

















Preview text:
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING MANAGEMENT -Talent
Ultimate (cơ bản) foundations of organizational performance
Intellectual capital is the collective brainpower or shared knowledge
of a workforce that can be used to create value: kiến thức của các
lllđ có thể tạo ra giá trị cho công ty.
-A knowledge worker’s mind: tài sản quan trọng, bổ sung vào
intellectual của cty Commitment x Competency = Intellectual Capital -Technology
Tech IQ: khả năng sử dụng Cn để cập nhật thông tin.
Checking inventory, making a sales transaction, ordering supplies: Telecommuting Virtual teams
Effective use of online resources: Databases, Job searches, Recruiting, Social Media
-Globalization: sự toàn cầu hóa: các dòng tài nguyên, thị trường
sp,.. của nền kte trong nước phụ thuộc lẫn nhau vs các nc trên TG.
-Job migration occurs when firms shift jobs from one country to another.
-Ethic: nguyên tắc đạo đức tiêu chuẩn về tốt hoặc xấu trong hành vi của 1 ng. - Diversity :
Workforce diversity reflects differences with respect to gender,
age, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, and able- bodiedness.
Lực lượng lao động đa dạng và đa văn hóa vừa thách thức vừa mang
đến cơ hội cho người sử dụng lao động
-Diversity bias can occur in the workplace:
oPrejudice: định kiến oDiscrimination
oGlass ceiling effect (rào cản vô hình): invisible barriers
prevent women and minorities to reach the top ranks of
management in major corporations.
-Careers: Organizations consist of three types of workers, sometimes
referred to as a shamrock organization:
Permanent full time workers
Freelance or contract workers
Temporary part-time workers
-Free-agent economy: people change jobs more often, and many
work on independent contracts: làm việc theo hợp đồng
-Self-management: Ability to understands oneself, exercise initiative,
accept responsibility, and learn from experience.
-Organization: a collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose pro
vide useful goods and/or services that return
value to society and satisfy customer needs. -Resource Inputs T
ransformation process Product outputs
-Organizational performance: “Value creation” : công ty vận hành
adds value to the original cost of resource inputs.
-When value creation occurs: Businesses earn a profit
Nonprofit organizations add wealth to society
-Productivity: số lượng và chất lượng tạo ra dựa trên việc sử dụng đủ nguồn lực cung cấp.
-Performance effectiveness: an output measure of task or goal accomplishment
-Performance efÏciency: an input measure of the resource costs
associated with goal accomplishment
-Preeminence: ưu việt
-Importance of human resources and managers
People are not ‘costs to be controlled ’
High performing organizations treat people as valuable strategic
assets: coi con người là tài sản chiến lược
Managers must ensure that people are treated as strategic assets
-Manager : directly supports, activates and is responsible for the work of others. -Levels of management
Board of directors make sure the organization is run right: tổ chức vận hành đúng đắn
Top managers are responsible for performance of an organization as a
whole or for one of its major parts : hiệu suất làm việc của cty và các bộ phận.
Middle managers oversee large departments or divisions: giám sát phòng ban và các bộ phận lớn
Team leaders supervise non-managerial workers: giám sát nhắn viên. -Types of Managers:
Line managers are responsible for work activities that directly
affect organization’s outputs
Staff managers use technical expertise to advise and support
the efforts of line workers
Functional managers are responsible for a single area of activity
General managers are responsible for more complex units that
include many functional areas
Administrators work in public and nonprofit organizations
-Managerial performance and accountability
Accountability is the requirement to show performance results to
a supervisor: giải trình việc đã làm cho ng quản lý
Effective managers help others achieve high performance and satisfaction at work
-Corporate Governance: Board of directors hold top management
responsible for organizational performance: HĐQT cao nhất, chịu trách
nhiệm về hiệu quả hđ của tổ chức:
Financial performance Ethical performance Sustainability
-Quality of work life (QWL): An indicator of the overall quality of
human experiences in the workplace.
-Management is the process of planning, organizing, leading, and
controlling the use of resources to accomplish performance goals:
Planning: the process of setting objectives and determining
what actions should be taken to accomplish them
Organizing: the process of assigning tasks, allocating
resources, and coordinating work activities
Leading: the process of arousing people’s enthusiasm to
work hard and direct their efforts to achieve goals
Controlling: the process of measuring work performance and
taking action to ensure desired results.
-Managerial agendas and networks :
Agenda setting: develops action priorities for accomplishing goals and plans
Networking: process of creating positive relationships with people who can help advance agendas
Social capital: capacity to get things done with help
-Learning: the change in a behavior that results from experience
-Lifelong learning: the process of continuously learning from daily
experiences and opportunities.
In this chapter, REMEMBER: 1. Organization 2. Manager: oLevel (mgt level) oManagerial function :
Planning: vision+ goals+ activities
Organizing: allocating resources:
budget+time+faculities/ structure Leading: leadership
Controlling: monitor, meet the standard oknowledge + Skills
CHAPTER 2 : INTRODUCING MANAGEMENT Party Unions ( work
ers want salaries) Management (employers
want profit) => Workers : now they treat them like asset not cost (pay their salaries)
-In 17th century: bùng nổ kinh tế, mgt think of specialization: công
nhân giỏi việc nào thì làm việc đó.
-Scientific management ( Federick Taylor): giống vua hề Chaplin,
cv làm hàng loạt: reveal unnecessary movements
Four guiding principles:
Develop for every job a “science” that includes rules of
motion, standardized work implements, and proper working conditions.
Carefully select workers with the right abilities for the job.
Carefully train workers to do the job and give them the
proper incentives to cooperate with the job “science.”
Support workers by carefully planning their work and by smoothing
the way as they go about their jobs.
-Scientific management (the Gilbreths):
Motion study: science of reducing a job or task to its basic physical motions
Eliminating wasted motions improves performance
-Administrative principles (Henri Fayol): to fit diverse to make to lead, efforts sure things to provide select, and C together n happen to complete and evaluate and ensure according to a plan of mobilize workers to information plan and to action for resources to get the best is shared take the future implement work and necessary the plan toward the problems corrective plan solved action
-Bureaucracy (quan liêu) : An ideal, intentionally rational, and very
efÏcient form of organization _ based on principles of logic, order, and legitimate authority
Clear division of labor
Clear hierarchy of authority
Formal rules and procedures Impersonality
Careers based on merit
-Possible disadvantages of bureaucracy:
Excessive paperwork or “red tape”
Slowness in handling problems
Rigidity in the face of shifting needs Resistance to change Employee apathy
Đôi khi nó sẽ bị conflict về việc promotion: có những ng được
thăng cấp sớm hơn những ng có kinh nghiệm: khi 1 ng lên sẽ có sự
điều chỉnh trong bộ máy vì nó phụ thuộc vào sự ăn ý của ng sếp và ng
mà họ làm việc chung.
-Behavioral management approaches:
Emphasize on the human side of the workplace
Authors: Mary Parker Follett; Elton Mayo; Douglas McGregor; Abraham Maslow; Chris Argyris. Organizations as communities Mary Parker
Follett Theory X and Hawthorne Theory Y studies Douglas Elton Mayo McGregor Human resource Theory of approaches Personality and human needs Assumption: organization Abraham People are social Chris Argyris Maslow and self- actualizing
-Organizations as communities (Mary Parker Follett): Making every employee an Business problems involve a Private profits relative to owner creates a sense of variety of inter-related public good collective responsibility factors precursor of employee precursor of systems thinking precursor of managerial ownership, profit sharing, ethics and social and gain-sharing responsibility
Making every employee an owner creates a sense of
collective responsibility: ví dụ: tặng cổ phiếu biến họ
thành chủ của cty, là thành viên của cty => gắn bó lâu dài với cty. -Hawthorne studies:
Social setting and human relations
oManipulated physical work conditions to assess impact on output
oDesigned to minimize the “psychological factors” of previous experiment
oMayo and colleagues concluded:
New “social setting” led workers to do good job
Good “human relations” = higher productivity
Vd: làm việc càng lâu càng gắn kết, có những nơi 1 ng đòi tang lương thì
cả 1 nhóm cx sẽ đòi tăng lương.
Employee attitudes and group processes
oSome things satisfied some workers but not others
oPeople restricted output to adhere to group norms
-Maslow’s theory of human needs:
A need is a physiological or psychological deficiency a person feels compelled to satisfy Need levels: oPhysiological oSafety oSocial oEsteem oSelf-actualization
Thuyết của Maslow trong marketing: nhu cầu của con ng tang khi thu
nhập tăng, mục đính chính là để cho nhiều ng biết đến món hang mik sở hữu.
-Deficit principle: A satisfied need is not a motivator of behavior
-Progression principle: A need becomes a motivator once the
preceding lower-level need is satisfied
-Both principles cease to operate at self-actualization level
-McGregor’s Theory X assumes that workers: Dislike work Lack ambition Are irresponsible Resist change Prefer to be led
-McGregor’s Theory Y assumes that workers: Willing to work Capable of self control
Willing to accept responsibility Imaginative and creative Capable of self-direction
-Argyris’s theory of adult personality:
Classical management principles and practices inhibit worker
maturation and are inconsistent with the mature adult personality
Psychological success occurs when people define own goals
Management practices should accommodate the mature personality by:
oIncreasing task responsibility oIncreasing task variety
oUsing participative decision making
-Modern Management Foundations:
Foundations for continuing developments in management Quantitative analysis Systems view of and tools organizations Commitment to Contingency thinking quality and performance Knowledge management and Evidence-based learning management organizations
-Management science or operations research Quality control Inventory Queuing management theory Supply chain Linear management programming The scientific applications of mathematical Value chain techniques to Network analysis management models problems
-Organization as systems:
System: collection of interrelated parts that function together to achieve a common purpose
Subsystem: a smaller component of a larger system
Open systems: organizations that interact with their environments in
the continual process of transforming resource inputs into outputs -Contingency thinking:
oTries to match managerial responses with problems and
opportunities unique to different situations
oNo “one best way” to manage
oAppropriate way to manage depends on the situation -Knowledge management :
Vd: tên thương hiệu cx là 1 loại tài sản: các cty nhượng quyền thu đc
lợi nhuận từ việc nhượng quyền ại cho các chi nhánh ở các quốc gia khác nhau.
CHAPTER 4 : Environment, Innovation, and Sustainability
-Marginal practices: Planning/ Organizing/ Leading/ Controlling/
StafÏng (HRM) Last chapter
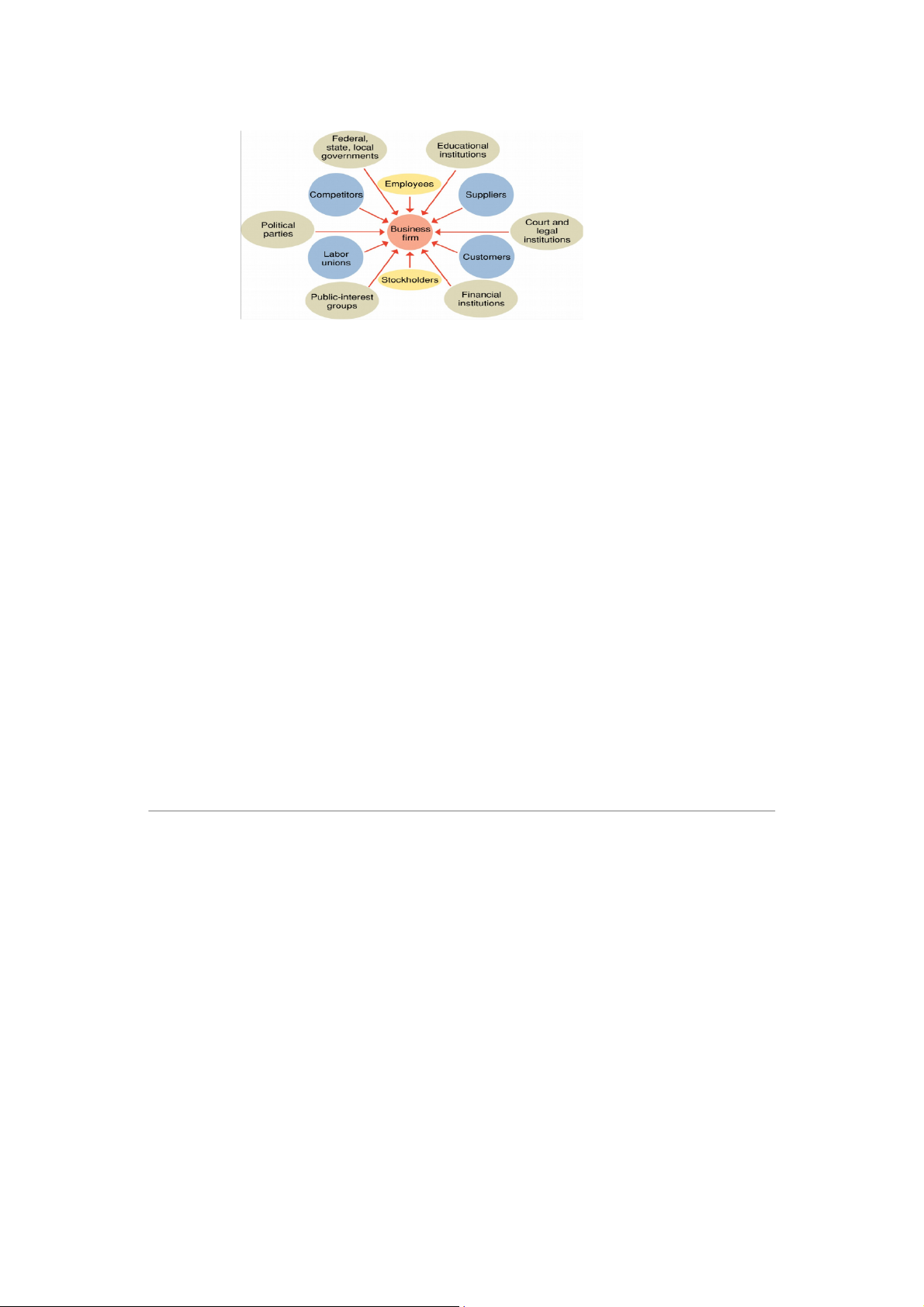
-Stakeholders: directly or indirectly affect the whole organization.
-Organization develop theo kiểu pyramid.
-Background conditions in the external environment: effect
directly or indirectly: we have to accept it: Economic Legal-political Socio-cultural Technological Natural environments -Economic conditions: Overall Health
EX: China hiện nay làm việc chủ yếu cho các cty trong nước, là nc lớn
nên thường sẽ mở cơ sở sx ở nước ngoài (trong nc k xuất hiện factories,..)
Try to pay off loans (use your own money to do biz is not a good idea,
therefore, we have to borrow money from the bank ).
Kinh doanh dưới dạng Accomodation ( hotel, motel, homestay): tiền
cho vay ngắn hạn: something supplied for convenience or to satisfy a need
Inflation rate is not too low or too high: good bcs lạm phát quá thấp
“gặm nhấm” doanh số và nguồn thu thuế, cản trở việc tăng lương, ăn mòn lãi suất cận biên
Venezuela là nc lạm phát cao nhất
EX: To lower the inflation, they ask State Bank (Ngân hàng Nhà nước:
chức năng là điều tiết nền kinh tế, khác vs Trade bank: ngân hàng
thương mại) to collect more money by increasing the interest rate: vì
khi muốn thu tiền vào thì phải tăng lãi suất cho người gửi tiền, đồng
thời phải tăng lãi suất của người đang vay.
Khả năng bị khủng hoảng rất cao, vì thế nên nh à nước phải đưa ra pp
để giải cứu bất động sản,
Income Level: Các nước lớn sẽ mở các nhà máy sx ở các nước có nguồn
thu nhập bình quân đầu người thấp. (vd: Apple mở nhà máy sx chính ở
China hay Samsung mở ở VN,..) Offshoring:
Outsourcing: thuê từ bên ngoài về làm cho công ty.
Là hình thức một pháp nhân sử dụng các nguồn lực từ nước khác vào
việc sản xuất-kinh doanh của mình, không phụ thuộc vào việc các
nguồn lực đó có thuộc về cơ cấu tổ chức của pháp nhân đó hay không.
Khi các nước lớn đã đạt đến 1 mức độ thịnh vượng nhất định, họ sẽ
thay đổi các thức vận hành, tập trung tải tạo nhiều hơn cho môi
trường, đặt trụ sở sx ở các quốc gia kém pt và giá thành nhân công rẻ hơn.
Vd: Singapore đặt nhà máy sx ở khu CN Việt Sing. Reshoring:
Reshoring còn được gọi là offshoring, là sự bù đắp ngược lại và liên
quan đến việc trả lại sản xuất và sản xuất hàng hóa cho đất nước ban đầu của công ty.
Vd: Trong nhiều thập k , nhiều công ty của Hoa Kỳ tham gia vào hoạt ỷ
động kinh doanh, thường gửi các nhà máy sản xuất của họ đến Trung
Quốc, Malaysia, Việt Nam và các quốc gia khác với chi phí lao động
thấp hơn. Tuy nhiên, sau cuộc đại suy thoái năm 2008, các công ty này
đã tìm ra những cách khác để cắt giảm chi phí bằng cách bán lại và trả
lại doanh nghiệp của họ cho Hoa Kỳ để tạo việc làm cho người Mỹ thất nghiệp
-Legal-political conditions:
Vd: Khi thay đổi chính phủ của các Đảng khác nhau thì chính sách và
phúc lợi của người dân và người nhập cư sẽ khác nhau:
Ở Úc: Đảng bảo thủ: tập trung chủ yếu vào người giàu, bắt thi lấy quốc tịch
Những điều luật này có ảnh hưởng đến công ty VN ko?
Luật là mua nhà chung cư k phải là tài sản vĩnh viễn, hay ai mua 2 căn
nhà trở lên mà k phải để ở thì bị đánh thuê cao hơn.
-Sociocultural conditions: tín ngưỡng, tôn giáo: Nhập gia tùy tục
Allocate factory depends on those conditions: vd: HCM city bcs ppl can
easily gain access to their workplace.
-Technological conditions: vd: chatGPT, Metaverse
-Natural environment conditions: giảm tải ô nhiễm kkhi, tiếng ồn Regulator: ở đây là Govn
-Competitive advantage: Lợi thế cạnh tranh
Reduce the cost: xem input là như nhau: Economies of scale: tăng
quantity để sx, giảm bớt tgian sx,…
How to control product’s quality?
-Environmental uncertainty: những vấn đề xảy ra mà mik k kiểm soát đc : Covid-19
Degree of complexity: đôi lúc k dự đoán được
Rate of change: bổ sung cho nhau, cái nào low thì cái còn lại high
để rate change in envi nó cân bằng




