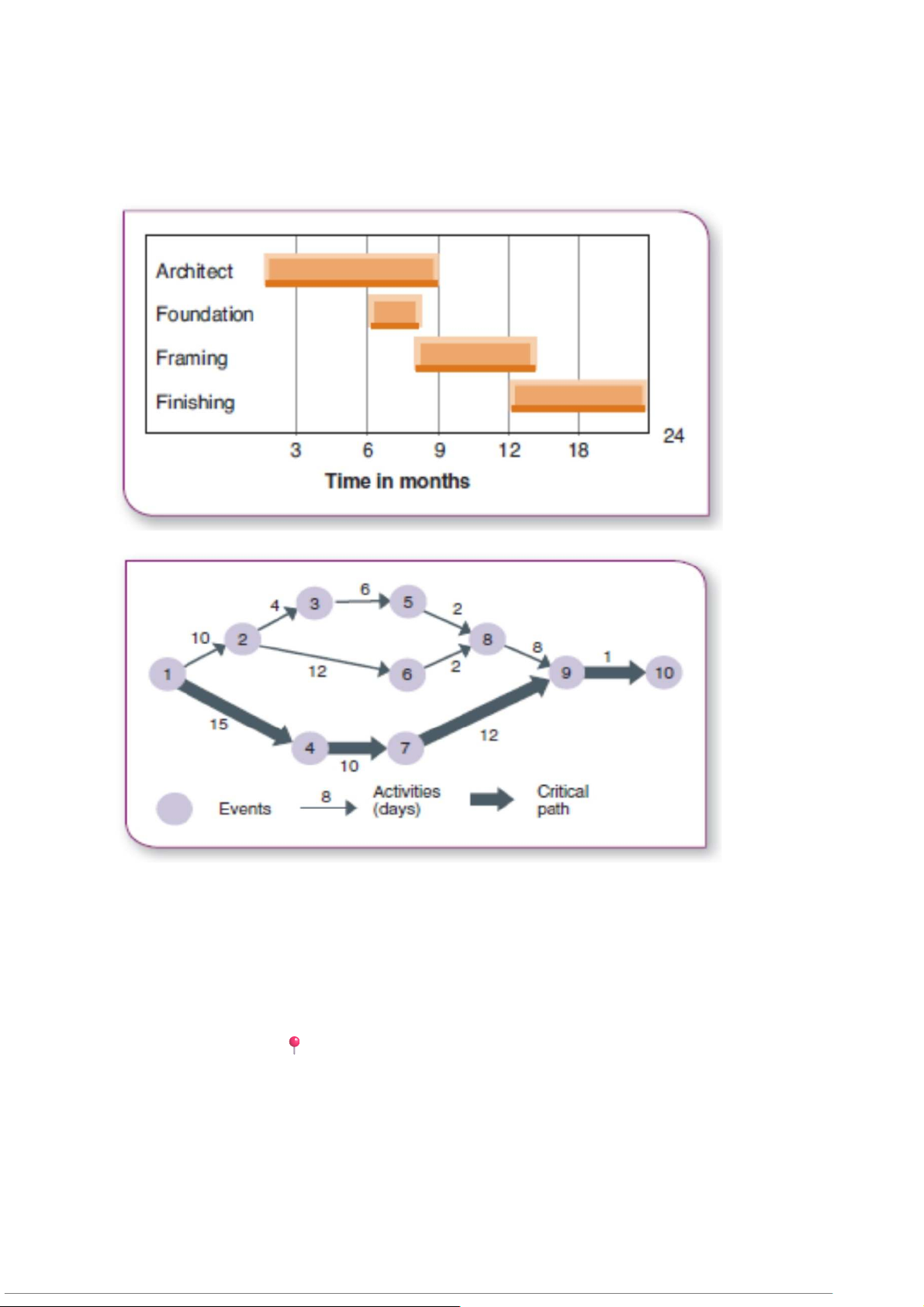
Gantt chart – graphic display of scheduled tasks required to complete a
project (Biểu đồ trực quan thể hiện lịch trình và tiến độ )
CPM/PERT – combination of the critical path method (công việc quan trọng
nhất) and program evaluation and review technique (kỹ thuật đánh giá và xem xét)
-Inventory control (kiểm soát hàng tồn kho)
Ensures that inventory is only big enough to meet immediate needs
Economic order quantity (lượng đặt hàng kinh tê)
oPlaces new orders when inventory levels fall to predetermined points
Hệ thống tự động đặt hàng khi tồn kho giảm xuống một mức xác định trước.
📍 Ví dụ: Một nhà máy sản xuất ô tô đặt hàng linh kiện khi số lượng
trong kho đạt mức tối thiểu
Just-in-time scheduling (sx đúng thời điểm)
oRoutes materials to workstations just in time for use
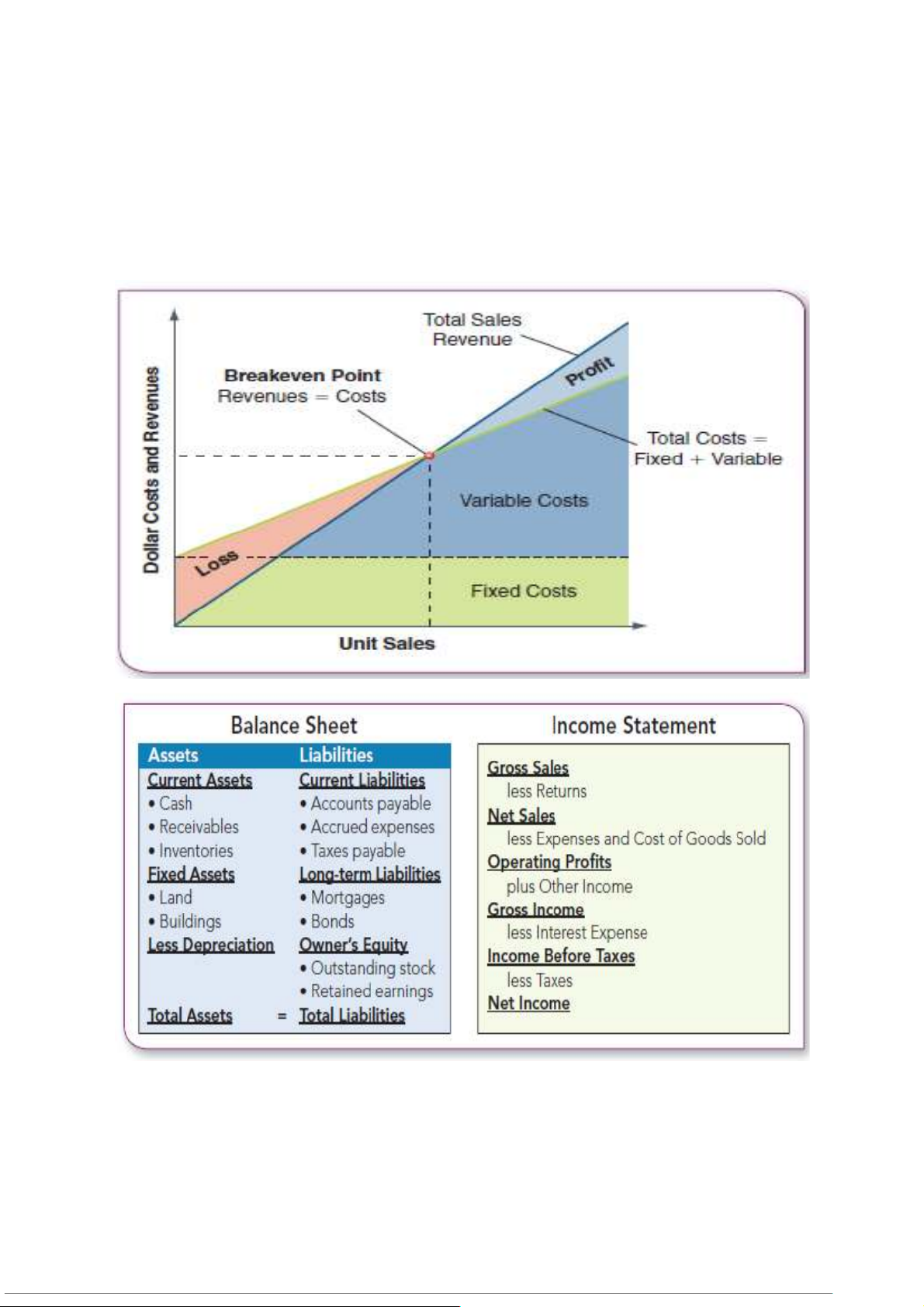
-Breakeven analysis (Phân tích điểm hòa vốn)
oBreakeven point: Occurs where revenues just equal costs tổng doanh thu
bằng tổng chi phí.
oBreakeven analysis: Performs what-if calculations under different revenue and cost conditions
Ví dụ: Một doanh nghiệp cần bán 5.000 sản phẩm mỗi tháng để hòa vốn, dưới mức này sẽ lỗ.
-Basic Financial Ratios (các chỉ số tài chính cơ bản)
Liquidity (khả năng thanh khoản)
The ability to generate cash to pay bills
Leverage (đòn bẩy tài chính)
The ability to earn more in returns than the cost of debt (khả năng kiếm được lợi
nhuận cao hơn chi phí vay vốn.)
Asset management (Quản lý tài sản)
The ability to use resources efÏciently and operate at minimum cost
Profitability (Khả năng sinh lời)
The ability to earn revenues greater than costs
Ví dụ: Return on Assets (ROA – Lợi nhuận trên tài sản) = Lợi nhuận ròng / Tổng tài sản.
-Balanced Scorecard (thẻ điểm cân bằng)
-Phương pháp đánh giá hiệu suất toàn diện dựa trên 4 yếu tố chính:
+ Factors used to develop scorecard goals and measures: oFinancial performance oCustomer Satisfaction oInternal process improvement oInnovation and learning
1 .Financial Performance (Hiệu suất tài chính) → Đánh giá doanh thu, lợi nhuận, dòng tiền.
2 .Customer Satisfaction (Sự hài lòng của khách hàng) → Đo lường mức độ hài lòng và trung thành của khách hàng.
3 .Internal Process Improvement (Cải tiến quy trình nội bộ) → Kiểm tra hiệu quả của quy
trình làm việc và sản xuất.
4 .Innovation and Learning (Đổi mới và học hỏi) → Đánh giá khả năng sáng tạo và phát triển nhân sự trong tổ chức.
📍 Ví dụ: Một công ty sử dụng Balanced Scorecard để đánh giá thành công của chiến lược
kinh doanh bằng cách theo dõi doanh thu, phản hồi của khách hàng, hiệu suất làm việc và mức độ đổi mới.




