









Preview text:
1.Intro to Management 1. Who is a manager?
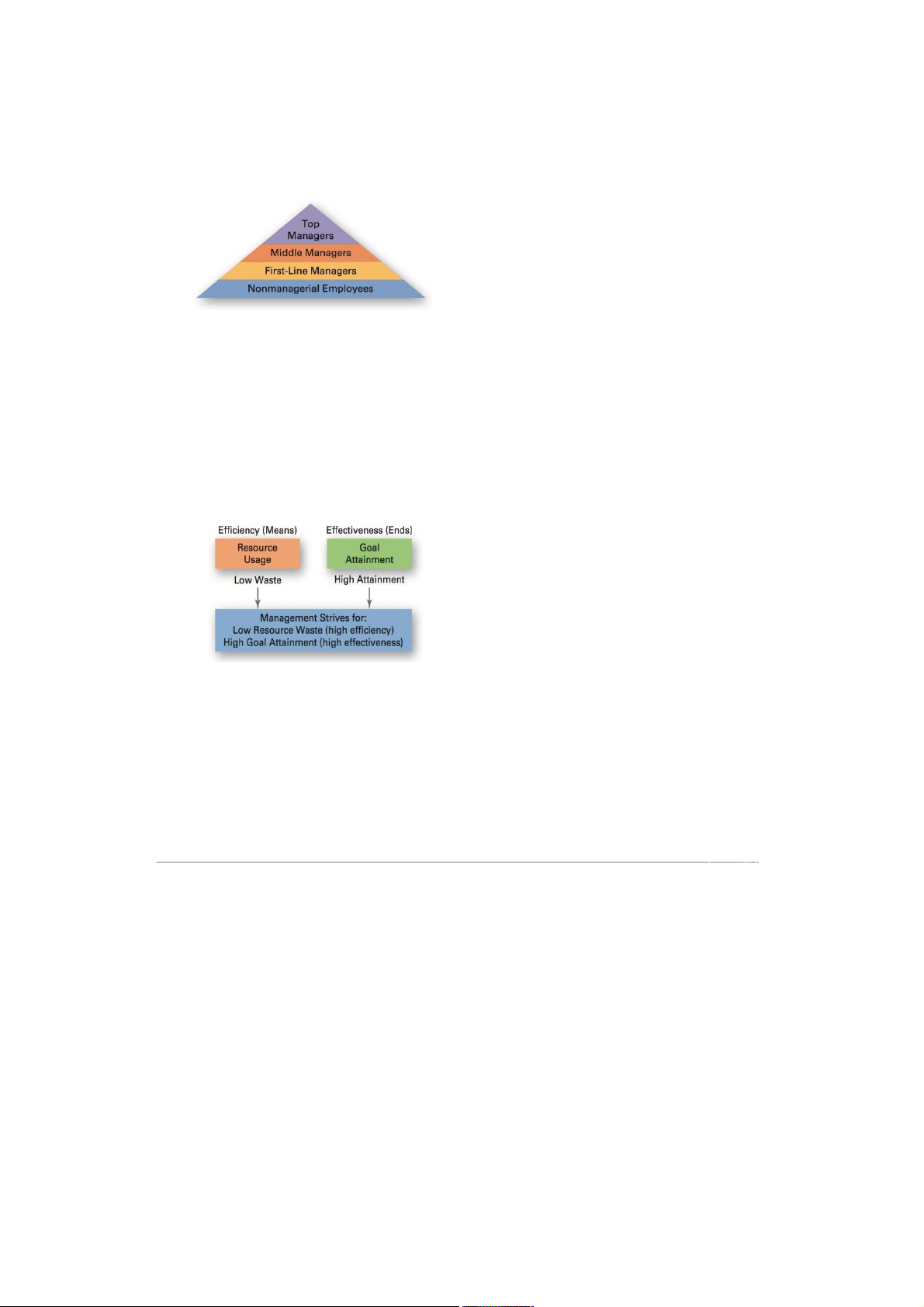
- Manager: coordinates and oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplised. 2. Levels of management
3. Organization: a deliberate arrangement of
people to accomplish some specific purpose.
4. Organization: a deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purpose.
5. Why are managers important?
-Organizations need their managerial skills and abilities now more than ever.
-Managers are critical to getting things done.
-Managers do matter to organizations.
6. Efficiency and Effectiveness
- Efficiency: doing things right. (getting the most output from the least amount of input.
- Effectiveness: doing the right things (attaining organizational goals) 7. Management Functions
- Planning: Defining goals, establishing stategies to achieve goals, and developing plans to intergrate and coordinate activities.
- Organizing: Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational goals.
- Leading: Working with and through people to accomplish goals
-Controlling: Monitoring, comparing and correcting work
8. Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles and a Contemporary Model of Managing
- Interpersonal: Figurehead, leader, liaison.
- Informational: Monitor, disseminator, spokeperson.
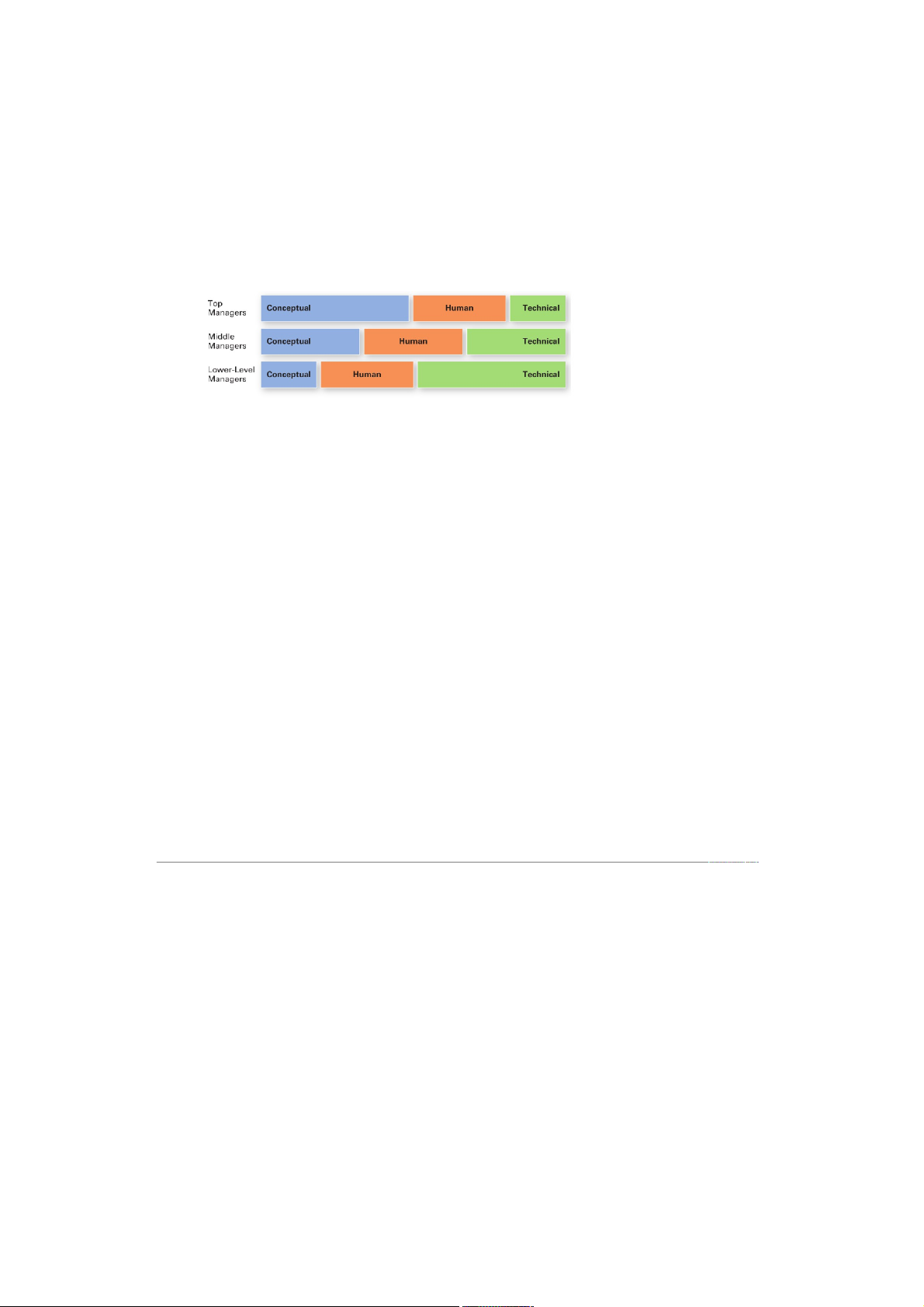
- Decisional: Entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator. 9. Management Skills
- Technical skills: knowledge and proficiancy in a specific field
- Human skilss: the ability to work well with other people
- Conceptual skills: the ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and comples situations concerning the organization. Slide 19 -end (tu doc) 2. Leadership
1. Who are Learers and What is Leadership?
-Leader: someone who can influence others and who has managerial authority
-Leadership: a process of influencing a group to achieve goals 2. Leadership behavior
-Behavioral theories: leadership theories that identify behaviors that differntiate effective leaders from ineffective leaders
3. University of Iowa Studies
-Autocratic style: a leader who dictates work methods, makes unilateral decisions and limits employees participation
-Democratic style: a leader who involves employees in decision-making, delegates authority and
uses feedback as an opportunity for coaching employees
-Laissez-feire style: a leader who lets the group make decisions and complete the work in whatever way it sees fit. 4. Ohio State Studies
-Initiating stucture: the extent to which a leader defines his or her role and the roles of group members in attaining goals
-Considerration: the extent to which a leader has work relationships characterized by mutual
trust and respect for group members’ ideas and feelings.
-High-high leader: a leader high in both initiating structure and consideration behaviors.
5. University of Michigan Studies
-Employee oriented: emphasizing interpersonal relationships
- Production oriented: tended to emphasize the task aspects of the job 6. The Fiedler model
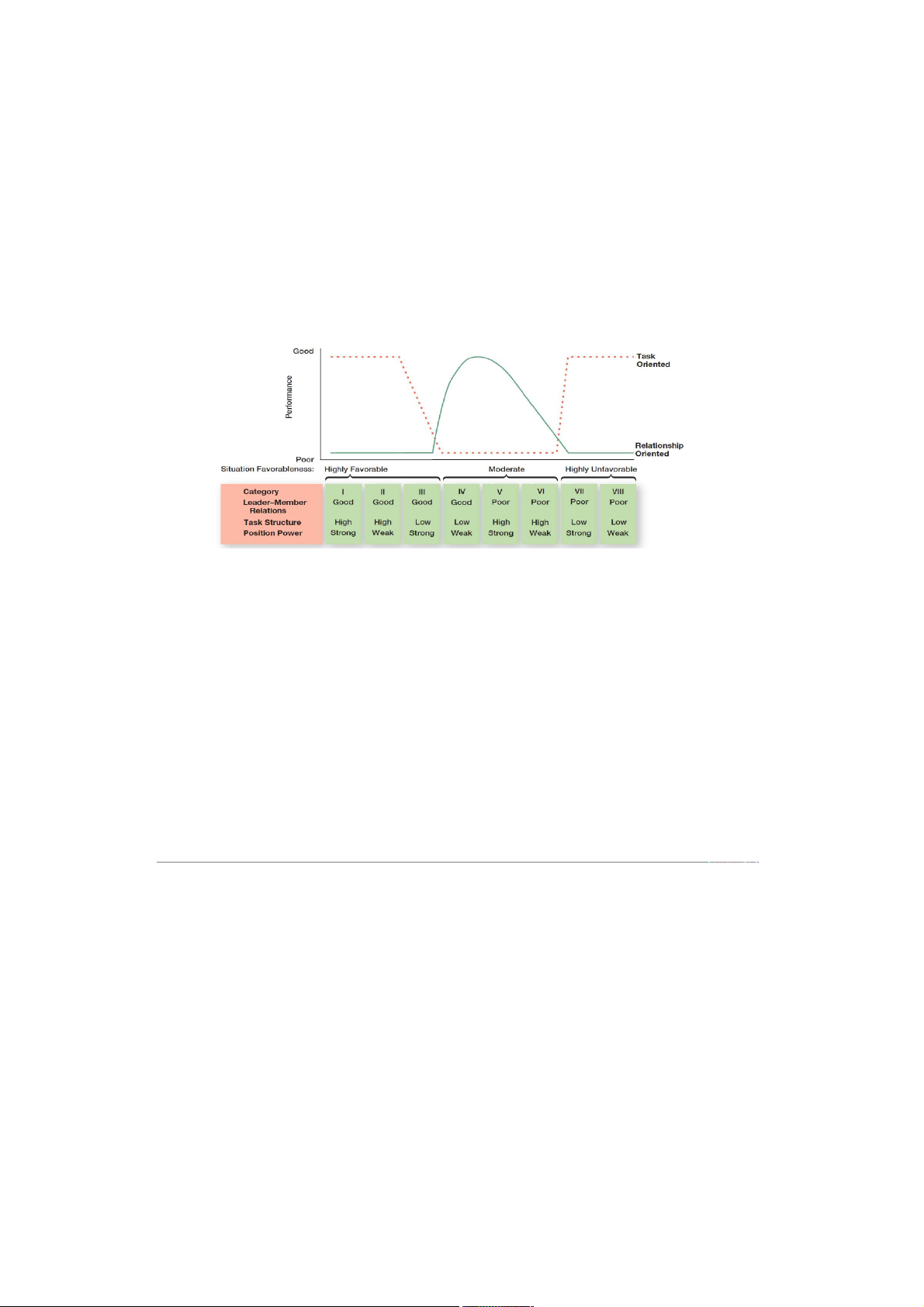
-Fiedler contigency model: a leadership theory proposing that effective group performance
depends on the proper match between a leader’s style and the degree to which the situation
allows the leader to control and influence
-Least-preferred coworker (LPC) questionnaire:
a questionnaire that measures whether a leader is task or relationship oriented
Fiedler’s Situational Contingencies
- Leader-member relations: describes the degree of confidence, trust and respect employees have for their leader.
- Task structure: decribes the degree to which jod assignments are formalized and structured.
- Position power: describes the degreee of influeance a leader has over activities such as hiring,
ring, discipline, promotions, and salary increases.
7. Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leaderhsip Style
-Situational leadership theory (SLT): a leaderhsip contingency theory that focuses on followers’ readiness
-Readiness: describes the degree to which job assignments are formalized and structured SLT leadership style
-Telling (high task – low relationship)
-Selling (high task – high relationship)
-Participating ( low task – high relationship)
-Delegating ( low task 0 low relationship)
Four stages of Followe Readiness
- R1: both unable and unwilling -R2: unable but willing
- R3: able but unwilling
- R4: both able and willing 8. Path - Goal Model
-Path-goal theory: a leadership theory that says the leader’s job is to assist followers in attaining
their goals and to provide direction or support needed to ensure that their goals are compatible
with the goals of the group or organization.
9. Leader - Member Exchange (LMX) Theory: the leadership theory that says leaders create in-
groups and oout-groups and those in the in-group will have higher peerformance ratings, less
turnover and greater job satisfaction.
10. Transformational/Transactional Leadership:
-Transactional leaders: leaders who lead primarily by using social exchanges (or transactions)
-Transformational leaders: leaders who stimulate and inspire (transform) followers to achive extraordinary outcomes.
11. Charismatic – Visionary Leadership
-Charismatic leader: an enthusiatic, self-confident leader whose personality and actions
influence people to behave in certain ways.
-Visionary leadership: the ability to create and articulate a realistic, credible and attractive vision
of the future that improve upon the present situation.
12. Authentic Learship: leaders who know who they are, know what they believe in and act on those
values and beliefs openly and candily.
13. Ethical Leadership: an ethical leader puts public safety ahead of profits, holds culpable
employees accountable, and creates a culture in which employees feel that they could and should do a better job. 14. Team Leadership
- Two priorities: Managing team’s external boundary and Facilitating team process 15. Managing Power
-Legitimate power: the power a leader has as a result of his or her position in the organization
-Coercive power: the power a leader has to punish or control
-Reward power: the power a leader has to give positive reward
-Expert power: power that’s based on expertise, special skills or knowledge
-Referent power: power that arises because of a person’s desirable resources or personal traits 16. Developing trust
-Credibility: the degree to which the followers perceive someone as honest, competent and able to inspire.
-Trust: the belief in the intergrity, character and ability of a leader.
-Five dimensions of trust: integrity, competence, consistency, loyalty, openess
17. Empowering Employees: Empowerment involves increasing the decision-making discretion of
workers. Millions of individual employees and employee teams are making the key operating
decisions that directly affect their work.
18. Leading across Cultures: National culture is certainly an important situational variable in
determining which leadership style will be most effective. 3. Managing Communication
1. What is Communication?
- Communication: the transfer and understanding of meaning
- Interperonal communication: communication between two or more people
- Organizational communication: all the patterns, networks and systems of communication within an organization
2. Functions of Communication: Control, Motivation, Emotional expression, Information
3. Methods and Challenges of Interpersonal Communication
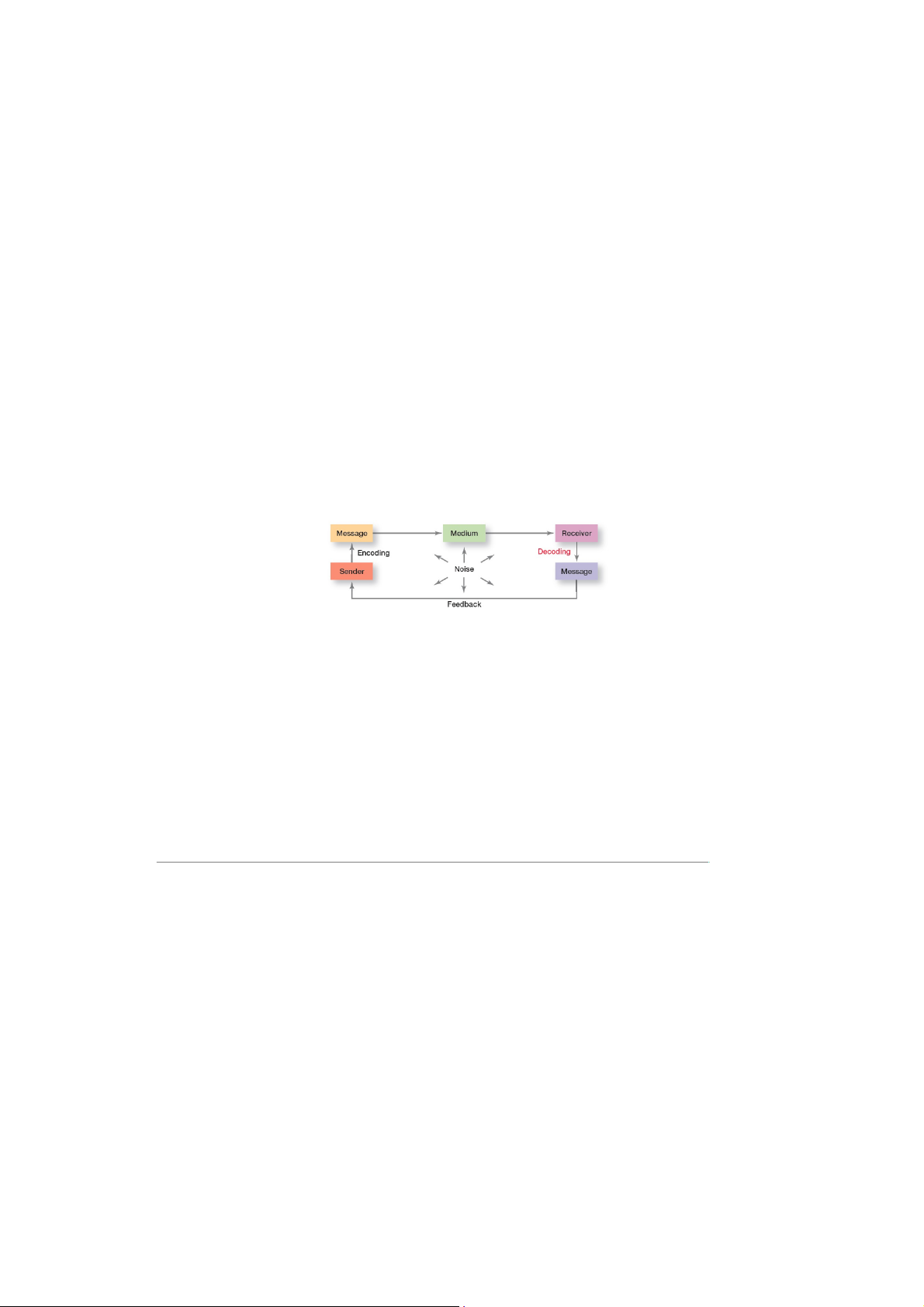
- Message: a purpose to ba conveyed
Encoding: converting a message into symbols
Channel: the medium a messgae travels along
Decoding: retranslating a sender’s message
-Communication process: the seven elements involved in tranferring meaning from one person to another.
-Noise: any disturbances tht interfere with the transmission, receipt or feedback of a message.
4. Which Communication Method should be used?
5. Comparison of Communication Methods 6. Barriers
- Information overload: when information exceeds our processing capacity
- Filtering: the deliberate manipulattion of information to make it appear more favourable to the receiver
-Jargon: specialized terminology or technical language that members of a group use to communicate among themselves
7. Overcoming the Barriers - Use feedback - Simplify language
- Listen actively: listening for full meaning without making premature judgments or interpretations - Constrain emotions - Wath non verbal cues
8. Active listening behavior
9. Formal versus Informal
- Formal communication: communication that takes place within precribed organization work arrangements
-Informal communication: communication that is not defined by the organization’s structural hierachy 10. Direction of Flow
- Downward: communication that flows downward from a manager to employees
Town hall meeting: informal public meetings where information can be relayed, issues can be
disscussed or employees can be brought together to celebrate accomplishment
- Upward communication: communication that flows upward from employees to managers
- Lateral communication: communication that takes place among any employees on the same organizational level
- Diagonal communication: communication that cuts across work areas and organization levels
11. Organizational Communication Networks -
Communication networks: the variety of patterns of vertical anf horizontal flows of orgaanizational communication -
Grapevine: the informal organizational communication network
12. Open workplace: workplaces with few physical barriers and enclosures
13. The 24/7 work environment
- IT has made it possible to stay connected around the clock, seven days per week.
- IT has made it possible for people in organizations to be fully accessible, at any time, regardless of where they are.
14. Working from anywhere: Wireless communication technology has the ability to improve work for managers and employees.
15. Choosing the right media
- Devoting a channel for information exchange about a specific topic can help compartmentalize the conversation.
- It can also start a useful conversation in which employees can share their experiences and make
suggestions for creating competitive advantage.
- Communication and the exchange of information among organizational members are no longer
constrained by geography or time.
- Constantly staying connected has its downsides, such as impeding creativity.
- It is important for managers to understand the situations in which one or more media facilitates effective communication. 4. Valuing a Diverse Workforce
1. What is workplace diversity?
- Workforce diversity: the ways in which people in an organization are different from and similar to one another. 2. Types of Diversity
- Surface-level diversity: Easily perceived differences that may trigger certain stereotypes, but
that do not necessarily reflect that ways people think or feel.
- Deep-level diversity: Differences in values, personality and work preferences.
3. Why is Managing Workplace Diversity so important?
-People management: their workforce diversity efforts revolve around attracting and retaining a talented workforce.
- Organiztional performance: cost savings and improvements in organizational functioning.
-Strategic: with a diverse workforce, organizations can better anticipate and respond to changing consumer needs.
4. Benefits of Workforce Diversity
5. Types of Diversity Found in Workplaces 6.
Challenges in Managing Diversity:
- Bias: a tendency or preference toward a
particular perspective or ideology
-Prejudice: a preconceived belief, opinion, or
judgment toward a person or a group of people
-Stereotyping: judging a person based on a
perception of a group to which that person belongs
- Discrimination: when someone acts out their
prejudicial attitudes toward people who are the targets of their prejudice
7. Glass Ceiling: the invisible barrier that seperates women and minorities from top management positions.
8. Mentoring: a process whereby an experienced organizational member (a mentor) provides advice
and guidance to a less experienced member (a protégé)
9. Diversity Skills Training: specialized training to educate employees about the importance of
diversity and to teach them skills for working in a diverse workplace
10. Employee Resource Groups: groups made up of employees connected by some common dimension of diversity. 5. Managing Communication 1. The case for Change
- Organizational change: any alteration of people, structure or technology in an organization
-Change agent: someone who acts as a catalyst and assumes the responsibility for managing the change process
2. External and Internal Forces for Change
3. Calm Waters vs White-Water rapids Metaphor - Calm water metaphor: Unfreezing the status quo Changing to a nes state
Refreesing to make the change permanent
-White-water rapids metaphor: the lack of environent stability and predictability requires that
managers and organization continually adapt and mange change active to survive
4. Reactive vs Proactive Change Processes:
- Reactive: reacting to a situation that has
- Proactive: acting in advance of a situation accurred
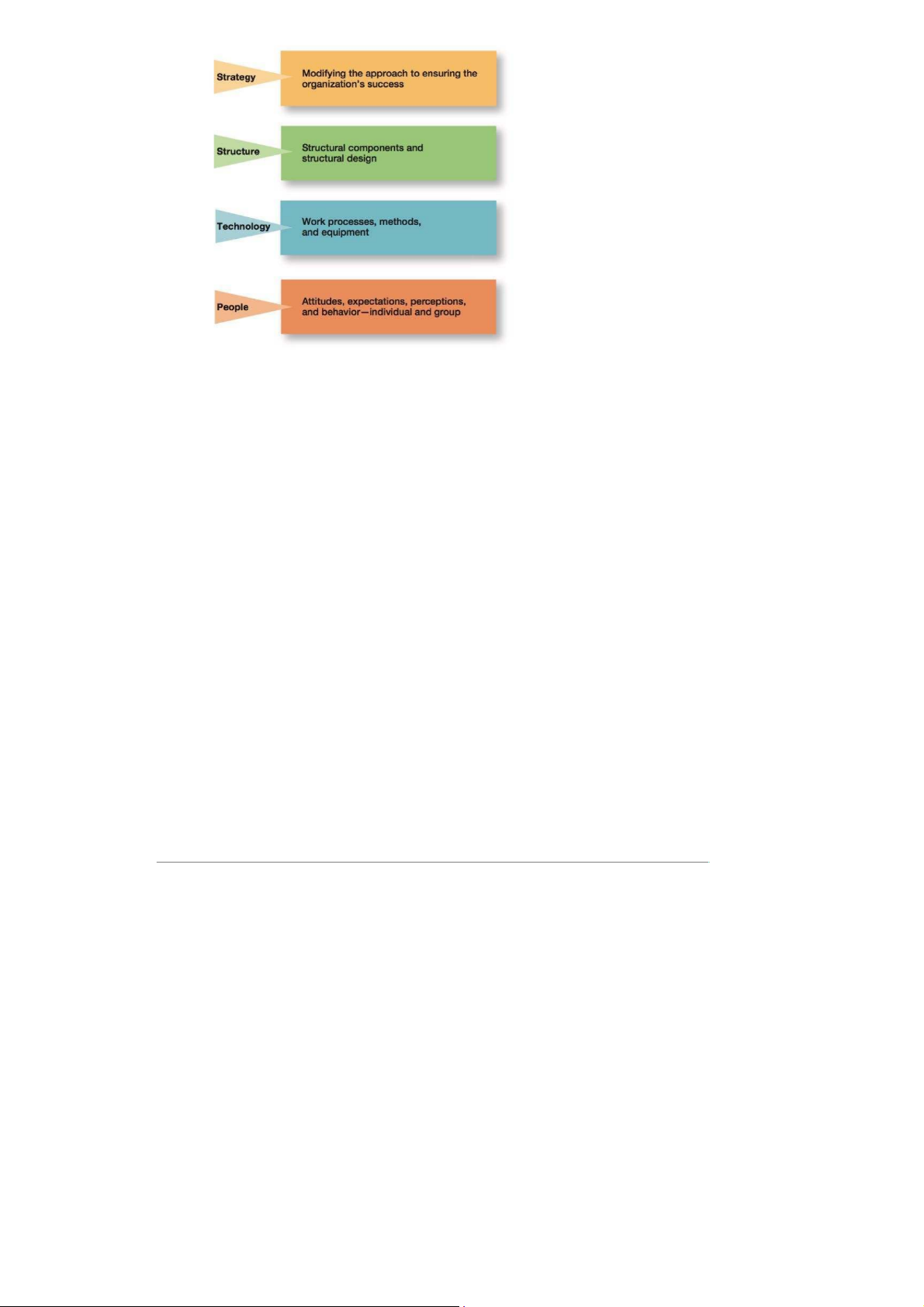
5. Four types of Changes
- Strategy: Failure to change strategy when circumstances dictate could undermine a company’s success. - Structure:
Changing structural components Changing structural design - Technology:
New equipment, tools, or methods Automation Computerization - People
Organizational development: change methods that focus on people and the nature and quality
of interpersonal work relationships
6. Why do people resist change?
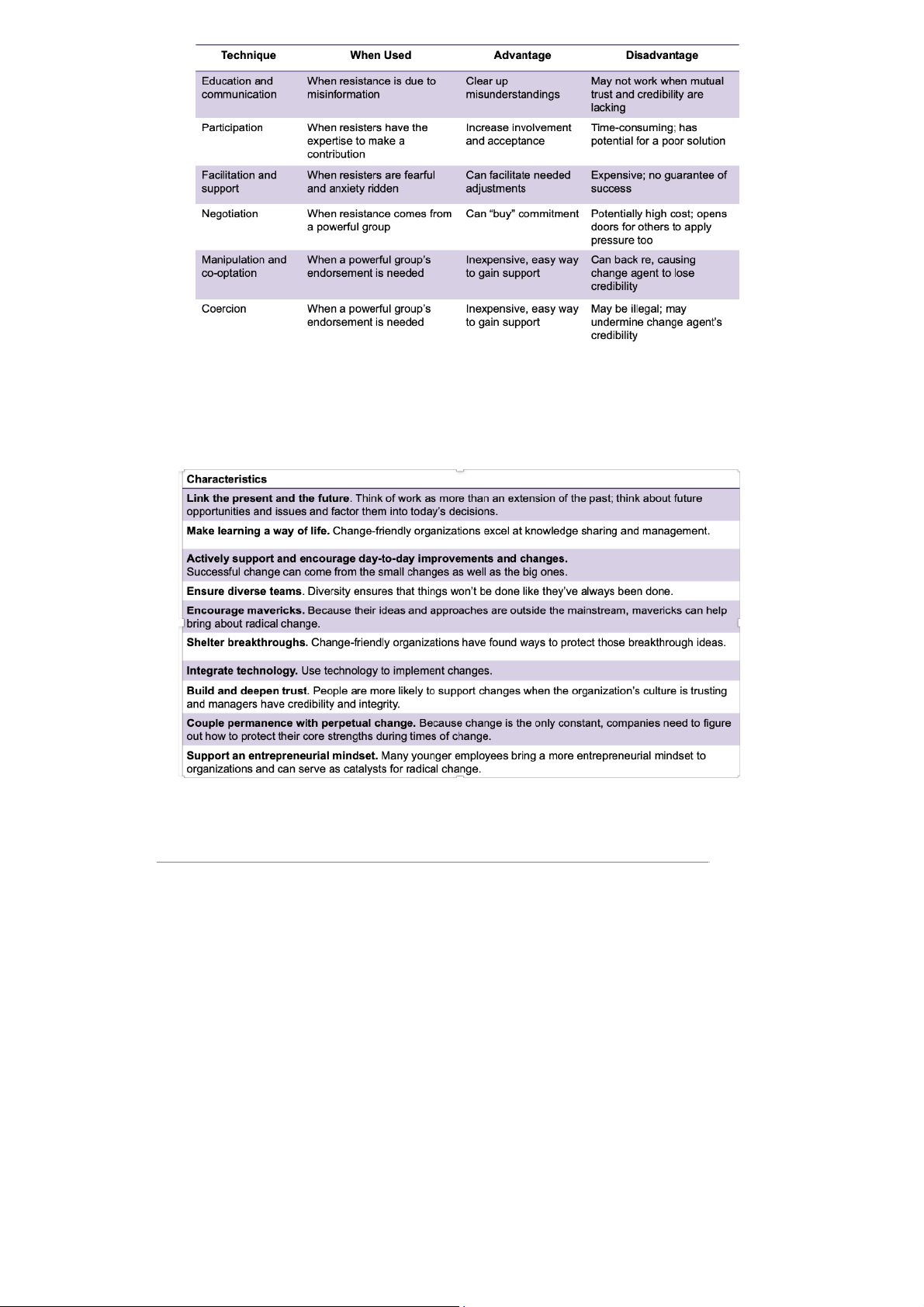
7. Techniques for Reducing Resistance to - Uncertainty change - Habit - Education and communication - Fear of loss - Participation
- Belief change is inconsistent with goals of - Facilitation and support organization - Negotiation - Manipulation and co-optation - Coercion 8. Leading change
- Managers can make change happen successfully by:
making organization change capable
understanding their own role in process
giving employees a role in the change
9. Change-capable Organizations 10. Personal Factors
-Type A personality: people who have a chronic sense of urgency and an excessive competitive drive
-Type B personality: people who are relaxed and easygoing and accept change easily
11. Creativity vs Innovation -
Creativity: the ability to combine ideas in a unique way or to make unusual associations between ideas -
Innovation: taking creative ideas and turning them into useful products or work methods
12. Stimulating and Nurturing Innovation: an environment that stimulates innovation includes 3
variables: the organization’s structure, culture, and human resource practices. Structural Variables Cultural variables
Human resource variables -Organic structures - Acceptance of ambiguity
- Idea champion: individual -Abundant resources - Tolerance of the impractical who actively and -High interunit - Low external controls enthusiatically supports new communication - Tolerance of risks ideas, builds support, -Minimal time pressure - Tolerance of conflict overcomes resistance and
-Work and nonwork support - Focus on ends ensures that innovations are - Open-system focus implemented. - Positive feedback
13. Innovation and Design Thinking: when a business approaches innovation with a design-thinking
mentality, the emphasis is on getting a deeper understaning of what customers need and want
14. Disruptive Innovation Definition -
Disruptive innovation: innovations in products, services or processes that radically change an industry’s rules of the game -
Sustaining innovation: small and incremental changes in established products rather than dramatic breakthroughs -
Why Disruptive innovation is important: disruptive innovations are a threat to many
established businessed and responding with sustaining innovations isn’t enough. -
Who’s vulnerable: large, established and highly profitable organizations are most vulnerable to
disruptive innovations because they have the most to lose and are most vested in their current markets and technologies. 6. Planning and Goal-Setting 1. What is planning?
- Planning: management function that involves setting goals, establishing strattegies for achieving
those goals and developing plans to integrate and coordinate work activities - Formal planning
- Specific, time-oriented goals - Goals written and shared
2. Why do managers plan?
-Provides direction: When employees know what their organization or work unit is trying to
accomplish and what they must contribute to reach goals, they can coordinate their activities,
cooperate with each other, and do what it takes to accomplish those goals. Without planning,
departments and individuals might work at cross-purposes and prevent the organization from
efficiently achieving its goals.
-Reduces uncertainty: by forcing managers to look ahead, anticipate change, consider the impact
of change, and develop appropriate responses.
-Minimizes waste and redundancy: When work activities are coordinated around plans,
inefficiencies become obvious and can be corrected or eliminated.
-Established the goals and standards for controlling: When managers plan, they develop goals
and plans. When they control, they see whether the plans have been carried out and the goals met.
Without planning, there would be no goals against which to measure work effort.
3. Planning and Performance
- Formal planning is associated with positive financial results
- Quality of planning/implementation more important than the extent of it
- External factors can reduce the impact of planning on performance
- Planning-performance relationship seems to be influenced by the planning time frame 4. Goals and Plans
- Goals (objectives): desired outcomes or targets
-Plans: documents that outline how goals are going to be met 5. Types of Goals - Financial goals - Strategic goals
- Stated goals: official statemetns of what an organization says and what it wants its various
stakeholders to believe, its goals are
- Real goals: goals that an organization actually pursues, as defined by the actions of its members. 6. Types of Plans
- Strategic plans: plans that apply to the entire organization and establish the organization’s overall goals
- Operational plans: plans that encompass as particular operational area of the organization
- Long-term plans: plans with a time frame beyond 3 years
-Short-term plans: plans covering one year or less
-Specific plans: plans that clearyly defined and leave no room for interpretation
-Directional plans: plans that are flexible and set out general guidelines
-Single use plans: a one-time plan specifically designed to meet the needs of a unique situation
-Standing plans: ongoing plans that provide guidance for activities performed repeatedly
7. The downside of Traditional Goal-setting
- Traditional goal-setting: an approach to setting goals in which top managers sets goals that than
flow down through the organization and become subgoals for each organizational area.
8. Means-ends Chain and MBO
- Means-Ends chain: an integrated network of goals in which the accomplishedment of goals at
one level serves as the means for achieving the goals, or ends, at the next levels
- Management by objectives (MBO): a process of setting mutully agreed upon goals and using
those goals to evalute emplyee performance. Steps in MBO
9. Steps in goal-setting
1. Review the organization’s mission, or purpose.
2. Evaluate available resources.
3. Determine the goals individually or with input from others.
4. Write down the goals and communicate them to all who need to know.
5. Review results and whether goals are being met. 10. Developing plans -
Planning and Organizational Level
- Environmental Uncertainty: when incertainty is high, plans should be specific, but flexible.
- Length of Future Commitments: Commiment concept: plans should extend far enough to meet
those commiments made when the plans were developed
11. Approaches to Planning
- Formal planning department: a group of planning specialist whose sole responsibility is
helping to write organization plans.
12. Contemporary issues in planning
- How can managers plan effectively in dynamic environments
Develop plans that are specific but flexible
Keep planning even when the environment is uncertain
Allow lower organization levels to set goals and develop plans
- How can managers use environmental scanning?
Environmental scanning: screening information to detect emerging trends
Competitor intelligence: gathering information about competitors that allows managers to
anticipate competitors’ actions rather than merely react to them - Digital tools
Business intelligence: data that managers can use to make more effective strategic disicions
Digital tools: technology, systems or software that allow the user to collect, visualize, understand, or analyze data.
- 3 prevalent digital tools Date visualization tools
Cloud computing: refer to storing and accessing data on the Internet rather than on a
computer’s hard drive or a company’s network
Internet of things (IoT): allows everyday “things” to generate and store and share daa across the Internet 7. Planning and Goal-Setting 1. What is a group?
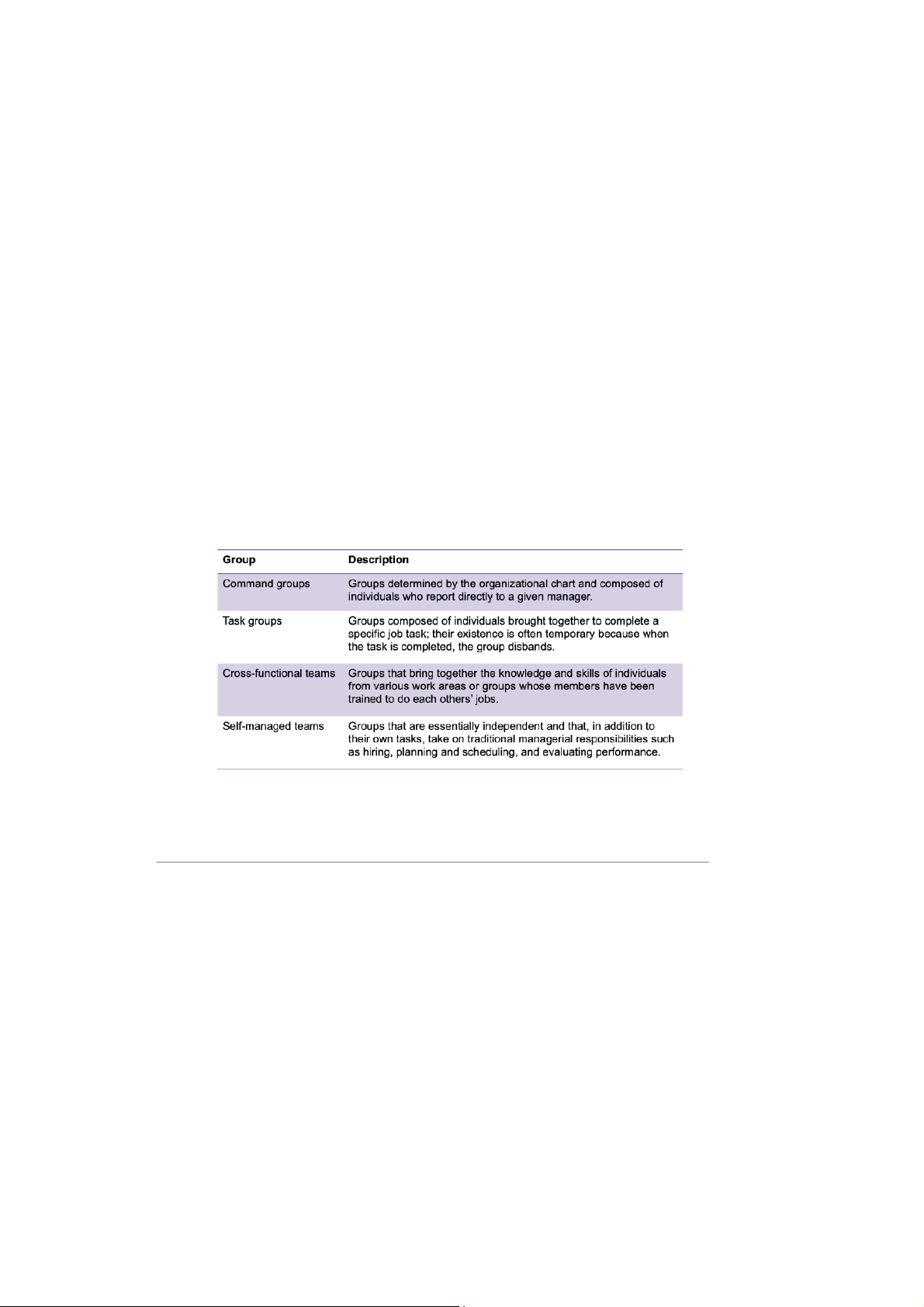
- Group: two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve specific goals
-Formal groups: work groups defined by the organization's structure and have designated work
assignments and specific tasks directed at accomplishing organizational goals.
- Informal groups: social groups
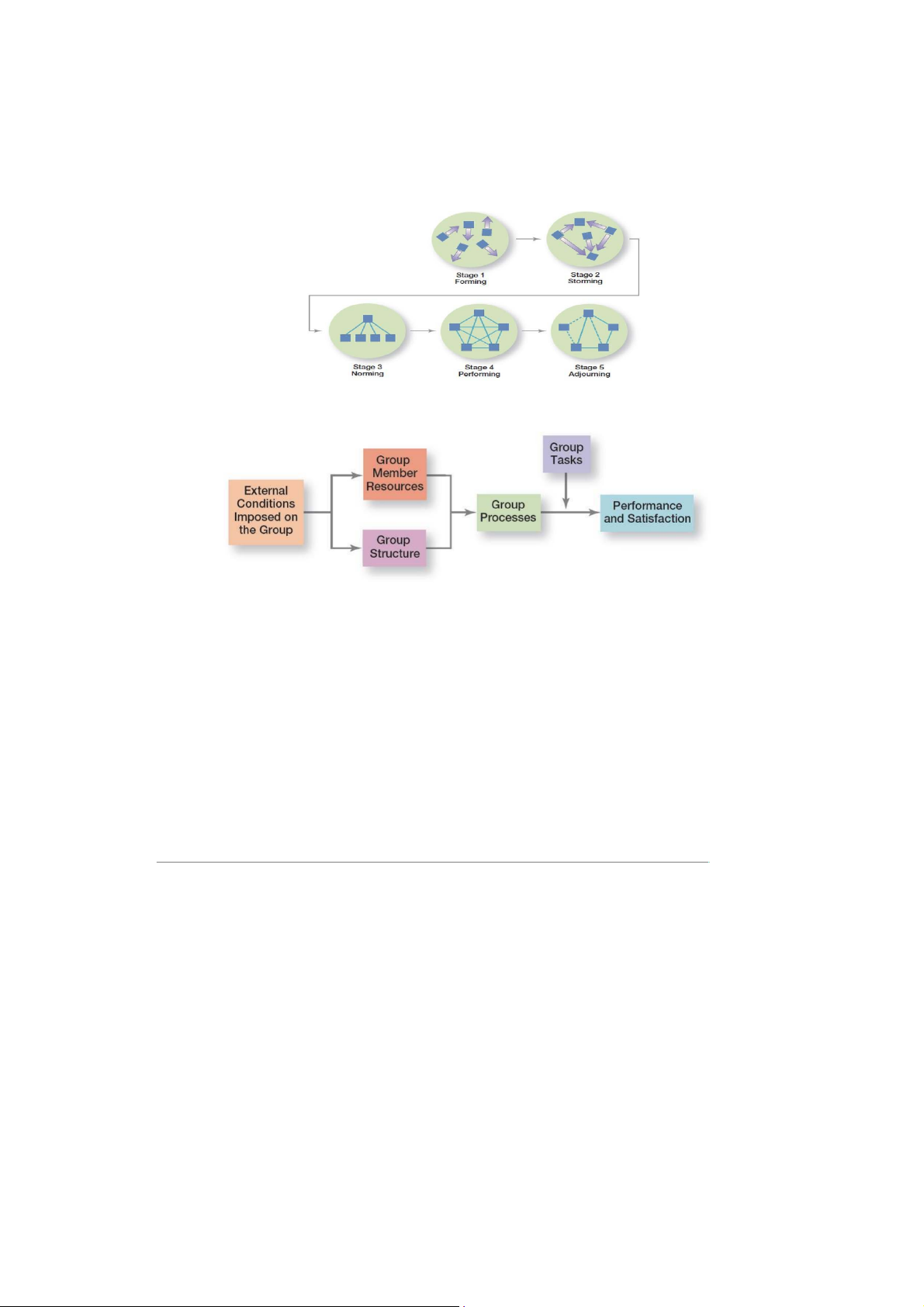
2. Stages of Group development
- Forming: the first stage of group development in which people join the group and define the
group’s purpose, structure and leadership
- Storming: the second stage of group development, characterized by intragroup conflict
- Norming: the third stage of group development, characterized by close relationships and cohesiveness
-Performing: the fourth stage of group develoopment when the group is fully functional and works on group tasks
- Adjouring: the final stage of group development for temporary groups during which group
members are concerned with wrapping up activities rather than task performance
3. Group performance /Satisfaction model
4. External Conditions Imposed on the group
- External conditions include: Organization’s strategy Authority relationships
Formal rules and regulations Availability of resources Employee selection criteria
5. Group members resources: Knowledge, Abilities, Skills, Personality traits 6. Group structure
- Role: behavior patterns expected of someone accupying a given position in a social unit
- Norm: standards or expectations that are accepted and shared by a group’s members - Conformity
Groupthink: when a group exerts extensive pressure on an individual to align his or her
opinion with others’ opinions - Status systems:
Status: a prestige grading, position or rank within a group - Group size:
Social loafing: the tendency for individuals to expend less effort when working collectively than when working individually
- Group cohesiveness: the degree to which group members are attracted to one another and share the group’s goals
7. Group cohesiveness and productivity 8. Group processes Decision-Making - Advantages:
Generate more complete information and knowledge
Increase acceptance of a solution Increase legitimacy - Disadvantages Take more time
A dominant minority can unduly influence outcome groupthink
Individual responsibilities are ambiguous Conflict mangement
- Conflict: perceived incompatible differences that result in interference or opposition
Traditional view of conflict: the view that all conflict is bad and must be avoided
Human relations view of conflict: the view that conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome in any group
Interactionist View of Conflict: the view that some conflict is nessary for a group to perform effectively
-Functional conflicts: conflicts that support a group’s goals and improve its performance
-Dysfunctional conflicts: conflicts that prevent a group from achieving its goals




