








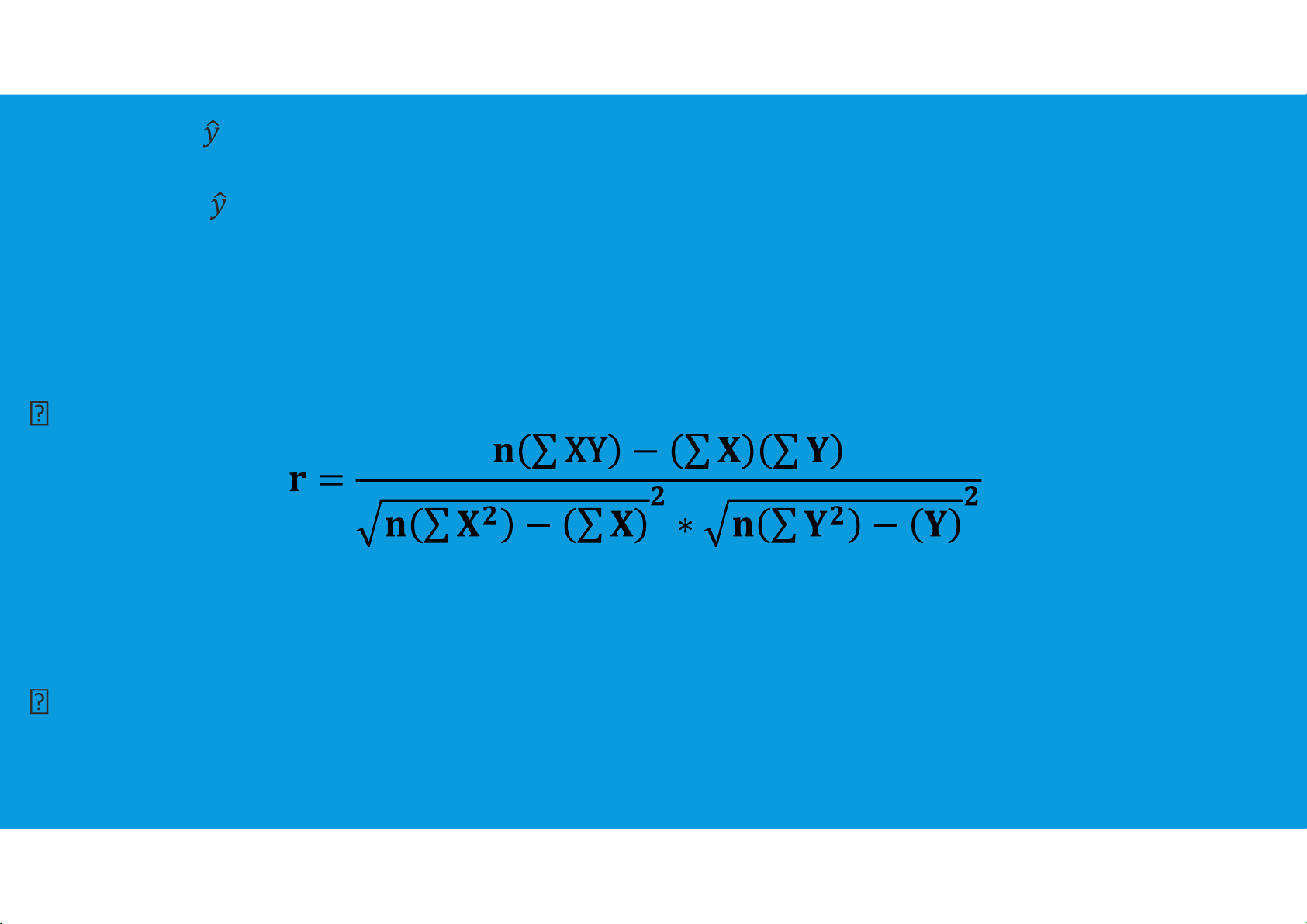







Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 APPLIED STATISTICS COURSE CODE: ENEE1006IU Lecture 15:
Chapter 8: Time series analysis and forecasting
(3 credits: 2 is for lecture, 1 is for lab-work)
Instructor: TRAN THANH TU Email: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 1 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CHAPTER 8: TIME SERIES ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING •8.1. Time series patterns •8.2. Forecast accuracy •8.3. Trend projection
•8.4. Time series decomposition tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 2 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 LINEAR MODEL
Each of the independent variables zj (where j = 1, 2, . . . , p) is a function of x1, x2, . . . , xk (the variables for which data are collected).
In some cases, each zj may be a function of only one x variable. straight-line relationship
simple first-order model with one predictor variable curvilinear relationship
second-order model with one predictor variable interaction
second-order model with two predictor variable tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 3 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 4 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
LINEAR REGRESSION ESTIMATION PROCESS tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 5 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 Simple regression tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 6 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
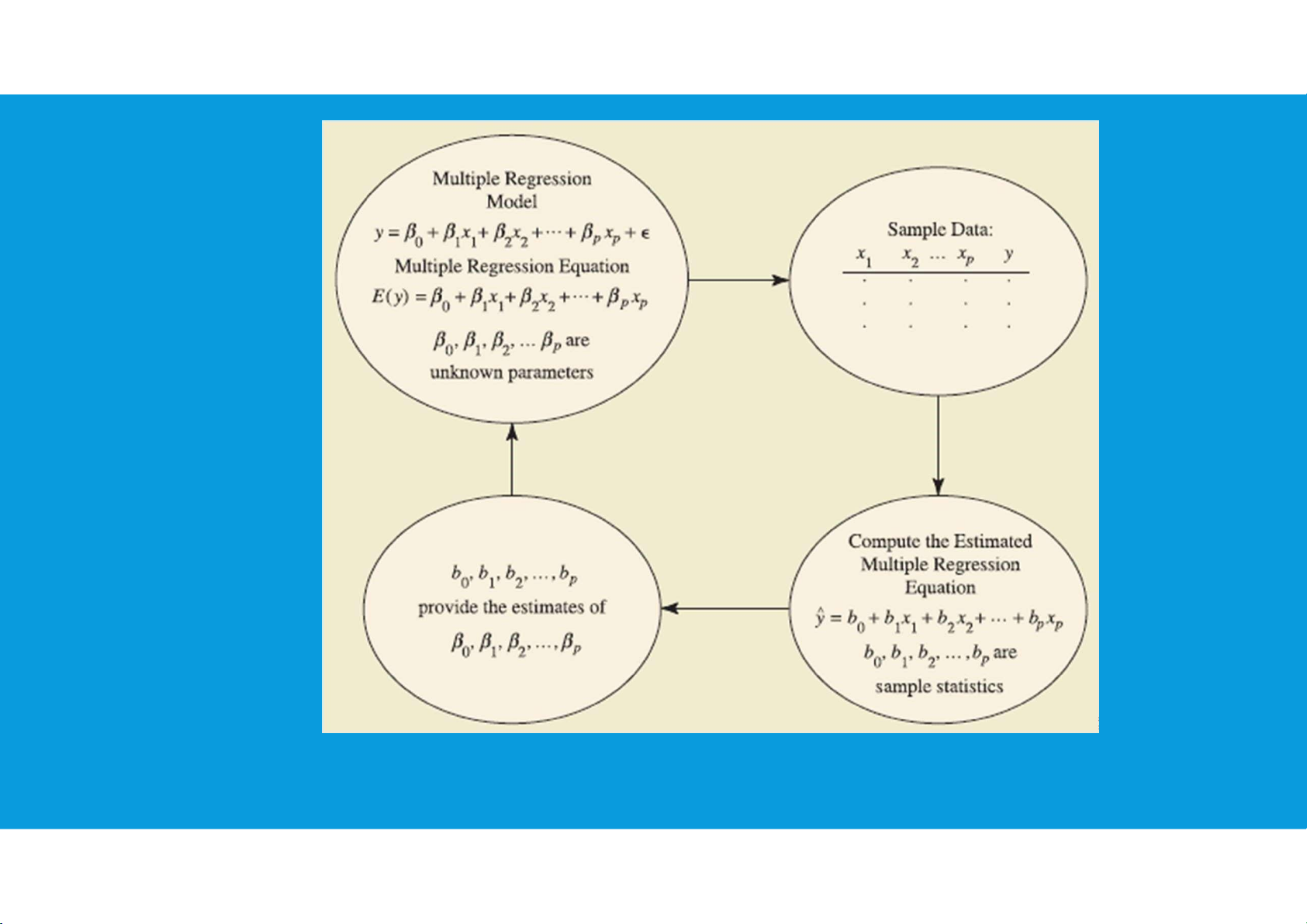
LINEAR REGRESSION ESTIMATION PROCESS tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 7 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 Multiple regression tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 8 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 8.3. TREND PROJECTION
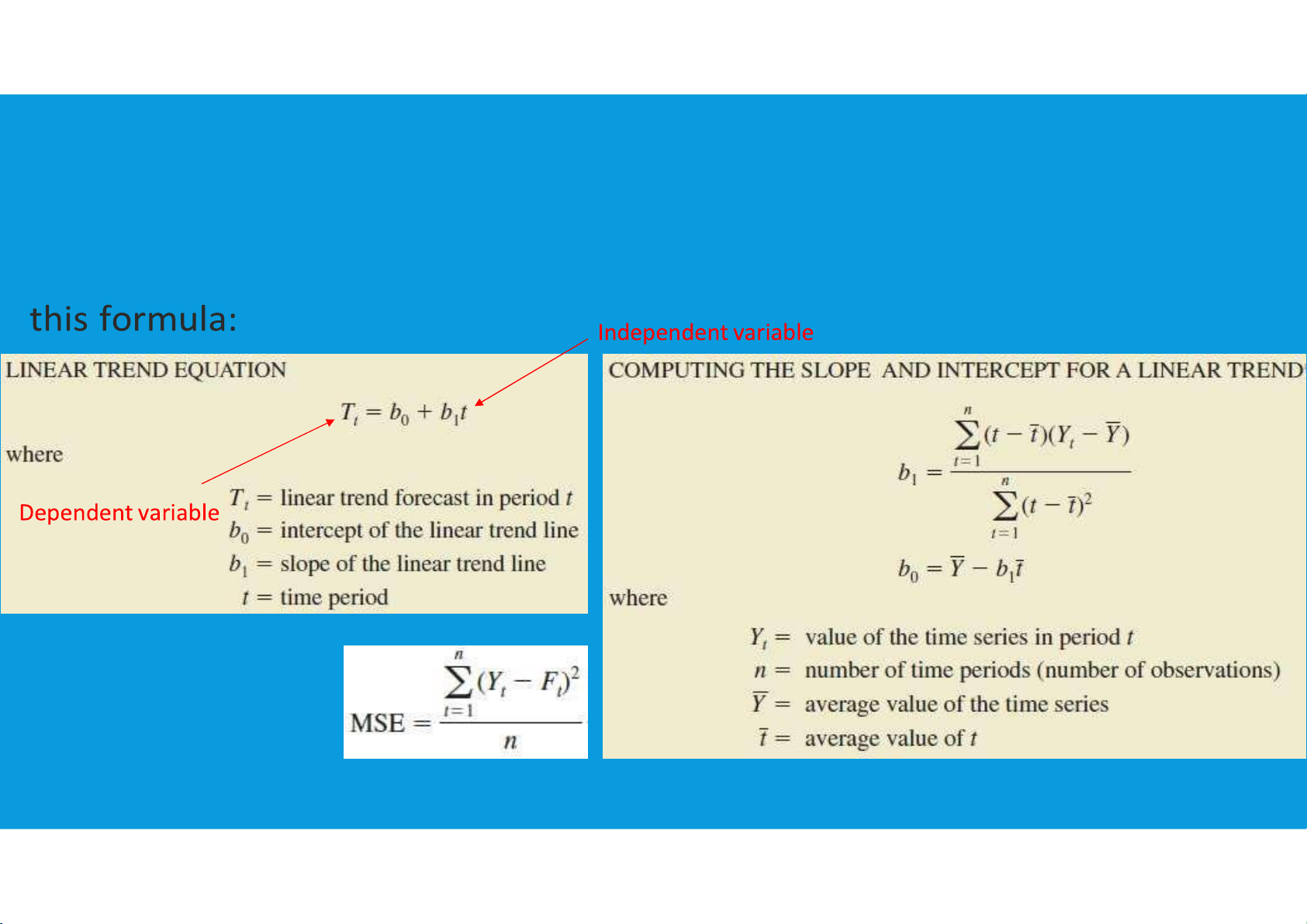
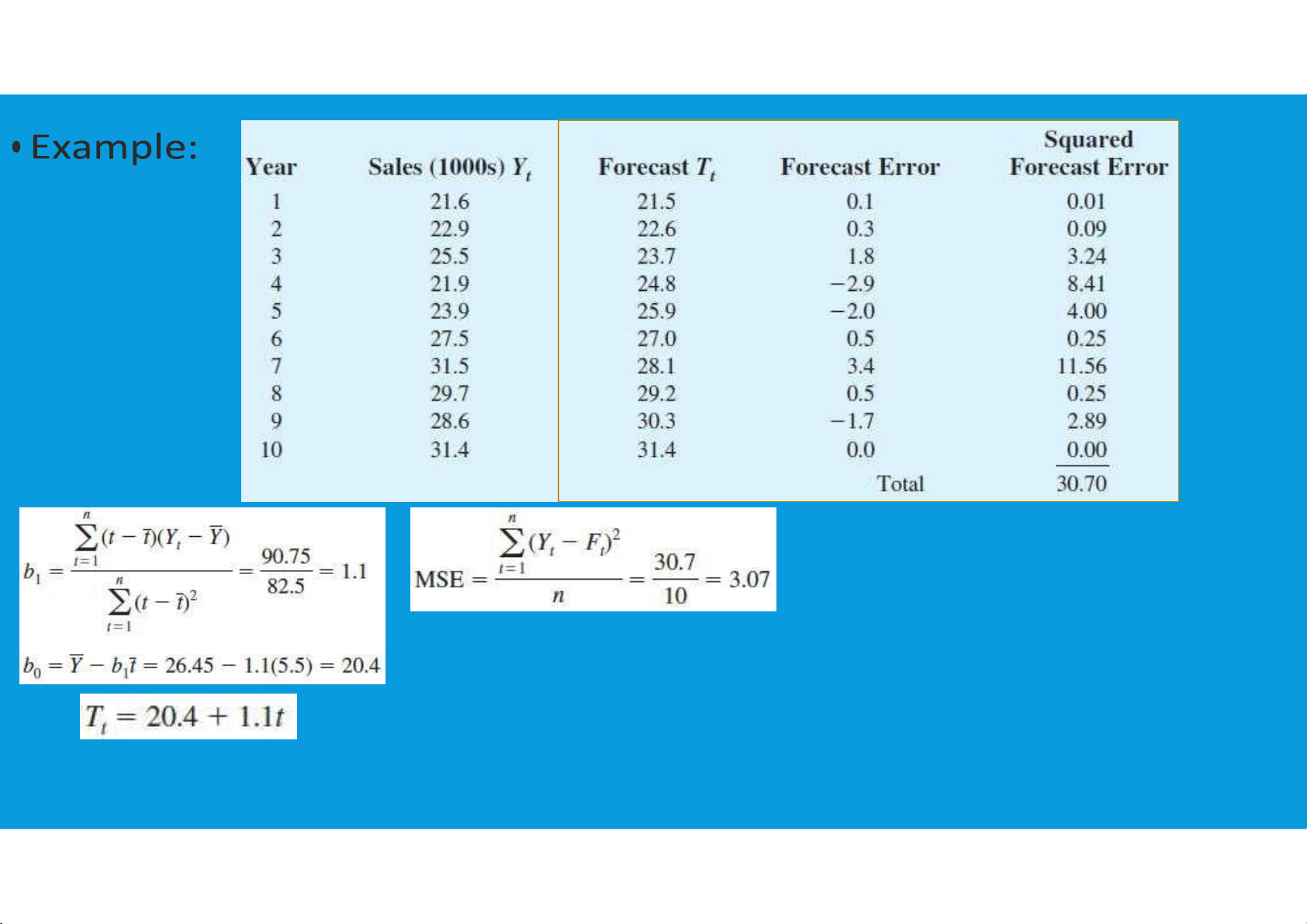
•Linear Trend Regression: A time series technique that computes a forecast with
trend by drawing a straight line through a set of data using tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 9 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 8.3. TREND PROJECTION tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 10 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 11 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 8.3. TREND PROJECTION
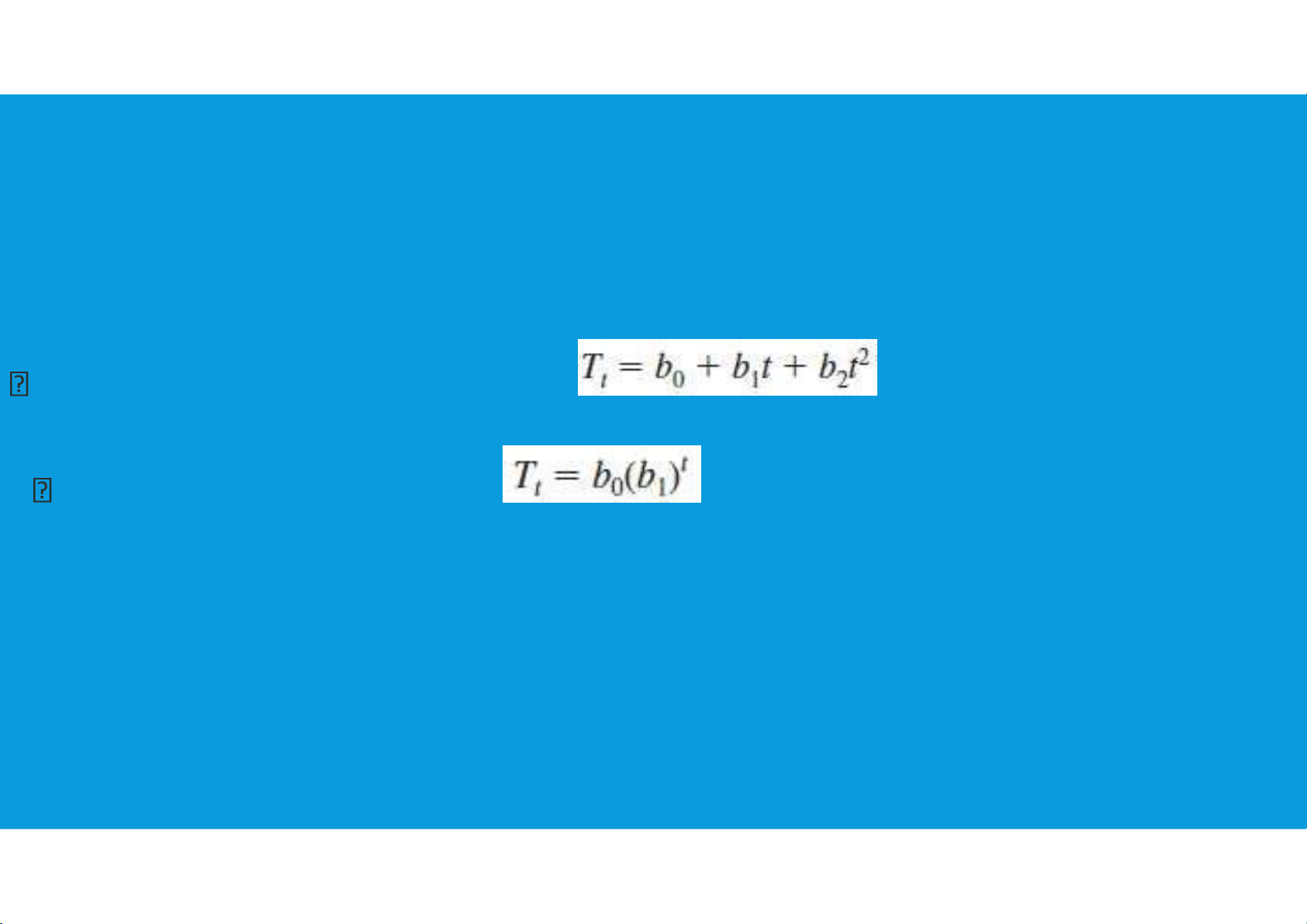
•Nonlinear Trend Regression: a curvilinear function appears to be needed to model the long-term trend: Quadratic trend equation: Exponential trend equation: tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 12 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 13 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 i i i i i i i i i tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 14
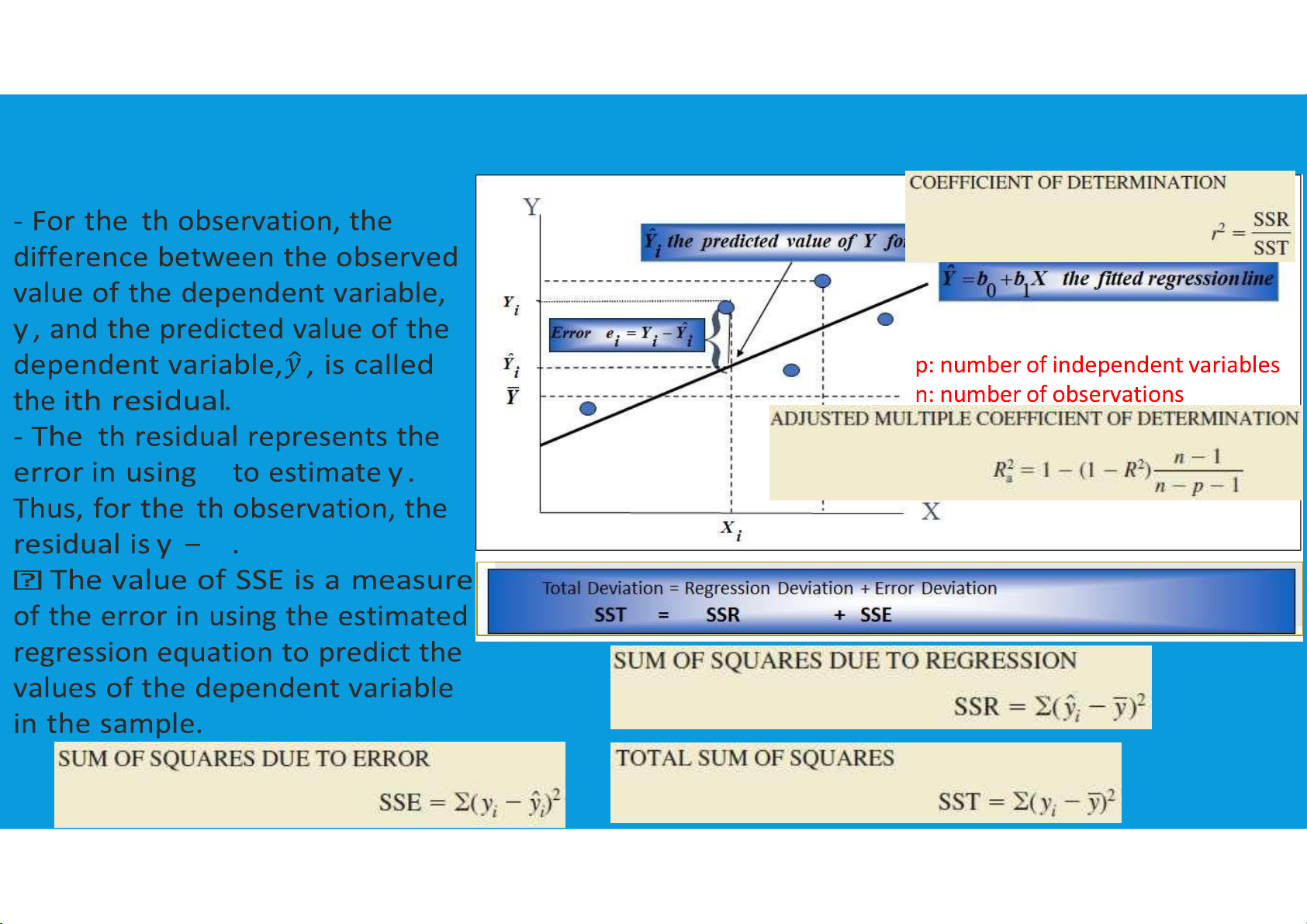
DECOMPOSITION OF THE TOTAL DEVIATION IN A LINEAR lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
CORRELATION COEFFICIENT - HOW GOOD IS THE FIT?
•Correlation coefficient (r) measures the direction and strength of the linear
relationship between two variables.
The closer the r value is to 1.0 the better the regression line fits the data points.
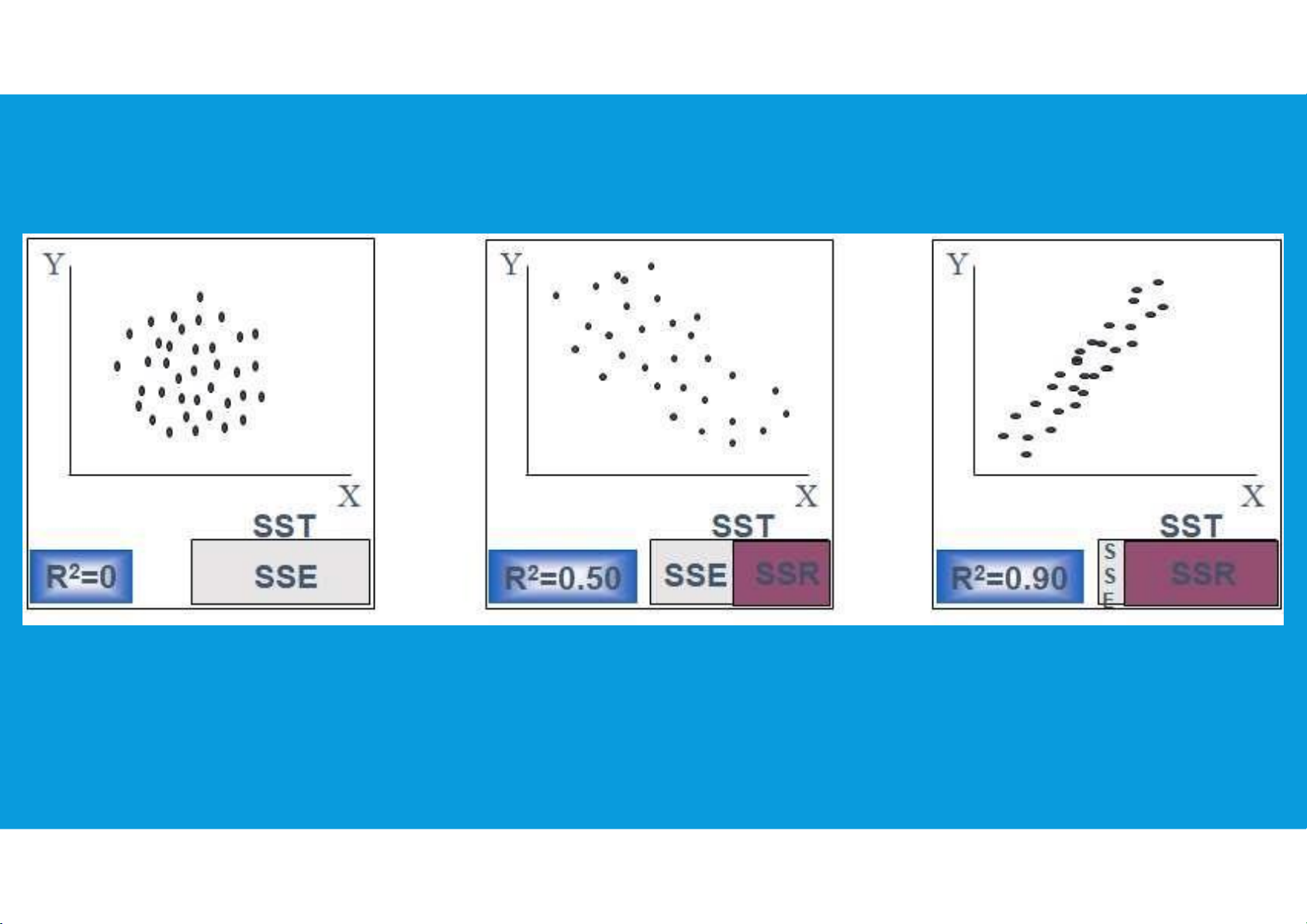
•Coefficient of determination (r2) measures the amount of variation in the
dependent variable about its mean that is explained by the regression line.
provides a measure of the goodness of fit for the estimated regression equation tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 15 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
•Values of (r2) close to 1.0 are desirable. HOW GOOD IS THE REGRESSION tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 16 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 RESIDUAL ANALYSIS i i tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 17 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
DETECTING OUTLIERS AND INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS
•Outliers: The presence of one or more outliers in a data set tends to increase s,
the standard error of the estimate increase , , the standard deviation of residual i
•Influential observations: the value of the independent variable may have a
strong influence on the regression results tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 18 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
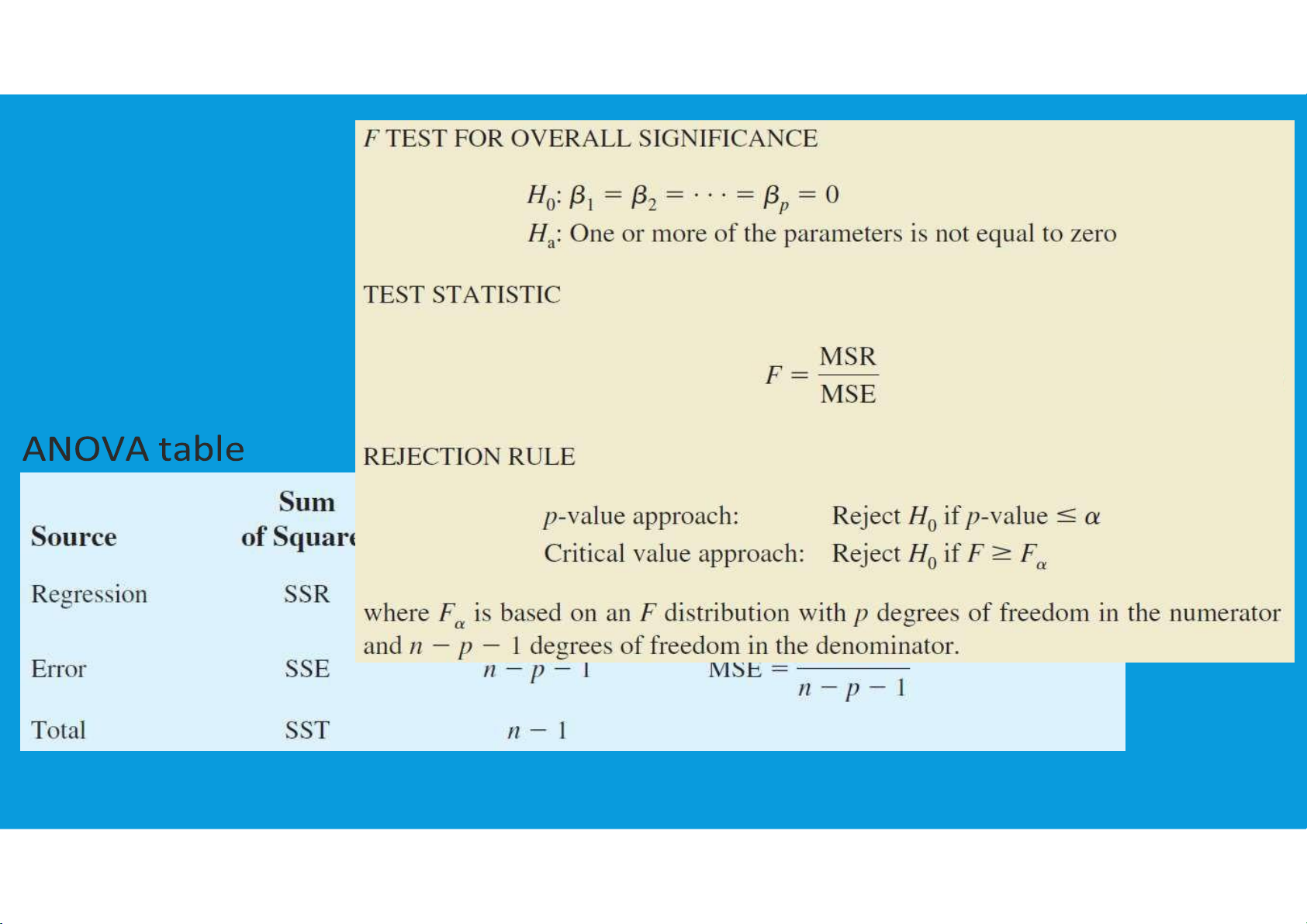
THE F TEST OF A MULTIPLE REGRESSION MODEL tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 19 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 20 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
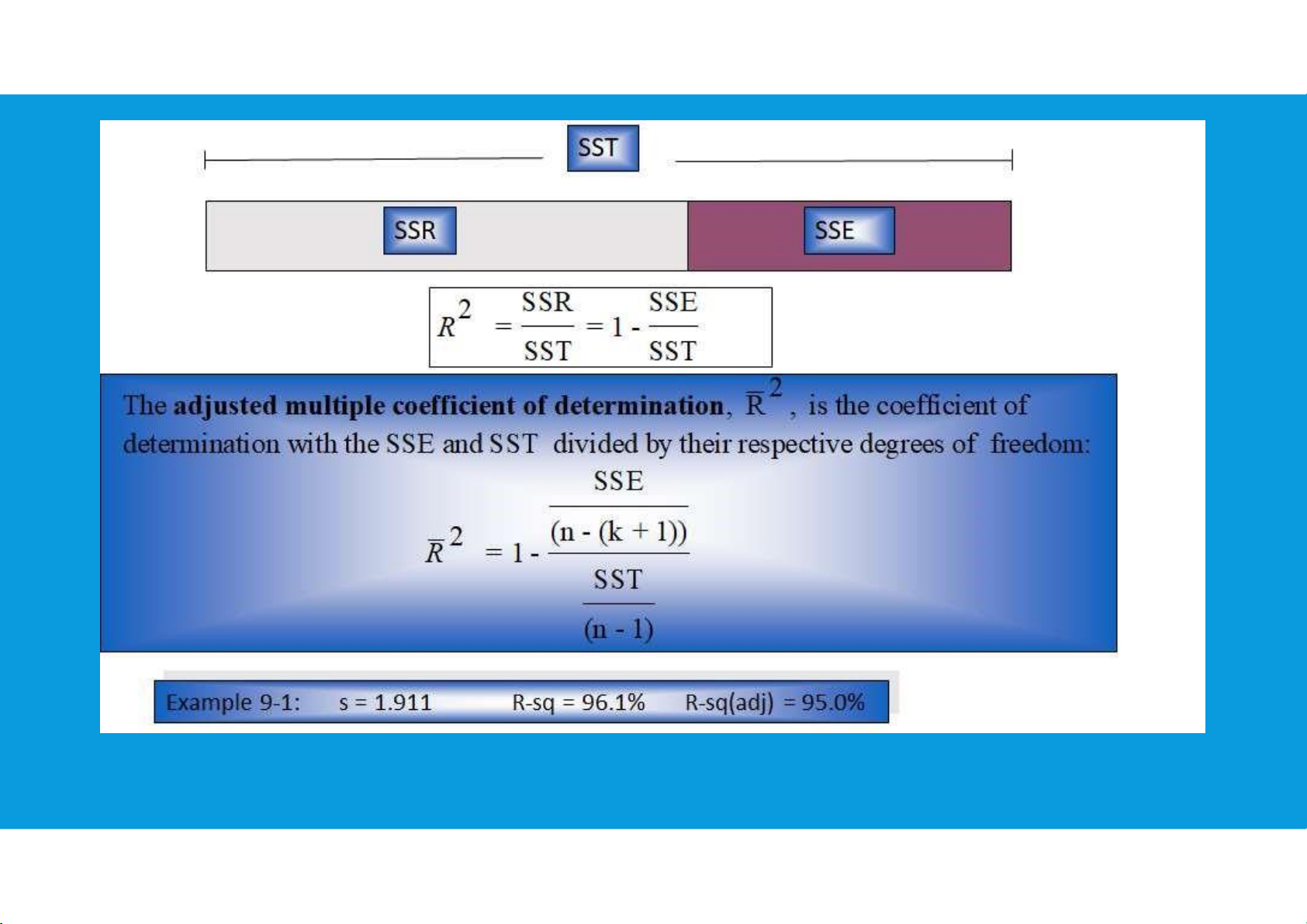
DECOMPOSITION OF THE SUM OF SQUARES AND THE ADJUSTED COEFFICIENT OF DETERMINATION tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 21 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 22 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
MEASURES OF PERFORMANCE IN MULTIPLE REGRESSION AND THE ANOVA TABLE tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 23 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 24 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
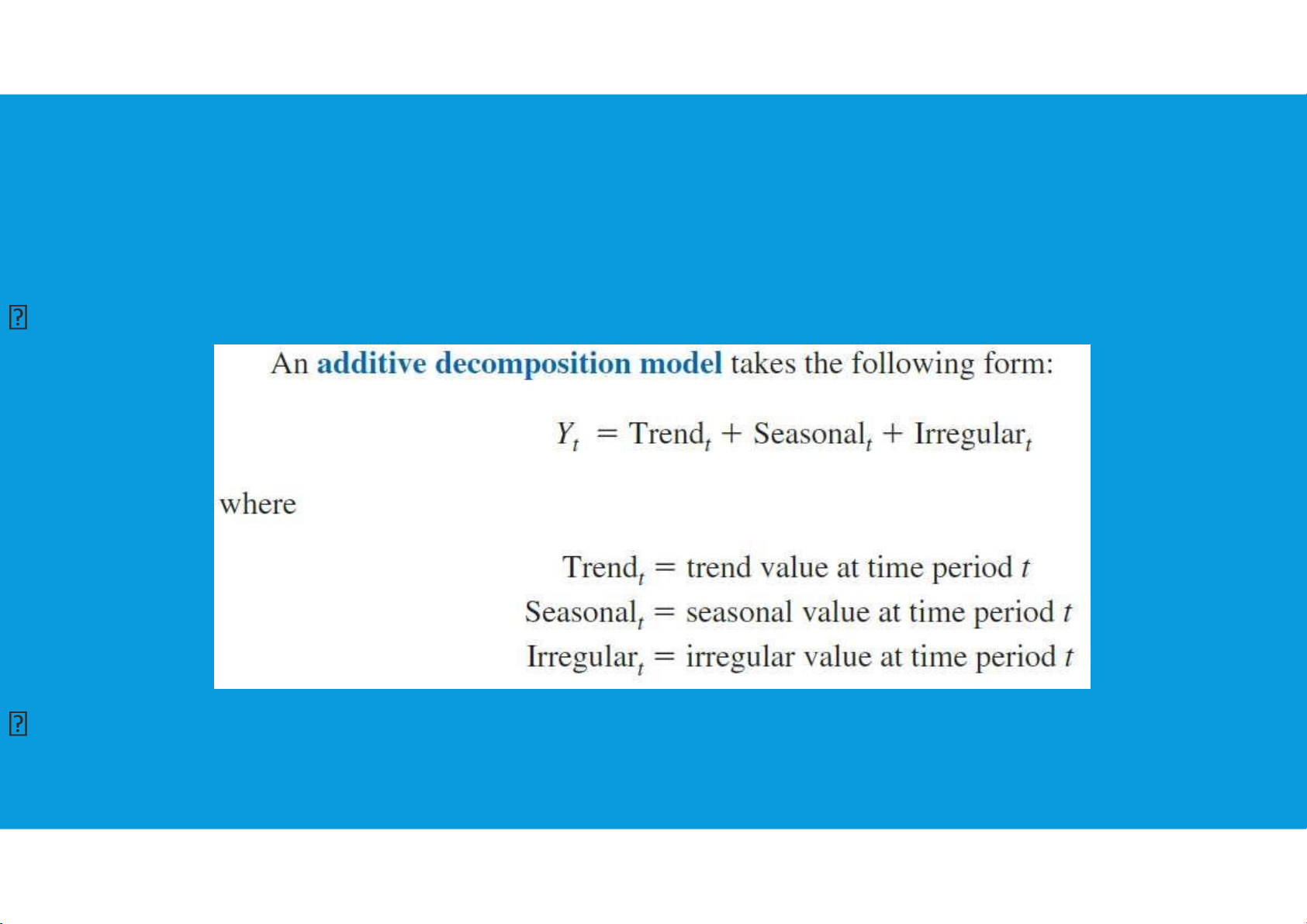
8.4. TIME SERIES DECOMPOSITION
•Time series decomposition can be used to separate or decompose a time series
into seasonal, trend, and irregular components.
get a better understanding of the time series
an additive model is appropriate in situations where the seasonal fluctuations do
not depend upon the level of the time series. tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 25 lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
8.4. TIME SERIES DECOMPOSITION
•If the seasonal fluctuations change over time, growing larger as the sales volume
increases because of a long-term linear trend, then a multiplicative model should be used tttu@hcmiu.edu.vn 26
Document Outline
- APPLIED STATISTICS
- CHAPTER 8: TIME SERIES ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING
- LINEAR MODEL
- LINEAR REGRESSION ESTIMATION PROCESS
- LINEAR REGRESSION ESTIMATION PROCESS (1)
- 8.3. TREND PROJECTION
- 8.3. TREND PROJECTION (1)
- 8.3. TREND PROJECTION (2)
- DECOMPOSITION OF THE TOTAL DEVIATION IN A LINEAR
- HOW GOOD IS THE REGRESSION
- DETECTING OUTLIERS AND INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS
- THE F TEST OF A MULTIPLE REGRESSION MODEL
- DECOMPOSITION OF THE SUM OF SQUARES AND THE ADJUSTED COEFFICIENT OF DETERMINATION
- MEASURES OF PERFORMANCE IN MULTIPLE REGRESSION AND THE ANOVA TABLE
- 8.4. TIME SERIES DECOMPOSITION
- 8.4. TIME SERIES DECOMPOSITION (1)




