


Preview text:
ĐỀ KIỂM TRA ĐỊNH KÌ LẦN 1 MÔN KINH TẾ VI MÔ 1 Mã đề 1
Microeconomics 1: First Periodic Exam
Time: 70-90 minutes. This test contains 3 parts, in 4 pages.
Thời gian: 70-90 phút. Đề kiểm tra bao gồm 3 phần, trong 4 trang.
Part 1/3. Fill in these 6 questions below with short answers, into the answer sheet. Follow each
question's rule to understand the concept of that question. (6 points)
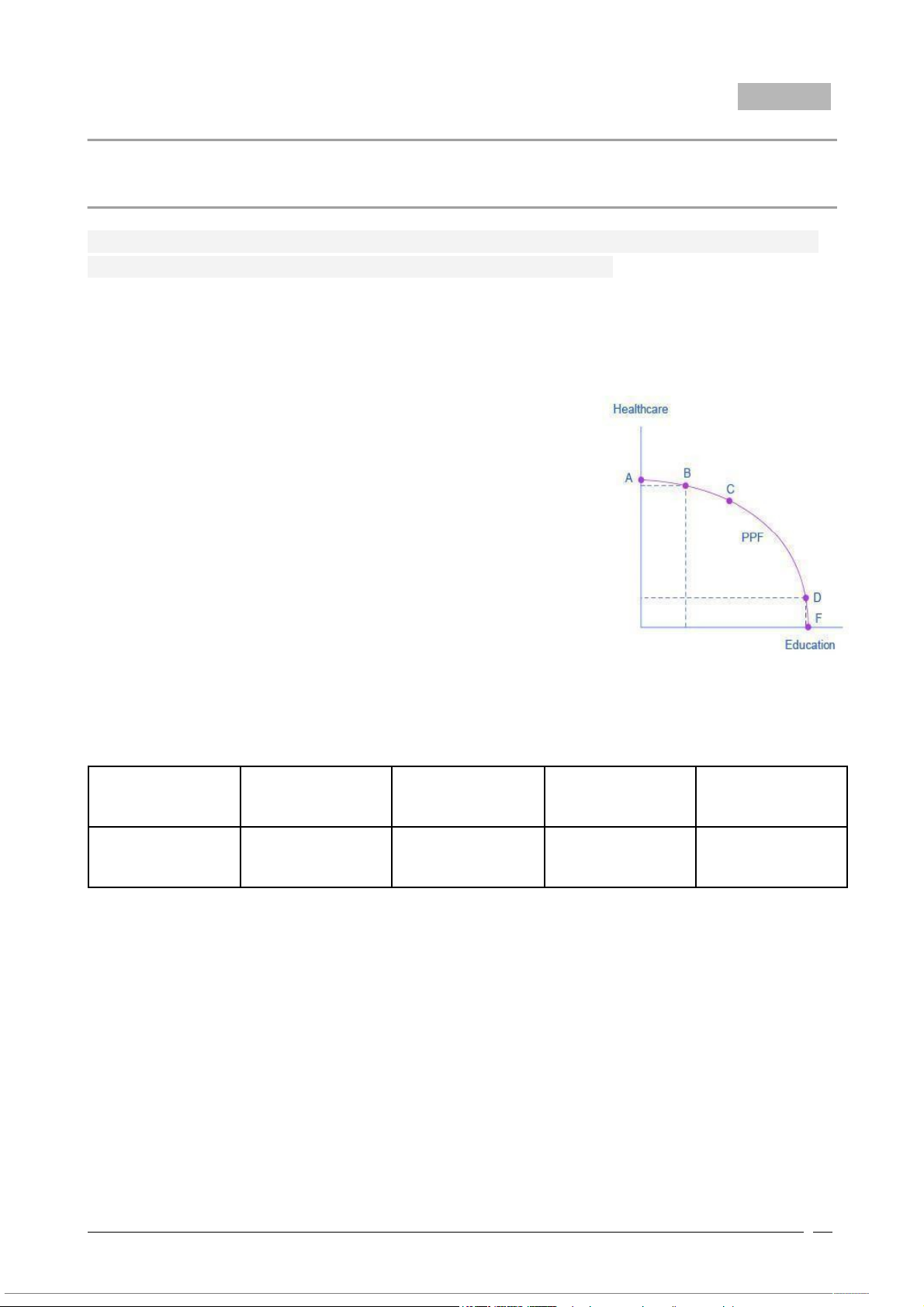
Question 1/6: Fig.1 is a model of Healthcare vs. Education Production Possibilities Frontier .
This production possibilities frontier shows the distribution of social resources to 2 factors:
healthcare and education. Which of the following statements is correct, incorrect? (1 points)
A. In the graph, healthcare is shown on the horizontal
axis and education is shown on the vertical axis.
B. At A, all resources go to healthcare, and at B, most
go to healthcare. At D most resources go to
education, and at C, all go to education.
C. The production possibilities frontier clearly shows
the tradeoff between healthcare and education.
D. Suppose the society considers moving from point
C to point B. The opportunity cost for the
additional education would be the healthcare society has to give up.
E. Because the PPF is downward sloping from left to
right, the only way society can obtain more
education is by giving up some healthcare.
Question 2/6: Fill in the blanks with the given words in the box. You might not need all of the
words. Each word can only be used once. (1 points) Quantity Price Law of demand Law of supply Inferior goods demanded Expectation Normal goods Income Quantity Demand supplied
A. The (1) _____ states that when the (2) _____ of a product goes up, the quantity
demanded will go down – and vice versa.
B. An (3) _____ is an economic term that describes a good whose demand drops when people's (4) _____ rise.
Question 3/6: Fill in the blanks with logical words or phrases. (1 points)
A change in (1) _____ refers to a movement along the existing (2) _____ due to a change in
price. This means that producers are willing to supply a different quantity at the same price level.
Question 4/6: Fill in the blanks with the correct word. (1 points) Microeconomics Exam. Page 1/4
A change in supply leads to a shift in the (1) _____ (supply curve/quantity supplied point),
which causes an (2) _____ (imbalance/balance) in the market that is corrected by changing
prices and demand. An (3) _____ (increase/decrease) in the change in supply shifts the
supply curve to the right, while a (4) _____ (increase/decrease) in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left.
Question 5/6: Input a specific value in each problem below. You might need the definition of
those underlined words. (1 points)
Problem 1: Consider a local car dealership that gathers data on changes in demand and
consumer income for its cars for a particular year. When the average real income of its
customers falls from $50,000 to $40,000, the demand for its cars plummets from 10,000 to
5,000 units sold, all other things unchanged.
The value of the income elasticity of demand is (1) _____,which indicates local customers are
particularly sensitive to changes in their income when it comes to buying cars.
Plummet(v): to fall very quickly and suddenly. Indicate(v): to show, point or make clear in another way.
Problem 2: What Does an Income Elasticity of Demand of 1.50 mean?
Since the value is positive, the good is elastic. It implies that for every 1% increase in income,
people will demand an increase of 1.5% in the number of goods. Thus, if the average income is
$100,000 and at that level of income people desire 70 restaurant meals a year, they would
demand up to 71 meals a year if income rose to $(2) _____.
Question 6/6: Decide whether these statements are true or false ? (1 points)
A. Inelastic means that a 1% change in the price of a good or service has less than a 1%
change in the quantity demanded or supplied.
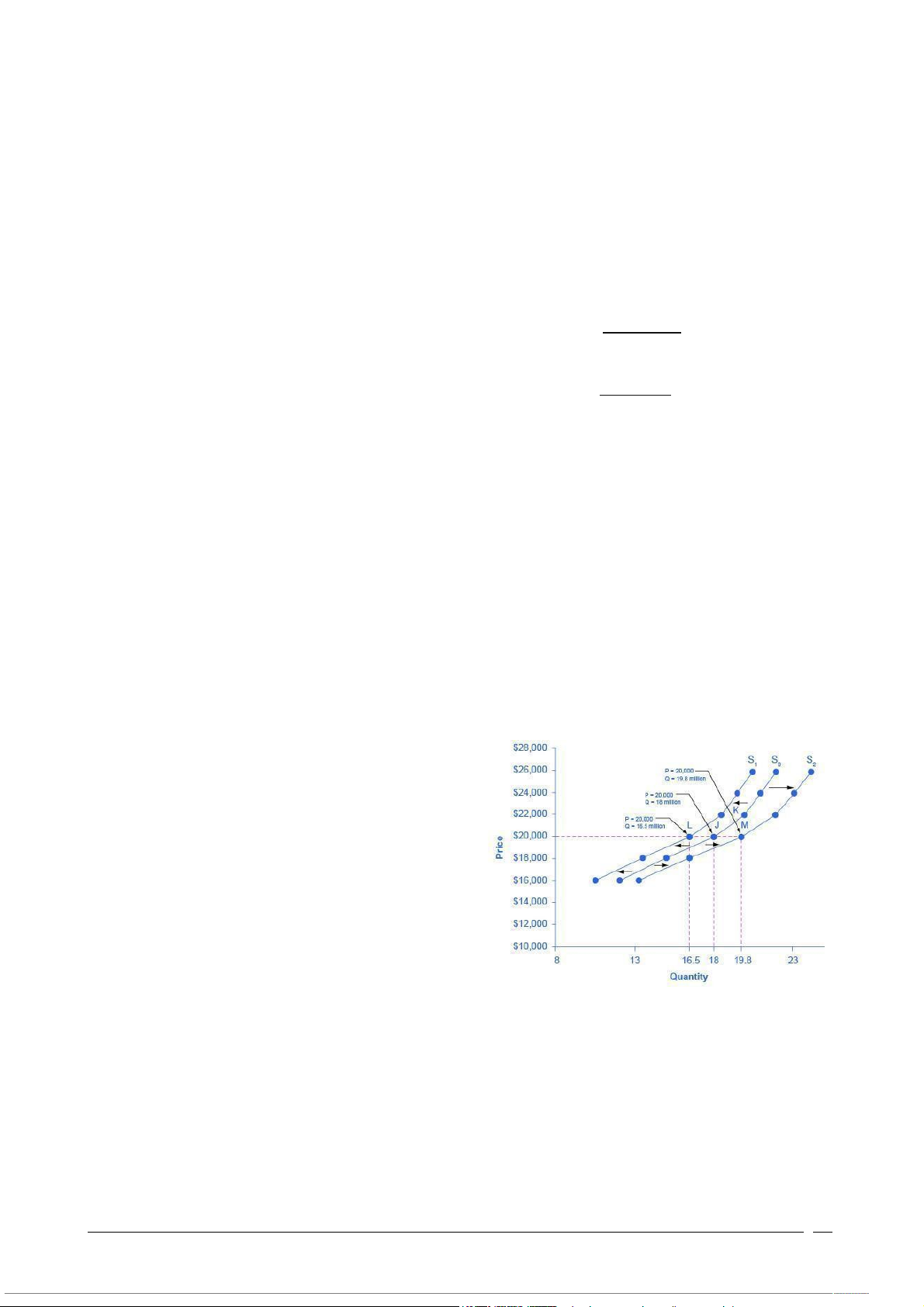
B. Fig.2 shows the Shifts in supply: a car
example. As a result of the higher
manufacturing costs, the supply
curve shifts to the left, toward S1.
Firms will profit less per car, so they
are motivated to make fewer cars at a
given price, decreasing the quantity
supplied. A decrease in costs would
have the opposite effect, causing the
supply curve to shift to the right,
toward S2. Firms would profit more per car, so they would be motivated to make more
cars at a given price, increasing the quantity supplied.
C. Deadweight loss (DWL) refers to the loss to society that occurs when supply and
demand are not at equilibrium. Deadweight loss directly affects the welfare of both
consumers and producers. On the consumer Surplus, the difference between what
consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus what they actually pay. On the
Producer Surplus, the difference between what producers are willing to sell a good or Microeconomics Exam. Page 2/4
service for versus what they actually receive. A market with efficiency would shrink
these surpluses, making both parties worse off.
D. When a consumer moves upward along an indifference curve, his/her total utility remains constant.
E. A consumer is in equilibrium at the point of tangency of his/her indifference curve and
the price line because he/she cannot go below it.
Part 2/3. Solve this exercise below. Remember to show your work clearly and logically in the answer sheet. (2 points) The information given:
A consumer has a total money income of $250 to be spent on two goods X and Y with prices of
$25 and $10 per unit respectively.
On the basis of the information given, answer the following questions:
1. Show the equation of the budget line for that consumer.
2. What is the value of slope of the budget line?
3. How many units can the consumer buy if he spends all his money income on goods X?
4. Draw a budget line for that customer.
5. How does the budget line change if there is a fall in price of goods Y?
Part 3/3. Answer this question below. Remember to show your work clearly and logically in the answer sheet. (2 points) The paragraph given: New technology Microeconomics Exam. Page 3/4
When a firm or an individual discovers a new technology, it boosts the production process of
goods or services that allows it to produce at a lower cost. For instance, in the 1960s, a major
scientific effort nicknamed the Green Revolution focused on breeding improved seeds for
basic crops like wheat and rice. By the early 1990s, more than two-thirds of the wheat and
rice in low-income countries around the world was grown with these Green Revolution
seeds-and the harvest was twice as high per acre.
On the basis of the information given, answer the following questions:
1. The technological improvement that reduces costs of production will shift the supply curve to what side?
2. The technological improvement makes the change in the quantity supplied to be greater or smaller?
3. Draw a model of supply and demand to clarify your statements. THE END. Microeconomics Exam. Page 4/4




