







Preview text:
Chapter 1: Introduction to business
1. Definition of organization: -4 key words:
+Social arrangement: individuals gathered together for a purpose
Ex: pp work in different divisions, making different cars
+Controlled performance: performance is monitored against the goals and adjusted if necessary to
ensure the goals are accomplished
Ex: Cost and quality are reviewed and controlled. Standards are constantly improved
+Collective goals: the organization has goals over and above the goals of the pp within it Ex: Sell car, make money
+Boundary: the organization is distinct from its environment Ex: Physical: factory gates Social: employment status
-Reasons for organization to exist:
+Overcome people’s individual limitations: physical, intellectual limitation
+Let people specialize in specific areas: let people do what they are best +Save time: working together +Accumulate: sharing knowledge +Pooling their expertise
+Synery: combined outputs of more than one person; combining ideas, knowledge of different
individuals, outcomes of an individuals cannot excess outcome of many individuals (kết quả của nhiều
người sẽ tốt hơn kết quả của một người)
-> Organization enable people to be more productive 2. Business
-Criteria to determine a business: primary ofjectives
-Classifying business and not-for-profit organization.
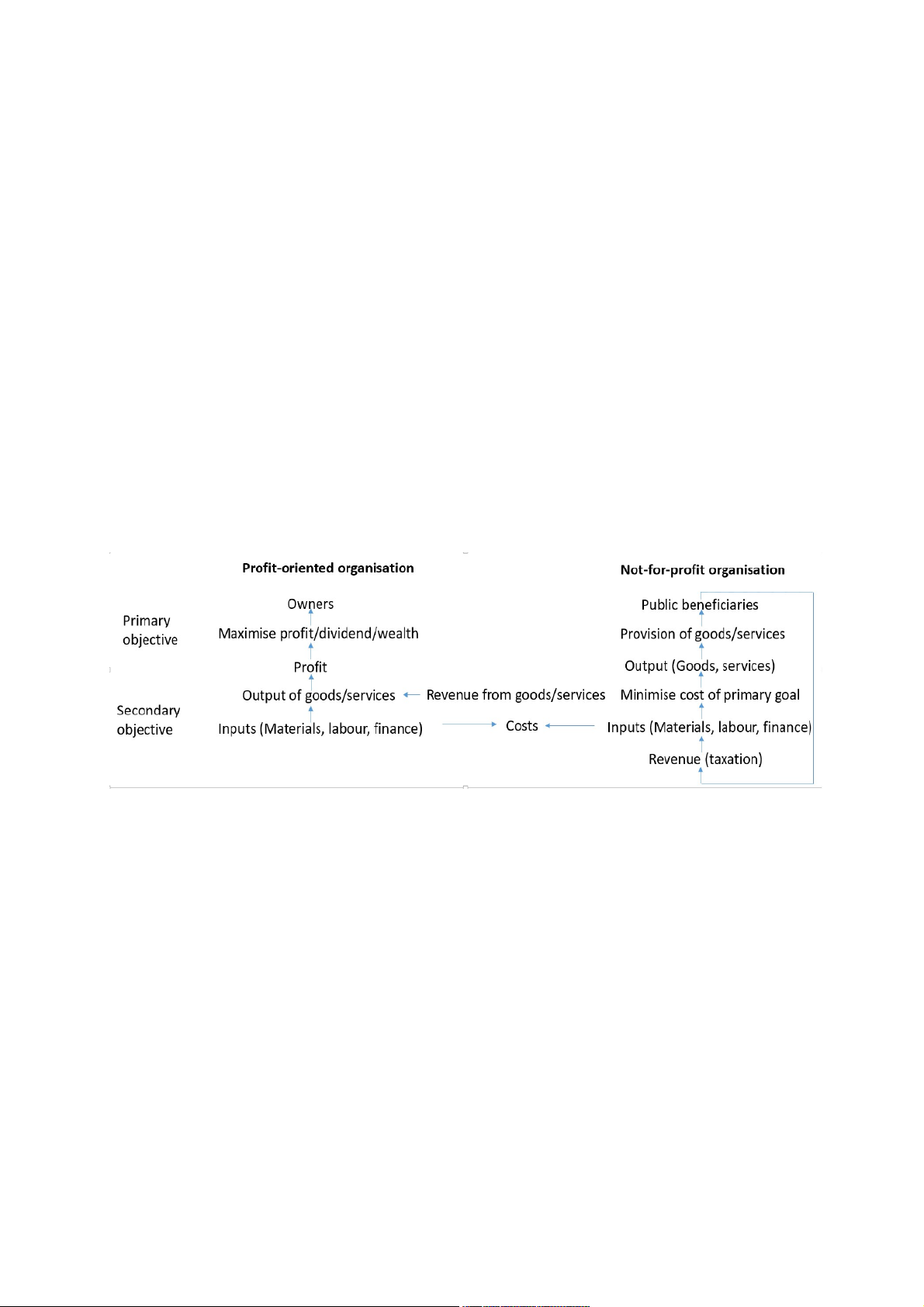
+Business (profit-oriented organisations): is oriented towards making a profit for its owners as to
maximize their wealth, can be regarded as an entity separate from its owners
+Not-for-profit organisations: a charity (UNICEF), a trade union, a local authority, an army, a club
/NFP focused on providing goods and services to their beneficiaries at minimised costs.
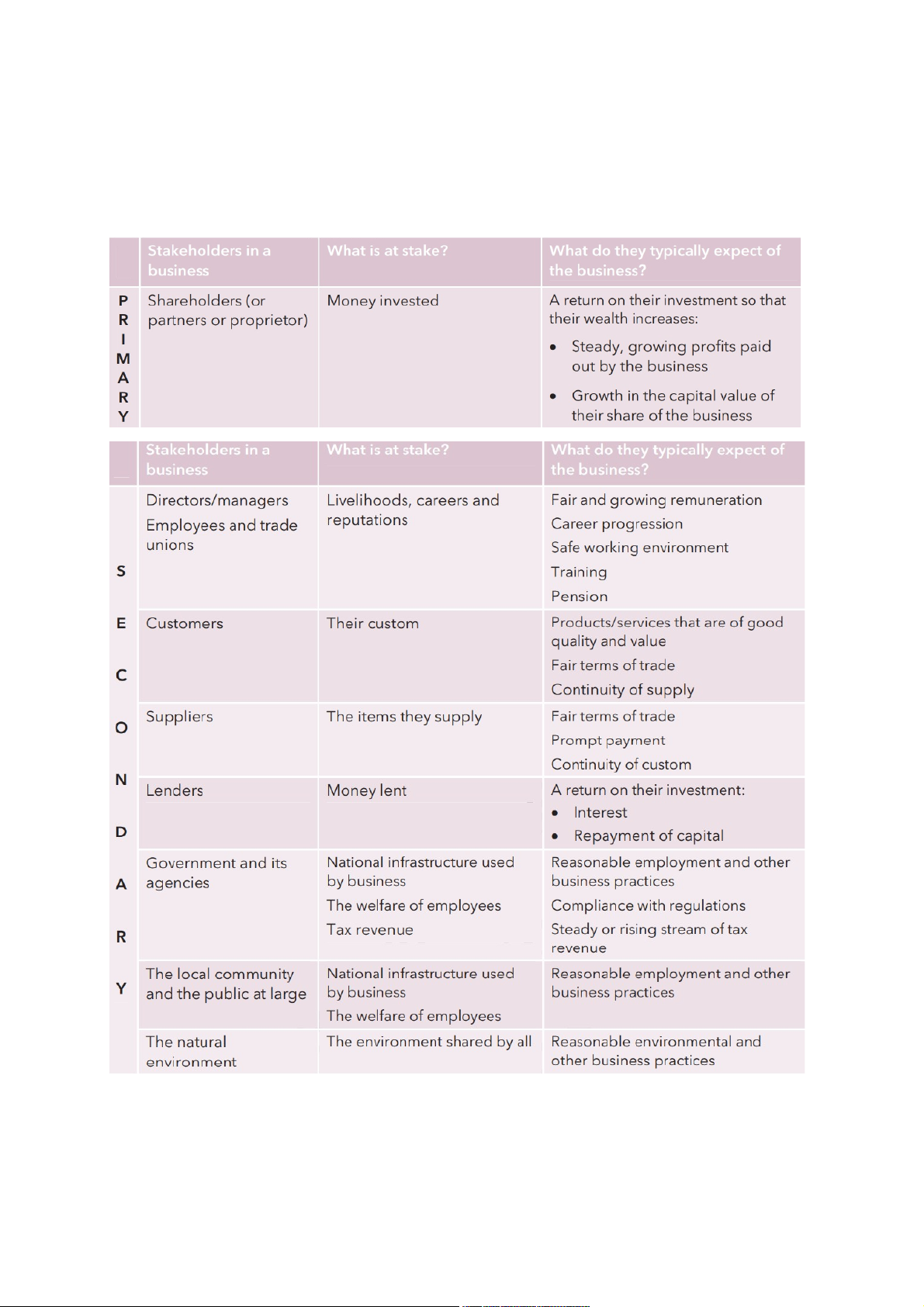
-Stakeholders: level of interest of stakeholders in a business -> Where their interest rests? How these interest are?
-Sustainability and sustainable development goals
+Sustainability concerns the use of both of the following: Tangible resources (natural capital and
energy) and intangible resources (human/ intellectual capital and relationship with stakeholder)
+Sustainability is the ability to “meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of
future generations to meet their own needs” +Sustainable development:
+End poverty, fight inequality, stop climate change
+Decent work and economic growth
+Industry, innovation and infrastructure
+Responsible consumption and production
-Hierarchy of objectives: Primary objectives, secondary objectives (business and not-for-profit organization)
+For a business the primary object is: making as much profit as possible (profit maximisation) so as to
increase shareholder wealth /How the business create value
/Shareholder wealth only maximized if profit is earned at an acceptance level of risk
/Profit can’t be pursued at any cost
3. Instead of pursuing shareholder wealth:
-Satisficing: maintain satisfactory profit for shareholders rather than maximizing shareholders’ wealth
-Revenue maximization: A business may act to maximise revenue in order to maintain or increase its
market share, ensure survival, and discourage competition. (manager profit personally by following
this objective because of the prestige of running a large company)
-Constrain theory: the need to satisfy customers with quality products and services, which may lower profitability
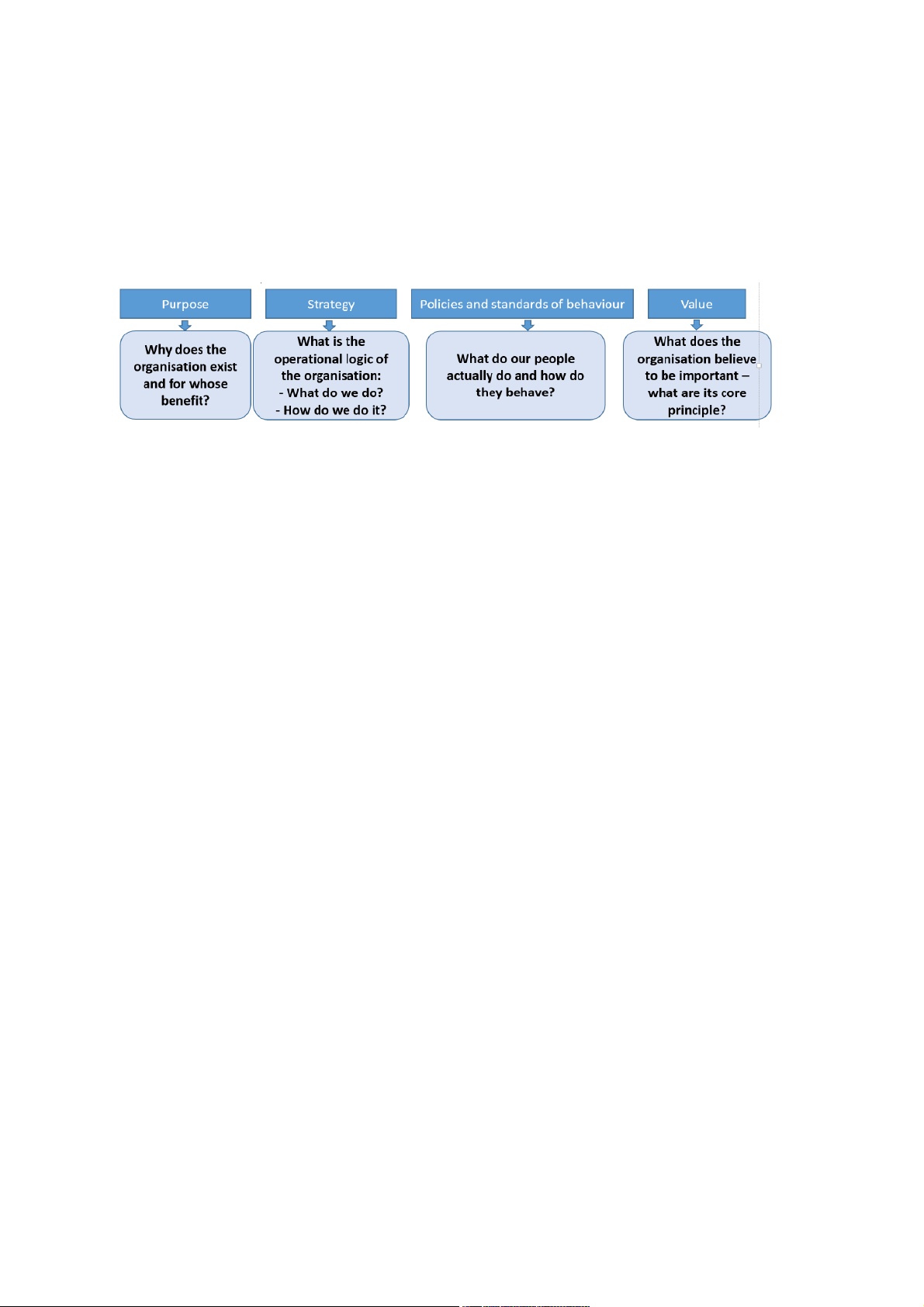
4. Mission, vision, goals, plans, standards
-Mission: expressed in terms of how it satisfies its various stakeholder /Element of mission:
-Vision: some business also have a vision of the future state of the industry or business which
determines what its mission should be
-Goals: SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achiveable, Relevant, Time-bound)
-Plans: State what should be done to achieve the operational objectives. Standards and targets specify a
desired level of performance (physical standards, cost standards, quality standards)
Chapter 2: Managing a business
A. Management and business function
1. EfÏcient management:
Power, authority, accountability, responsibility and delegation
-Power: sources of powers (quyền lực)
+Coercive (cưỡng ép): physical force or punishment
+Reward (khen thưởng) control over valued resources
+Legitimate (position power) manager has the power to authorise expense, issue instructions
+Expert (chuyên gia) experiences, qualifications
+Referent power (personal power) force of personality or charisma, which can attract, influence or inspire other pp
+Negative (nhân viên đình công)
-Authority: thẩm quyền, quyền hạn
-Accountability: nghĩa vụ giải trình đối với cấp trên về công việc của mình
-Delegation: giving someone else the responsibility and authority to do sth, while remaining
responsible and accountable for that thing being done properly (ủy thác nghĩa vụ) 2. Types of manager:
Line manager, staff manager, functional manager and project manager
+Line manager: người có quyền managing over subordinates (người chịu trách nhiệm cho từng phần cụ thể)
+Staff manager: giving advices for other managers in other department (chỉ có trách nhiệm đưa ra lời
khuyên chứ không có thẩm quyền yêu cầu manager khác làm gì)
+Functional manager: là sự kết hợp của staff manager và line manager, có quyền yêu cầu các phòng ban
khác phải thực hiện theo yêu cầu, nhiệm vụ mà functional manager đề ra.
+Project manager: over project team members (temporary
3. Management hierarchy:
Top manager, middle line managers, first line managers, operational staffs
Power and authority: descending Accountability: ascending 4. Management process
Planning -> Organising -> Controlling -> Leading
+Planning: determining objectives, aims, goals, potential resources to deploy, forecast and resources
+Organizing: allocating resources (human resources, financial resources, machine capability, ..), determining process, standards
+Controlling: comparing actual outcomes and implementation to plans
+Leading: leader’s role, role model for team members +Feedback! 5. Managerial roles
+Informational roles: receive data -> passing to relevant person; acting as “spokenperson” (đại diện cho
team để communicating- mang tính về giải trình công việc, presenting about team’s tasks to other managers
+Interpersonal roles: acting as team leaders, linking with managers of other teams (là người đi đại diện,
ngoại giao, tạo dựng mối quan hệ)
+Decisional roles: making decisions (allocating resources; handling problems, disturbances; negotiating;
solving problems; acting as entrepreneur) 6. Business culture:
Combining flexibiliy and control with in-outward looking: 4 models of business culture
-Flexibility+ Outward looking: Open system culture
-Flexibility+ Inward looking: Human relation cultre
-Control+ Outward looking: Rational goals culture
-Control+ Inward looking: Internal process culture 7. Business functions *Marketing: -Marketing
-Marketing orientation (considering customers’ needs as a basis for development); sales orientation;
product orientation (fall in love with the company’s products); production orientation (providing variety of products)
-Differences between consumers and consumers (khách hàng và người tiêu thụ)
-Consumer markets –B2C: fast moving consumer goods(high volume, fast consumption, low value);
Consumer durables (white goods, brown goods, soft goods); services -Industry market –B2B -Marketing mix: +Tangible products : 4Ps Product
Price: factors affecting price policy: 4 main factors: costs, competitors, customers, corporative objectives
Promotion: advertising, sale promotion, public relation
/Pull promotion: direct marketing, advertising, making product to be outstanding -> persuade customer to buy the company product
/Push promotion: using intermediaries to introduce goods or services to customers
Place (distribution): pros and cons of direct selling and using intermediaries •Using direct selling Pros
- No need to share profit margins - Control over ultimate sale
- Speed of delivery to ultimate consumer likely to be quicker •Using intermediaries - More efÏcient logistically - Cost usually lower
- Consumers expect choice at point of sale
- Producers may not have sufÏcient resources to sell dirrect
+Intangible products (services): 7Ps – 3 added Ps: People, Process, Physical evidences
**Operation (production)
-4Vs: Volume; Variety (wide range of products); Variation in demand; Visibility -> affects to unit cost? Level of inventory?
+Volume: differ in the volume of inputs and outputs //Higher volume: lower COGS
//Low volume: higher value per unit
+Variety: tính đa dạng của sp (high variety thì high COGS và ngược lại)
+Variation in demand: sự thay đổi trong nhu cầu theo mùa vụ, thời gian (high thì fluctuating demand, low thì stable demand)
+Visibility: sự tiếp xúc với khách hàng
//High: dvu tư vấn tài chính, nhân viên bán bảo hiểm, ngân hàng
//Low: doanh nghiệp sản xuất
-Balancing main variables (những nhân tố mà DN cần phải cân đối để xác định các mức độ về nhu cầu) +Interal and external demands +Current resources +Capacity of fixed assets +Inventory levels +Performance of processes
***Research and development
-Pure research: original research to get new scientific and technical knowledge or understanding, no
obvious commercial and pratical
-Applied research: has obvious commercial and practical application
-Development: using existing knowledge, techniques to produce new products ****Procurement:
5 right: quantity, quality, place, price, time *****HRM
4Cs: commitment, congruence, competence and cost- effectiveness.
+Commitment: employees’ motivation, loyalty, job satisfaction
+Competence: employees’ skills, ability, potential (tính đồng thuận vì một mục đích chung)
+Congruence: managers and employers share a common vision
+Cost-effectiveness: operational efÏciency and productivity
B. Organisational behaviors
1. Organisational iceberg:
Overt factors: Formal goals, technology, surface competencies and skills, organizational design, financial
resources, rules and regulations
Covert factors: AtÝtudes, communication patterns, informal team processes, personality, conflict,
political behavior, underlying competencies
2. Taylor’s scientific model: 3 main features: -Main motivator: high wage
-Managers: tell workers what to do -Workers: do what manager tell
3. Theory X and theory Y: main characteristics -Theory Y:
▪ Physical and mental effort in work is as natural as rest or play
▪ Commitment to objectives is driven by rewards – self-actualisation is the most important reward
▪ External control and threats are not the only way to achieve objectives – self-control and direction are very important
▪ People learn to like responsibility
▪ The intellectual potential of the average human is only partially used – it needs to develop further
-Theory X: Individuals dislike work and avoid it where possible
▪ Individuals lack ambition, dislike responsibility and prefer to be led
▪ A system of coercion, control and punishment is needed to achieve business objectives
▪ Above all, the individual desires security 4. Motivation
-Maslow hierarchy of needs: basic needs -> safety needs -> social needs -> status needs/ ego needs -> self- actualization needs
-Hygiene and motivating factors:
Dissatisfaction -> Hygiene factors -> No longer dissatisfied -> Motivating factors -> Motivations
Hygiene factors: working conditions, supervison, staffs’ relations, company policy, salary (làm cho nhân
viên bớt chán nản trong công việc)
Motivating factors: challenging, a sense of achievement, recognition, responsibility (làm cho nhân viên
có thêm động lực làm việc) 5. Group behaviors
**Stages to develop a group
Forming -> Storming -> Norming -> Performing
Forming: determining objectives, aims, goals of group
Storming: determining responsibility of each team members
Norming: determining process, standards, group behavior Performing: performing tasks **Team roles:
Leader, shaper, plant, evaluator (người sẽ critize ideas of others), resources- investigator, company
worker (nguời chịu trách nhiệm về mqh giữa các team và team members với nhau), finisher
6. Leadership style (phong cách quản lý)
-Authority: having sufÏcient rights to control and judge the actions of subordinates.
- Autonomy: giving subordinates necessary and reasonable freedom of action to carry out their roles
- Leadership: exercising the power conferred by right in such a way as to win a willing and positive response from subordinates
Exploitative -> Authoritative -> Consultative -> Participative -5 main characteristics:
+Trust in subordinates’ ability: Increase
+Participative motivation style (khả năng sẽ tạo dựng ra động lực cho nhân viên): method to motivate employees: Increase
+Delegation: centralized or decentralized decision making: Increase
+Communication style: communicating manager and subordinates: Increase
+Teamworking: relationship between subordinates and managers: Increase
*** 4 main characteristics of effective managers -Employee-center
-Encouraging participative leadership style
-High standards- but using flexible methods to obtain objectives
-Natural delegation with high level of trust
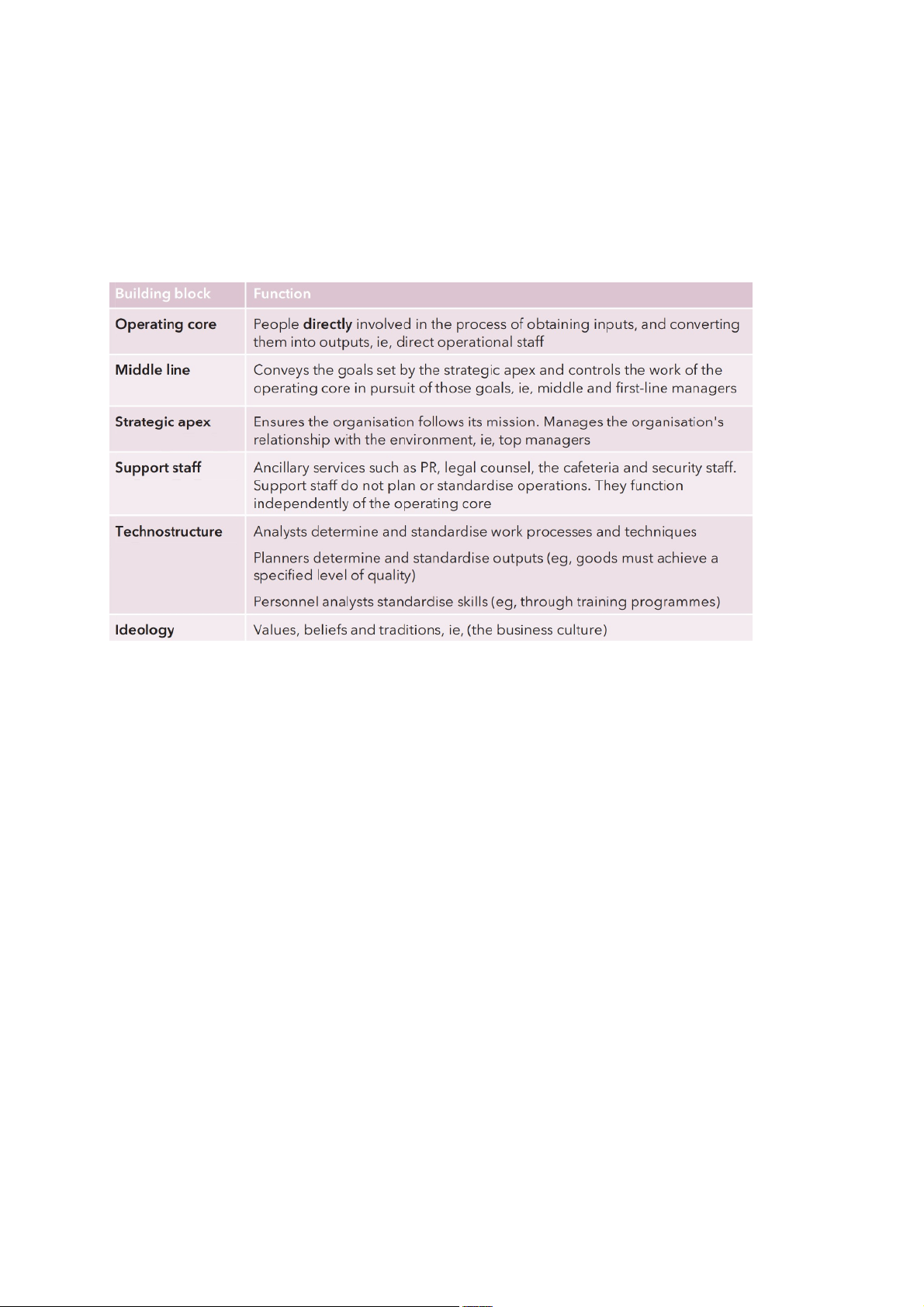
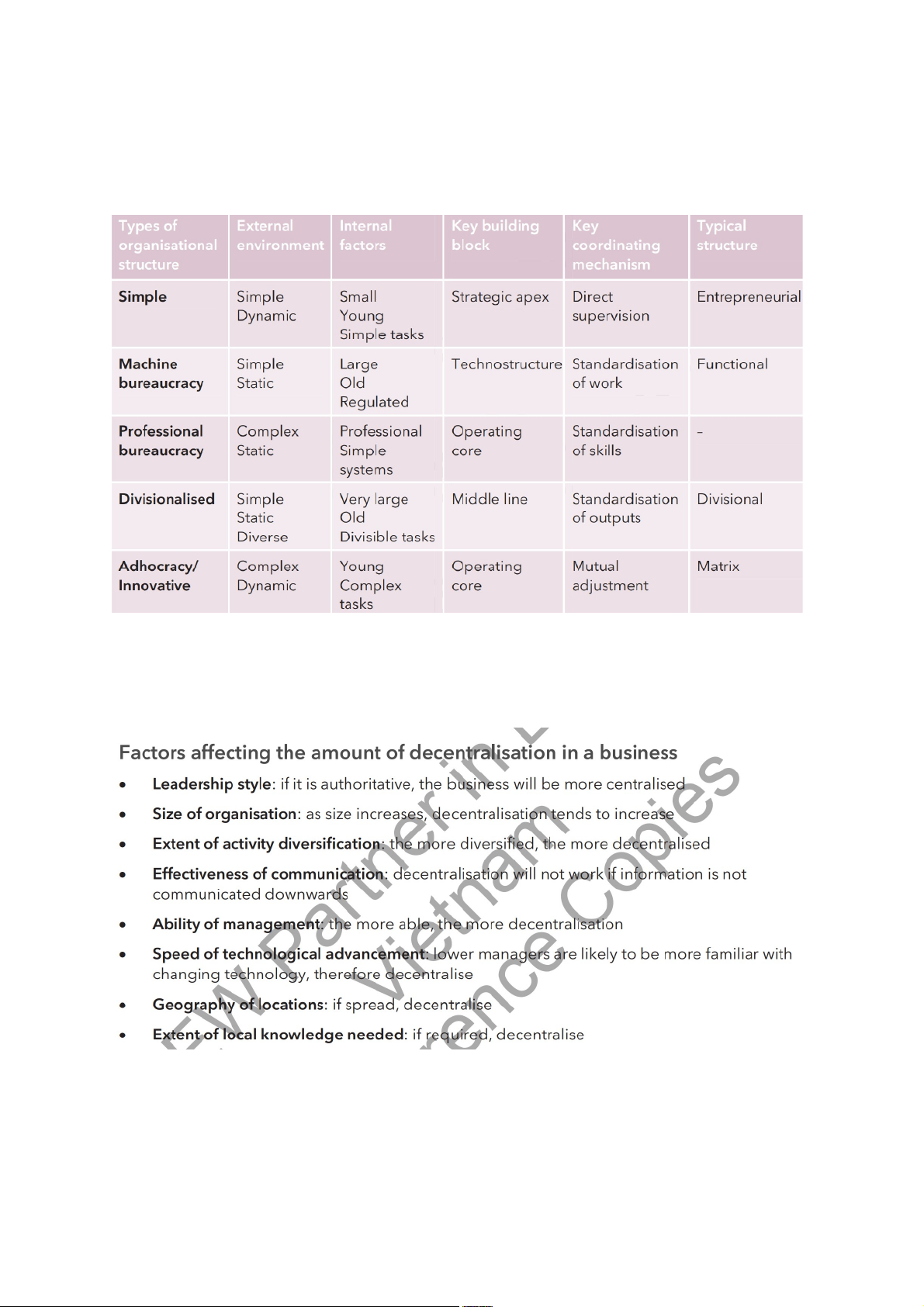
Chapter 3: Organisational and business structure 1. Building blocks 6 blocks: 5 co-ordinating mechanisms:
+Direct supervison: giving of orders by a superior to a subordinate
+Standardisation of works: laying down standard operating procedures
+Standardisation of outputs: specification of results such as the setÝng of targets
+Standardisation of skills: requiring workers to have particular skills or qualifications
+Mutual adjustment: informal communication and self-government
2. Operating structure (phần quan trọng cũng cần phải chú ý)
3. Span of control (slide)
4. Business structure (slide)
Phải nhớ về các factors gây ảnh hưởng đến centralized and decentralized
Chapter 4: Introduction to business strategy




