
Preview text:
DEMAND MANAGEMENT Definition
Demand management: The creation across the supply
chain and its markets of a coordinated flow of demand.
Link to other function: Procurement & Purchasing,
Production, Transportation, Distribution, Sale, Inventory.
Estimate and manage customer demand => shape operating decisions:
Better than just forecasting
Intergration of demand and supply
Improves communication, coordination, collaboration
Improves basic supply chain flows Why important: Maximize revenue Optimize cash Control cost
The bullwhip effect: The small changes in demand => A whip-like effect upstream.
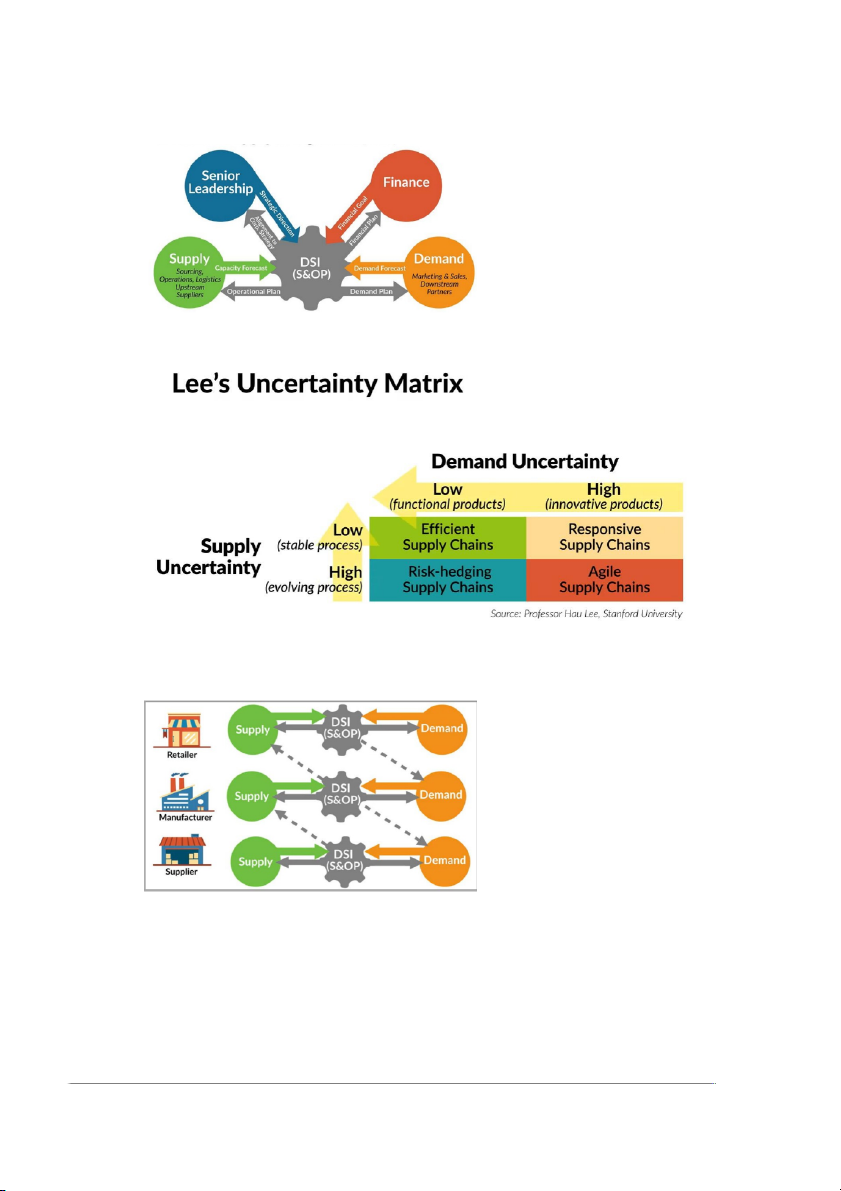
Demand Supply Intergration
DSI (or Sales & Operation Planning):
Lee’s Uncertainly Matrix:
DSI – Across the SC: DSI (or S&OP) control supply and
demand from Retailer to Manufacturer and Supplier: Demand Forecasting Techniques:
Qualitative: Expert opinions, Market research,…
o Methods: Executive Opinion, Delphi Method,
Sales Force Estimates, Consumer Surveys.
Qualitative: Simple Moving Average, Weighted Moving Average.
o Analyse and assess the situation
o Establish forecasting model and statistical forecast o Post-forecast
o Methods: Naive Approach, Moving Averages,
Exponential Smoothing, Trend Projection. Demand (sales) forecasting:
Helpful in make-to-stock situations, make-to-order situations. Process:
Three basic types: Judgmental, Time series, Cause and effect (associative) Issuses:
o An inappropriate technique → reduce forecast accuracy.
o Accuracy leads to important logistical implications.
o Software unable to completely eliminate forecast errors.
Demand (material ) forecasting: Determined demand:
Identifying department materials requirement:
o Purchase requisition (Internal document): Department name, …
o Table of materials demand estimation: N = Q x M
Summing up the company materials requirement:
o Supply department will be received purchase
requisition then check the accuracy and
completeness each type of material data.
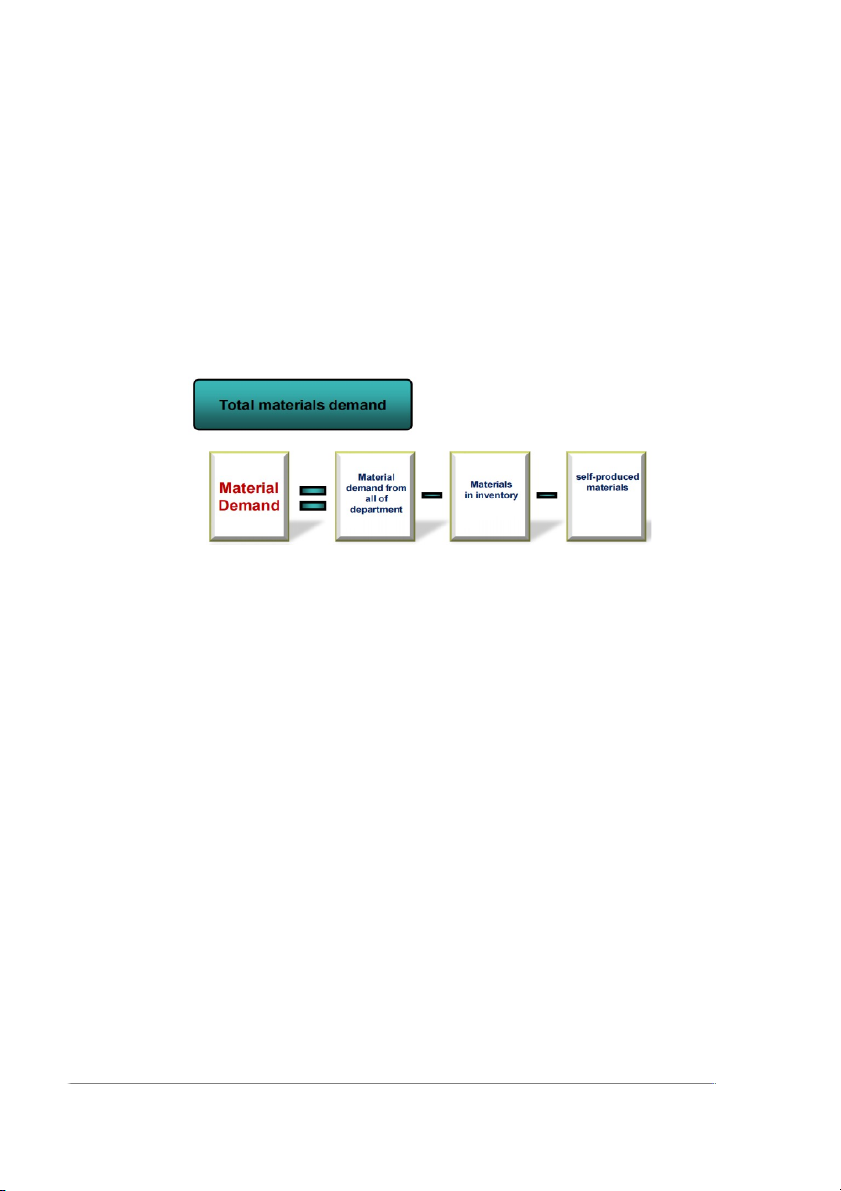
o To build up the table of total company material demand Total materials demand: Role:
o No accurate data on production plan and raw material uses for production.
o Prepare a material supply plan
o Calculate the amount of necessary materials reserve




