









Preview text:
Supply chain management is defined as: “The planning and management of all activities involved
vice providers, and customers” – –
rs all know each other’s future plans and are willing to
work together → the planning process is easier and much more productive.
Up stream: Suppliers → Factory
Downstream: Factory → Customer o o
ves materials from suppliers to the organisation’s receiving sales of £10 million a year £7.5 million a year £20 million 10 million × 0.25 £ × × 0.2 = £0.5 million/
stock = 7.5 million + 0.5 million = £8 million
= sales − total costs = 10 million − 8 million = £2 million
= other assets + stock = 20 million + (10 million × 0.25) = £22.5 million = 10 million × 0.2 = £2 = stock × holding cost = × 0.2 = £0.
= 7.5 million + 0.4 million = £7.9 million
= 10 million − 7.9 million = £2.1 million
= £20 million + (£10 million × 0.20) = £22 million s → Affect
organization’s performance over many years.
A poor facility location leads to poor performance → low productivity, unreliable suppliers, o o ế ạ ợp đồ ặ ằ ⇒
Mergers (Sáp nhập) và Acquisitions (Mua ạ dairies,…).
Location of suppliers and materials (natural resources,…). materials, utilities, …).
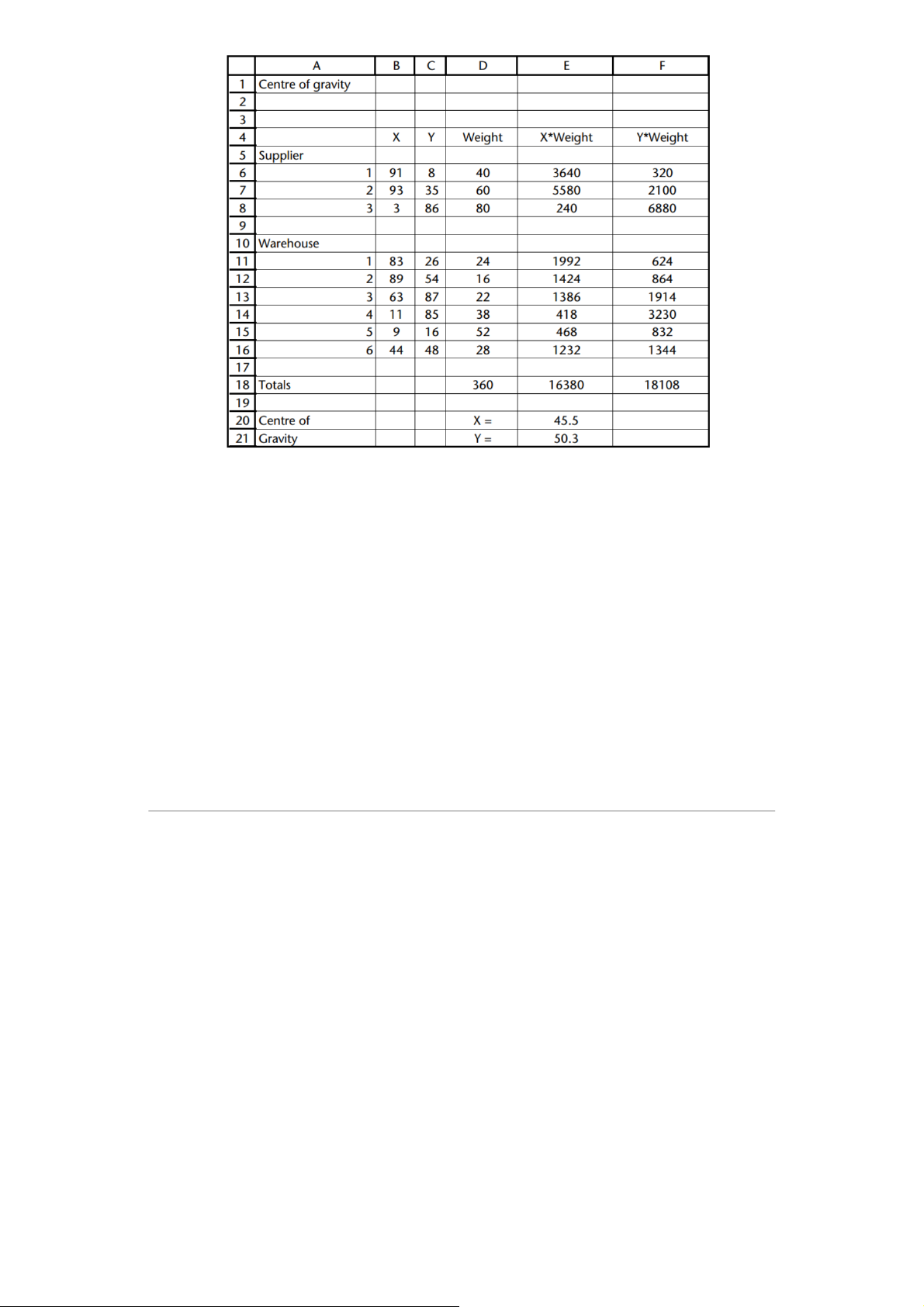
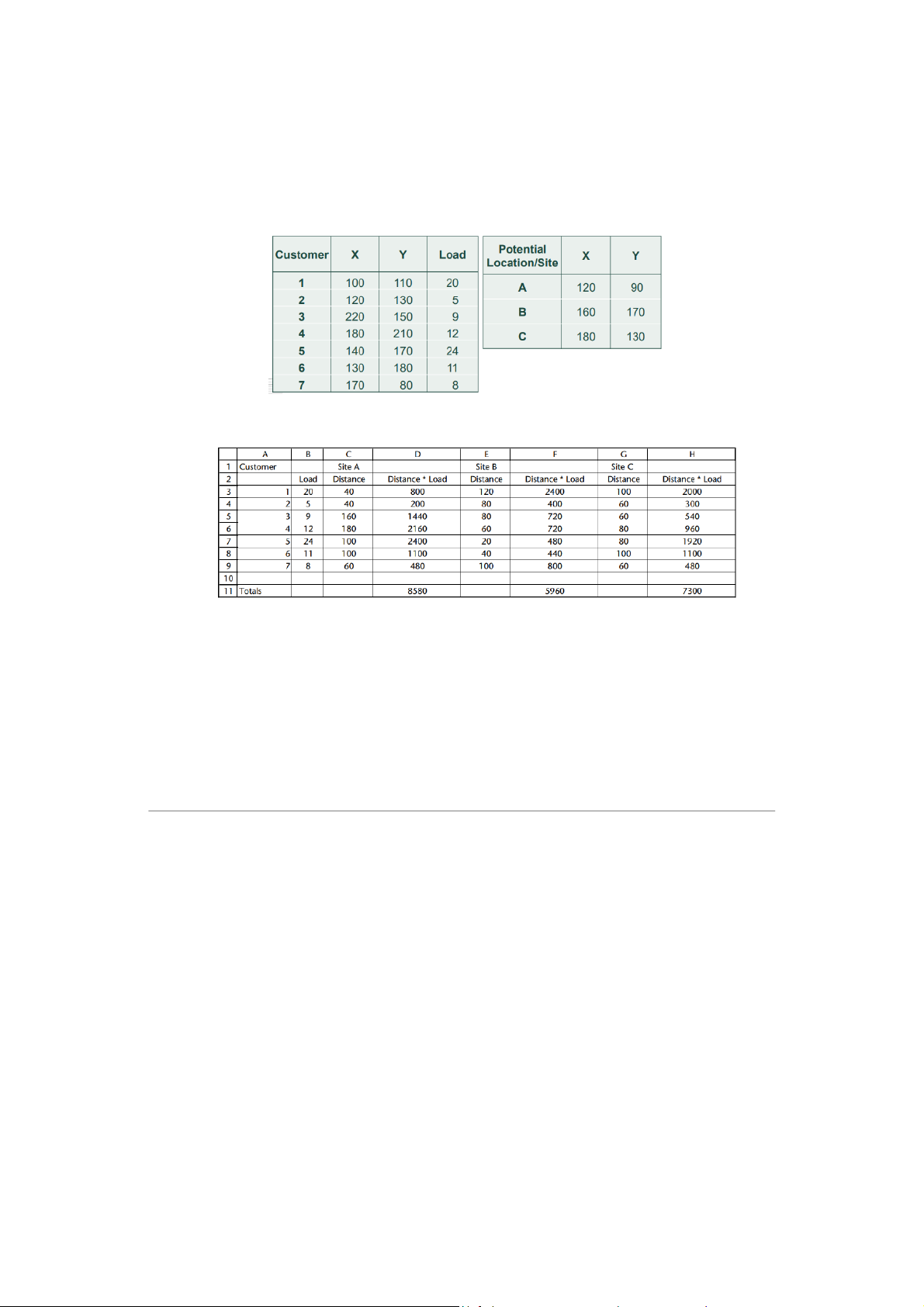
→ finds the best location in principle and then looks for a site nearby. 𝑋 𝑌 𝑋𝑖 𝑌𝑖 𝑖 𝑊𝑖 𝑖 𝑖 𝑋0=∑𝑋𝑖𝑊
∑ 𝑖𝑊𝑖=91.40 +93.60 + 3.80 +83.24 +89.16 +63.22 +11.38 + 9.52 +44.28
40 +60 +80 +24 +16 +22 +38 +52 +28 =16380 360 =45.5 𝑌0=∑𝑌𝑖𝑊
∑ 𝑖𝑊𝑖=8.40 +35.60 +86.80 +26.24 +54.16 +87.22 +85.38 +16.52 +48.28
40 +60 +80 +24 +16 +22 +38 +52 +28 =18108 360 =50.3 ⇒ ⇒
In practice, many of the costs of running a facility are fixed regardless of its location → we
Assume that the operating costs in nearby locations are the same → we only concentrate of
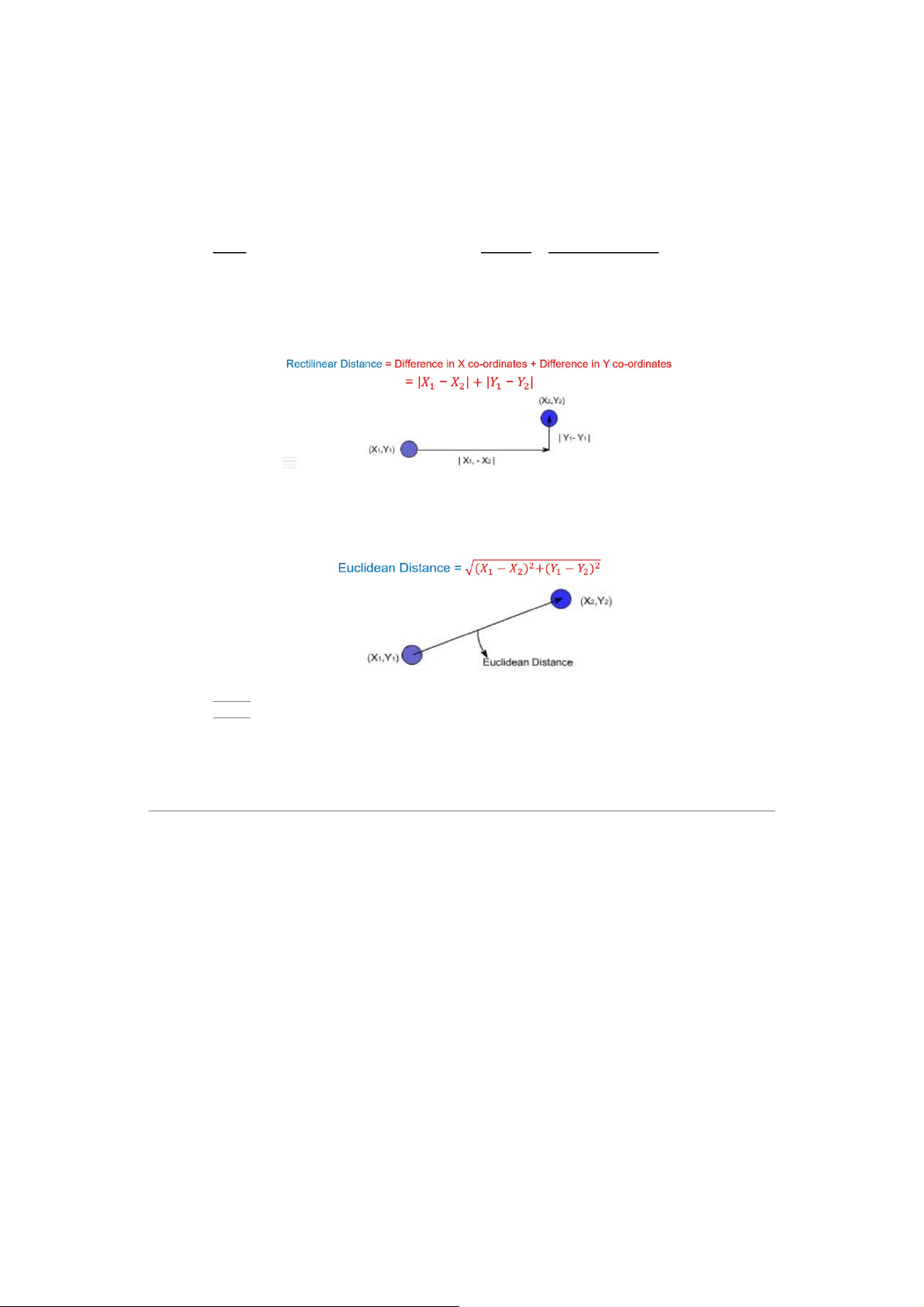
Assume that the transport cost is proportional to the distance moved → Rectilinear distance → the distance is ca 𝑋 𝑌 𝑋 𝑌 ) → the
th between the two facilities → the distance 𝑋 𝑌 𝑋 𝑌 ) → the 𝐿𝐷 𝒏
𝑳𝑫 =∑𝒍𝒊× 𝒅𝒊 𝒊=𝟏 𝑙𝑖 𝑖 𝑑𝑖 𝑖 𝑛
→ To avoid these problems, other method for comparison is used. – –
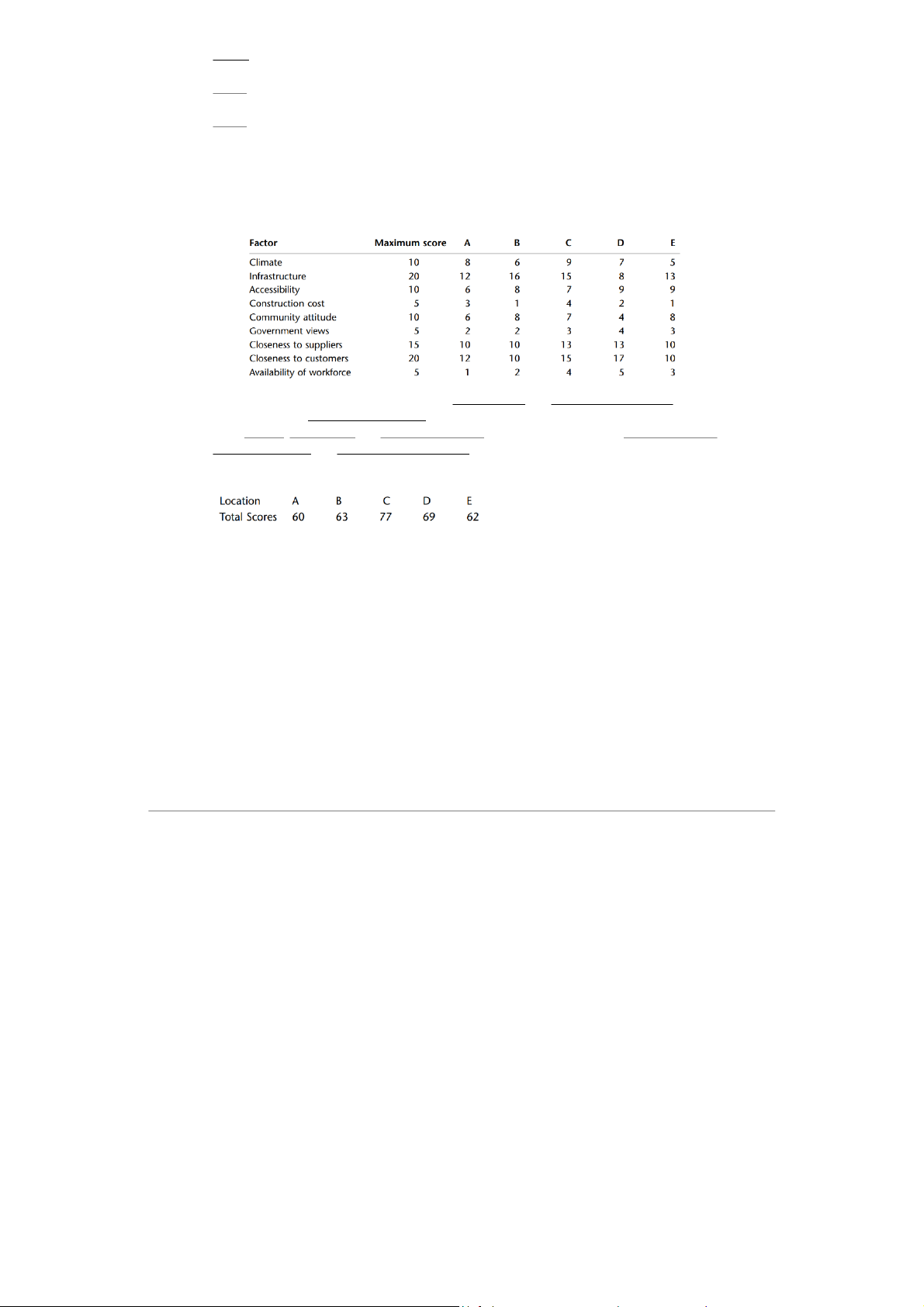
Although we cannot quantify these factors directly → giving each a score. The scoring model → Standard analysis
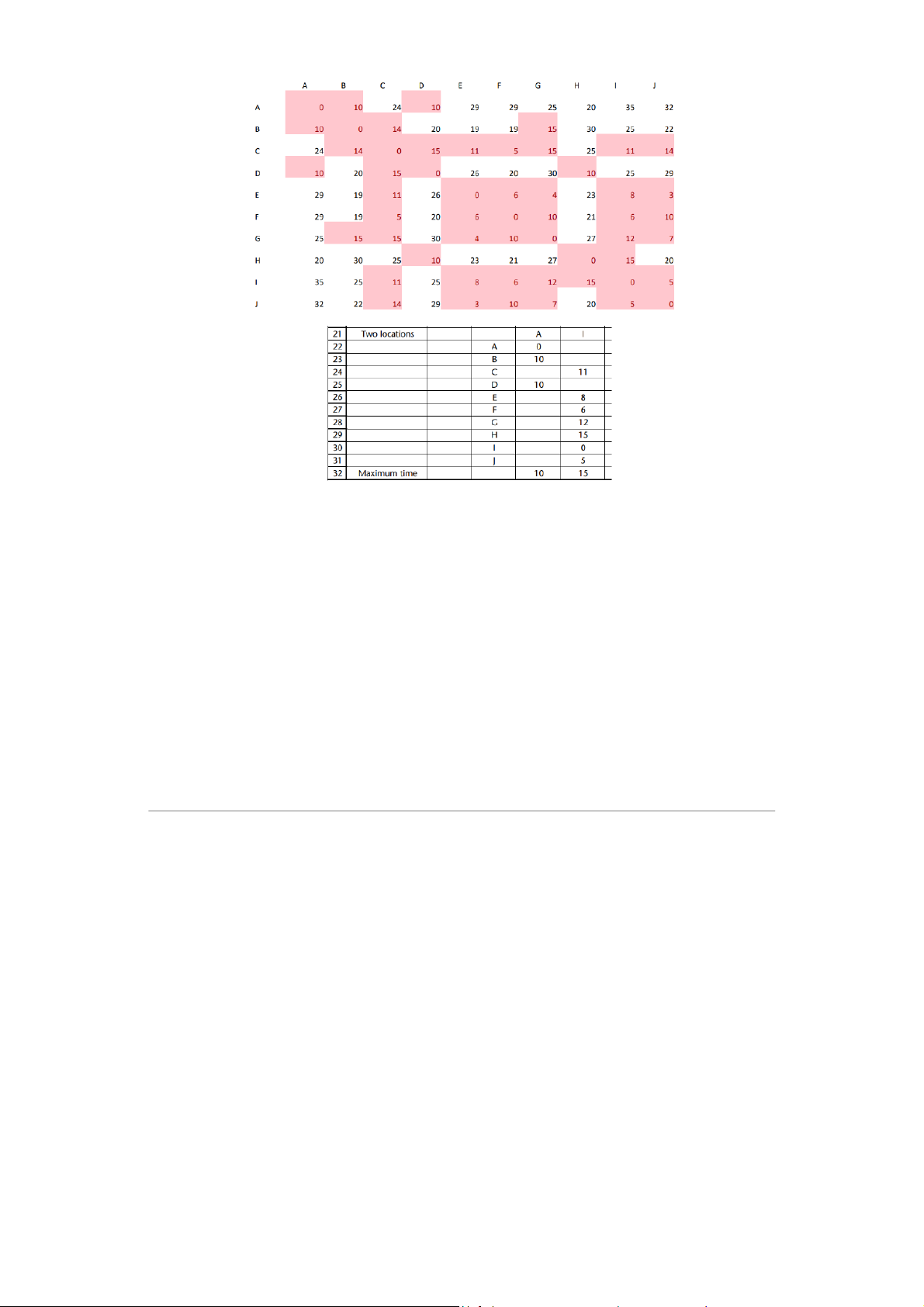
distance of a centre at AL = (10 × 0) + (15 × 15) + (25 × 22) + (20 × 24) + (20 × 31) +
(10 × 28) + (10 × 32) + (15 × 36) = 3015 → To solve this problem,
Specifies a level of service that must be achieved → Find the number of facilities needed to
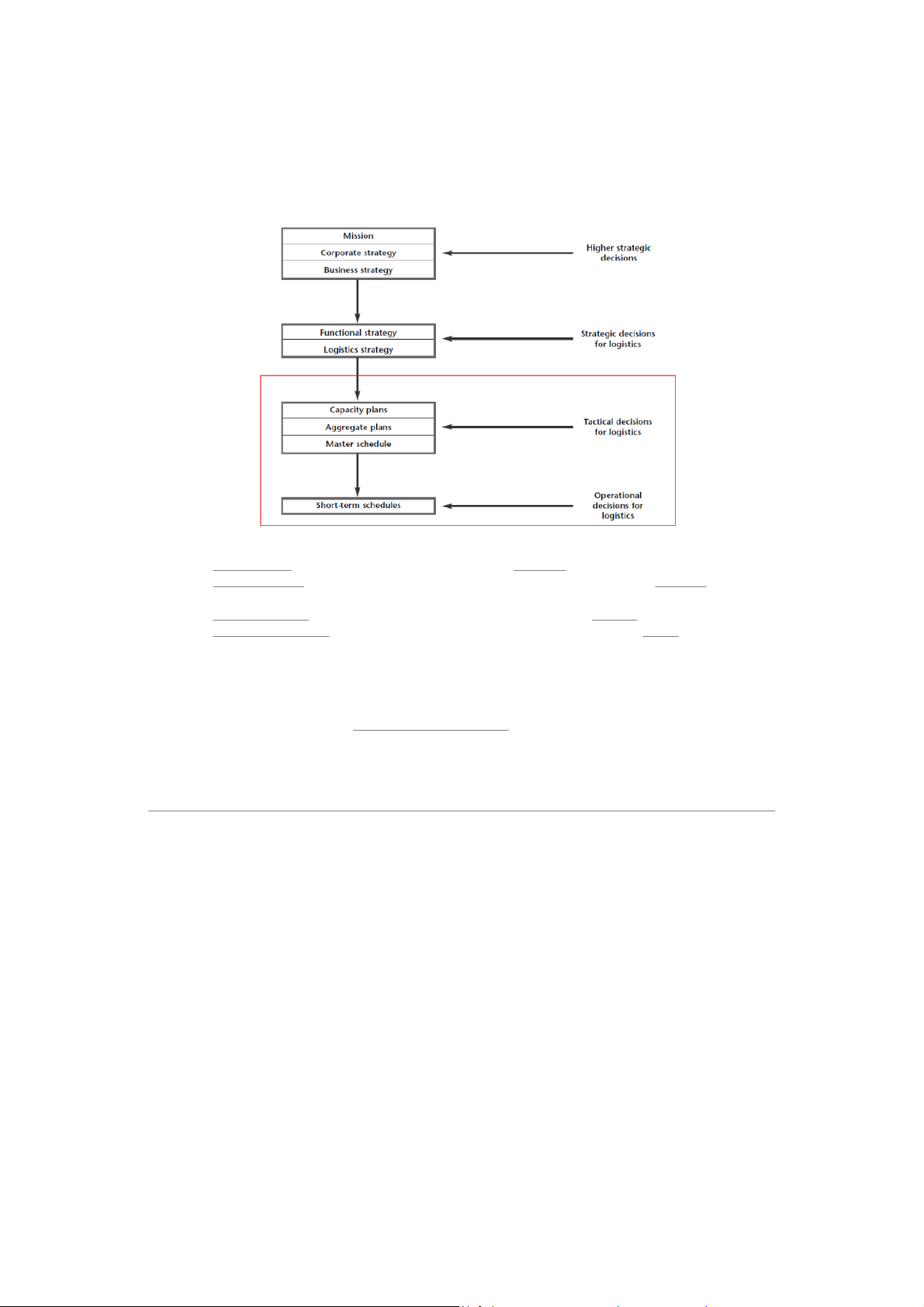
All activities along the supply chain have to be planned → It means that we design timetables
If an organization does not plan for the future → it can be in danger of ⇒
𝐸𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
𝐸𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑐𝑎𝑝𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 ×100%
𝐷𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
𝐷𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝑐𝑎𝑝𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 ×100%
𝐸𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = 𝐸 𝐴 𝑓 𝑐 𝑓 𝑡 𝑒𝑢 𝑐 𝑎 𝑡 𝑙 𝑖 𝑣𝑜 𝑒𝑢 𝑡 𝑐 𝑝 𝑎 𝑢 𝑝 𝑡
𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 ×100% = 200 230 ×100% = 86.9%
𝐷𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = 𝐴 𝐷𝑐 𝑒𝑡𝑢 𝑠𝑖 𝑎 𝑔 𝑙 𝑛 𝑜 𝑐𝑢 𝑎𝑡𝑝 𝑝 𝑢 𝑎 𝑡 𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 ×100% = 200 300 ×100% = 66.7%
utilization shows that the company didn’t use its fully capacity
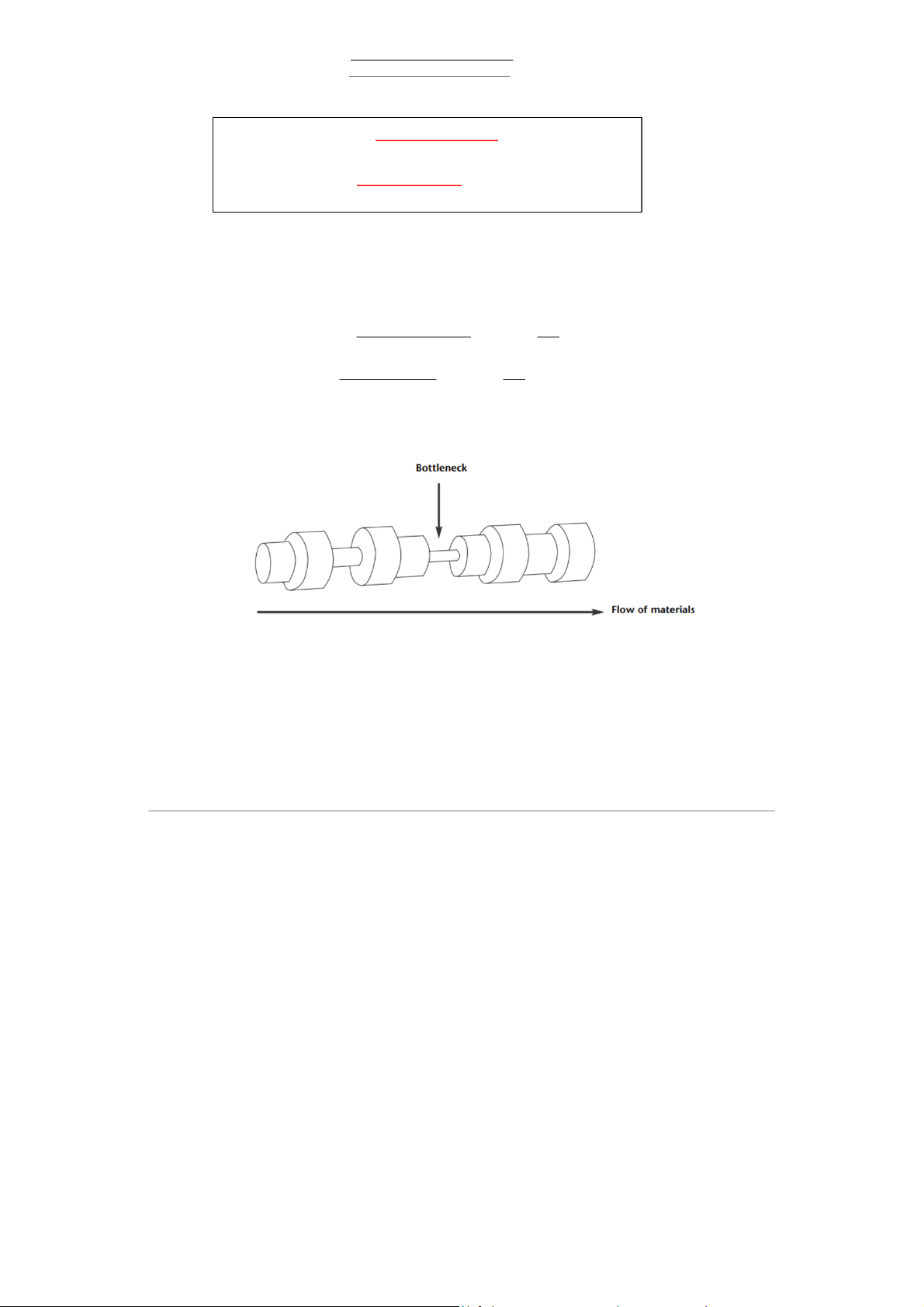
Not all parts of a supply chain have the same capacity → Some parts limit overall throughput,
→ The bottlenecks in a supply chain limit its overall




