















Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 APPLIED STATISTICS COURSE CODE: ENEE1006IU Lecture 11:
Chapter 7: Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
(3 credits: 2 is for lecture, 1 is for lab-work)
Instructor: TRAN THANH TU Email: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 1 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA)
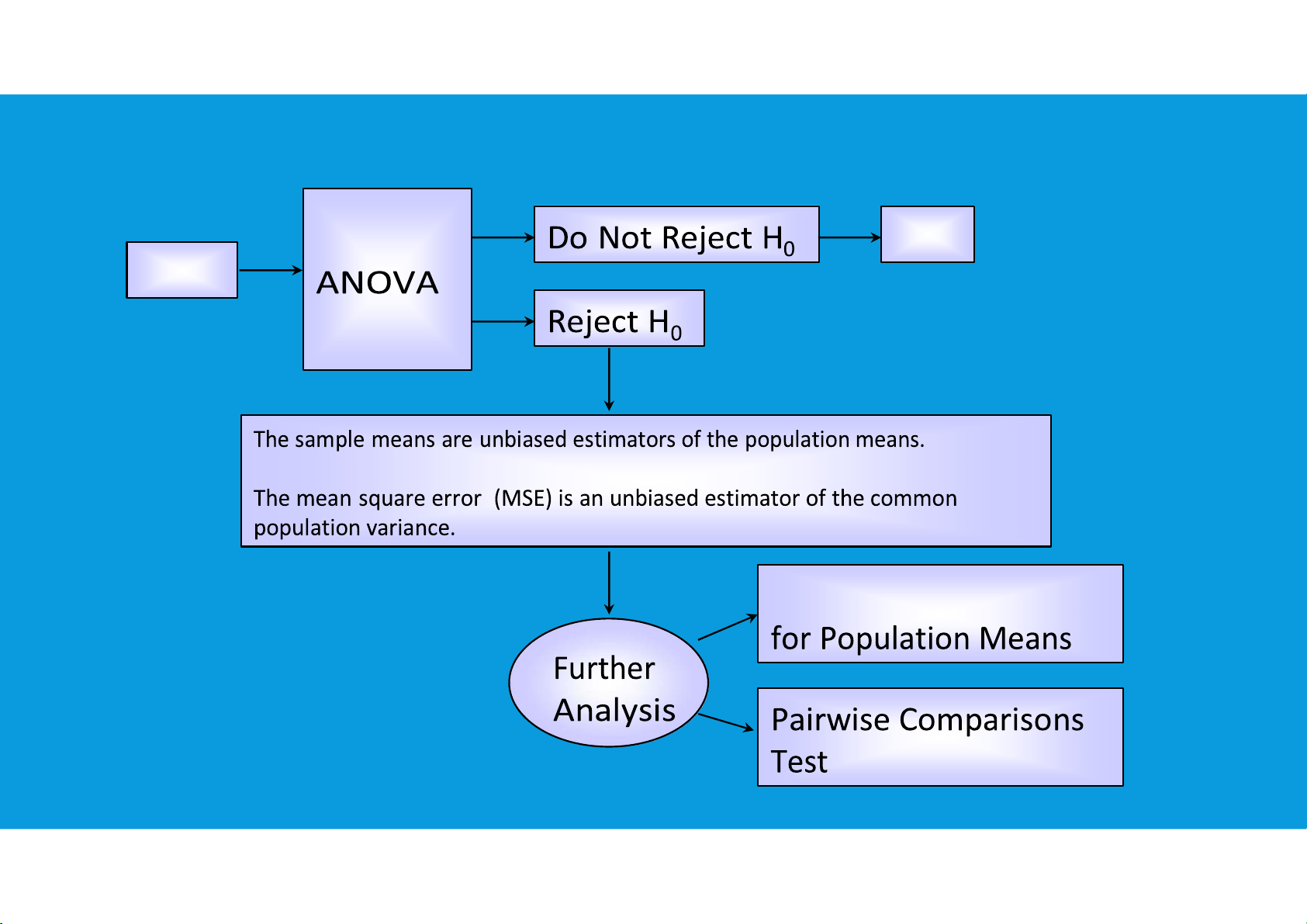
•ANOVA (ANalysis Of VAriance) is a statistical method for determining the
existence of differences among several population means. ANOVA is designed
to detect differences among means from populations subject to different treatments (or set-up) ANOVA is a joint test
The equality of several population means is tested simultaneously or jointly. ANOVA
tests for the equality of several population means by looking at two estimators of
the population variance (hence, analysis of variance). tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 2 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA)
•In an analysis of variance:
We have k independent random samples, each one corresponding to a population subject to a different treatment. We have:
n = n1+ n2+ n3+ ...+nk total observations.
k sample means: 1, 2 , 3 , ... , k
These k sample means can be used to calculate an estimator of the population variance.
If the population means are equal, we expect the variance among the sample means to be small. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 3 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 k sample variances: s 2 2 2 2 1 , s2 , s3 , ...,sk
These sample variances can be used to find a pooled estimator of the population variance σ 2 k . tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 4 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) Stop Data Confidence Intervals tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 5 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA)
•7.1. Inferences about a population variance
•7.2. Inferences about two population variances
•7.3. Assumptions for analysis of variance •7.4. A conceptual overview •7.5. ANOVA table •7.6. ANOVA procedure
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE
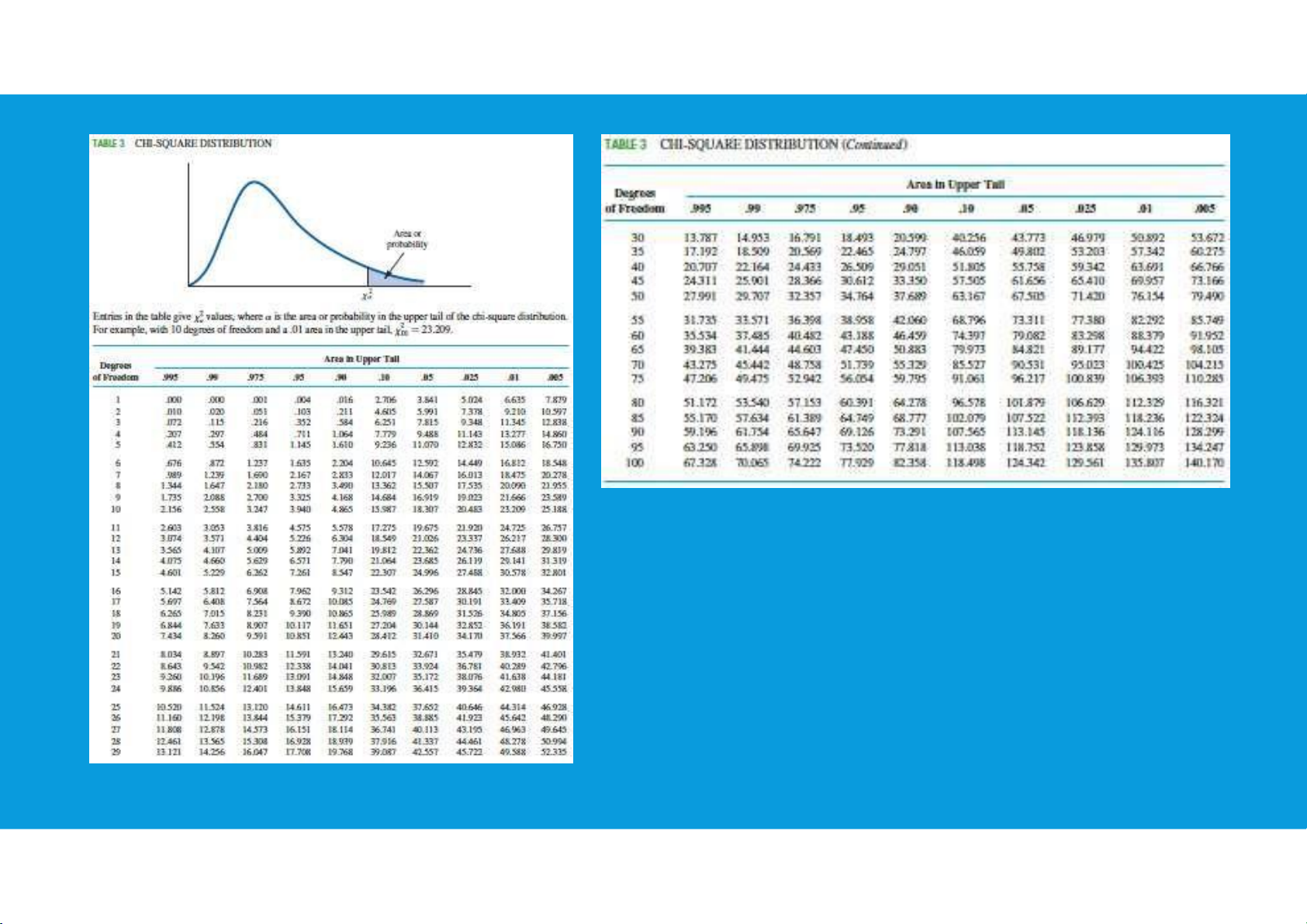
•The sample variance s2 is the point estimator of the population variance σ2 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 6 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 - nonnegative - is skewed to the right
- as k increases, the distribution becomes more symmetric
- as k ∞, the limiting form of the
chisquare distribution is the normal distribution tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 7 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE
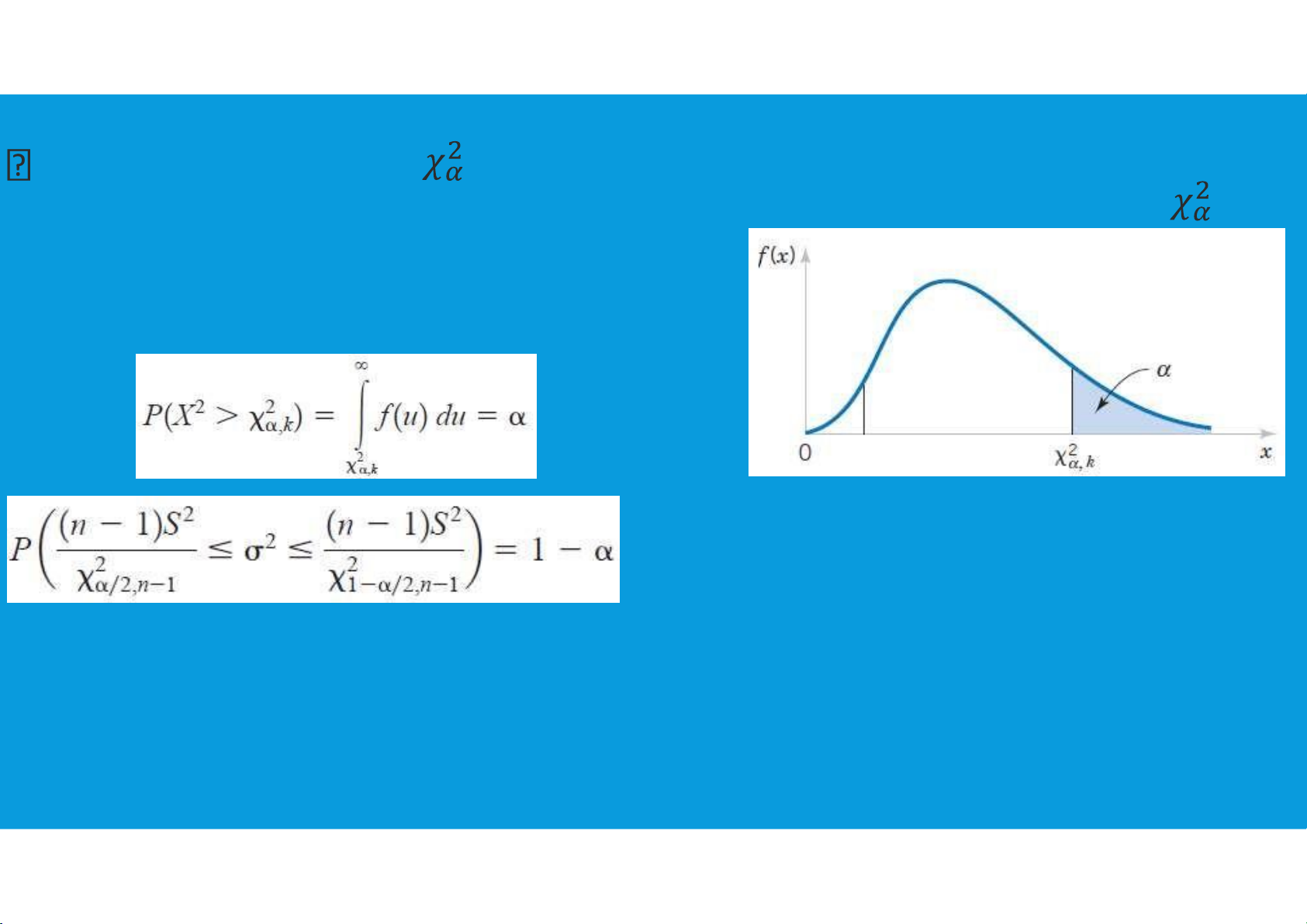
•Interval Estimation: since the sampling distribution of (n − 1)s2/σ2 is known
to have a chi-square distribution whenever a simple random sample of size n is
selected from a normal population, we can use the chisquare distribution to
develop interval estimates and conduct hypothesis tests about a population variance. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 8 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
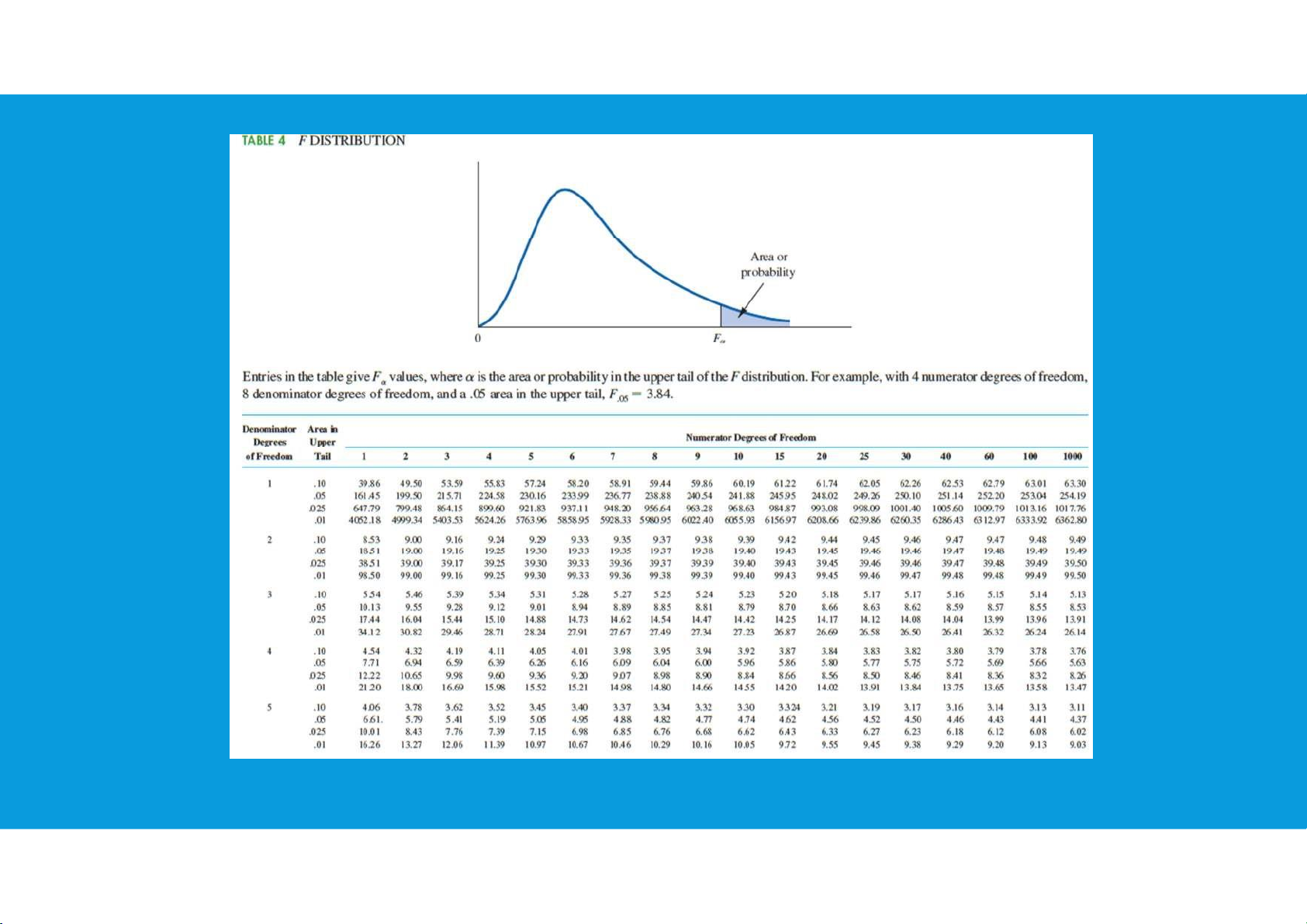
we will use the notation to denote the
value for the chi-square distribution that
provides an area or probability of α to the right of the value.
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE •Interval Estimation: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 9 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
We illustrated the process of using the chi-square distribution to establish
interval estimates of a population variance and a population standard deviation.
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE •Hypothesis Testing: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 10 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
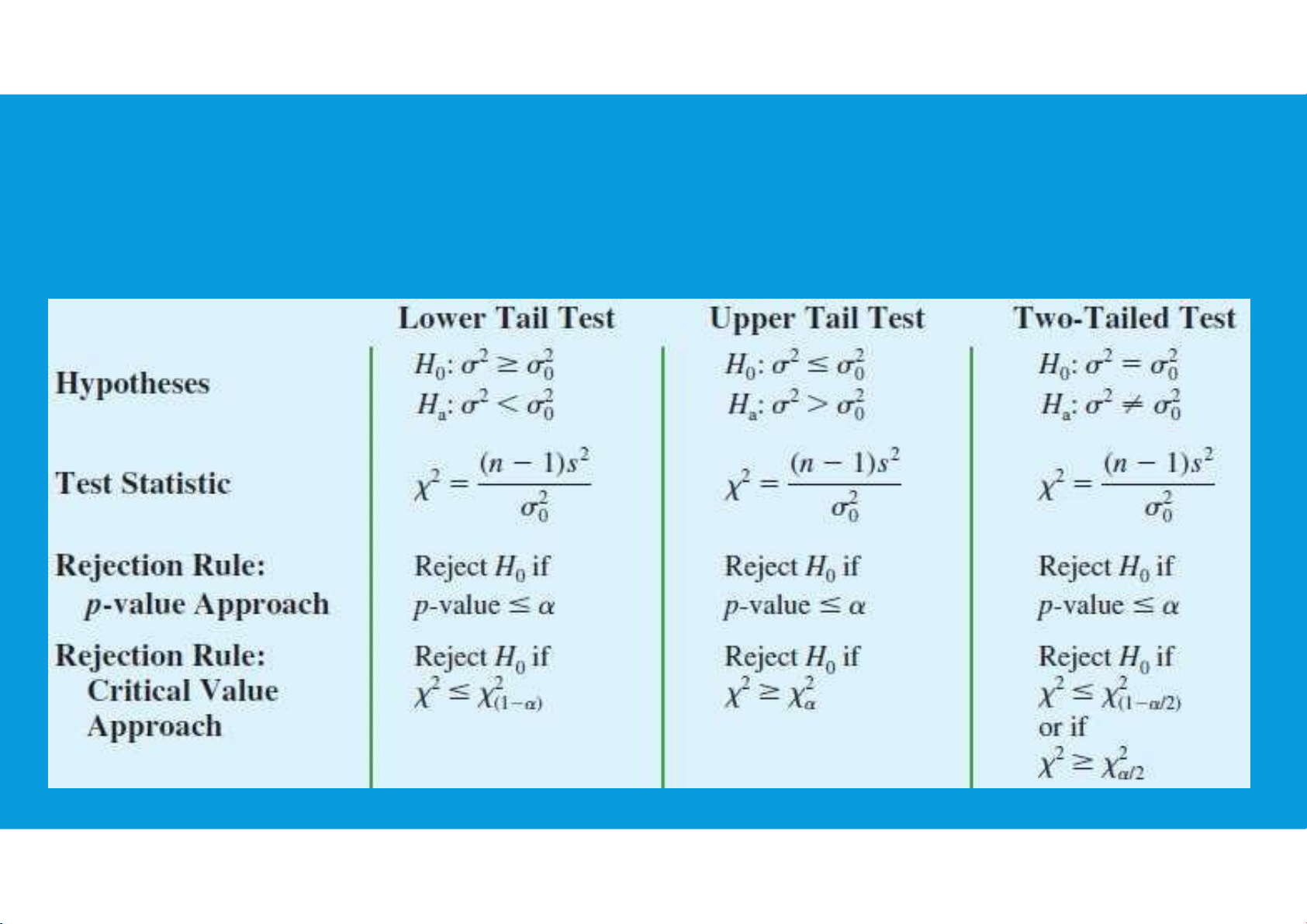
•Using to denote the hypothesized value for the population variance, the three
forms for a hypothesis test about a population variance are as follows:
•Assuming that the population has a normal distribution, the test statistic is as follows:
either the p-value approach or the critical value approach may be used to
determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 11 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE SUMMARY OF
HYPOTHESIS TESTS ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 12 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 13 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 14 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES
•In making comparisons about the two population variances, we will be using data
collected from two independent random samples, one from population 1 and another from population 2.
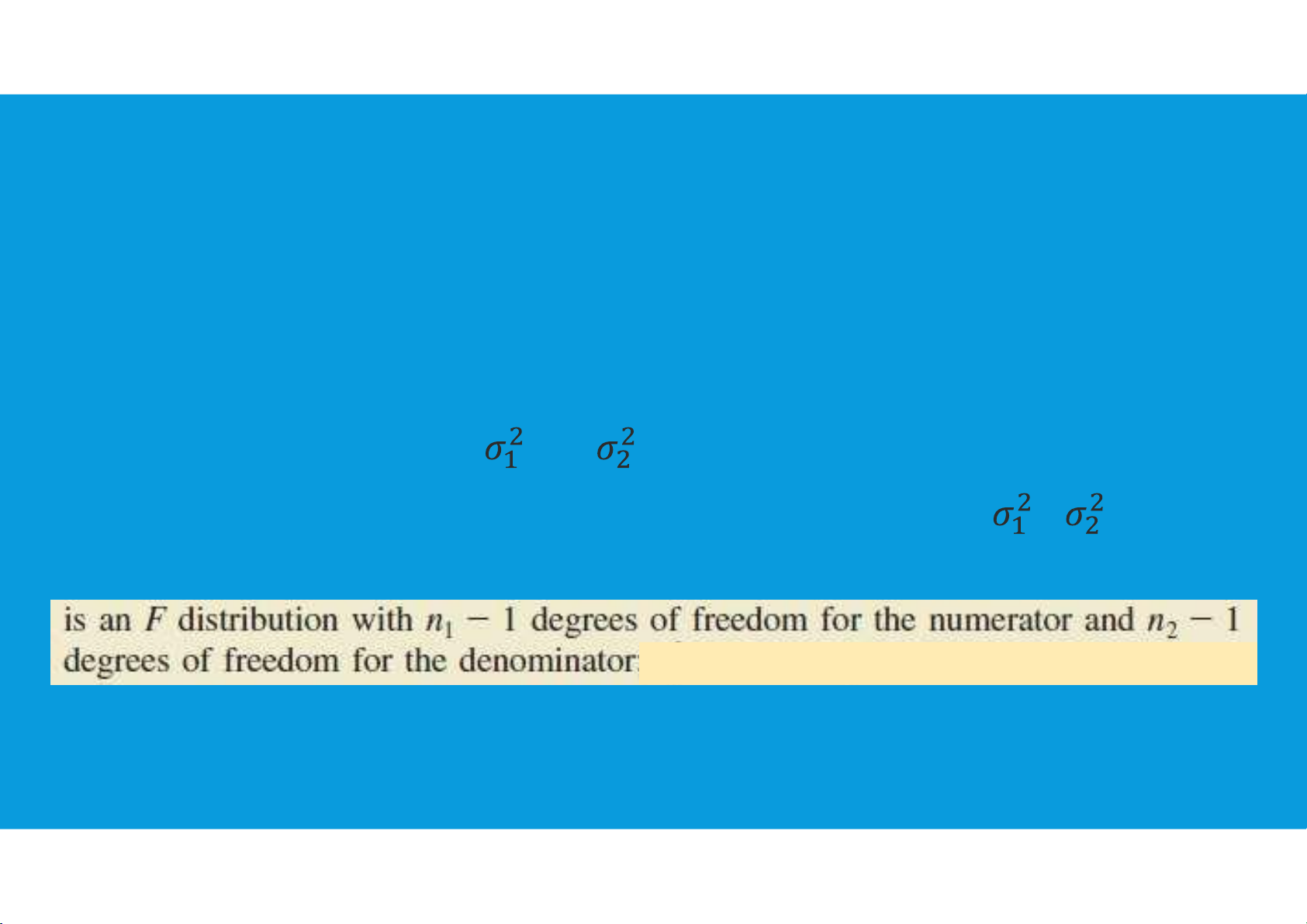
•The two sample variances s 2 2
1 and s2 will be the basis for making inferences about
the two population variances and .
•Whenever the variances of two normal populations are equal ( = ), the
sampling distribution of the ratio of the two sample variances s 2 2 1 / s2 is as follows: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 15 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES
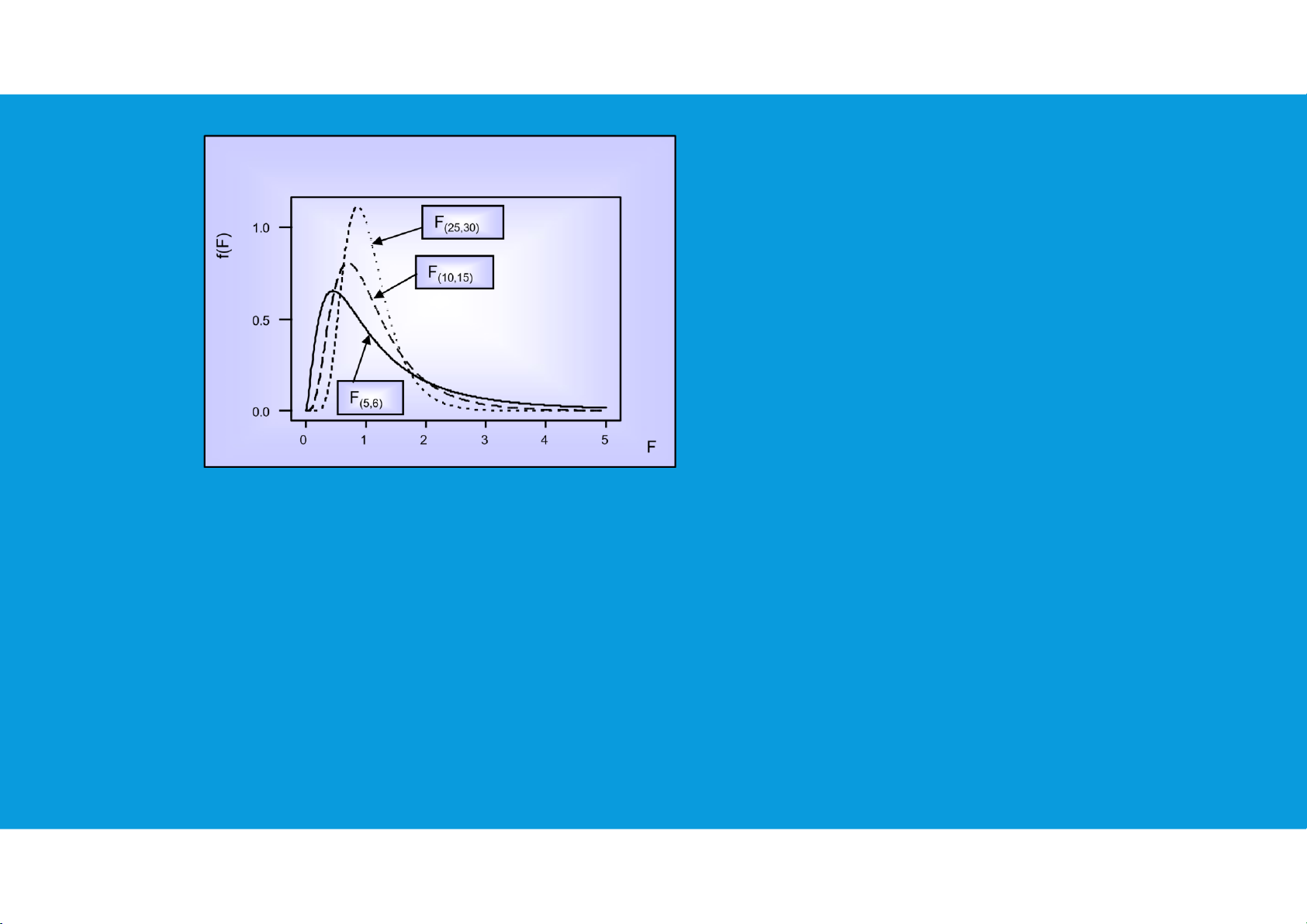
• The F distribution is not symmetric, and the F values can never be negative. The shape of any
particular F distribution depends on its numerator and denominator degrees of freedom.
we will use Fα to denote the value of F that provides an area or probability of α in the upper tail of the distribution
• The F distribution is bound by zero on the left, and skewed to the right. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 16 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
F Distributions with different Degrees of Freedom tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 17 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES
• Because the F test statistic is constructed with the larger sample variance s 2 1 in the numerator,
the value of the test statistic will be in the upper tail of the F distribution. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 18 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
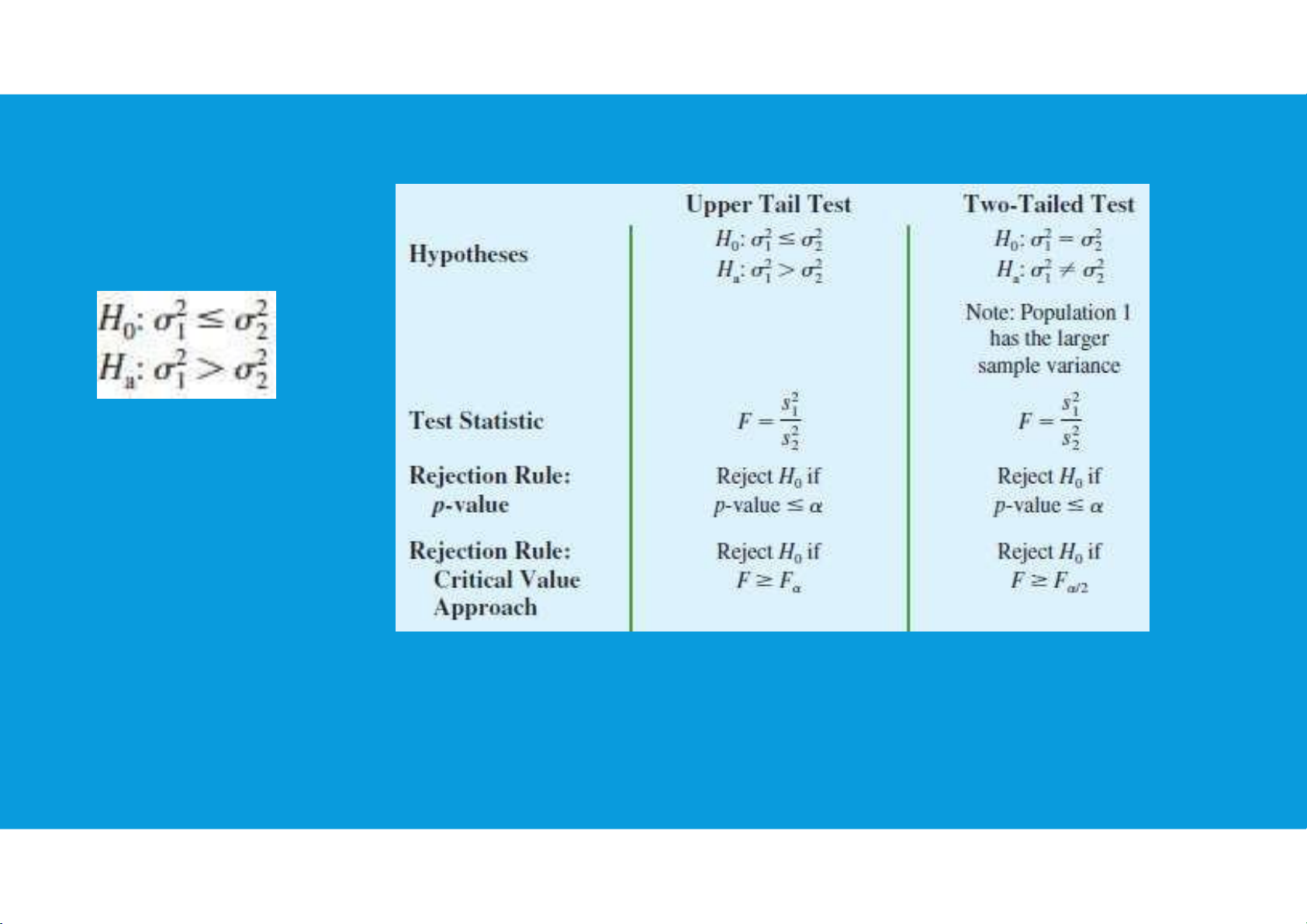
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES
• One-tailed tests involving two population variances are also possible. In this case, we use the F
distribution to determine whether one population variance is significantly greater than the other. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 19 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
• A one-tailed hypothesis test about two population variances will always be formulated as an upper tail test. •Hypothesis Testing: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 20 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 21 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 22 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 23 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 24
Document Outline
- APPLIED STATISTICS
- CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA)
- CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) (1)
- CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) (2)
- CHAPTER 7: ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) (3)
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE (1)
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE (2)
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE (3)
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE SUMMARY OF HYPOTHESIS TESTS ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE
- 7.1. INFERENCES ABOUT A POPULATION VARIANCE
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES (1)
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES (2)
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES (3)
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES (4)
- 7.2. INFERENCES ABOUT TWO POPULATION VARIANCES (5)




