





Preview text:
DUY TAN UNIVERSITY
SOURTHSTAR MANATEMENT INSTITUTE 2023-24 Term II
SMI-ECO 152 – Introduce on to Macroeconomics Group Project
Macroeconomic Study of Selected Economy: Japan Date : 15th May, 2024
Submi 琀琀 ed by: AUNG KYKAW NGUYỄN CAO THỤC UYÊN No. Full Name ID Signature Point Achieved ( INSTRUCTION ONLY ) 1
Trần Thị Thanh Loan 29204654188 2
Nguyễn Thị Hoài Nhi 29204660601 3
Nguyễn Thị Kiều Ngân 29204355236 4 Phạm Xuân Nhi 29294658641 5 Lê Anh Thi 29204658922 6 1. Information about Japan
Country name: Japan 日本. The official English name is Japan Capital Tokyo
Geographic location: Japan is an island nation in Northeast Asia, part of a submarine
mountain range stretching from Southeast Asia to Alaska
Area: 377,972.75 km2 (ranked 61st out of 197 countries in the world)
Climate: Temperate climate, with 4 distinct seasons.
Population: 126,740,000 people (2017). Ethnicity: Japanese
2. Location - Japanese geography
Japan is located in East Asia, in the western part of the Pacific Ocean, made up of four large
archipelagos: Kuril Islands (Japanese call them Chishima Islands), Japan Islands, Ryukyu and Izu-Ogasawara.
This is an island nation completely not contiguous with any country or territory on the mainland, surrounded by seas:
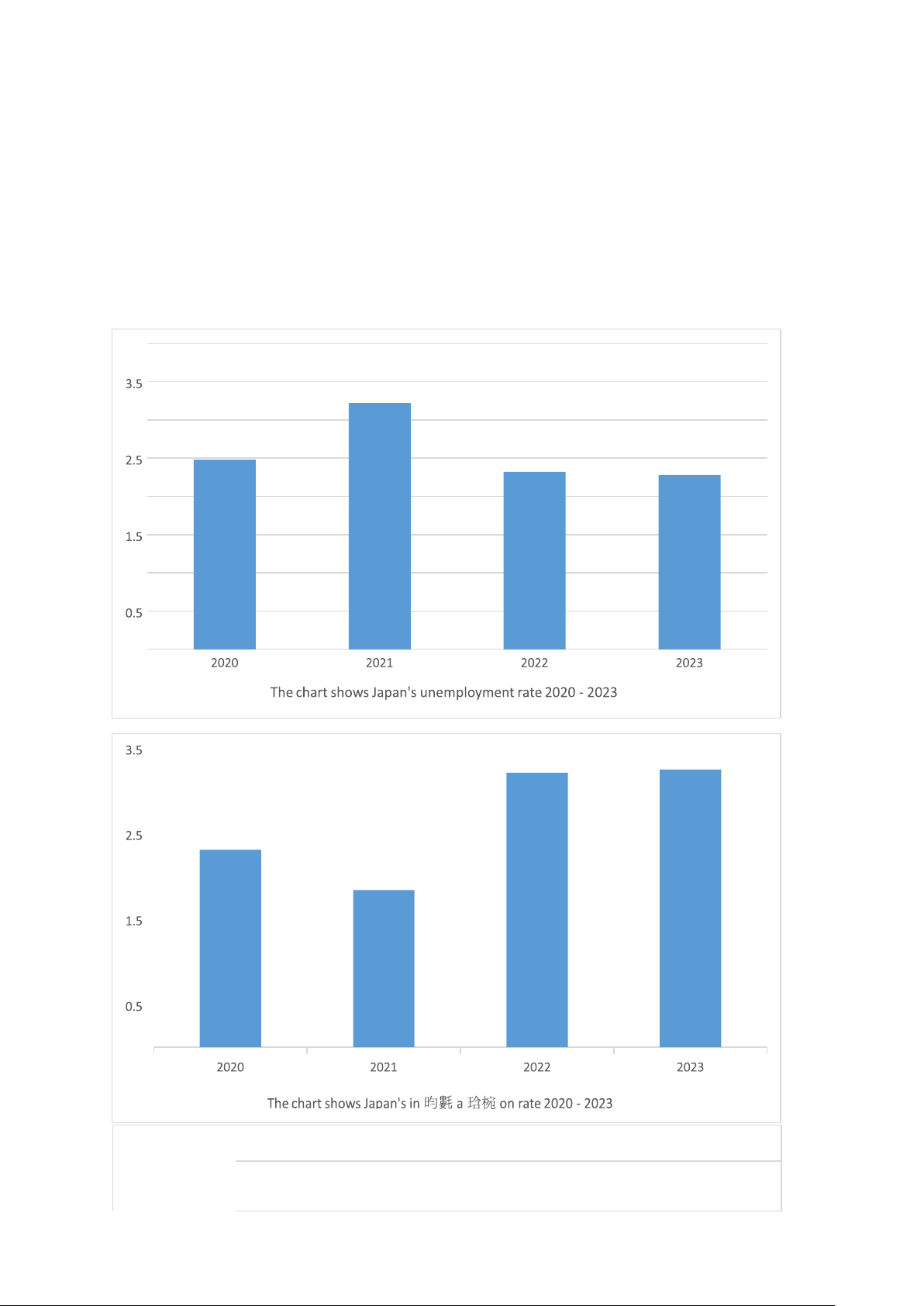
- East and South: Pacific Ocean. - Northwest: Sea of Japan. - West: East Sea - Northeast: Sea of Okhotsk. Japan's unemployment rate: • 2.6% (2023)[12]
• 3.7% of young people are unemployed (15 to 24 years old; May 2023)[12]
• 1.8 million unemployed (May 2023)
Japan's average unemployment rate in 2020 has reached a record high in the past 11 years due
to the impact of the COVID-19 acute respiratory infection epidemic.
The total number of unemployed workers is 19.1 million, an increase of 290,000 people
compared to 2019. The number of workers temporarily out of work in 2020 also recorded a
record level since 1968 of 2.56 million people, an increase of 800,000 people.
Japan's total unemployment rate has maintained a high level in recent months, of which the
rate in December 2020 was 2.9%. Accordingly, in December 2020, the total number of
unemployed workers in Japan was 2.04 million people, an increase of 60,000 people
compared to the previous month. The unemployment rate for men was 3.1%, down 0.1
points, while the unemployment rate for women was 2.7%, up 0.3 points.
As of December 2020, the total number of Japanese workers was 66.95 million, down 60,000
people compared to the previous year. An official from the Japanese Ministry of Health,
Labor and Social Welfare said that Japan's complete unemployment rate in December 2020
was stable compared to the previous month. However, the country's labor market is still
negative when the number of workers decreases and the recruitment rate does not improve.
On January 29, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Social Welfare also said that the
country's recruitment demand in 2020 has decreased sharply due to the impact of the COVID 19 epidemic.
Accordingly, Japan's average recruitment rate in 2020 is 1.18, down 0.42 points compared to
2019. This decrease has surpassed the time of the 2009 financial and economic crisis and
ranks third in History after the oil crisis of 1974 and 1950.
Japan's unemployment rate in 2022 is 2.60% according to the latest data from the World
Bank. Accordingly, the Japanese unemployment rate index decreased by 0.23 percentage
points compared to 2.83% in 2021. It is estimated that the Japanese unemployment rate in
2023 is 2.39% if the socio-economic situation remains the same as last year. . With the
assumption that the Japanese economic situation and the world economy do not change much. Japan's unemployment
rate data recorded in 1960 was 1.70%, over a period of 62 years, until now the latest
unemployment rate data is 2.60%. Japan's unemployment rate peaked at 5.39% in 2002.
(Source: https://solieukinte.com/ty-le-that-nghiep-nhat-ban/ ) 2.Economic Indicators Economic
Japan Vietnam Poten 琀椀 al Policies for
Poten 琀椀 al Policies for Indicator (2022) (2022) Japan Vietnam GDP Growth Rate 1.1% 8.0%
Implement structural reforms Maintain stable to boost produc 琀椀 vity, macroeconomic policies, encourage business invest in infrastructure, investment, increase labor develop human capital
force par 琀椀 cipa 琀椀 on In 昀氀 a 琀椀 on 2.5% 3.6%
Maintain accommoda 琀椀 ve Tighten monetary policy Rate monetary policy while gradually to control in 昀
monitoring in 昀氀 a 琀椀 on 氀 a 琀椀 on Unemployment 2.6% 2.3% Promote labor market 昀氀 Invest in job crea 琀椀 on, Rate
exibility, provide training and par 琀椀 cularly in high- reskilling programs growth sectors Current Account 2.9%
-1.1% de Encourage domes 琀椀 c Diversify export markets, Balance (% of
surplus 昀椀 cit demand and investment to a 琀琀 ract foreign direct GDP) reduce reliance on exports investment
Public Debt (% of 263.0% 43.1% Implement 昀椀 scal Maintain 昀椀 scal GDP)
consolida 琀椀 on measures, discipline, improve tax
increase tax revenue, reform collec 琀椀 on, invest in pension system produc 琀椀 ve sectors
Poten 琀椀 al policies for Japan: •
Implement structural reforms to increase produc 琀椀 vity and compe 琀椀琀椀
veness in various sectors, such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services. •
Encourage business investment through tax incen 琀椀 ves, deregula 琀椀 on, and
improving the business environment. •
Increase labor force par 琀椀 cipa 琀椀 on, par 琀椀 cularly among women and the
elderly, through be 琀琀 er childcare support, 昀氀 exible work arrangements, and skills training. •
Promote innova 琀椀 on and technological development through increased research
and development funding and collabora 琀椀 on between academia and industry.
Poten 琀椀 al policies for Vietnam: •
Maintain stable macroeconomic policies, including prudent 昀椀 scal and monetary
policies, to support economic growth and investor con 昀椀 dence. •
Invest in infrastructure development, par 琀椀 cularly in transporta 琀椀 on, energy,
and telecommunica 琀椀 ons, to facilitate economic ac 琀椀 vi 琀椀 es and a 琀琀 ract foreign investment. •
Develop human capital through investments in educa 琀椀 on, voca 琀椀 onal
training, and healthcare to improve produc 琀椀 vity and support the transi 琀椀 on to a knowledge-based economy. •
Enhance the legal and regulatory framework to improve the business environment,
protect intellectual property rights, and promote compe 琀椀琀椀 on. •
Diversify export markets and a 琀琀 ract foreign direct investment in high-value-
added sectors to reduce reliance on a few major trading partners. 4 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 2020 2021 2022 2023
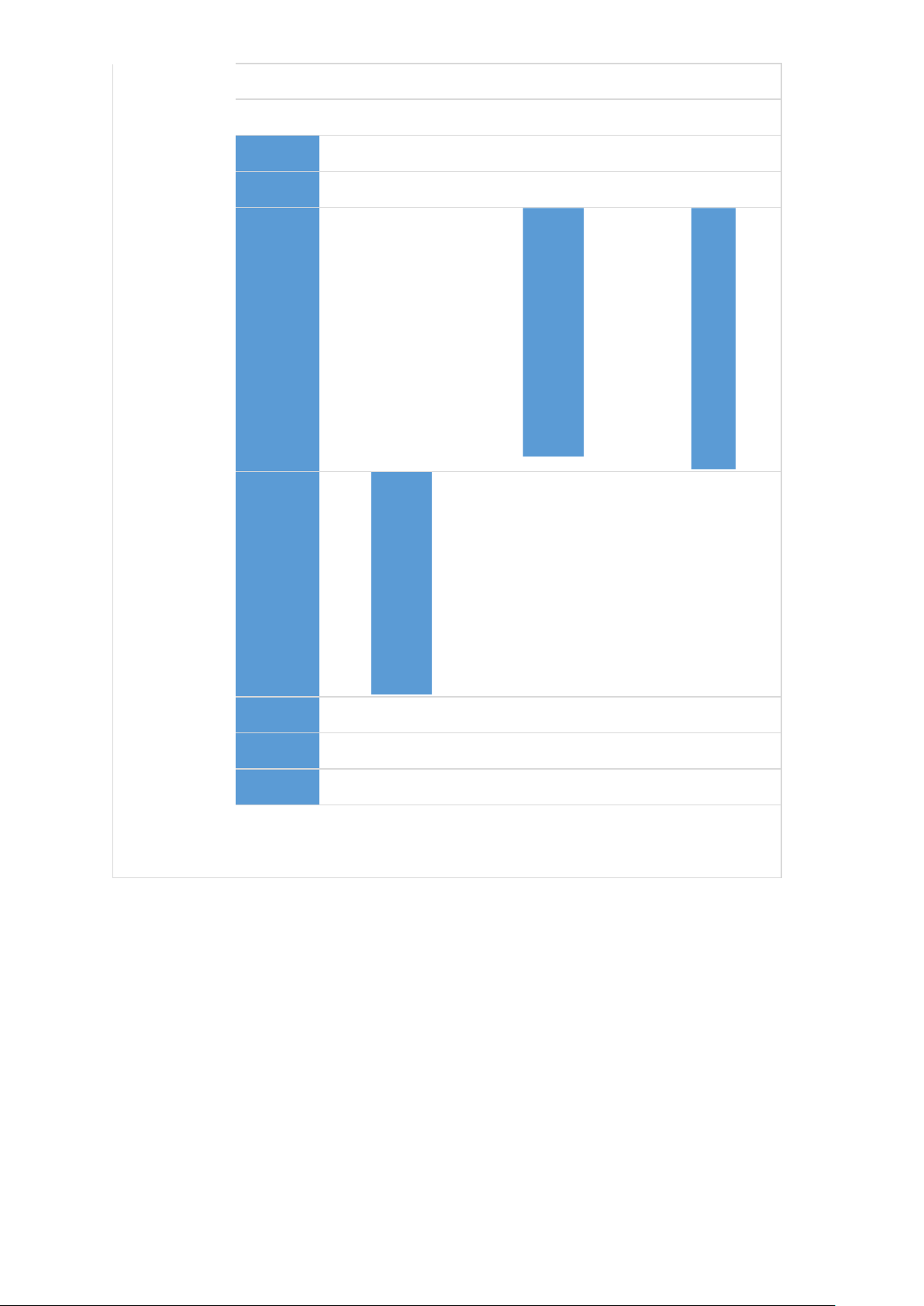
The chart shows Japan's GDP from 2020 - 2023 ---
The unemployment rate among the working-age population in 2020 was 2.48%, 0.31
percentage points higher than in 2019. The unemployment rate for youth (aged 15-24) in
2020 was 7.10%. The unemployment rate among the working-age population in urban areas
was 3.88%, an increase of 0.77 percentage points.
The number of unemployed individuals among the working-age population in 2021 was over
1.4 million, an increase of 203.7 thousand compared to the previous year. The unemployment
rate among the working-age population was 3.22%, an increase of 0.54 percentage points from the previous year.
The number of unemployed individuals among the working-age population in 2022 was
nearly 1.07 million, a decrease of 359.2 thousand compared to the previous year. The
unemployment rate among the working-age population in 2022 was 2.32%, a decrease of
0.88 percentage points from the previous year.
In 2023, the country had nearly 1.07 million unemployed individuals among the working-age
population, a decrease of 14.6 thousand compared to the previous year. The unemployment rate
among the working-age population in 2023 was 2.28%, a decrease of 0.06 percentage points from the previous year.
The inflation rate in Vietnam in 2020 increased slightly by 2.31% compared to the previous
year's average. This achieved the National Assembly's target of below 4%. For the
macroeconomy, the government has managed and directed appropriately to ensure Vietnam's
more positive growth with macroeconomic indicators being secured.
In 2021, despite being affected by many factors, Japan's inflation was still well controlled.
With an inflation rate of 1.84%, in 2022, the inflation rate increased slightly to 3.21%.
Currently, Vietnam is among the few countries with an average inflation rate of 4-6%.
In 2022, the inflation rate increased slightly to 3.21%, and Japan is among the few countries
with an average inflation rate of 4-6%. In the first quarter of 2023, the Consumer Price Index
(CPI) increased by 4.18% compared to the same period last year; core inflation increased by 5.01%.
In 2023, the January CPI increased sharply by 4.89%, with significant inflationary pressures,
but then gradually decreased. By June, the increase was only 2%, and by December, it increased by
3.58%. The average inflation rate for the whole year of 2023 was 3.25%, achieving the National Assembly's target.
According to the General Statistics Office, Japan's GDP scale at current prices in 2023 is
estimated to reach 10,221.8 trillion dong, equivalent to 430 billion USD. According to the
General Statistics Office, Japan's GDP scale at current prices in 2022 is estimated to reach
408.8 billion USD. According to the General Statistics Office, Vietnam's GDP scale at current
prices in 2021 is estimated to reach 366.1 billion USD. According to the General Statistics
Office, Japan's GDP scale at current prices in 2020 is estimated to reach 346.6 billion USD. 3. Summary and conclusion
Japan's average unemployment rate in 2020 was
reached a record level in the past 11 years due to the in 昀氀 uence of Covid 19 acute respiratory infec 琀椀 on
- The total unemployment rate has remained high throughout the yearIn recent
months January, December 2022 increased by 60,000 compared to last month
with an unemployment rate of 2.04 million people
Table comparing the unemploymeny rate in the working age over the years Year 2021 2022 2023 Amount of people Increase 203,7 increase 359,2 Reduced 14,6 thousand compared thousand thousand to 2019
compared to 2021 compared to 2022 Unemployment 3,22% 2,32% 2,28% rate
- The Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare and Society has said that recruitment
demand has decreased sharply because of the impact of the covid epidemic
- From 2019 to 2020 the recruitment rate decreased by to 0.42 points
- The 2020 in 昀氀 a 琀椀 on rate in Vietnam increased slightly by 2.31%
compared to 2019. In 2021, despite being subject to many factors, the rate is s 琀
椀 ll well controlled with in 昀氀 a 琀椀 on at 1.84%. In 2022, the rate will
increase slightly at 3.21%. In 2023, the in 昀氀 a 琀椀 on rate is 3.25%
- According to data from the General Sta 琀椀 s 琀椀 cs O 昀케 ce, the scale of
GDP at current prices from 2020 to 2022 tends to increase slightly, from 2022 to 2023 it increases sharply. Japan's Economy -
Japan contracted for the second consecu 琀椀 ve quarter in the period October-
December 2023, dropping it to fourth place in the global economic rankings. -
Data from the Interna 琀椀 onal Monetary Fund (IMF) shows that, measured in USD,
the Japanese economy will decrease from 6,300 billion USD in 2012 to about 4,200 billion
USD in 2023. Part of the reason is said to be due to the impact of the weaker Yen and aging popula 琀椀 on. -
At this 琀椀 me, Japan's GDP is lower than Germany's in USD terms. Meanwhile, the
Indian economy is considered ready to surpass both economies in the next few years. -
Japan's decline in economic rankings is partly a sign of the Yen weakening against the
USD. At the same 琀椀 me, the weakening of the Japanese currency is also reducing
consumer purchasing power by contribu 琀椀 ng to in 昀氀 a 琀椀 on through rising import costs.
Spiritual life of Japanese people -
We can say that there is no na 琀椀 on as sensi 琀椀 ve to foreign cultures as the
Japanese. They constantly monitor changes in the external situa 琀椀 on, evaluate and
consider the e 昀昀 ects of the main currents and trends taking place on Japan, and if they
discover which trend is prevailing, they will They tend to be willing to learn and research to keep up with that trend. -
At work, Japanese people o 昀琀 en put aside their egos to promote the common
good, 昀椀 nding harmony between themselves and those around them. Teams can
compete with each other very 昀椀 ercely, but there are 琀椀 mes when they join hands to
achieve a common goal, such as defea 琀椀 ng a foreign compe 琀椀 tor. Therefore, the ul
琀椀 mate taboo is to lose the collec 琀椀 ve honor. -
The sense of respect for hierarchy has probably existed for a long 琀椀 me in the
lives of Japanese people. The a 琀 tude of being humbled before people with status and
authority also exists in some other countries in modern 琀椀 mes, but especially in Japan, it is s 琀椀 ll strong today. -
Japanese people are famous for being diligent workers, viewing the company's work
as their own, always dedicated, some 琀椀 mes they do not work for their own personal
bene 昀椀 t, they see their work as their own. Theirs is not only an "economic ac 琀椀 vity"
but also an "aesthe 琀椀 c ac 琀椀 vity". -
Compare with Vietnam's economy -
Japan is one of the most developed economies in the world, with a high GDP and
several leading mul 琀椀 na 琀椀 onal companies such as Toyota, Sony, Honda. Meanwhile,
Vietnam is an emerging economy, growing rapidly and a 琀琀 rac 琀椀 ng a lot of foreign investment. -
Japan has a developed high-tech industry, while Vietnam relies mainly on the
processing industry, services and agriculture. -
Japan has a developed and modern infrastructure system, while Vietnam is in the
process of inves 琀椀 ng and improving its infrastructure. -
Japan has developed into a developed economy and society, while Vietnam is in the
process of development and has great poten 琀椀 al. Referenve materials
- h 琀琀 ps://vov.vn/kinh-te/vi-sao-nhat-ban-mat-vi-tri-nen-kinh-te-so-3-the-gioi- post1077225.vov
- h 琀琀 ps://fqa.vn/cau-hoi/64a57a7f27a7b61731a39ec9
- h 琀琀 p://leesco.vn/index.php?route=common/home
- h 琀琀 ps://nhandan.vn/gdp-binh-quan-dau-nguoi-nhat-ban-lan-dau-琀椀 en-giam-xuong-
muc-thapnhat-trong-g7-post789273.html CONTENTS
COUNTRY BACKGROUND.........................................................................................................1 Introduc 琀椀
on.........................................................................................................................1
Country Name......................................................................................................................1
Geographical loca 琀椀 on...............................................................................................1
ECONOMIC INDICATORS..........................................................................................................2
Economic Output (GDP).......................................................................................................2
GDP Growth Rate.................................................................................................................2
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION.................................................................................................3
REFERENCES.............................................................................................................................4
APPENDIXES.............................................................................................................................5
Appendix-A. Title of your data.............................................................................................5
Appendix-B. Title of your dat................................................................................................6
Appendix-C. Team members’ Roles and Responsibili 琀椀 es..........................................7
Appendix-D. Other appendixes you want to add.................................................................



