














Preview text:
Keypoint for Final Exam (Chap 4,5,6) CHAP 4: COMMODITY CHAINS 1. Study streams
• The commodity chain allows us to chart the complex geographical journeys taken by commodities
• They are transformed from initial raw materials and ideas into finished products and services
• They serve from product to product, add value activities in every commodity chain (design, marketing, etc.)
• The connections between distant producers and consumers
• Different combinations of modes of governance
• Social relations that enable capitalism to extend its global reach
• Strategic alliance relationships, inter-place competition
• The commodity chain is an extremely important integrative idea that allows us to reveal the
interconnections between the many actors s
– tates, firms, workers and consumers.
Why the brand often come from one country but made from another country like China?
Because inside this unique, some components provides in another countries like China. Dynamic of economic space
Complex geographical journeys: each item to combine into finished one product come from
different countries. For instance, in the UK, people only import certain goods in certain countries
that have gone through security and quality assurance checks.
→ Commodity chain is not simple about manufacturing processes; many of the inputs to the chain,
and many of the final commodities produced, will take the form of intangible services.
(Commodity chains belong to this country. Like Codak camera t
– he brand name of camera in
the US but made from China. Another example, Boeing aircraft originated from the USA, but
some components come from another countries)
DIFFERENT BETWEEN SUPPLY CHAINS AND COMMODITY CHAINS?
Supply chains: Inputs – Process O – utputs
Commodity chains: Supply chains + Markets
Example: Iphone, there are any components come from many countries and each country involve in
each component. At the end, each component is combined into completed product. Components have it own value w
– hen adding component to finish products, they add their value for their components.
Another example: Like Coca – Cola, they have different brands for their water, soft drink. Each brand
control different other brand.
→Governments have different field to control. Each field control other small field – there are many levels m – odes governance.
Global reach: it one firm can extend to many countries. It can call “Global Reach”
Mở rộng: Commodity chains such as airplane is global commodity chains. In the past,
commodity chains products often come from only one country but nowadays this can come from many countries.
Question: Why the US just import one item in only one country?
For example like Vietnam, if Vietnam has a natural disaster affecting the product, Vietnam cannot
deliver the product to the US and at that time the US will not have products to consume, causing
many economic consequences for the US.
In addition, each product in each country has its own strengths such as topography, climate, and soil
to create specific characteristics for each product to make the product better.
This helps countries with globalization and the US have developed economies, so they will accept to
spend large amounts of money to get good quality products for their people.
2. Linking producers and consumers: The commodity chain approach
• Basic commodity chains: input-output structure
• The transformation includes primary activities (Example: production, marketing, delivery,and
services) and support activities (Example: merchandising, technology, finance, human resources and overall infrastructure.
• Upgrading strategies in global commodity chains:
▪ Process upgrading: improving the efficiency of the production system → reorganizing the production process
▪ Product upgrading: moving into making more sophisticated products or services.
▪ Functional upgrading: acquiring new roles in the chain (and/or abandoning existing
functions) to increase the overall skill content and level of ‘value-added’ of the ▪ activities undertaken.
▪ Inter-sectoral upgrading: using the knowledge derived from a particular chain to move into different sectors.
What is the value of industrial?
For service factors: less cost even but big profit
Farmer: pay a lot of cost, small profit.
Industry receive more value rather than agriculture.
Agriculture-industry-services: economy development.
How can UK importer can get high
profit the same price they get?
Why people in the UK accept the
high product with high price
compared to other countries?
Maybe advertising, the seller UK mixed
coffee creating the special products. If
the UK seller do more inside the
products, they accept with high price.
3. Capitalism, commodities and consumers
• Capitalism can be thought of as a commodity exchange system.
• A commodity is simply something useful that enters the market and is available for purchase.
• In the contemporary world, more and more areas of our everyday life have become caught up in processes of commodification.
• The exchange value of a commodity i – .e. the price i
– s often indicative of how the commodity was created:
▪ The cost of the human labor that went into its production,
▪ The costs of machinery, buildings, electricity, trucks and so on that were required
▪ The profits extracted at various points in the process.
• The consumers can benefit from the use value of whatever they have purchased.
• The commodities in our everyday life may actively serve to further conceal the origins of commodities. • Advertising a
– significant economic sector in its own right i – s extremely important.
• Through the creation of various images, advertisers seek to establish time a – nd place specific
meanings for particular goods and services that may be a far cry from the realities of their production.
QUESTION ABOUT WALMART:
a. How many partners of Wal-Mart in China?
Wal-Mart have many partners in China because each products they sell, they have each vendors to provide.
Walmart is not alone means other retailers can be corporated with China (metro, marko and
so on) bring more benefits and opportunities abt profit for China.
b. What are Wal-Mart benefits? Walmart benefit:
The cost of product lower lead to more profit they can get. The labor cost is cheaper, low
material cost lead to the cost of inputs lower. So,they can expand more market, it means they
can sell product with big markets in China and they can receive more benefit.
Win-win solution: the benefit receive not only for Walmart but also for china markets. Lead
to the commodity chain can bring more benefits for every countries.
In commodity chain, the country can involve more sections they can get more benefits as well as the product more value.
The lower cost → lower price → more consumer use Walmart product.
But when the price is lower, how they can get more profit?
Because they can cut more cost so they can get more profit(Walmart have full time and part
time job and because the unemployment is high so china people must accept part time job =>
therefore Walmart can cut a lot of profit.(While china full time pay well faire and
insurance,the part time job is not)
Beside that, linking producers and consumers: the commodity chain approach-market vaue/ value chain.
c. How China firms cooperate to outsource the products?
d. What are China’s benefits? Who are China’s beneficiaries?
First, increasing GDP - means China government show big problems about economy. China
very poor, high population. Many China people unemployment, more labor need job. China
government give more job for people through expanding processing for foreign countries.
Leads to China GDP increase
– China unemployment decrease. → GNP and GDP increase,
unemployment decrease. Having some good policies (social welfare,…)
Second, China labor: have opportunities to apply the job → income increase → living
standards increase (better life). Skill improving, application of new technologies to product
manufacturing leads to employees having much skills and in-depth knowledge.
e. What is your most interesting in this story?
4. Linking producers and consumers: The commodity chain approach – Market value/value chain Question:
Why does farmer produce coffee bean but
receive less profit and the provider received more?
If we can earn more in the importer section, we can
get more profit and value; we have a plan, we have coffee bean.
We can have more value. Like TrungNguyen, they
have many coffee stores in some countries.
TrungNguyen exporter form UK product but can
bring more profit for Vietnam. 5 categories of activities:
+ Section 1: primary activities
+ Section 2: secondary activities
+ Section 3: tertiary activities
+ Section 4: quaternary activities
+ Section 5: quinary activities
Why primary activity is the first section and it
includes agriculture, gathering industries and extractive industries?
Function upgrading bring more functions that make product better
Two factors depend on the field of industry:
+producer driven commodity chain: control whole process.
+buyer-driven: just control finish product (not need control whole process) (walmart) What is
Buyer-driven: global firm buys a commodity chain. Bc most of porduct is in commodity chain, china
will produce product and walmart just keep track finish product.
Producer-driven: come to check each component in commodity chain. Ex: automobile: each section
must be careful, if one component have problems, they cannot continue producing.
How company can manage/control commodity chain when they ask many partners involved in
producing the same products?
Based on the standard. Depending on the region, they have different standards. If standard in national
scale, they just sell in their countries. Global scale, apply global standard, sell products for global
market. Europe has high value market→have high standard for the product → have high price.
The standards of goods are not only based on safety, but demanding markets demand satisfactory
goods as well as they care about human rights, and they require the country to apply laws on labor →
goods. European prices are very high. If the inspection does not receive the benefits requested by the
worker, they will not import the goods even though they meet the required criteria.
5. Linking producers and consumers: The commodity chain approach - Management processes
• How commodity chains are constituted by a mix of intrafirm and inter-firm linkages,and a
combination of near and distant connections.
• Two factors: Producer-driven and Buyer-driven
➢ Producer-driven chains are commonly found in industries where large industrial
transnational corporations (TNCs) play the central role in controlling the production system.
➢ Buyer-driven: chains tend to be found in industries where large retailers (Wal-Mart,
Carrefour, Ikea, etc.) and brandname merchandisers (Adidas, Nike, The Gap, etc.) play the
central role in establishing and controlling production systems.
6. Linking producers and consumers: The commodity chain approach -
Institutional processes
• Global commodity chains are complex and divided into intersections.
• Rules and regulations that determine how economic activity is undertaken in particular places
(e.g. trade policy, tax policy, incentive schemes, health and safety/environmental regulations, etc.)
• Institutional context is different at spatial scales.
▪ At national scale, a huge range of policy measures to try and promote, and steer, economic
growth within their boundaries.
▪ At macro-regional scale, a variety of regional blocs have considerable influence on trade
and investment flows within their jurisdiction.
▪ At global scale, institutions as WTO and IMF shape the rules-of the - game for global
financial and trade relationships.
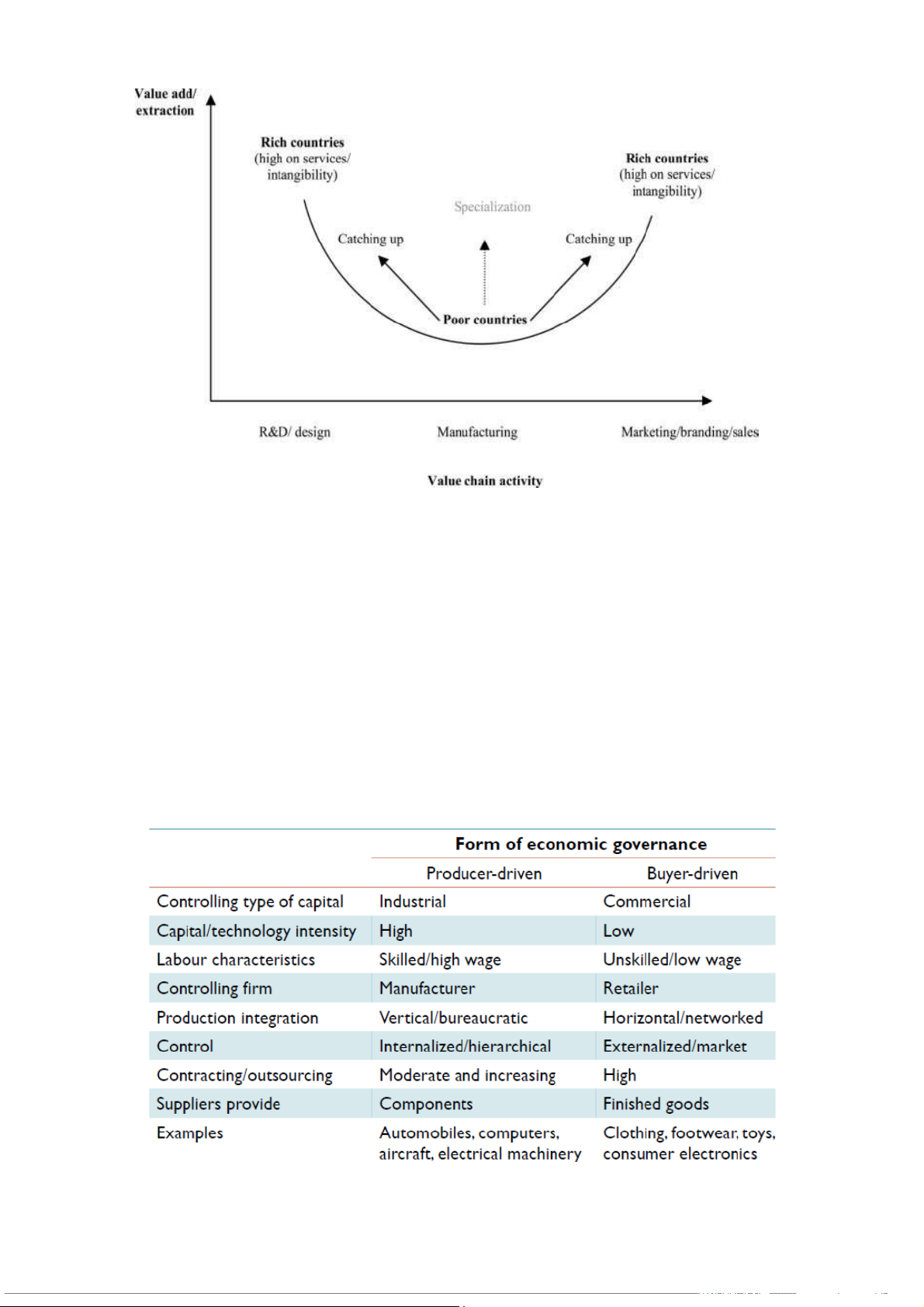
• However, joining into the global trade/commodity, the percentage of income from developed
markets has gone up much higher than from the growers (e.g. farmers) (see p.106- 107).
• The changing institutional frameworks can significantly affects all three of basic dimensions of a
commodity chain: the inputoutput structure, territoriality, and governance)
CHAP 5: GLOBAL SERVICES
1. Where is sector of services? Services going global:
The main sectors of the economy do not stand alone. They are connected and integrated by
transportation and communication services and facilities not assigned to any single sector but not common to all.
What is service: activity someone serve for you. If use service, have to pay. Service increase
different in different scale(national, international). Global service means the service serve for global
customer(especially by online because people can access to the service more easily and directly.)
2. Services sold with a manufactured product over its lifetime
3. National and global stimuli to the growth of services • Rising per capita incomes
• Growing demand for healthcare and educational services
• Increasingly complex division of labor
• Growing size and role of the public sector (services and regulation)
• Increasing international trade in services (service exports r
– egional and international - EPZs)
• Rapid growth in outsourcing service functions (externalization processes)
4. Why services increase when incomes would increase?
Why service will increase when income increase?
If people have more income they
can go to hospital to check their
health and always maintain the
doctor help them → increase health service.
Or: when they have high income,
they have a need to save money so
they can send money to the bank →
increase service to keep and protect money of customers. (banking services)
If people have less money, they
cannot spend their money for their
child to study in quality school,
check their health and cannot buy organic (quality) food de →
crease service. (edu service, shopping service)
If people have less money, parents can just bring their child to local school, but when they have more
money, they can bring their child to big city, even other countries to study (global service).
If people have less money, they just meet their basic needs. But when they have a high income, they
can spend money on entertainment, travelling ,...
Public service: express service, high-way, visa document (need to travel)
Global service in different scale: Tiki (national service: they serve normal quality service), lazada
(global service: they come from other country).
Service outsourcing is like international banking.
Same as outsourcing, global service has different product services to serve different people.
Global customers want to cut more costs: IBM computer com. Sell for global customer, iff they don’t
have externalization service, they cannot sell that item.
Service outsourcing: benefits and drawbacks for all?
India has service outsourcing and china have industrial outsourcing. Bc working in service
outsourcing, they need less cost, machinery, and less risk than industrial outsourcing. India bring
profit for global company when use global service and china bring profit for walmart.
(service>industrial: profit) so what is the problem of india that why China have well economy than india.
Limit to service export growth in developed and poor countries? (technology, infrastructure,
education and training, government and regulation, co-operation)
Internet in poor countries is sometimes poor or broke: pp can not access to internet to served by
global service and vice versa.
Labor working need skill and knowledge, poor countries can not serve service well bc they don’t
have well training or education or maybe infrastructure.
Government knows how to impose tax for amazon so that they can expand their service to serve
global customer and vice versa.
Co-operate strategy: if a partner cannot co-operate well, they can not serve well that service.
Question: What kind of sevices can get more profit?
Online services that compare online shopping sites with supermarkets: Online sales do not hace to
cost money to build, who have the network can easily buy goods between countries, while
supermarkets only sales when they build, so, it costs a lot. Moreover, in some countries that do not
have that supermarket, they will not be able to buy the products they need like buying online. As
online services are free of some fees charges (Such as employee fees or construction fees), they will
have many promotions and discounts for customers and will attract more customers than
supermarkets. Not only that, but for busy people, buying online is a good way because it does not
take a lot of time (just a few clicks, customers can buy what they like and just stay home waiting for
the shipper). It takes no time to go to the supermarkets, buying online will connect with customers around the world. Example: …
5. What are services? - Diversity of global services – Producer services Financial services
Trade in services (differences in export orientation by industry and by size of establishment)
Technological change in services Electronic funds transfer
Offshore banking & back-office locations Consumer services
6. Externalization processes in the producer services When?
Transactions cost considerations: the “make or buy” decision. Flexibility Why?
Risk reduction (agglomeration, environment, etc.)
Concentration on core skills de
→ concentration on semi- and periphery Service requirement: New types of services Third-party objectivity New regulations
Question: Service outsourcing: Benefits and drawbacks for all?
Cost advantages: the most obvious and visible benefit relates to the cost savings that outsourcing
brings about. You can get your job done at a lower cost and at better quality as well. Due to the
difference in wages between Western countries and Asia, the same kind of work that is done over
there can be done in India at a fractionn of the cost. There is a cost savings of around 60% by
outsourcing your work to India. The quality of services provided is high thereby ensuring that low-
cost does not mean low-quality.
Increased efficiency: When you outsource your business needs to an outsourcing partner like
Flatworld Solutions, they bring years of experience in business practices and expertise in delivering
complex outsourcing projects. Thus, they can do the job better with their knowledge and
understanding of the domain. This leads to an increase in productivity and efficiency in the process
thereby contributing to the bottom-line your company.
Focus on core areas: outsourcing your business processes would free your energies and enable you
to focus on building your brand, invest in research and development and move on to providing higher value added services.
Save on infrastruture and technology: Outsourcing eliminates the need for investment in
frastructure as the outsourcing partner takes responsibility of the business processes and hence
develops infrastructure for the same.
Access to skilled resources: You no longer need to invest in recruiting and training expensive
resources for your business. Providers like Flatworld Solutions take care of the resourcing needs with
their pool of highly skilled resources. The resources employed by Flatworld Solutions are well
educated in the respective business areas and are experienced in handiling the business needs of
companies that want to outsource. Further, Flatworld Solutions employs world-class business
practices perfected over the years by catering to customers around the globe. Get access to the
expertise and capabilities of Flatworld Solutions.
Time zone advantage: Apart from the cost advantage, the other much touted benefit has to do with
the time zone differential between your coutry and the location you are outsourcing to. Get your job
done while you are closed for the day andd wake upp to your service being delivered the next
morning. This unique advantage gives you the benefit of round-the-clock business operations.
Faster and better services: Make your service better with high quality deleverables and decrease
the lead time it takes for your product to reach the marketplace. Thus, you would be faster in getting
your ideas converted into products and better at delivering the value-added proposition.
Limits to service export growth in the semi-periphery (kém phát triển) and periphery?
▪ Technology and infrastructure ▪ Education and training
▪ Government regulation and policies ▪ Co-operate strategies.
7. Service export in semi-periphery and periphery
The structure of FDI from DCs has shifted toward services.
Export processing zones (EPZs) in LDCs are increasingly used to attract investment in export- oriented services.
Eco-tourism”, special tradable service, can offer for economic development in some peripheral regions.
8. National and global stimuli to the growth of services - Service labour and GPD per capita -
Geography of services (spatial change) • Patterns and trajectories
• International trade in services
• Transnational investment patterns
• Export processing zones (EPZS)
• Agglomeration and new business service concentrations
Variety in the internationalization of services
• Internationalization of retailing: • International tourism
• Internationalization of finance
• Internationalization of business services
9. Geography of services - Patterns and trajectories
Variety in the internationalization of services - Internationalization of retailing –
As the largest retailers (like Wal-Mart, traditional shopping) expanding into foreign markets, E-
shopping (like eBay, Amazon) has an additional dimension to retailing.
There are different between advantages and disadvantages of two kind of global retailor:
One shop at store and one shop online. They are different but in the future each of them depends on
the customer. For example, customers like shopping online. Most of them have little time (busy) to
go to shop at store because they buy something on shop online. → More discount more selling
products for customer. Another is to shop at store, customer go to supermarket have enough time to
go. Benefits: They can check the products, and easily choose thing they like.
Internationalization of services – Internationalization business services –
The same as outsourcing industry. Global firms want to export products to other country. If they are
outsourcing in the poor developing country, they can reduce and get more costs→ Get more profit,
specially creating the opportunity job for developing country. Important is the big partner
outsourcing, they can invest in developing country like India, Israel, South Africa.
BPO (Business process outsourcing): such as • Offshore banking, • Call centers, • Computer network support, • Legal services,
• Accounting and procurement, • Software development,
• Research and development (R&D),
• Engineering services, etc.
Question: Why these services can be outsourced in other/developing countries? Explain
Global services have outsourcing which is the most activities. Services
Because online services for global customers. The services must use international language, they
country that labor can speak well international language that those country can outsource better than.
It can provide HR, process, and technologies to conduct effectively (accountants who always do
financial statement for many companies will have more experience for accountants who just work for only one individual company).
Reduce time to help business focus on their core goal. (In a textile company, instead of taking
notice of looking for finance accountants or IT support, they can find BPO and focus on their main
role is producing textile to meet the demand of customers or other business).
Provide flexible methods in management. (For each project, they can easily manage depend on the
goal of the project. For example, project A of textile company, they have to prove uniform firm for
another company so their focus goal is producing, which means they have to concentrate on
engineering services, manufracturing services, and other services like IT support, R&D for workers,…they can use BPO).
Reduce cost of the process (Almost in LDCs, the process is cost less than LDCs and workers in
LDCs still have the necessary skills, speed and attention to complete work.)
Internationalization of services – Internationalization business services B – ack Offices – Def:
The front office includes sales personnel and corporate finance.
The middle office manages risk and IT resources.
The back office provides administrative and support services. Such as: • Call centers, • Computer network support, • Legal services,
• Accounting and procurement, • Software development,
• Research and development (R&D),
• Engineering services, etc.
Call-centers in Bangalore, India (Tr l ả ời cu i ố bài)
• Where (locations) could be call-centers, IT supports, etc.? Why there?
• Is there any challenge or competitiveness? • What are pros and cons?
Variety in the internationalization of services I
– nternationalization finance –
The internationalization of finance has created opportunities and challenges for the LDCs become the
transnational banks and FDI in financial services.
The continued dominance of London, New York and Tokyo over foreign exchange transactions
despite the increasing use of electric money (e.g. online-banking), and the concentration of offshore banking centres in the LDCs.
Internationalization of services – Internationalization finance O – ffshore Banking
What is offshore banking? Offshore banking simply means you have a bank account in a location
outside the country you're living in. This location is usually a low tax jurisdiction.
What are the main benefits of banking offshore?
Convenience - stay with the same bank, no matter how many times you move country.
Choice of currencies - a wide selection of multicurrency savings and investments to help you grow your wealth.
Expat expertise - specialists who can help you structure your investments and choose the right foreign exchange solutions.
Tax efficiency - banking offshore could be a tax efficient way to manage your money.
Consequences of externalization (Outsourcing)
It may shift risks to suppliers
The suppliers (industrialized countries) may reduced costs if they are able to exploit scale economies
It may allow acquisition of expertise that cannot be provided internally due to lack of knowledge on the part of the purchaser.
Working life of service
Complexity in defining and measuring services The working-life of service: Productivity of service Flexibility of service Elasticity of service Explain:
Productivity of service: the circle of service can be working well to support customer with next circle, improve to…..
Flexibility of service: easy to move in any situation. Service more flexible can be survived longer→
change city or follow customer demand→ more customers→ more income→ more productivity.
Elasticity of service: it depends in physiological needs like food, healthcare service, the elasticity of
service is low while other service like entertainment, advanced technology, these services has a high elasticity.
Constraints on service productivity
Personal (human) labor is necessary
The co-presence need for seller and buyers for many services (haircuts, tailors)
Proximity requirements may grant monopolistic power to sellers, restraining productivity
Opacity (slow development) in markets (buyer not knowledgeable about service)
Often a relational matter between buyer and seller (design services)
Labor markets in the service economy The shifting level of jobs i
– ndustry & occupation again
Labor intensity in services compared to goods production
Income distribution of service work
EXPORT PROCESSING ZONES (EPZs) Def: Type of free trade zone (FTZ)
By government, to promote export.
Also called development economic zone or special economic zone.
Offer incentives to attract foreign investment. Ex:
EPZs in Vietnam Quang Trung Software City:
-Location: District 12, HCM.C.
-Constructed in 2000, operated in 2001. -104 enterprises (55% is foreign enterprises). -Includes:
consultant service, telecom service, advertising service, offices for lease… Sai Gon High Tech Park -Location: District 9, HCM.C. -Operated in 2002
-A lot of foreign investor: Intel (USD $1 billion),Nidec (USD $1 billion) …
-Includes: microelectronic, informationtechnologies, telecom, biotechnology, precision
mechanics - automation - robonics, advanced materials - nanotech - new energy.
Chap 6: TECHNOLOGY AND AGGLOMERATION
1. Introduction of technology The end of geography: Relational proximity Node in global networks
2. The rise of “Placeless” Production
“Placeless” Production:
End of geography → Placeless production:
Internationalized financial services Online shopping
“Placeless” production
Overlapping financial markets in different time zones:
Engage in 24- hours-a-day trading
Connections between different markets
Space-shrinking: new technology can make the time and space shorter.
eBay – a very real and uneven geographies, is largely a rich country phenomenon r → eplying as it
does upon both the availability and affordability (in local terms) of internet access, which is very patchy at global scale.
Comparing between eBay and Walmart: Walmart eBay • Traditional supermart • Online shop
• Deal with producer, intermediate sellers,
• Most buyers + sellers transact within
and consumers within and aboard/oversea
their ‘home’ national territory countries
• Goods exchanged still have to be moved
through the real world of postal, freight,
and logistics services and customs, and
import/export taxes and duties
Question: Some people think that eBay will knock-down Walmart in these days?
Answer: NO. The estimated revenue in eBay and Walmart is the same. In addition, Walmart can
meet the needs of consumers. Some people prefer to go shopping compared to buy online.
3. Understanding technological changes and their geographical impacts
• Technology must be seen not as a technical process with a life of its own, but rather as a social
process through which individuals and organizations deploy technologies to achieve certain ends
• Different kinds of space-shrinking technology: transport and communications technologies
• Different levels of technological change: partly application, robot replaced human workers,
automobile production lines, etc.
• Technological change needs to be placed in a long-term or evolutionary perspective: The different
spatial outcomes of each wave of new technology have interacted with patterns of activity left over form the preceding wave. (p.124)
Impact of geography to the new technology: Talk about the physical field
About the limits about political, cultural, society. Just in time: New technologies New transportation: New communication technology: High-way road Information technologies: Airplane Internet connection Ship Wifi, V-Lan, etc. Train
GPS (Geographical Position System) Cable Pipelines, etc.
Done with uneven in social and geographical terms
Placeless technology reality full of spatial inequalities and contradictions of different kinds
More exactly, flexibly and various forms
Shrinking technology to reinforce existing patterns of inequality
Allow more people and places (locations) to interact with the global capitalist system
New trend/propensity for related firms to agglomerate in cluster intangible → new nodes in global
economy New transportation
Done in ways that are hugely uneven in social and geographical terms
Transfer more goods (include people) and services
New information technologies
‘Placeless’ technology – end of geography
More exactly, flexibly and various forms
Reality full of spatial inequalities and contradictions of different kinds
Space-shrinking technologies
Space-shrinking technologies:
Have in common, ability to help their users partially overcome the constraints of space and time.
Connect firms workers, governments, and consumers together in different ways
Two important kinds of space-shrinking technologies:
Transportation systems: means by which material goods (and people) are transferred between places
Communications systems: enable the transmission of various kinds of information (text, numbers,
images, video clips, music files, computer programs) between places
Space-shrinking transportation technologies
Advent of commercial jet aircraft: more people, high value terms, and fresh products Advent of containerization
Space-shrinking communication technologies
Satellite and optical fibre technology: voice, images, and other data transfer/transmit
Optical fibre with high electricity: data transfer very high speed
The internet: mass users – interactive Mobile telecommunications Electronic mass media: 1980s c
– ombination of deregulation and new outlet of cable and satellite
television: BBC, CNN, MTV, Fashion TV, radio, etc.
more TV channels available in many countries
inequality in access to the media across the globe
more users in high-income countries
Geographical impacts on space-shrinking technologies?
Internet and computer using in Cuba In 1998:
Cuban IP connectivity was minimal, with perhaps as few as 100 users.
IP point of network connectivity was only at CENIAI in Havana
mMore than 10% of the ministries had email accounts Poor telephone infrastructure
Space-shrinking technologies: Call center w
– ide range of support services Space-shrinking
Question: What do Vietnamese country do to apply space-shrinking?
Answer: Transportation technology.( It is important to build and develop infrastructure)
Communication technology
Services provided via telephone:
Sales, marketing, technical supports, claims enquiries, market research, reservations, information provision.
Other services from Call center:
Claim and accounts processing, payroll processing, data processing, and invoice administration, etc.
Information technology services: software development application testing, and content development, etc.
Leading sectors involved in offshoring services.
Types of offshoring services: finance, telecommunications, health, services and public sector, transport services.
India → cluster of services (p. 130)
China →cluster of producing (p.88-89) Questions:
What are differences of outsources/offshoring in these 2 cluster countries?
There is an emerging discussion on China, the emerging strong economy. However, India would
grow faster and gain the rank of China. Could India be? Why?
Production process technologies in competitive capitalist economy:
Firms have to improve the rate to develop new products and services, and efficiency of production processes.
Firms’ three important decisions:
An appropriate technique (product quality, internationalized standards, etc.)
Scale of product determined economy of scale achievable by increasing production volumes (for various consumer and markets)
Television production <> handmade furniture?
Fast food retailing <> corporate banking? The location of production Cheap/high skilled labor
Sourced input: raw materials, advised from management consultants, and/or
Market (final consumers, other businesses and/or government department Production flexibility
Nowadays, the heart of the enhanced flexibility is the use of information technologies in machines
and their operation to allow more sophisticated control over the production process
In industrial manufacturing: small or large Textile → sewing
Dental → 3D computer for making a new teeth
Set a process of making a cake: measure input materials, manage process Or making a key copy In biotechnologies: Insect control in agriculture
GPS application in agriculture
Israel case studies in agricultural development
Israel supports Vietnam in planting Dragon fruit in Bình Thuận
With computer: could allows firm to tailor products to the requirements of individual customer → more value added
Wide range and variety of products for different market niches To craft products:
Design with skilled craft workers
Craft industries: shoes, jewelry, clothing, furniture, etc.
Skilled craft workers using flexible machinery to produce small volumes of customized goods
→Flexibly specialized production system
Flexibly specialized production system are skilled craft workers using flexibly machinery to produce
small volumes of customized goods
‘just-in-case’ and ‘just-in-time’
4. Proximity matters: Traded and untraded interdependencies within clusters
Two types of agglomeration economies:
Urbanization economies:
Growing people create urban areas,
Cost sharing of wide range of infrastructure (airports, road, rail networks, etc.) and services
(universities, hospitals, etc.)
Diverse firms and large markets.
Localization economies:
Cost savings of firms within the same or related industry in the same place
Specialized pools of skilled labor,
From access to industry-specific services and institutions,
Or from development of a local knowledge base
Vertical disintegration: Agglomeration of firms
Cluster of suppliers surrounding assemblers and manufactures in sectors Core competencies:
Firms shed many activities and purchase them instead from their suppliers
More inter-firm relationship → spatial agglomeration to minimize the costs associated with
sustaining those relationships.
→ Stronger agglomerative forces
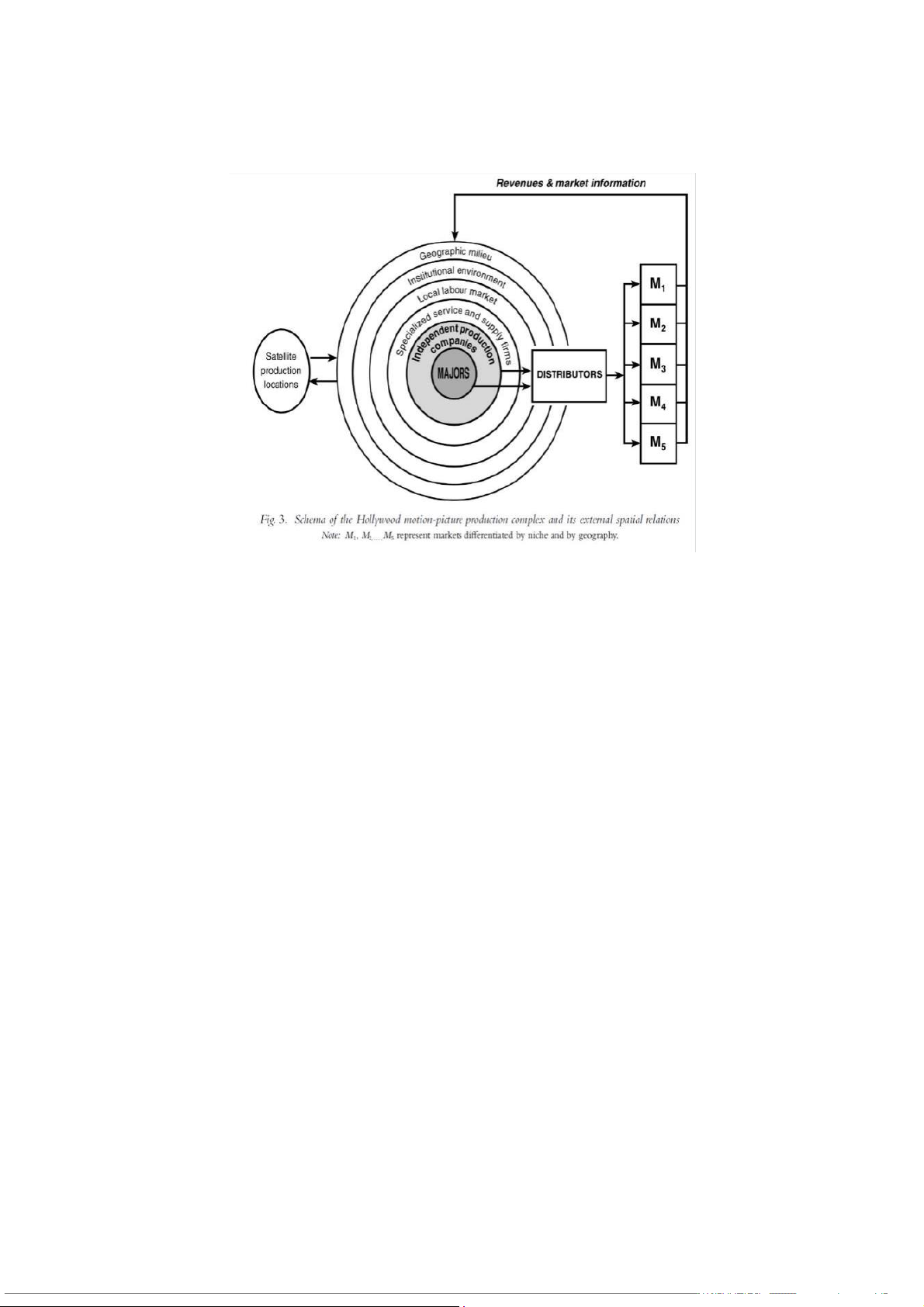
Traded interdependencies within clusters Hollywood, Los Angeles c
– enter of global film industry Over 5,500 firms Employs 150,000 people
MAJORS: MGM, Sony/Columbia, 20th Century Fox, Paramount, Universal, Warner Bros, and Disney
Untraded interdependencies within clusters Tacit knowledge ‘know-how’
Shared through people doing things together in real life.
May only be accessible by being immersed in the untraded social and cultural interactions of a locality. Codified knowledge
Ideas and know-how that can be made tangible through writing it down or creating a diagram.
Codified knowledge is able to travel across space, while tacit knowledge is much stickier geographically.
Example: The Motorsport Valley in UK
Radius of 50 miles around the counties of Oxfordshire and Northamptonshire
40,000 employees; 25,000 highly skilled engineers
Annual turnover of US$ 9 billion
Six interacting ways that knowledge is disseminated: Staff turnover Shared suppliers Firm births and deaths Informal collaboration Industry gossip Trackside observation
A typology of agglomerations
Seven significant cluster types:
1. Labor-intensive craft production clusters:
Often high immigration labor firms involved in tight sub-contracting networks, use homeworkers:
garment production districts of Los Angeles, New York, Paris, etc.
2. Design-intensive craft production clusters
Dense agglomerations of small and medium-sized firms, high-quality good and services: Third




