



















Preview text:
1. The Pauli exclusion principle states that
A) the wavelength of a photon of light times its frequency is equal to the speed of light.
B) no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
C) both the position of an electron and its momentum cannot be known
simultaneously very accurately.
D) the wavelength and mass of a subatomic particle are related by .
E) an electron can have either particle character or wave character. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: State the Pauli exclusion principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
2. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy one p orbital? A) 14 B) 2 C) 10 D) 1 E) 6 ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: State the Pauli exclusion principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
3. What is the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the = 2 shell? A) 8 B) 4 C) 16 D) 22 E ) 24 ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: State the Pauli exclusion principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
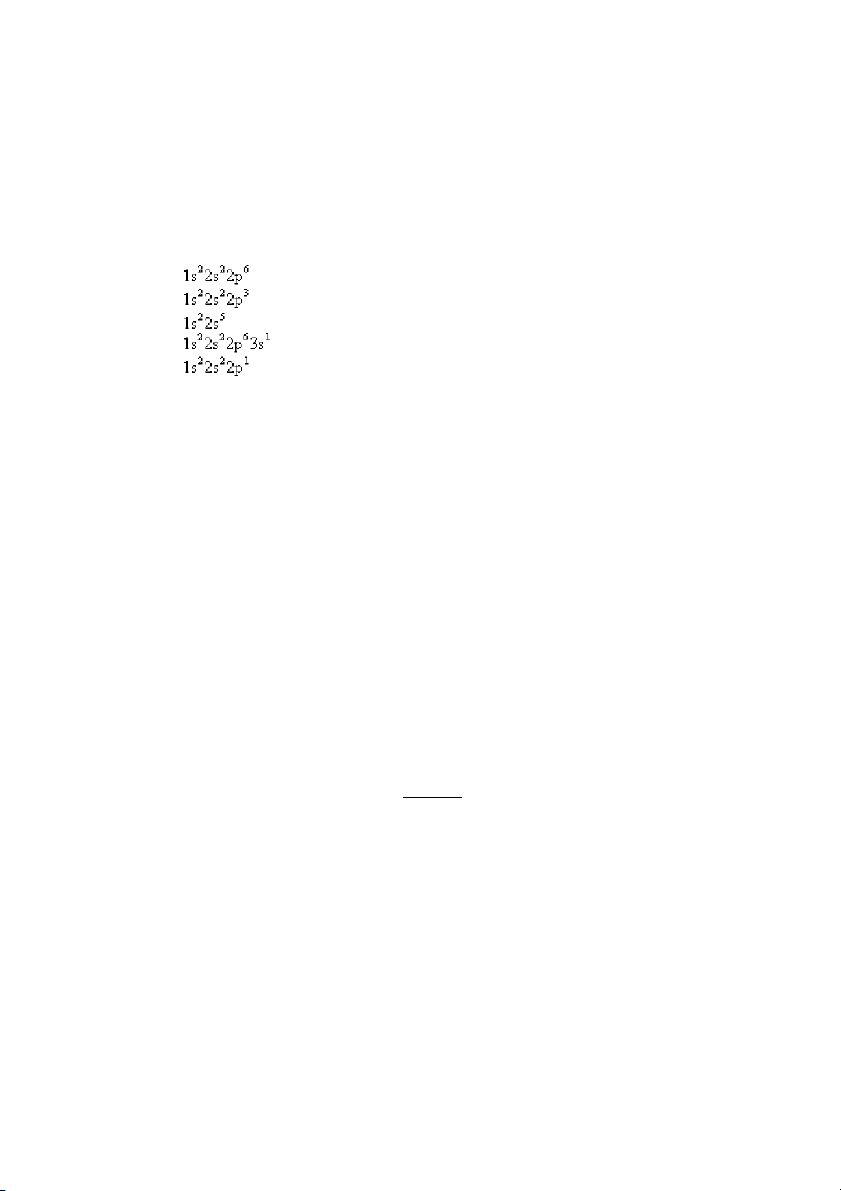
4. Which of the following orbital occupancy designations is incorrect? A) 3d7 B) 2p6 C) 4f6 D) 1s2 E) 4f15 ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
5. The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in an f subshell is A) 2. B) 10. C) 6. D) 1. E) 14. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
6. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that have the set of quantum numbers = 1 and = 0? A) 6 B) 14 C) 10 D) 18 E ) 2 ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
7. Which of the following orbital diagrams violates the Pauli exclusion principle? 1s 2s 2p A) B) C) D) E) ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
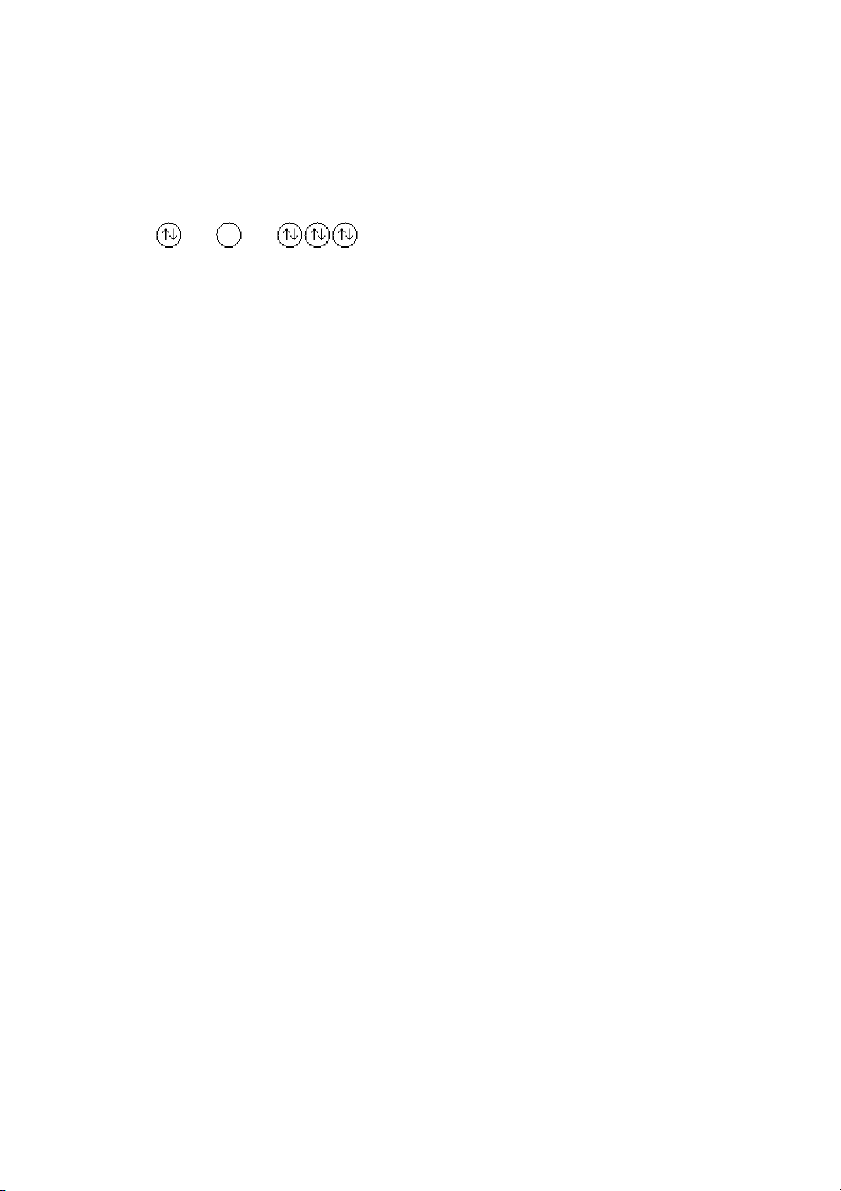
8. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state? 1s 2s 2p A) Pauli exclusion principle B) Aufbau principle
C) No rules or principles are violated by this orbital diagram.
D) Heisenberg uncertainty principle E) Hund's rule ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
9. Which of the following electron configurations is impossible, according to the Pauli exclusion principle? A) B) C) D) E) ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.1
OBJ: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle. (Example 8.1)
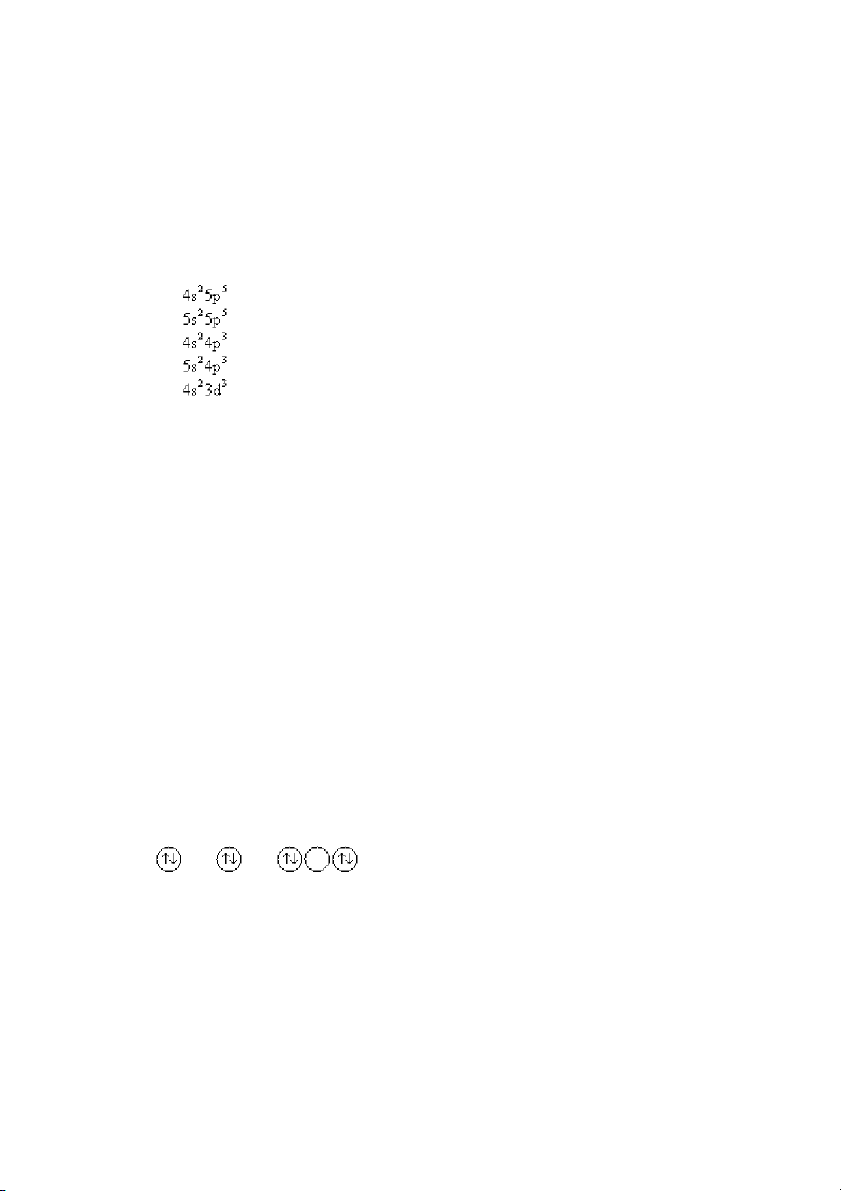
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Pauli exclusion principle MSC: general chemistry
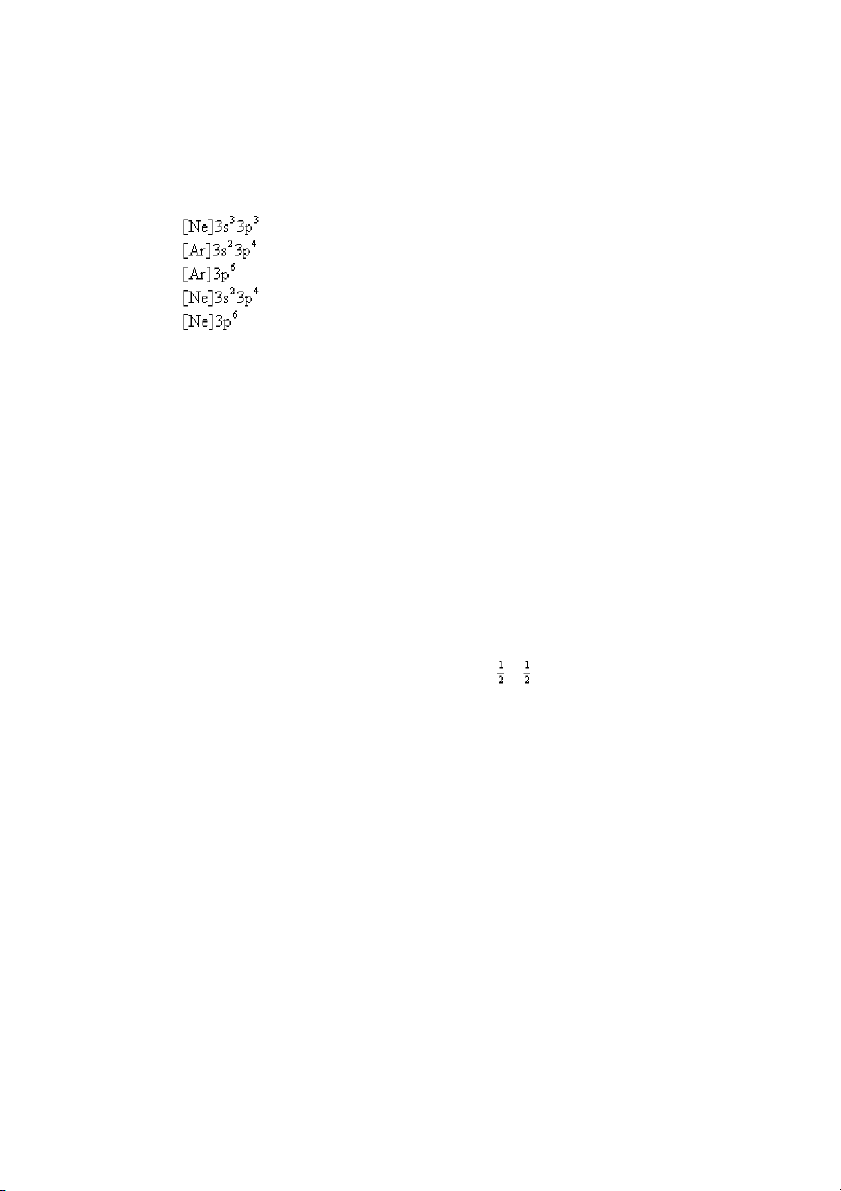
10. Which of the following statements is true concerning the electron configuration [Kr]5p2?
A) This configuration cannot be the ground-state electron configuration for a Sr atom
because it violates the Pauli exclusion principle.
B) This configuration cannot be the ground-state electron configuration for a Sr atom
because it violates Hund's rule.
C) This configuration is the ground-state electron configuration for a Sr atom.
D) This configuration cannot be the ground-state electron configuration for a Sr atom
because it violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
E) This configuration cannot be the ground-state electron configuration for a Sr atom
because it violates the Aufbau principle. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define building-up principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | aufbau principle MSC: general chemistry
11. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Stern and Gerlach discovered electron spin by passing silver atoms through a magnetic field.
B) Hund’s rule states that electrons are placed in the orbitals of a subshell in such a
way as to give a maximum number of unpaired electrons.
C) The Pauli exclusion principle states that each electron in an atom must have its
own unique set of quantum numbers.
D) Valence electrons consist of those electrons not contained within a noble-gas core or a pseudo-noble-gas core.
E) The building-up principle states that electrons are added to atoms in order of
increasing principal quantum number. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define building-up principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | aufbau principle MSC: general chemistry
12. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state? 1s 2s 2p A) Pauli exclusion principle B) Hund's rule
C) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
D) No rules or principles are violated by this orbital diagram. E) Building-up principle ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define building-up principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | aufbau principle MSC: general chemistry
13. Which of the following electron configurations represents an excited state of the indicated atom? A) Ne: 1s2 2s2 2p6 B) N: 1s2 2s2 2p3 C) P: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 4s1
D) Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 3s1 E) He: 1s2 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define building-up principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | aufbau principle MSC: general chemistry
14. Which of the following have one or more filled d subshells in their ground state electron configuration? A) Ga B) Cl C) Si D) He E) Ar ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define noble-gas core, pseudo-noble-gas core, and valence electron.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
15. Two elements that have the same ground-state valence shell configuration of s2 p2 are A) K and Mg. B) O and Se. C) Al and Ga. D) Ge and Pb. E) Mg and Ca. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define noble-gas core, pseudo-noble-gas core, and valence electron.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
16. Which element is found in the s-block of the periodic table? A) H B) Rn C) Mo D) Pr E) none of the above ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define noble-gas core, pseudo-noble-gas core, and valence electron.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
17. According to the building-up principle or aufbau principle, which subshell is typically filled next after the 3d subshell? A) 4p B) 5f C) 6p D) 5d E) 1s ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define building-up principle.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
18. Which of the following electron configurations corresponds to the ground state of an atom of a transition element? A) 1s22s22p5 B) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p63d64s2 D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 E) 1s22s22p63s23p4 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define main-group element and (d-block and f-block) transition element.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
19. The ground-state valence-shell configuration of a particular atom is . The
element to which this atom belongs is a A) noble gas. B) inner transition element.
C) p-block main-group element. D) transition element.
E) s-block main-group element. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define main-group element and (d-block and f-block) transition element.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
20. The ground-state valence-shell configuration of a particular atom is . The
element to which this atom belongs is a A) noble gas.
B) s-block main-group element.
C) p-block main-group element. D) transition element. E) inner transition element. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define main-group element and (d-block and f-block) transition element.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
21. The ground-state valence-shell configuration of a particular atom is 5s24d5. This
valence-shell electron configuration identifies the atom as A) a transition element.
B) an inner transition element.
C) an s-block main-group element.
D) a p-block main-group element. E) a noble gas. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define main-group element and (d-block and f-block) transition element.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
22. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) A p-block main-group element belonging to period has a completely filled ( – 1)d subshell.
B) All noble gases have completely filled shells.
C) All s-block main-group elements have only one or two valence electrons.
D) Carbon and silicon have the same number of valence electrons. E
) All elements in the = 4 period have a partially or completely filled = 4 shell. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.2
OBJ: Define main-group element and (d-block and f-block) transition element.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
23. Which of the following statements is true concerning the electron configuration [Ne]3s13p1?
A) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Al+ cation.
B) It may represent an excited-state electron configuration of a Mg atom.
C) It may represent an excited-state electron configuration of a Ne– anion.
D) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Mg+ cation.
E) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Na+ cation. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: difficult REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table | writing electron configurations using the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
24. Which of the following may represent an excited-state electron configuration for a cobalt atom? A) [Ar]3d54s1 B) [Ar]3d64s2 C) [Ar]3d84s1 D) [Ar]3d64s1 E) [Ar]3d74s2 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: difficult REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table | writing electron configurations using the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
25. All of the following ground-state electron configurations are correct except A) . B) . C) . D) . E) . ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
26. What is the total number of electrons in p orbitals in a ground-state vanadium atom? A) 6 B) 18 C) 12 D) 24 E) 30 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
27. Which ground-state electron configuration is incorrect? A) B) C) D) E) ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | aufbau principle MSC: general chemistry
28. How many valence electrons does an arsenic atom have? A) 5 B) 8 C) 7 D) 2 E) 33 ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
29. Which of the following sets of four quantum numbers ( , , , ) correctly describes one of
the valence electrons in a ground-state radium atom? A) 7 1 0 B) 6 1 1 C) 7 2 0 D) 7 2 0 E) 7 0 0 + ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
30. What is the ground-state electron configuration of tantalum (Ta)?
A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p64d104f145s25p3
B) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p3
C) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d104f145s25p65d36s2
D) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p65d3
E) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d104f3 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
31. What is the ground-state electron configuration of terbium (Tb)?
A) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p65d96s2
B) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d104f145s25p3
C) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p65d106s1
D) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d94f105s25p66s2
E) 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d104f95s25p66s2 ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
32. What is the ground-state electron configuration of sulfur (S)? A) B) C) D) E) ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
33. What noble gas core would be used when writing the ground state electron configuration for tungsten (W)? A) [Xe] B) [Rn] C) [Kr] D) [Ar] E) [Ne] ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
34. If the electron could have a third spin state (that is, , – , and 0), what would be the
ground-state electron configuration of carbon? A) 1s22s4 B) 1s22s32p1 C) 1s32s3 D) 1s22s22p2 E) 1s32s22p1 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: difficult REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the building-up principle. (Example 8.2) TOP:
atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms KEY: electron configuration MSC: general chemistry
35. The elements that are filling the 5f subshell are called A) alkali metals. B) transition elements. C) lanthanides. D) actinides. E) main-group elements. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table | writing electron configurations using the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
36. The quantum numbers of an atom's highest-energy valence electrons are = 5 and = 1.
The element to which this atom belongs could be a A) inner transition metal. B) alkali metal.
C) s-block main-group element. D) transition metal. E ) p-block main-group element. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: moderate REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
37. The angular momentum quantum number of the two highest-energy valence electrons in an atom of germanium is A) 4. B) 0. C) 1. D) 2. E ) 3. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: difficult REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
38. Which of the following sets of four quantum numbers ( , , , ) correctly describes an
electron occupying a d orbital of an element in the third row of the transition metals? A) 4 2 2 + B) 5 2 1 – C) 5 3 –1 D) 4 1 0 – E) 5 0 0 – ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table | writing electron configurations using the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
39. An element that has the same ground state valence-shell electron configuration as indium is A) boron. B) silicon. C) krypton. D) lithium. E) barium. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
40. What is the valence-shell electron configuration for the fourth-period element in Group VA? A) B) C) D) E) ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.3
OBJ: Determine the configuration of an atom using the period and group numbers. (Example 8.3)
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration and the periodic table | writing electron configurations using the periodic table MSC: general chemistry
41. The statement that "the lowest-energy configuration for an atom is the one having the
maximum number of unpaired electrons allowed by the Pauli principle in a particular set of
degenerate orbitals" is known as A) the aufbau principle. B) Hund's rule.
C) the Pauli exclusion principle.
D) Heisenberg uncertainty principle. E) the quantum model. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.4 OBJ: State Hund’s rule.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms
KEY: electron configuration | Hund's rule MSC: general chemistry
42. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state? 1s 2s 2p
A) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
B) No rules or principles are violated by this orbital diagram. C) aufbau principle D) Hund's rule E) Pauli exclusion principle ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: easy REF: 8.4 OBJ: State Hund’s rule.
TOP: atomic theory | electronic structure of atoms