
Preview text:
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY HCMC INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY School of Business COURSE SYLLABUS
Course Name: Principles of Management Course Code: BA123IU 1. General information Course
This subject will provide the fundamental theories and concepts of management as designation
they apply within the contemporary work environment. Semester(s) in 1, 2, 3 which the course is taught Person responsible for the course Language English Relation to Compulsory curriculum Teaching methods
Lecture; Case study; Group discussion Workload (incl.
(Estimated) Total workload: 120 contact hours,
Contact hours: 34 (15 sessions, 1 session = 3 periods, 1 period = 45 minutes) self-study hours)
Expected self-study hours: 86 (reading, research, working on group assignments) Credit points 3 Required and None recommended prerequisites for joining the course Course
Students will be provided with the fundamental theories and concepts of management Description
as they apply within the contemporary work environment. The course is an
introduction to the basic concepts on management roles such as planning and
controlling, organization, leadership and motivation. Through this course, students
will become acquainted with different management approaches and the challenges for
management in the twenty-first century. 1 Course learning
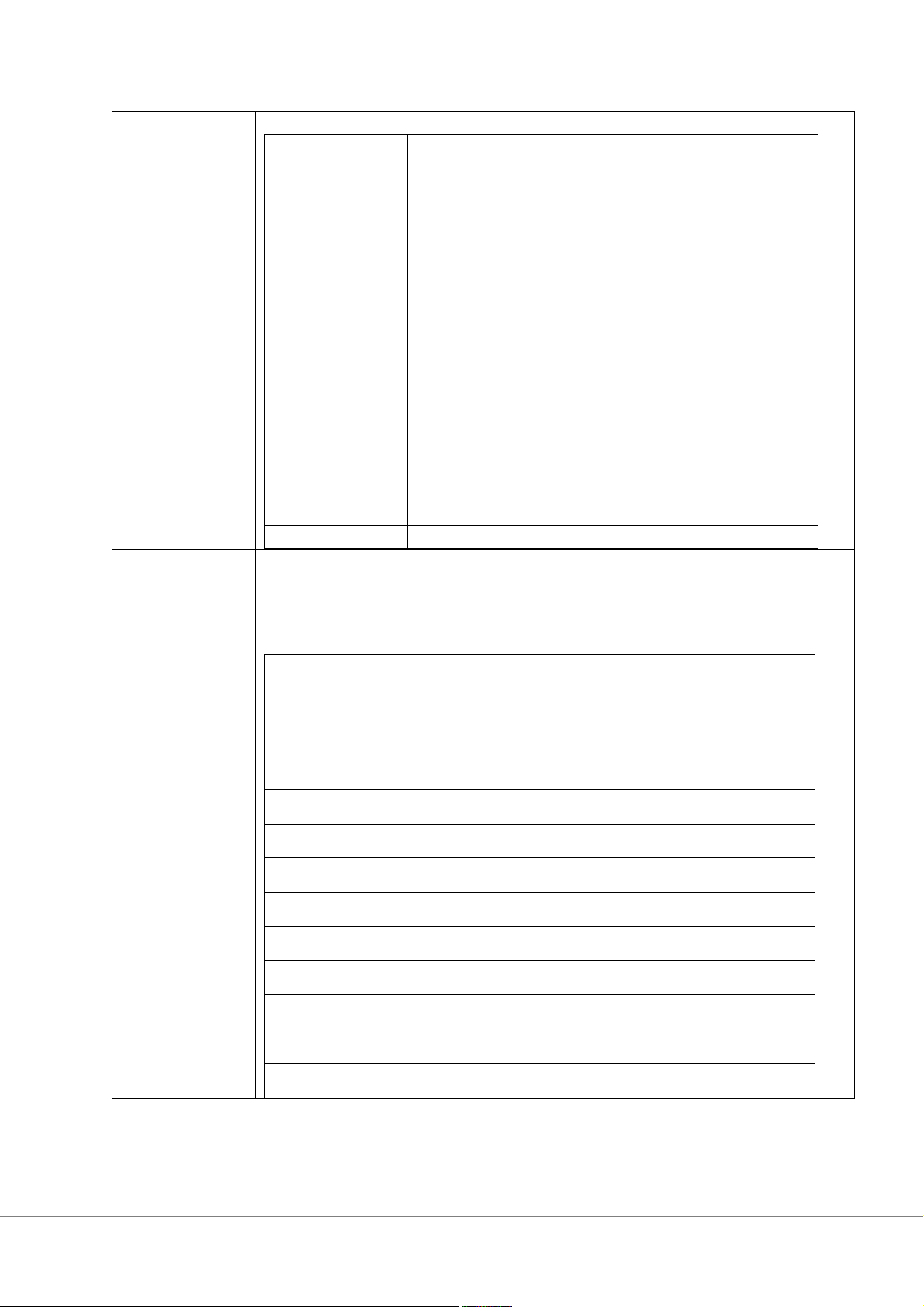
Upon the successful completion of this course students will be able to: outcomes Competency level Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) Knowledge (I, R)
CLO1. Identifying how managers use leadership theories,
motivation theories, and other basic concepts of
teamwork and communication in high-performance
organizations through group assignments.
CLO2. Explain four management functions: planning,
organizing, leading, and controlling
CLO3. Describe the challenges and opportunities that
today organizations are facing such as globalization,
diversity, technology, and social responsibility. Skill (R)
CLO4. Explain the managerial practices of an
organization through assignments and presentations.
CLO5. Develop communication skills via in-class
presentations (70% of students get 2/4 in the skill assessment rubrics).
CLO6. Develop teamwork skills via group assignments
(70% of students get 2/4 in the skill assessment rubrics). Attitude
CLO7. Follow ethical issues in managerial situations.
Content The description of the contents should clearly indicate the weighting of the content and the level.
Weight: lecture session (3 hours)
Learning levels: I (Introduce); T (Teach); U (Utilize) Topic Weight Level Introducing Management 1 I, T
Management Learning Past to Present 1 I, T
Environment, Innovation, and Sustainability 1 I, T
Global Management and Cultural Diversity 1 T, U
Planning Processes and Techniques 1 I, T Control Processes and Systems 1 I, T
Organization Structures and Designs 1 I, T
Leading and Leadership Development 2 I, T Individual Behavior 1 T, U Motivation Theory and Practice 2 I, T Teams and Teamwork 1 T, U
Communication and Collaboration 1 T, U 2 Examination Short-answer questions forms Study and
Regular and punctual attendance at lectures is expected in this course. University examination
regulations indicate that if students attend less than eighty percent of scheduled requirements
classes, they may not be considered for final assessment.
Discussions are strongly encouraged.
Students must gain more than 50/100 points overall to pass this course. Reading list
[1] Schermerhorn, John R. 2013. Management. 12th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
[2] Schermerhorn, J., Davidson, P., Woods, P., Factor, A., Simon, A. and McBarron,
E., 2017. Management, 6th Asia-Pacific Edition. 6th ed. Sydney: John Wiley.
[3] DuBrin, Andrew J. 2008. Essentials of Management. 8th ed. Cengage Learning.
2. Learning Outcomes Matrix (optional)
The relationship between Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) (1-7) and Program Learning
Outcomes (PLO) (1,3,4,5,6) is shown in the following table: CLOs PLOs 13456 1 x x x x x 2 x x x x x 3 x x x x x 4 xxxx 5 xxxx 6xxxx 7 xxxx
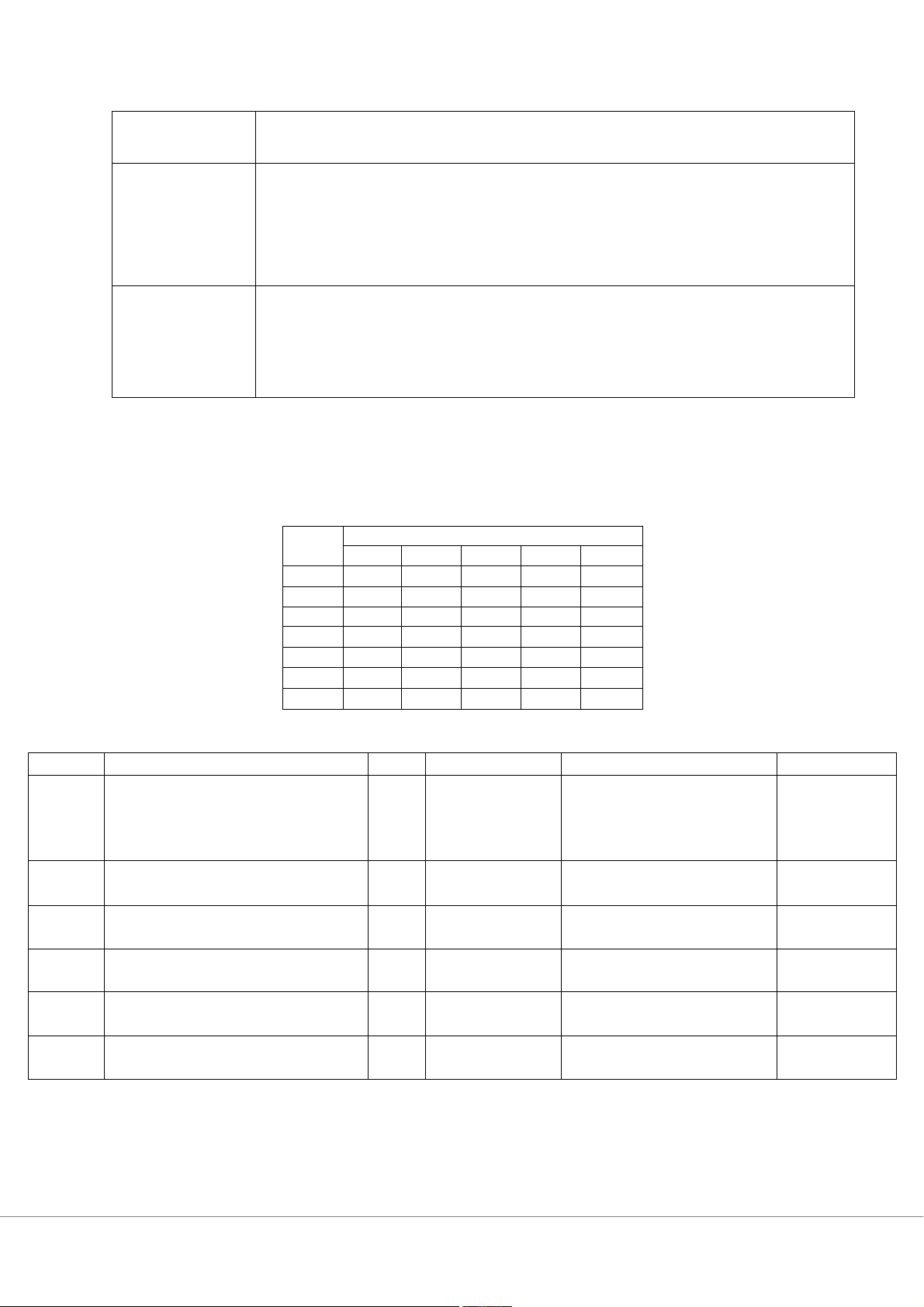
3. Planned learning activities and teaching methods Week Topic
CLO Assessment Learning activities Resources MCQs; Case Lecture, analysis Group discussion, Chapter 1: Introduction to Group’s assignment [1] 1 Management 1;2; guidelines Chapter 1. Chapter 2: Management MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 2 Learning Past to Present 1;2;3 analysis Group discussion Chapter 2. Chapter 4: Environment, MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 3 Innovation, and Sustainability 1;2;3 analysis Group discussion Chapter 4. Chapter 5: Global Management MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 4 and Cultural Diversity 1;2;3 analysis Group discussion Chapter 5. Chapter 8: Planning Processes MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 5 and Techniques 2; 4 analysis Group discussion Chapter 8.
Chapter 9: Control Processes and MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 6 Systems 2; 4 analysis Group discussion Chapter 9. 3 Chapter 11: Organization MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 7 Structures and Designs 2; 4 analysis Group discussion Chapter 11. Oral Oral Presentations; 4; 5; presentation Q&A (for CLO 7); 8 Group assignments 6; 7 (70% ) * Feedback Short- answer questions; 1;2;3 MCQs; Case ;4;5; analysis 9 MIDTERM EXAM 6;7 70%* Chapter 14: Leading and MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 10 Leadership Development 2; 4 analysis Group discussion Chapter 14. Chapter 15: Individual MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 11 Behaviour 2; 4 analysis Group discussion Chapter 15. MCQs; Case Lecture, Chapter 16: Motivation Theory analysis Discussion, [1] 12 and Practice 2; 4 Chapter 16. Chapter 17: Teams and 1; 6; MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] 14 Teamwork 7 analysis Group discussion Chapter 17. Chapter 18: Communication and 1; 5; MCQs; Case Lecture, [1] Collaboration 7 analysis Group discussion Chapter 18. MCQs; Case Oral Presentations; 4; 5; analysis Q&A (for CLO 7); 15 Group assignment 6; 7 Feedback Short- answer questions; 1;2;3 MCQs; Case ;4;5; analysis 16 Final examination 6;7 70%*
Note:* Target that 70% of students have scores greater than 70 out of 100. 4. Rubrics (optional)
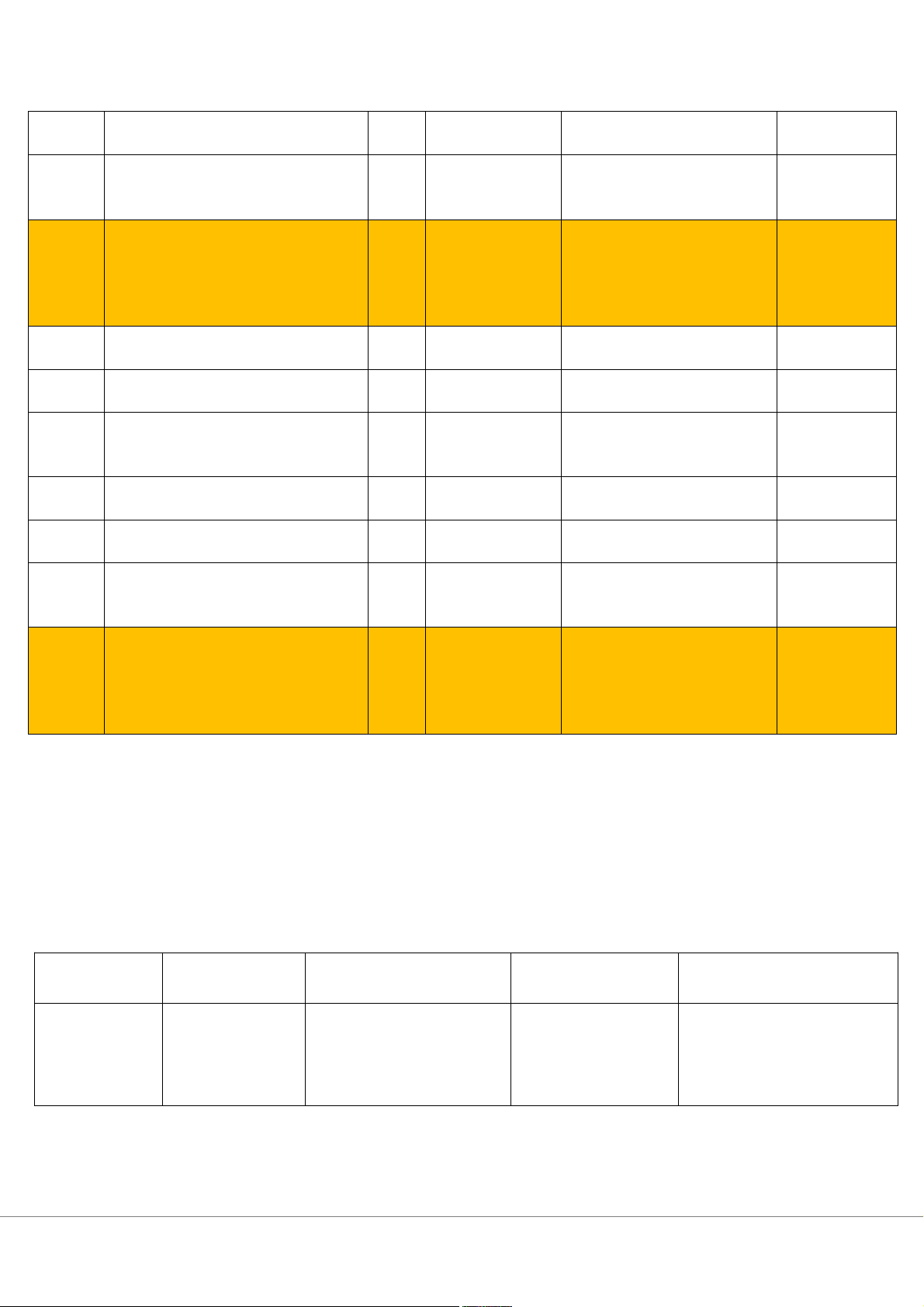
GRADING RUBRIC FOR WRITTEN COURSEWORK
MIDTERM EXAMINATION – Subject (ID subject)
Academic year: 2022 – 2023 (term …) Criteria INADEQUATE ADEQUATE ABOVE AVERAGE EXEMPLARY 10% – 49% 50% - 59% 60% - 74% ≥ 75% Organisation and Does not organise Generally organised Clear organization and Response is focused, detailed clarification ideas logically and logically, with evidence of progression. and non-tangential. with clarification progression Responds appropriately Shows a high degree of Limited evidence Occasionally, there may be a and relevantly,
attention to logic and reasoning of coherence lack of focus or ideas may be although some ideas of points. 4 Ideas lack tangential are underdeveloped
Clearly leads the reader to the consistence conclusion and stirs thought regarding the topic Demonstrates an
Shows ability to identify legal Shows strong ability to
Shows strong ability to identify incomplete grasp of issues, gather the facts and identify legal issues,
legal issues, gather the facts and the task. develop claims. gather the fact and
develop claims as well as link develop claims as well claims with evidence. Originality and There is no overall Argument are addressed well as link claims with usefulness of the sense of creative but no links with evidence Satisfactory solutions are evidence. analysis coherence. offered and supported Overall, an acceptable Arguments are solution is offered and addressed explained incompletely. Shows little Shows moderate amount of Draws upon sources to Draws upon primary and information from source information support most points.
secondary source information in sources. Poor incorporated.
useful and illuminating ways to Some evidence may not handling of sources support key points. Some key points supported support arguments or Use of by sources. may appear where
Excellent integration of quoted data/information inappropriate. material into paragraphs. Quotations may be poorly Source cited correctly integrated into paragraphs. Quotations integrated well into paragraphs. Some possible problems with source citations Sources cited correctly Shows limited Shows effort to link problems Shows ability to Shows ability to structure ability to structure with the theoretical structure problems in problems in correspondence to problems in frameworks. correspondence to theoretical frameworks Use of correspondence to theoretical frameworks correctly. frameworks There are still some mistakes theoretical correctly.
The problems are well resolved frameworks Minor mistakes in resolving problems Shows little Shows argument of poor Shows clear, relevant
Shows identifiable, reasonable attempt to offer quality. and logical arguments. and sound arguments. support for key Weak, undeveloped reasons Clear reasons are offered to Quality of claims or to relate are offered to support key support key claims. arguments evidence to claims analysis. Reasons offered are irrelevant. 5.
6. Date revised: August 23, 2022 5
Ho Chi Minh City, 23/08/2023
Head/Dean of Department/School 6




