




Preview text:
International University, VNU-HCMC
School of Computer Science and Engineering
Lecture 2: Relational Model and Algebra
Instructor: Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan
nttloan@hcmiu.edu.vn nthithuyloan@gmail , .com https://nttloan.wordpress.com/
International University, VNU-HCMC Course Website •Blackboard IU
•Please check frequently for updates!
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 2 2 1
International University, VNU-HCMC Outline •Relational model •Relational algebra
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 3 3
International University, VNU-HCMC Acknowledgement
•The following slides are referenced from Dr. Sudeepa Roy, Duke University.
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 4 4 2
International University, VNU-HCMC Edgar F. Codd (1923-2 3) 00
•Pilot in the Royal Air Forcein WW2 •Inventor of the relati a on l model an al d gebra whileat IBM •Turing Award, 1981 RDBMS = Relati a on l DBMS
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Edgar_F_Co .jpg dd Duke CS, Fall 2021 5 5
International University, VNU-HCMC
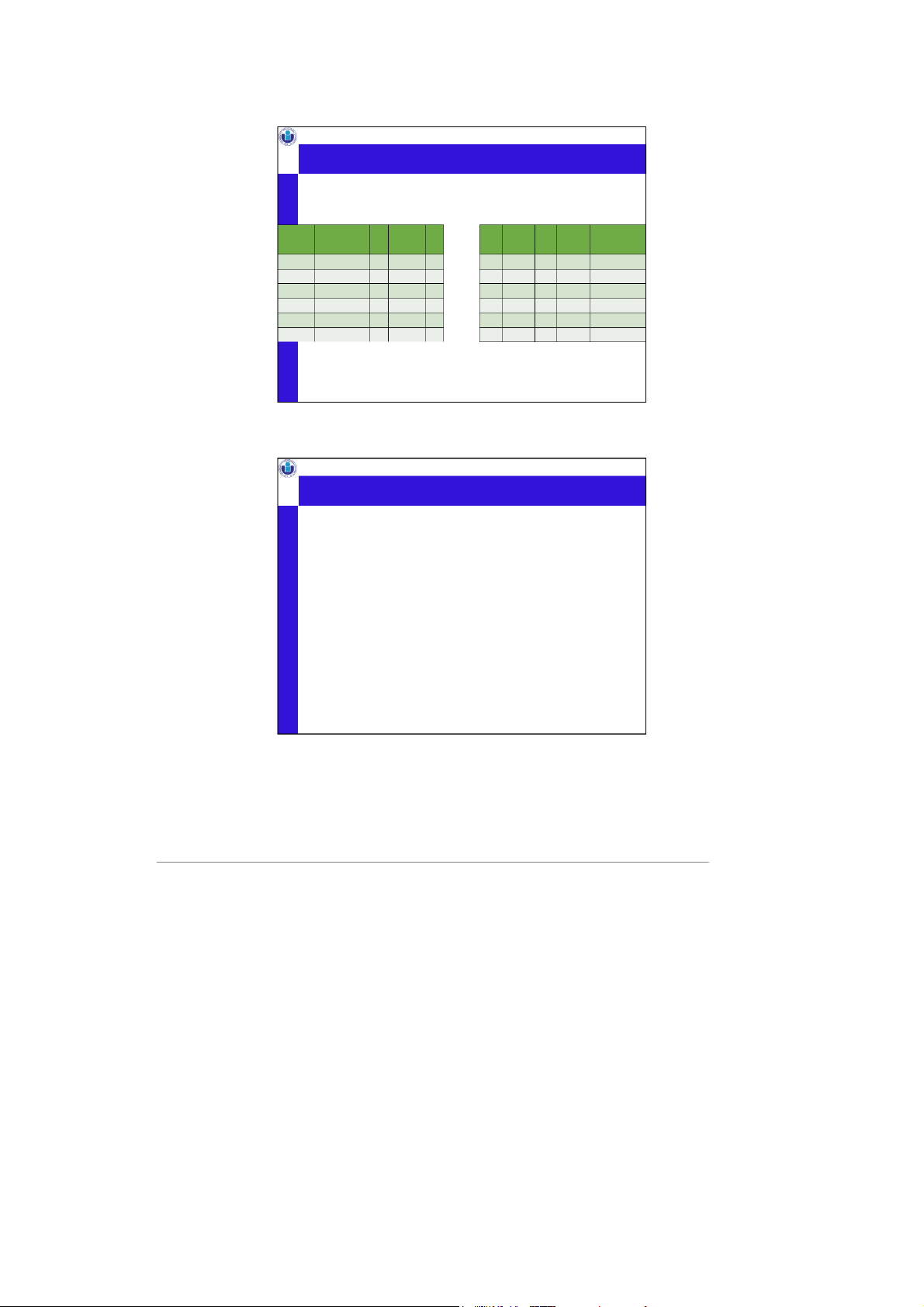
The famous “Beers” database Bars Drinkers Frequent Bars Each has an address “X” times a week BarsServe Beers At price “Y” Drinkers Likes Beers Drinkers Beers
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Each has an address
(Later in ER diagram – how to Each has a brewer design a relational database) Duke CS, Fall 2021 6 6 3
International University, VNU-HCMC
See online database for more tuples
“Beers” as a Relational Database Bar Serves bar beer price n ame address The Edge Budweiser 2.50 The Edge 108 Morris Street The Edge Corona 3.00 S f atis o acti n 905 W. Main Street Satisfaction Budweiser 2.25 Beer dri er nk bar times_a_week Name brewer Ben Satisfaction 2 Budweiser Anheuser-Busch Inc. Dan The Edge 1 Corona Grupo Modelo Dan Satisfaction 2 Dixie Dixie ewing Br Frequents Drinker dri er nk beer name address Amy Corona Amy 100 W. Main Street Dan Budweiser Ben 101 W. Main Street
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Dan Corona Likes Dan 300 N. Duke Street Ben Budweiser S, Fall 2021 7
International University, VNU-HCMC Relational data model
•A database is a collection of relations(or tables)
•Each relation has a set of attributes (or columns)
•Each attribute has a name and adomain (or type)
•Set-valued attributes are not allowed
•Each relation contains a “set” of tuples (or rows)
•Each tuple has a value for each attribute of the relation
•Duplicate tuples are not allowed (Two tuples are duplicates if they agree on all attributes) •Ordering of rows es
do n’t matter (even though output is always in some order) Serves bar beer price •However, SQL s o upp rts “bag” The Edge Budweiser 2.50 or duplicate tuples (w ?) hy The Edge Corona 3.00 Simplicity is a virtue!
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD S f atis on acti Budweiser 2.25 Duke CS, Fall 2021 8 8 4
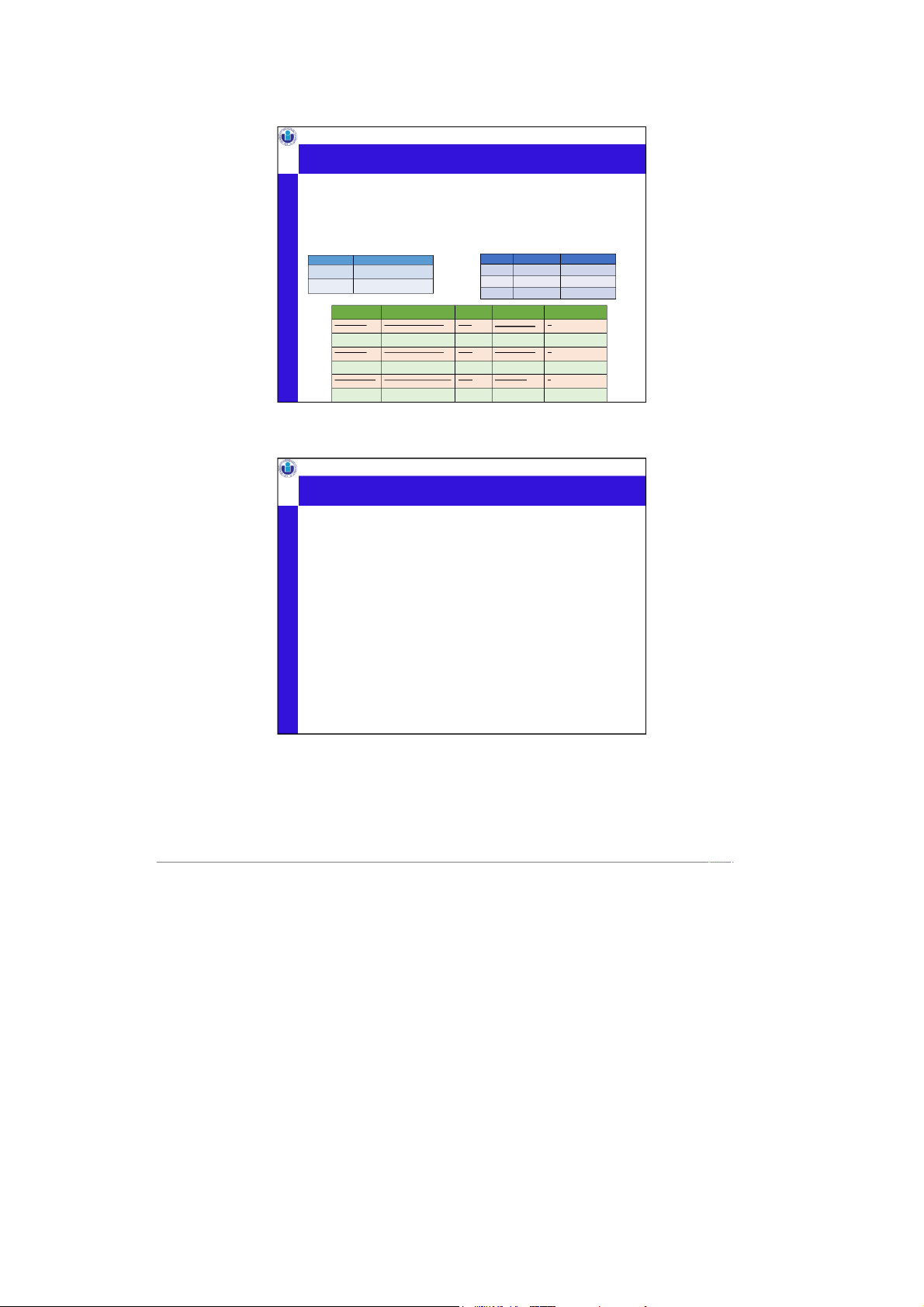
International University, VNU-HCMC Schema vs. instance Serves bar b eer p rice The Edge Budweiser 2.50 The Edge Corona 3.00 Satisfaction Budweiser 2.25 Beer Frequents Name brewer dri er nk bar times_a_week Budweiser Anheuser-Busch Inc. Ben Satisfaction 2 Corona Grupo Modelo Dan The Edge 1 Dixie Dixie ewing Br Dan Satisfaction 2
•Ordering of rows doesn’t matter (even though output is
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD always in some order) Duke CS, Fall 2021 9 9
International University, VNU-HCMC Schema vs. instance •Schema (metadata)
•Specifies the logical structure of data •Is defined at setup time •Rarely changes •Instance •Represents the data content
•Changes rapidly, but always conforms to the schema
Compare to types vs. collections of objects of these types in a programming language
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 10 10 5
International University, VNU-HCMC Example •Schema (metadata)
•Beer(name string, brewerstring)
•Serves(bar string, beerstring, price float)
•Frequents (drinker string, bar string, times_a_weekint) •Instance •Beer {, ,…} •Serves{,,..} •Frequents {,,…}
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 1 1 1 1
International University, VNU-HCMC Relational algebra
Alanguage for querying relational data based on “operators” RelOp RelOp •Core operators:
•Selection, projection, cross product, union, difference, and renaming •Additi al on , derived operators:
•Join, natural join, intersection, etc.
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD
•Compose operators to make complex queries Duke CS, Fall 2021 12 12 6
International University, VNU-HCMC Selection •Input: a table 𝑅 •Notation: 𝜎P𝑅
•𝑝is called aselection condition (orpredicate)
•Purpose: filter rows according to some criteria
•Output: same columns as 𝑅,but only rows of 𝑅that satisfy 𝑝 (𝑠𝑒𝑡!)
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 13 13
International University, VNU-HCMC Selection example Find beers with price < 5 2.7
Serves 𝝈𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 < 𝟐.𝟕𝟓 Serves bar beer price bar beer price The Edge Budweiser 2.50 The Edge Budweiser 2.50 The Edge Corona 3.00 Satisfactio n Budweiser 2.25 S f atis on acti Budweiser 2.25
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 14 14 7
International University, VNU-HCMC More on selection
•Selection condition can include any column of 𝑅, constants,
comparison (=,≤, etc.) and B lean oo connectives (∧: and, : ∨ or, ¬: not)
•Example: Serves tuples for “The Edge” or price >= 5 2.7
𝜎bar=&‘The&Edge’&∨&price&³2.75𝑆𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑠
•You must be able to evaluate the condition over each single rowof the input table!
•Example: the most expensive beer at any bar
𝜎price&³every&price&in&Servers 𝑈𝑠𝑒𝑟 WRONG! Serves bar beer p rice The Edge Budweiser 2.50 The Edge Corona 3.00
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Satisfaction Budweiser 2.25 Duke CS, Fall 2021 15 15
International University, VNU-HCMC Projection •Input: a table 𝑅 •Notation: 𝜋L𝑅
•𝐿is a list of columns in 𝑅
•Purpose: output chosen columns
•Output: same rows, but onlythecolumnsin 𝐿 (𝑠𝑒𝑡!)
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 16 16 8
International University, VNU-HCMC Projection
Example: Find all the prices for each beer
Serves 𝝅𝒃𝒆𝒆𝒓,𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 Serves bar beer price The Edge Budweiser 2.50 beer p rice The Edge Corona 3.00 Budweiser 2.50 Satisfaction Budweiser 2.25 Corona 3.00 Budweiser 2.25 Output of 𝜋beerServes?
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 17 17
International University, VNU-HCMC More on Projection
•Duplicate output rows are removed (by definition) •Example: beer on servers 𝝅 Serves 𝒃𝒆𝒆𝒓 Serves bar beer p rice beer The Edge Budweiser 2.50 Budweiser The Edge Corona 3.00 Corona S f atis on acti Budweiser 2.25 Budweiser
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 18 18 9
International University, VNU-HCMC Cross product
•Input: two tables 𝑅and 𝑆 •Natation: 𝑅×𝑆
•Purpose: pairs rows from two tables
•Output: for each row 𝑟in 𝑅and each 𝑠in 𝑆, output
a row 𝑟𝑠 (concatenation of 𝑟and 𝑠)
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 19 19
International University, VNU-HCMC Cross product Bar Frequents name address drinker bar times_a_week The Edge 108 Morris Street Ben Satisf action 2 Dan The Edge 1 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Dan Satisf action 2 Bar x Frequents n ame address drink er bar t imes_a_ w eek The Edge 108 Morris Street Ben Satisfactio n 2 The Edge 108 Morris Street Dan The Edge 1 The Edge 108 Morris Street Dan Satisfactio n 2 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Ben Satisfactio n 2 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Dan The Edge 1 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Dan Satisfactio n 2
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 20 20 10
International University, VNU-HCMC Cross product
•Ordering of columns is unimportant as far as contents are concerned. n ame address dr ink bar t im dr inker bar time n ame address er es_ s_a_ a_w w eek eek Th e Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Ben S atisfaction 2 Ben Satisfactio n 2 The Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Th e Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Dan The Edge 1 Dan The Edge 1 The Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Th e Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Dan S atisfaction 2 = Dan Satisfactio n 2 The Edge 10 Mo 8 rris Street Satisfaction 90 5 W. Main Street Ben S atisfaction 2 Ben Satisfactio n 2
Satisfactio n 905 W. Main Str eet Satisfaction 90 5 W. Main Street Dan The Edge 1 Dan The Edge 1
Satisfactio n 905 W. Main Str eet Satisfaction 90 5 W. Main Street Dan S atisfaction 2 Dan Satisfactio n 2
Satisfactio n 905 W. Main Str eet
• So cross product is commutative, i.e., for any R and Assoc. Pr hD
S, R X S = S X R (up to the ordering of columns) Duke CS, Fall 2021 21 21
International University, VNU-HCMC Derived operator:join
(Also known as “theta-join”: most general joins) One of themost important
•Input: two tables 𝑅and𝑆 operati s! on •Notation:𝑅⋈P𝑆
•𝑝is called a join condition (or predicate)
•Purpose: relate rows from two tables according to some criteria
•Output: for each row 𝑟in 𝑅and each row 𝑠in 𝑆,
output a row 𝑟𝑠 if 𝑟and 𝑠satisfy 𝑝
•Shorthand for 𝜎P(R×𝑆) Assoc. Prof. Nguyen •Predicate Thi p Thuy Loan, PhD
only has equality (A = 5 ∧B = 7) : equijoin Duke CS, Fall 2021 22 22 11
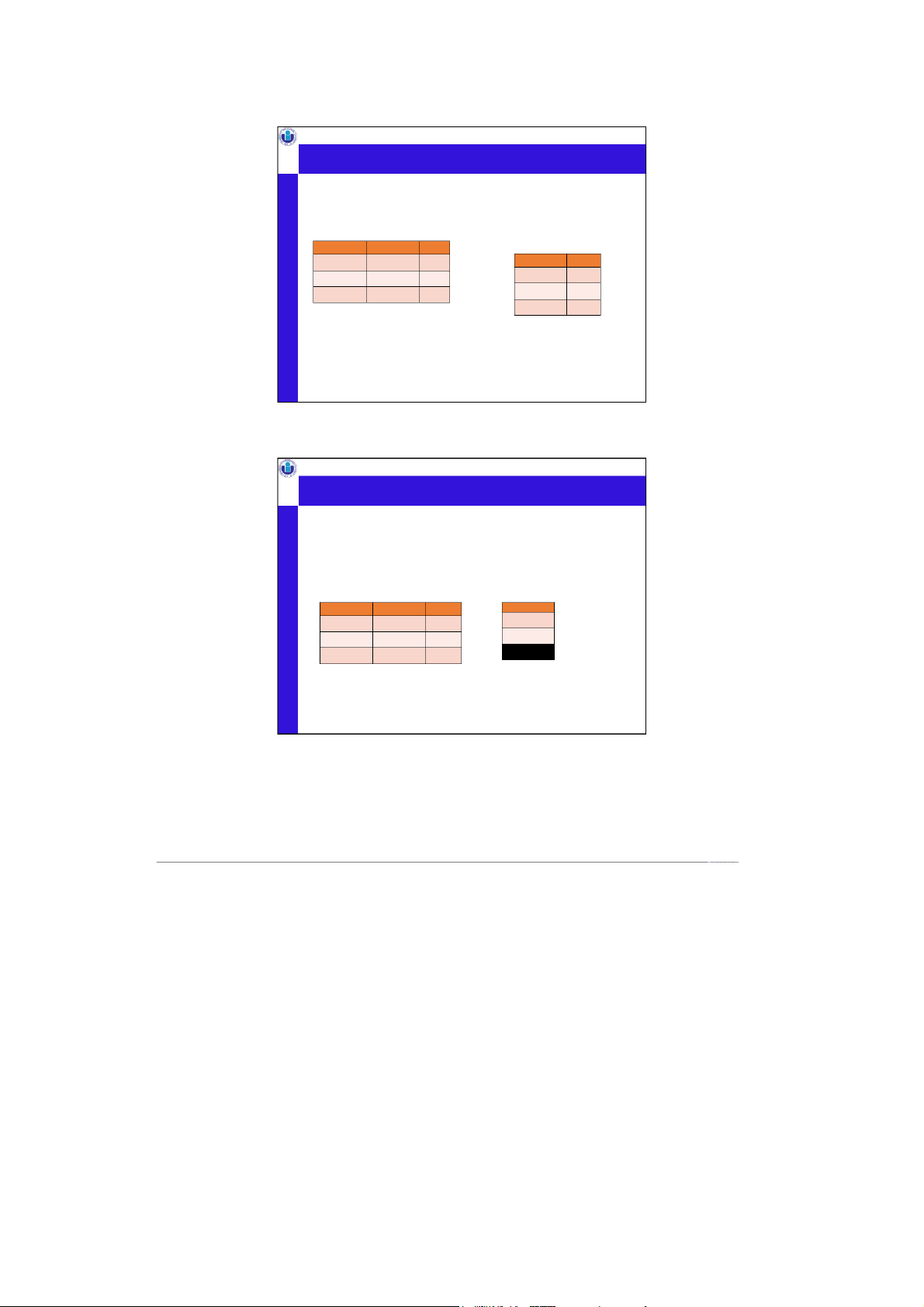
International University, VNU-HCMC Join example •Exten Freque d
nts relation with addresses of the bars
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 ⋈bar%=%name 𝐵𝑎𝑟
Ambiguous attribute? Prefix a column reference with table name and “.” to
disambiguate identically named columns from different tables. Ex. Use Bar. am n e Bar Frequents name address dr inker bar times_a_week The Edge 108 Morris Street Ben Satisfaction 2
Satisfaction 90 5 W. Main Street Dan The Edge 1 Dan Satisfaction 2 name address dri er nk bar times_a_week The Edge 108 Morris Street Ben Satisfaction 2 The Edge 108 Morris Street Dan The Edge 1 The Edge 108 Morris Street Dan Satisfaction 2 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Ben Satisfaction 2 Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Satisfacti Thi on Thuy Loan, PhD 905 W. Main Street Dan The Edge 1 Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street Dan Satisfaction 2 23
International University, VNU-HCMC Join Types •Theta Join •Equi-Join •Natural Join •Later, ( t/
lef right) outer join, semi-join
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 24 24 12
International University, VNU-HCMC Derived operator:natural join
•Input: two tables 𝑅and 𝑆
•Notation: 𝑅⋈𝑆(i.e. no subscript)
•Purpose: relate rows from two tables, and
•Enforce equality between identically named columns
•Eliminate one copy of identically named columns
•Shorthand for 𝜋L( R ⋈P𝑆) , where
•𝑝equates each pair of columns commonto 𝑅and 𝑆
•𝐿is theunion of column names from 𝑅and 𝑆(with duplicate columns removed)
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 25 25
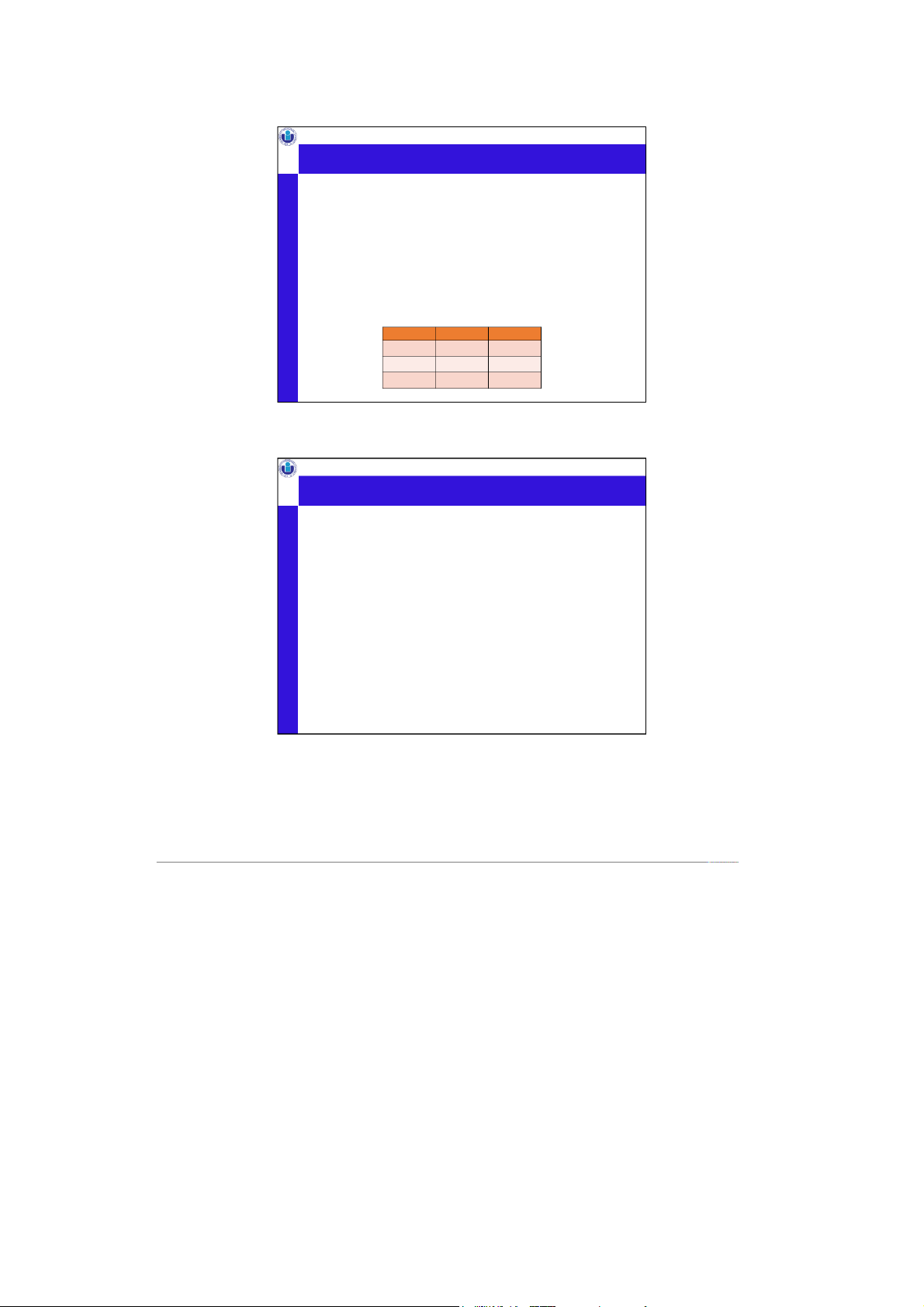
International University, VNU-HCMC Natural join example
Serves ⋈ 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒𝑠
=𝜋?(𝑆𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑠 ⋈? 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒𝑠)
=𝜋bar, beer, price, drinker (𝑆𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑠 ⋈Serves.beer = Likes.beer 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒𝑠) Serves Likes bar bee r price drinker beer The Edge Budweiser 2.50 Amy Corona The Edge Corona 3.00 Dan Budweiser Satisfaction Budweiser 2.25 Dan Corona Ben Budweiser
Serves ⋈ 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒𝑠 bar bee r price drinker The Edge Budweiser 2.5 0 Dan Natural Join is on beer Onl . on y e The Edge Budweiser 2.5 0 Ben column forbeer in the output The Edge Corona 3 .00 Amy What happens if the tables The Edge Corona 3 .00 Dan
have two or more common columns? ... …. …..
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 26 26 13
International University, VNU-HCMC Union
•Input: two tables 𝑅and 𝑆 Important for set operations: •Notation: Union Compatibility 𝑅∪𝑆
•𝑅and 𝑆must have identical schema •Output:
•Hasthesame schema as 𝑅and 𝑆
•Contains all rows in 𝑅and all rows in 𝑆(with duplicate rows removed) Example on board
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 27 27
International University, VNU-HCMC Difference
•Input: two tables 𝑅and 𝑆 Important for set operations: •Notation: 𝑅−:𝑆 Union Compatibility
•𝑅and 𝑆must have identical schema •Output:
•Hasthesame schema as 𝑅and 𝑆
•Contains all rows in 𝑅that are notin 𝑆 Example on board
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 28 28 14
International University, VNU-HCMC Derived operator:intersection
•Input: two tables 𝑅and 𝑆 Important for set operations: •Notation: 𝑅∩𝑆 Union Compatibility
•𝑅and 𝑆must have identical schema •Output:
•Hasthesame schema as 𝑅and 𝑆
•Contains all rows that are in both 𝑅and 𝑆
•How can you write it using other operators?
•Shorthand for 𝑅− (𝑅− 𝑆)
•Also equivalent to 𝑆− (𝑆− 𝑅) •And to 𝑅 ⋈ 𝑆
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 29 29
International University, VNU-HCMC Renaming •Input: a table 𝑅
•Notation: 𝜌S𝑅, 𝜌(A1,'A2 ,…)𝑅, or 𝜌S(A1,A2 ,…) R
•Purpose: “rename” a table and/or its columns
•Output: a table with the same rows as 𝑅,but called differently •Used to
•Avoid confusion caused by identical column names
•Create identical column names for natural joins
•As with all other relational operators, it doesn’t modify the database
•Think of the renamed table as a copy of the original
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 30 30 15
International University, VNU-HCMC Renaming example Frequents •Find drinkers who dri e nk r bar times_a_week frequent both “The Ben Satisfaction 2 Edge” and “Satisfacti ” on Dan The Edge 1 Dan Satisfaction 2 WRONG!
𝜋drinker 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 ⋈ Bar=%‘The%Edge%∧
𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 Bar%=%‘Satisfaction’∧% drinker%=%drinker Rename!
𝜌d1,%b1,%t1 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝜋uid1
⋈b1%=%‘The%Edge’∧b2%=%Satisfaction’%∧%d1=d2
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD
𝜌d2,%b2,%t2%%𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 Duke CS, Fall 2021 31 31
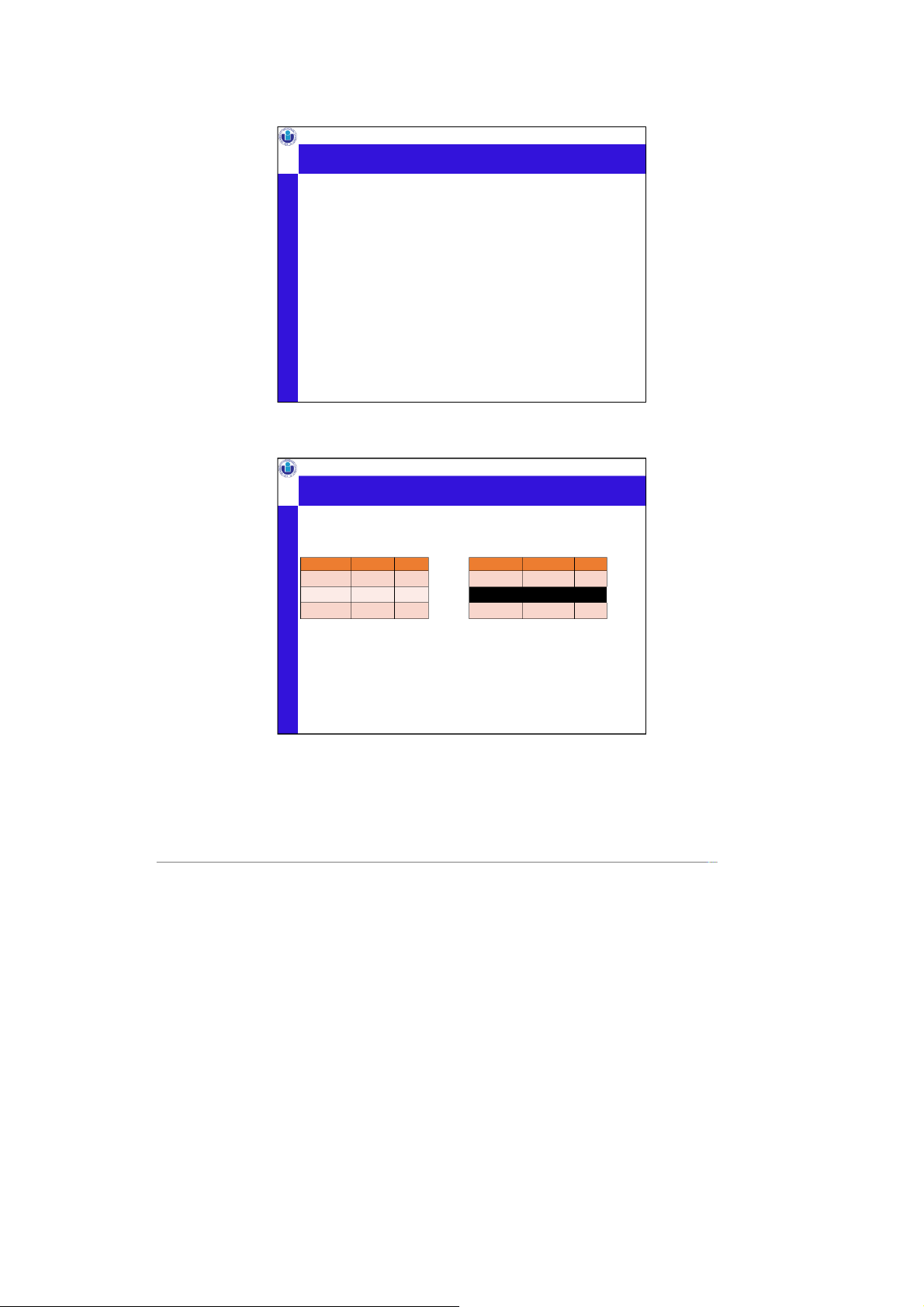
International University, VNU-HCMC Expression tree notation
•Find addresses of all bars that
What if you move 𝜎to the top? Still correct? ‘Dan’ frequents More or less efficient?
Bar Also called logical Plan tree name address The Edge 108 Morris Street 𝜋address Satisfaction 905 W. Main Street ⋈bar=name Frequents drinker bar t imes_a_week
𝜎drinker&=&‘Dan’ Ben Satisfaction 2 Dan The Edge 1
𝐵𝑎𝑟 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 Dan Satisfaction 2 Equivalent to
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD
𝜋address(𝐵𝑎𝑟 ⋈bar&=&name&(𝜎drinker&=‘Dan’𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠)) Duke CS, Fall 2021 32 16
International University, VNU-HCMC Summary of core operators •Selection:𝜎 P𝑅 •Projection:𝜋 L𝑅 •Cross product:𝑅×𝑆 •Union: 𝑅 ∪ 𝑆 •Difference: 𝑅−:𝑆
•Renaming: 𝜌S A1 , A2,… 𝑅
•Does not really add “processing” power
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 33 33
International University, VNU-HCMC Summary of derived operators •Join: 𝑅 ⋈ P 𝑆 •Natural join: 𝑅 ⋈ 𝑆 •Intersection:𝑅 ∩ 𝑆 •Many more
•Semijoin, anti-semijoin, quotient, …
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 34 34 17
International University, VNU-HCMC
Frequents(drinker, bar, times_of_week) Bar(name, address) Drinker(name, address) Exercise
•Bars that drinkers in address “30 N. Duk 0 e Street” do notfrequent
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 35
International University, VNU-HCMC 41
Frequents(drinker, bar, times_of_week) Bar(name, address) Drinker(name, address) A trickier Exercise
•For each bar, findthe drinkers who frequent it max no. times a week
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 36 18
International University, VNU-HCMC
Expressions in a Single Assignment
•Example: the theta-join R3 = R1 ⋈CR2 can be written: R3 := σC(R1 Χ R2)
•Precedence of relational operators: 1. [σ, π, ρ] (highest) 2. [Χ, ⋈] 3. ∩ 4. [∪ —] ,
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 37 37
International University, VNU-HCMC
Find names of sailors who’ve reserved boat #103
Sailors(sid, sname, rating, age) Boats(bid, bname, color) Reserves(sid, bid, day)
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 38 19
International University, VNU-HCMC
Find sailors who’ve reserved a red or a green boat
Sailors(sid, sname, rating, age) Boats(bid, bname, color) Use of rename operation Reserves(sid, bid, day)
•Can identify all red or green boats, then find sailors
who’ve reserved one of these boats:
Can also define Te m p b o a t s using union.Tr y the “AND” version yourself
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 39 39
International University, VNU-HCMC Division
•Not supported as aprimitive operator, but useful for expressing queries like:
Find sailors who have reserved all boats.
•Let A have 2fields, xand y;Bhave only field y:
A/B = p x(A)- p x ((p x (A)´B)-A) –i.e.,
A/B contains all x tuples (sailors) such that for
every y tuple (boat) in B, there is an xy tuple in A.
–Or:If the set of yvalues (boats) associated with an xvalue
(sailor) in Acontains all yvalues in B,the xvalue is in A/B.
Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Thi Thuy Loan, PhD Duke CS, Fall 2021 40 40 20



