


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246 MICROECONOMICS WEEK 3 Market and Competition
- Market: a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.
Ex car market, motorbike market, comestic market,…
- Buyer determine the demand of product - Sellerd determine the
supply of the product - Market take many forms:
+ Highly organized: market for wholesale agricultural
commodities. buyers and sellers meet at a specific time
and place, where an auctioneer helps set prices and arrange sales.
+ Less organized, more often consider the market for ice cream
in a particular town. Buyers of ice cream do not meet together at any one time.
- Competition market: a market in which there are many buyers
and many sellers so that each has a negligible impact on the market price
- Each seller has limited control over the price bcs other sellers are offering similar product
- A seller has little reasons to charge less than the going price
- Assumption: markets are perfectly competitive
- 2 must characteristics of a competitive market
- In that market, both buyer n seller must accept the price that
market determine Said to be price taker
- Not all goods are sold in perfectly competitive markets
+ some mar have only 1 seller. This seller sets the prices , called a monopoly +other fall between lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246
Demand: Behavior of buyers o Demand curve: the
relationship between price n quantity demanded
- Quantity demaned: the amount of the good that buyers are willing and able to purchase.
Ex : Price ice cream rose to 2$/scoop -> get expensive -> buy less
or buy sth similar instead / get cheap -> buy more
- Law of demand : the claim that, other things equal, the quantity
demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises
- Demand Curve ( đường cầầu ): the claim that, other things equal,
the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises
- Demand schedule : a table that shows the relationship between
the price of a good and thequantity demanded lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246
by all the buyers at each price.
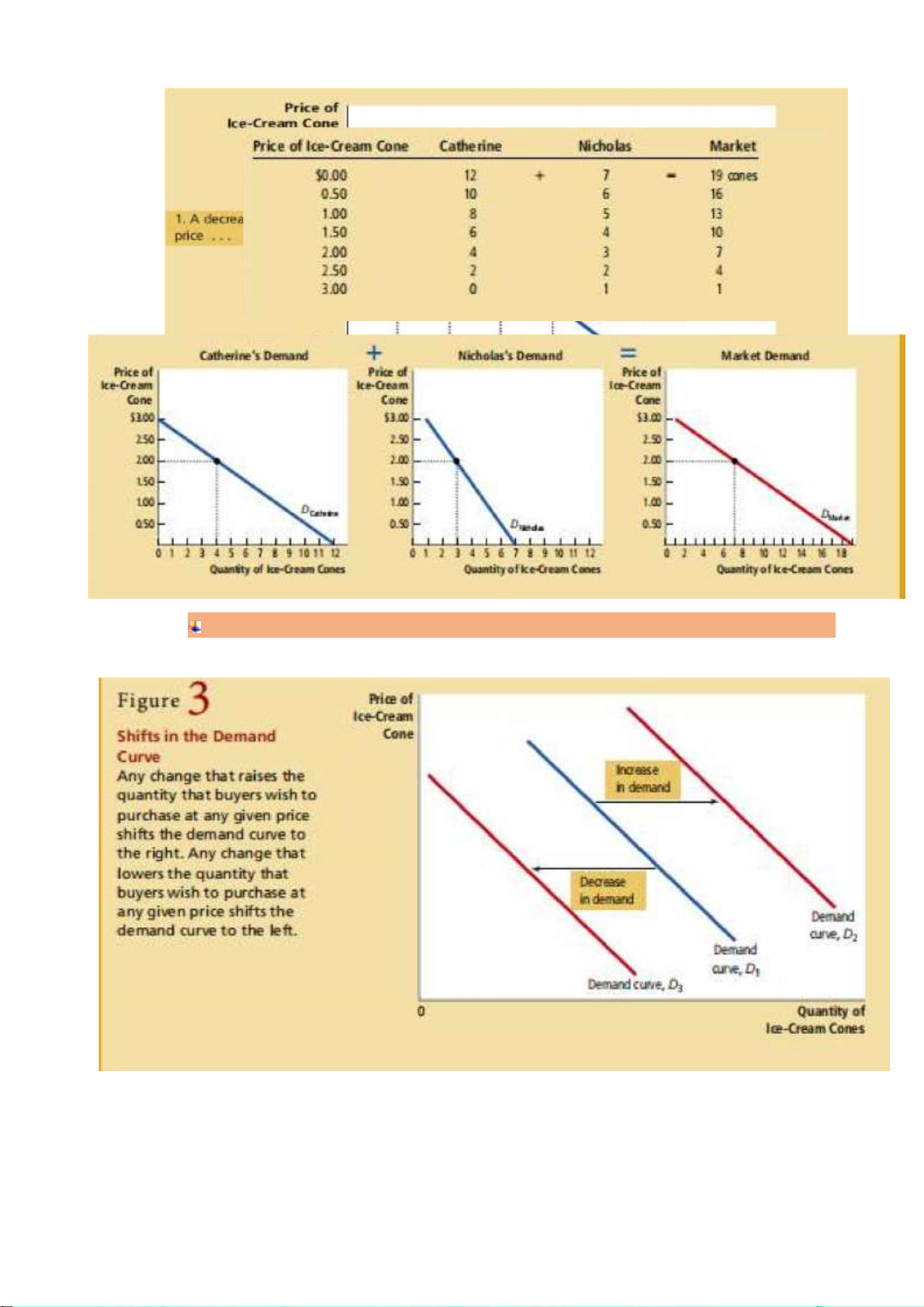
M arket demand vs Individual demand
- Market demand:
sum of the quantities demanded
Shifts in the Demand Curve
- If sth happens to alter the quantity demanded at any
given price, the demand curve shifts - If the Demands for a good
falls when income falls,, the goods is called normal good.
- If the demand for a good rises when the income falls , the good is called inferior good. lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246
EX: bus rides, instant noodle,..
Normal good: a good for which, other things equal, an increase in
income leads to an increase in demand
Inferior good: a good for which, other things equal, an increase in
income leads to a decrease in demand o Price of related goods
- Ice cream n frozen yogurt are bnoth cold, sweet n creamy desserts.
Thus, satosfy similar desires. Suppose price of frozen yogurt falls,
the quantity demanded of frozen yogurt increases. ( according to the Law of Demand )
- What happen to demand of ice cream then ? buy less ice cream
bcs they satisfy similar dessires Ice crea n yogurt are substitutes
When a fallin’ the price of 1 good reduces the demand for
anmother good, the 2 goods are called substitutes.
Substitutes are oftem offer pair of goods that are used in place of each other
Ex: hotdog n hamburger, sweater n sweatshirt,…
- Now suppose that the price of hot fudge falls. According to the law
of demand, you will buy more hot fudge. Yet in this case, you will
buy more ice cream as well because ice cream and hot fudge are
often used together. When a fall in the price of one good raises the
demand for another good, the two goods are called complements. o Taste -
This is the most obvious determinant of ur demand -
Economists don’t try to explain pple’s tatse , but do examine what
happens when atste change o Expectations -
Ur expectations about the futute may affctves ur demand for a good/ service today
+ expect higher income save less n spend more
+ expect prices fall less willing to buy at today’s price o Number of buyers -
Market demand depends on the number of these buyers lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246 Supply
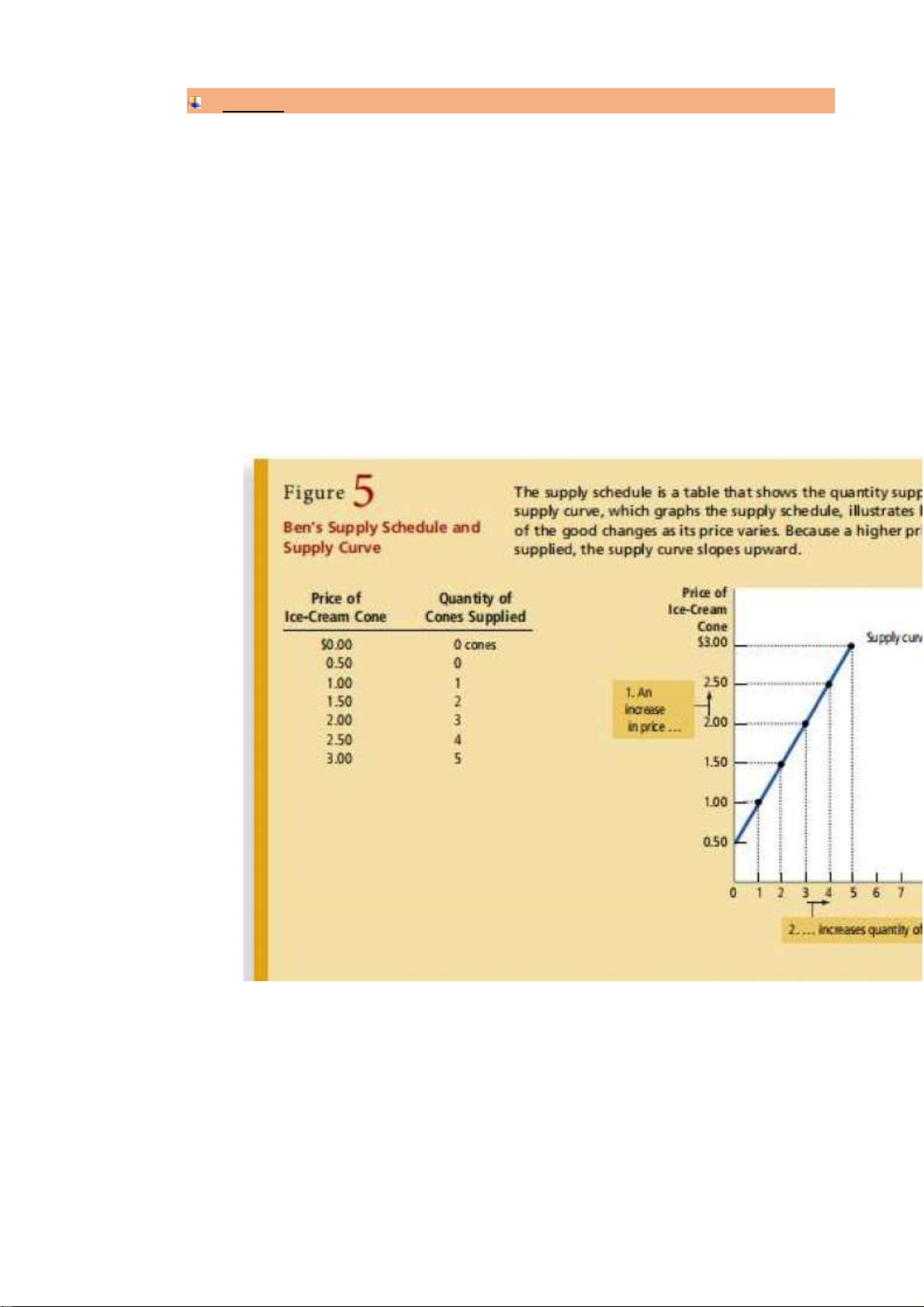
o The supply curve: the relationshp between price & quantity supplied -
The quantity supplied of any good or service is the amount that
sellers are willing and able to sell -
law of supply: the claim that, other things equal, the quantity
supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises -
supply curve: a graph of the relationship between the price of a
good and the quantity supplied ;;ơ -
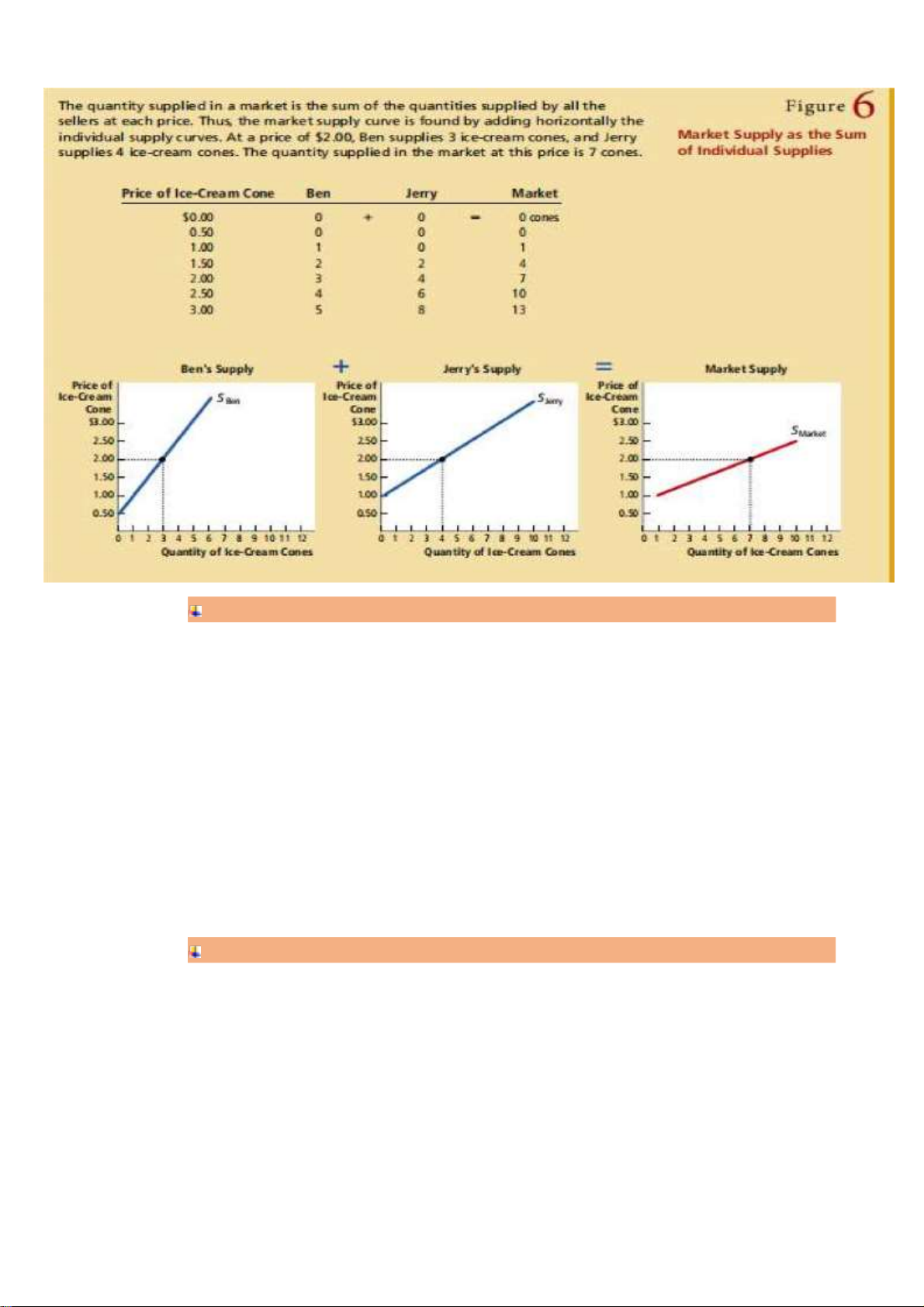
Marker Supply: Sum of the supplies of all sellers
constant, the curve shifts when one of the factors changes. For
example, suppose the price of sugar falls. Sugar is an input into
producing ice cream, so the fall in the price of sugar makes selling
ice cream more profitable. This raises the supply of ice cream: At lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246
Shifts in the Supply Curve
- Because the market supply curve holds other things
any given price, sellers are now willing to produce a larger
quantity. The supply curve for ice cream shifts to the right. -
Variables that can shifts the supply curve: + Input price + Technology + Expectation + Number of sellers
Supply and Demand together o Equilibrium -
Equilibrium: a situation in which the market price has reached the
level at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded -
At euilibrium price, auantity of the good that buyers are willing n
able to buy = quantity that sellers are willing n able to sell lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246 -
also called market -clearing price -
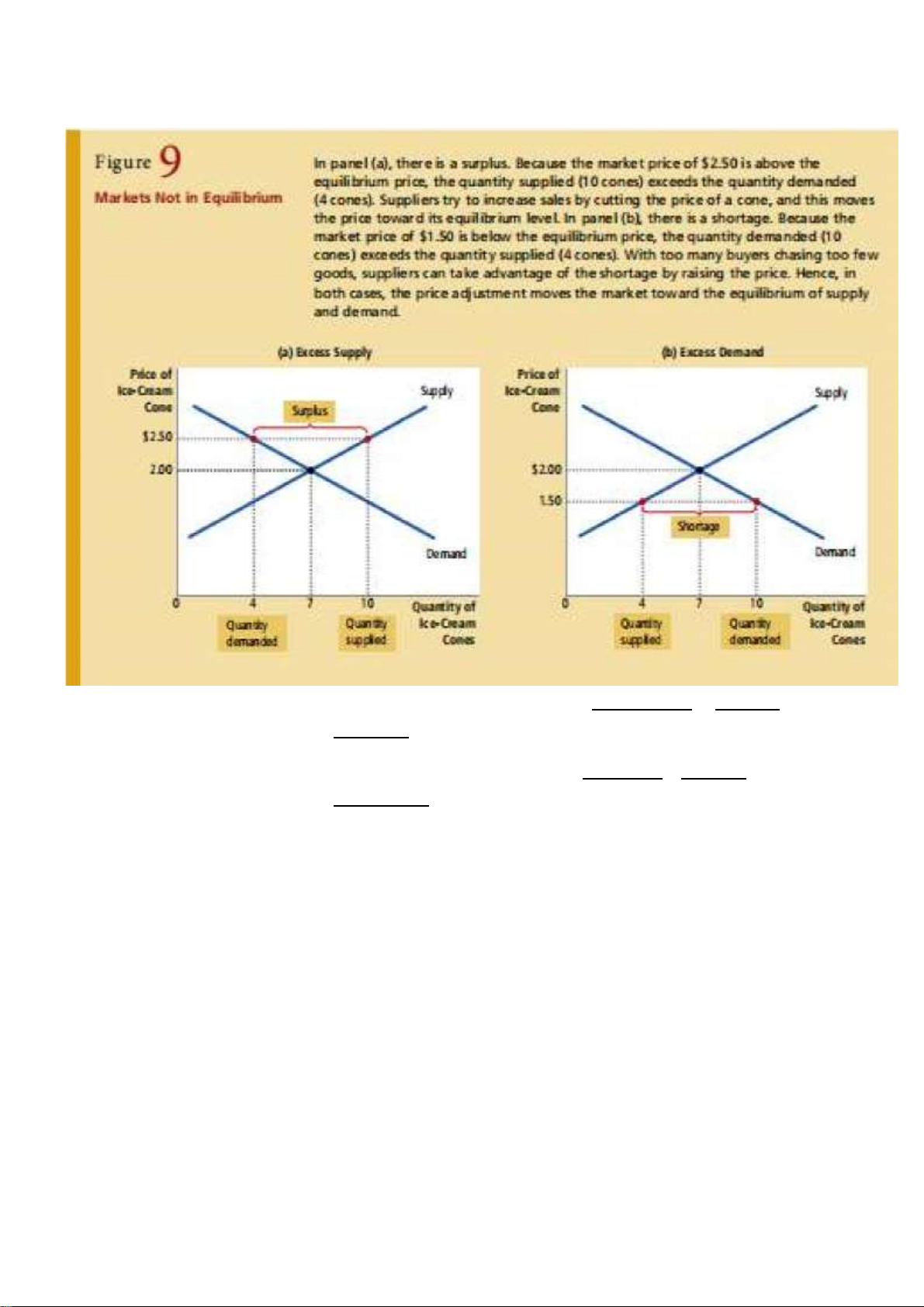
Shortage: a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied -
Surplus: a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
Law of supply and demand: The price of any good adjusts to bring the quantity
supplied n the quantity demanded for that good int balance.
o Three steps to analyze Changes in Equilibrium lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246
Ex : The allocation of beachfront
land. Bcs the amount of this land
is limited, not everyone can
enjoy the luxury of living by the
beach. Who get this resource ?
( The answer is whoever is willing
n able to pay the price. The price
of beachfront landadjust until the quantity of land demanded exactly balances the quantity supplied ) SHIFTS VS MOVEMENT o Movement - A movement along the demand curve will occur when:
+ price of good changes, and quantity demanded changes
In accordance to the original demand relationship -
In other words, a movemment occurs when a change in the
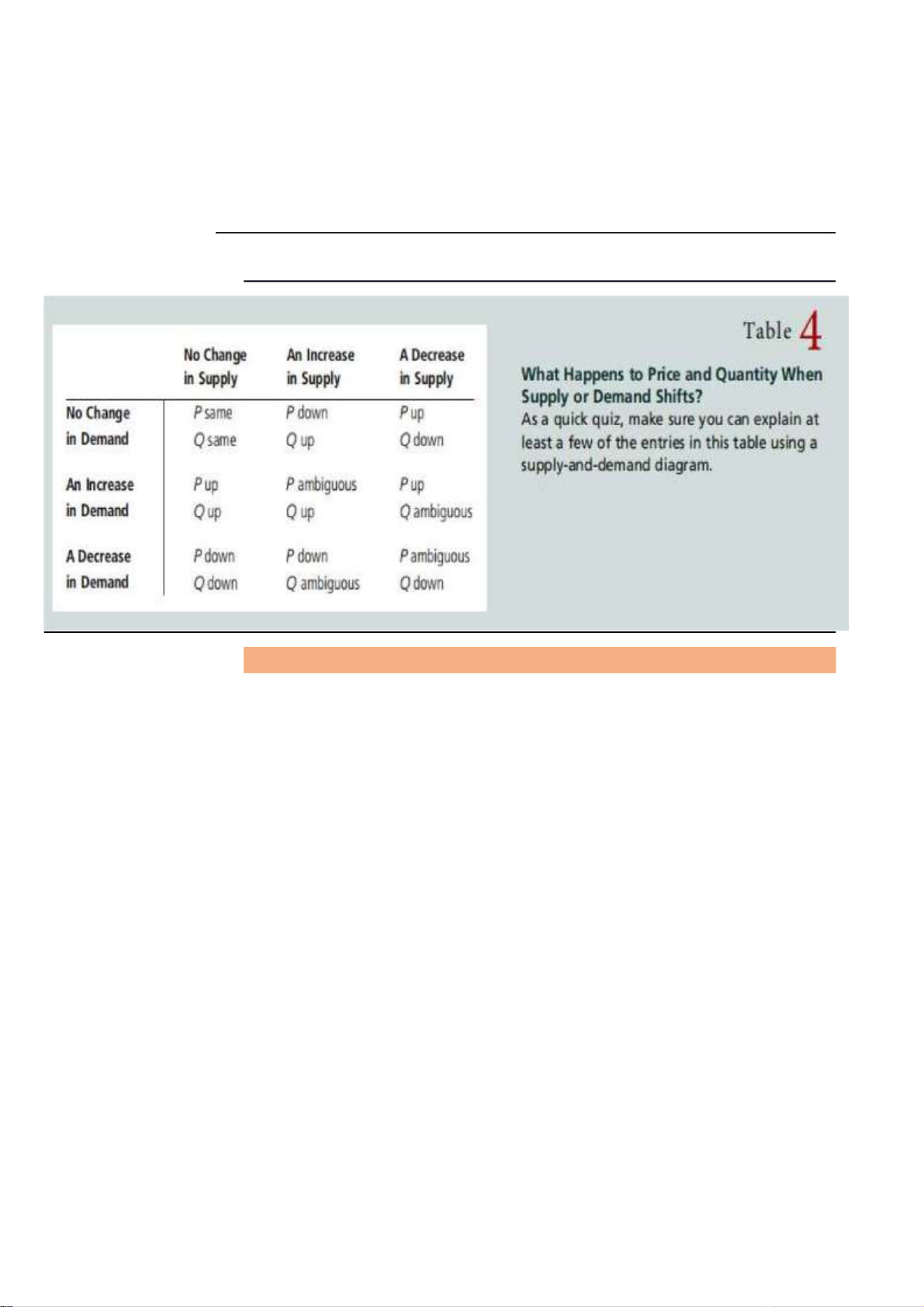
quantity demanded is caused only by a change in price, and vice versa. o Shift -
A shift in demand or supply curve occurs when a good ‘s quantity
demanded or supplied changes even though price remains the same.
Ex: ar the same price of $2 for a bottle of beer, consumers are
willing to buy a higher quantity - Shifts in the demand curve
+ imply that the original demand relationship has changed lOMoAR cPSD| 47270246 -
Shift in the supply curve imply that the original supply curve has
changed , meaning that Supplu curve shifts when the quantity
upplies is effected by a factor other than price -
A shift in the supply curve occur if for ex natural disasters
BÀI T Ậ P : 1 ,9 ( page 86)




