











Preview text:
MIDTERM REVIEW
• Course: Introduction to Vietnamese Legal System
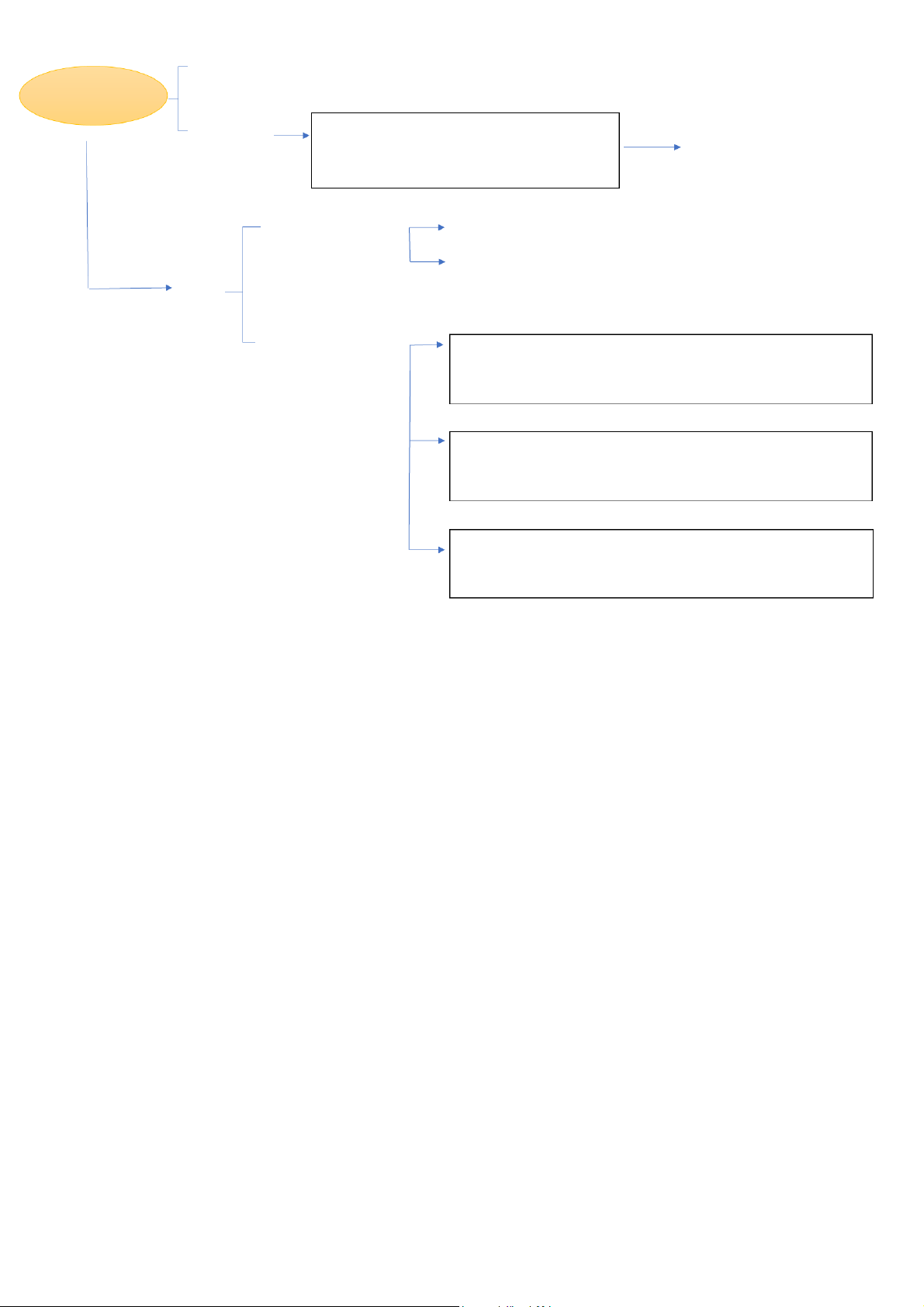
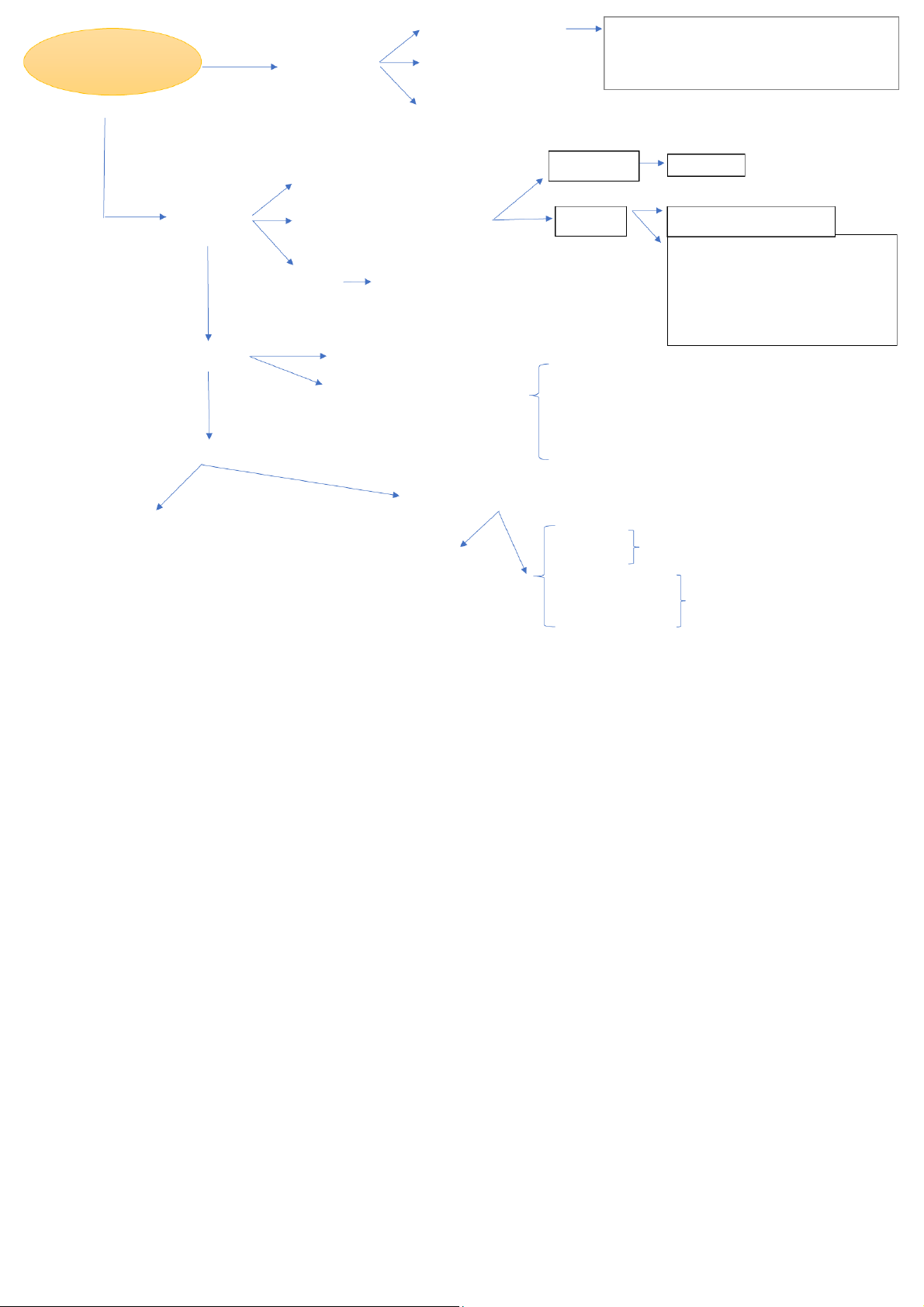
• Presenter: TA Pham Nhat Khanh Chi Organization STATE Legislative power: issue laws Political Power Govern Executive power: enforce laws
Society within the certain territory
Judicial power: interpret & adjudicate disputes Monarchy (king/queen)
Absolute: al state powers belong to king/queen (ex: Brunei, Oman...) Limited/ Constitutional: Forms
- state powers belong to citizen
- king/queen head of the state (ex: UK,..) Republic (no king/queen)
Parliamentary(VN): head of state # head of gov/executive body - People -> Parliament
- Parliament -> State organs
Presidential(US): head of state = head of gov/executive body
- People -> Parliament & President - President -> Cabinets
Semi-presidential(Russia): head of state = head of gov/executive body
- People -> Parliament & President - Parliament -> Cabinets Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
1. When mention is made to a state, we are referring to _________
A. The organisations holding state power B. The territory
C. The people with the territory D. Al of above
2. State power includes __________ A. Executive power B. Legislative power C. Judicial power D. Al of above
3. __________ is a form of state in which state power bel ongs to the people, and the head of state and the head of government are separate. A. Absolute monarchy B. Limited monarchy C. Parliamentary republic D. Presidential republic
4. __________ is the power to make and amend laws A. Legislative power B. Executive power C. Judicial power D. State power LAW
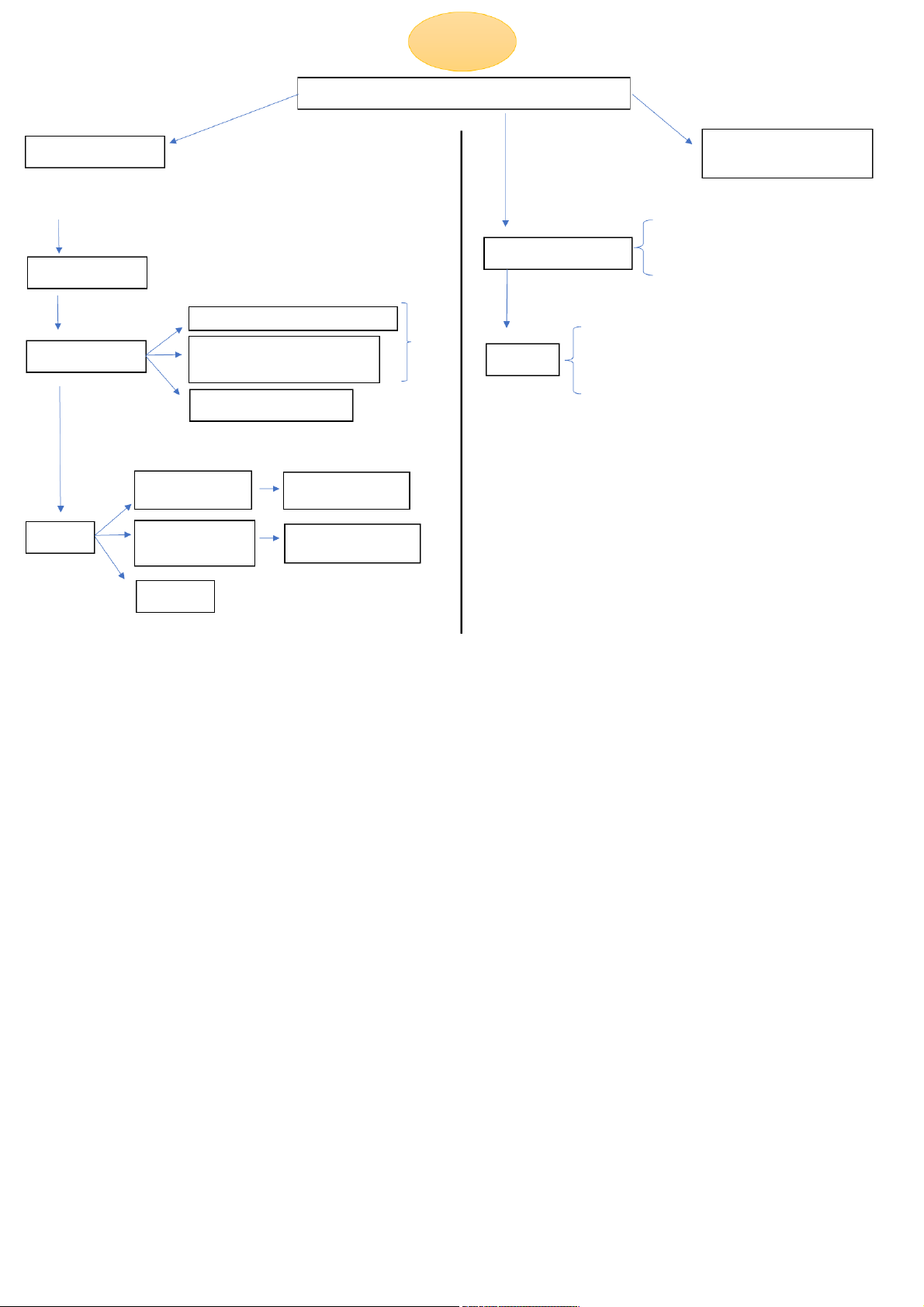
A system of rules/ guidelines + issued/recognized by state How to perform law Law branches (Base on legal norms)
(ngành luật, Vn có 12 ngành
luật, ex: civil law, labor law,) - Fail to perform law Violates (breach of law)
- Liability capacity: age + cognition
- Fault (intentional or unintentional) Legal institutions
Hypothesis: who, in which situation Always
- Civil law -> Civil sanction (fine, compensation...) Legal norms
Disposition: guidelines-how to exist Sanctions
- Administrative law -> Administrative sanction (fine,..) act rightly
- Criminal law -> Criminal sanction (jails,..)
- Labor law -> Labor discipline (fire,..) Sanction: consequences Statutes (legal Civil law system documents) (VN, France...) Forms Judicial precedent Common law system (court judgements) (US,UK...) (Where we can find the Customs law form) Pha m Nhat Khanh Chi
“Everyone has the obligation to pay taxes in accordance with the law” (Article 47, the constitution) • Hypothesis: everyone
• Disposition: has the obligation to pay taxes in accordance with the law
“Anyone who unintentionally causes the death of another person shal be sentenced to between 6 months and five
years of imprisonment” (Article 98.1, the criminal code)
• Hypothesis: Anyone who unintentional y causes the death of another person
• Disposition: Không được nêu rõ và ở dạng quy định ngầm => Quy định trong trường hợp này là không được vô tình
gây ra cái chết của người khác.
• Sanction: shal be sentenced to between 6 months and five years of imprisonment
“Any person who manufactures or deals in counterfeit medicines for treatment or prevention of diseases shal face
a penalty of 02 - 07 years' imprisonment.” (Article 194, the criminal code)
• Hypothesis: Any person who manufactures or deals in counterfeit medicines for treatment or prevention of diseases
• Disposition: Không được nêu rõ và ở dạng quy định ngầm => Quy định trong trường hợp này là không được buôn
bán thuốc giả để chữa hay phòng bệnh
• Sanction: shal face a penalty of 02 - 07 years' imprisonment
“Before overtaking, a vehicle shal give a signal by means of light or horn; from 22.00 hrs to 5.00 hrs in urban
centers & populous areas, only light signals can be used for this purpose” (Article 14, the law on road traffic)
• Hypothesis: Before overtaking, a vehicle
• Disposition: shal give a signal by means of light or horn; from 22.00 hrs to 5.00 hrs in urban centers & populous
areas, only light signals can be used for this purpose Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
Question: Which part of the fol owing legal norm is missed?
Any person who manufactures or deals in counterfeit medicines for treatment or prevention of diseases shal face a
penalty of 02 - 07 years' imprisonment. (Article 194.1, the penal code 2015) a. Hypothesis b. Disposition c. Sanction d. None of the above
Question: Which of the fol owing is the highlighted part?
“Any person who manufactures or deals in counterfeit medicines for treatment or prevention of diseases shal face a
penalty of 02-07 years’ imprisonment.” (Article 194.1, the penal code 2015) a. Hypothesis b. Deposition c. Sanction
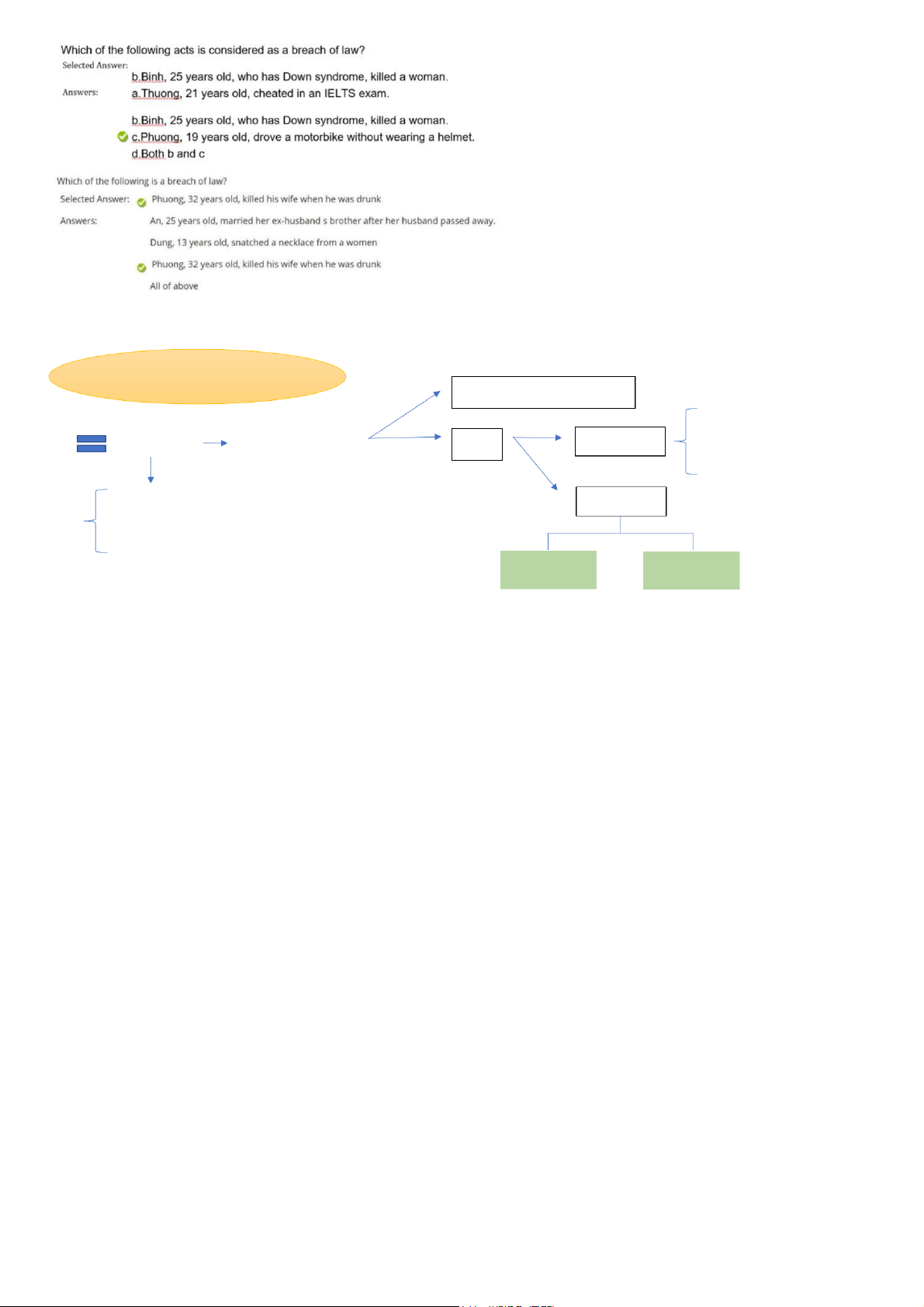
d. Both hypothesis and disposition CONSTITUTION
Citizen’s rights & obligations • Legislative: issue (NA) Supreme law Fundamental rules State State powers • Executive: enforce (Gov) =Mother law or Fundamental law
• Judicial: interpret, adjudicate (court, prosecutions)
- Other laws have to details the rules State organs
- Other laws have to comply with the rules
- Al people have to comply with the rules CENTRAL LOCAL LEVEL LEVEL Pham Nhat Khanh Chi Citizens: >= 18 elect NA Elect
Loca l people: >= 18 elect people’s council 1.Suggest / Propose CENTRAL National 2. Issue decision to appoint/ LEVEL Standing Committees of NA Assembly approve result Pay salary National President Supervise & discuss Report Government Court Prosecutions LOCAL LEVEL People’s Elect at the same level council People’s committees
Provincial people council -> Provincial people’s committees
District people council -> District people’s committees
Commune people council -> Commune people’s committees Pham Nhat Khanh Chi National Assembly (NA) Standing Committee s of NA • Legislative body • Permanent body •
Highest representative body of people
• Interpret laws, constitutions & ordinances • Highest state power organ
• Number of members wil be decided by NA • Amnesty
• Members can’t be government members at the same time • Duration: 5 years (normal y)
• Duration: follows the NA’s duration •
Deputies: <=500 (elected directly by the people) •
Decision: majority rule (> 1/2) Except:
Make & amend the constitutions, dismiss a deputy, decide on
National President (NA’s member)
shortening or extending the duration of the national assembly
(>= 2/3) deputies’ approval • Head of the state
• Represent VN & Promulgate/Announce law, constitutions & ordinances
Deciding ordens, medalsCommance the propie's Government • Grant pardon armed forces
• Duration: follows the NA’s duration • Executive body of NA
• Head of government: Prime Minister
• Highest executive body / state administrative body of NA People’s council
• Government cabinets: prime minister + 4 vice-prime
minister +18 ministers + 4 minister-levels • Local state power body
• Representative body of local people • draft the law
• Supervise compliance with the constitution and law in its locality Court People’s committees
• State judicial body (adjudicate disputes)
• Executive body of local people’s council
• 2 levels of adjudication: first instance and appel ate courts
• Local administrative organ
• 4 structures: supreme, high, provincial & district
Primeminister: enact legal documents
• Protect the socialist legislation, the socialist regime, human and citizenship rights. Notes
• Highest state power => citizens Prosecutions
• Highest state power body/organs => National Assembly
• Communist Party doesn’t have state power
• State judicial body (supervise courts & gov,
• If the decrees, laws... are different from what is stated in the prosecute criminals )
constitution -> obey the constitution
• 4 structures: supreme, high, provincial & district
• Administrative body: Gov, pp’s committees, 18 minister, 4
• Represent the country to sue pp who violate law
minister-levels, department of… Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
Gov- draft the law (soạn thảo luật)
NA- discuss & approve (xem xét và phê duyệt) NP- announce to everyone
Court – rely on that law to give a adjudgment
But if in law, we have some misunderstanding => NA’s standing committee will interpret
How do people perform/exercise state power?
+ Indirect: Exercise through representative organs: National assembly or people’s council by vote to select deputies
+ Direct: Standing for election to the National assembly or people’s council to become a deputy
Ex: deputy ask prime minister (chinh đại biểu của hd nhân dân & quốc hội vừa thực hiện quyền lực của ng dân giao cho và
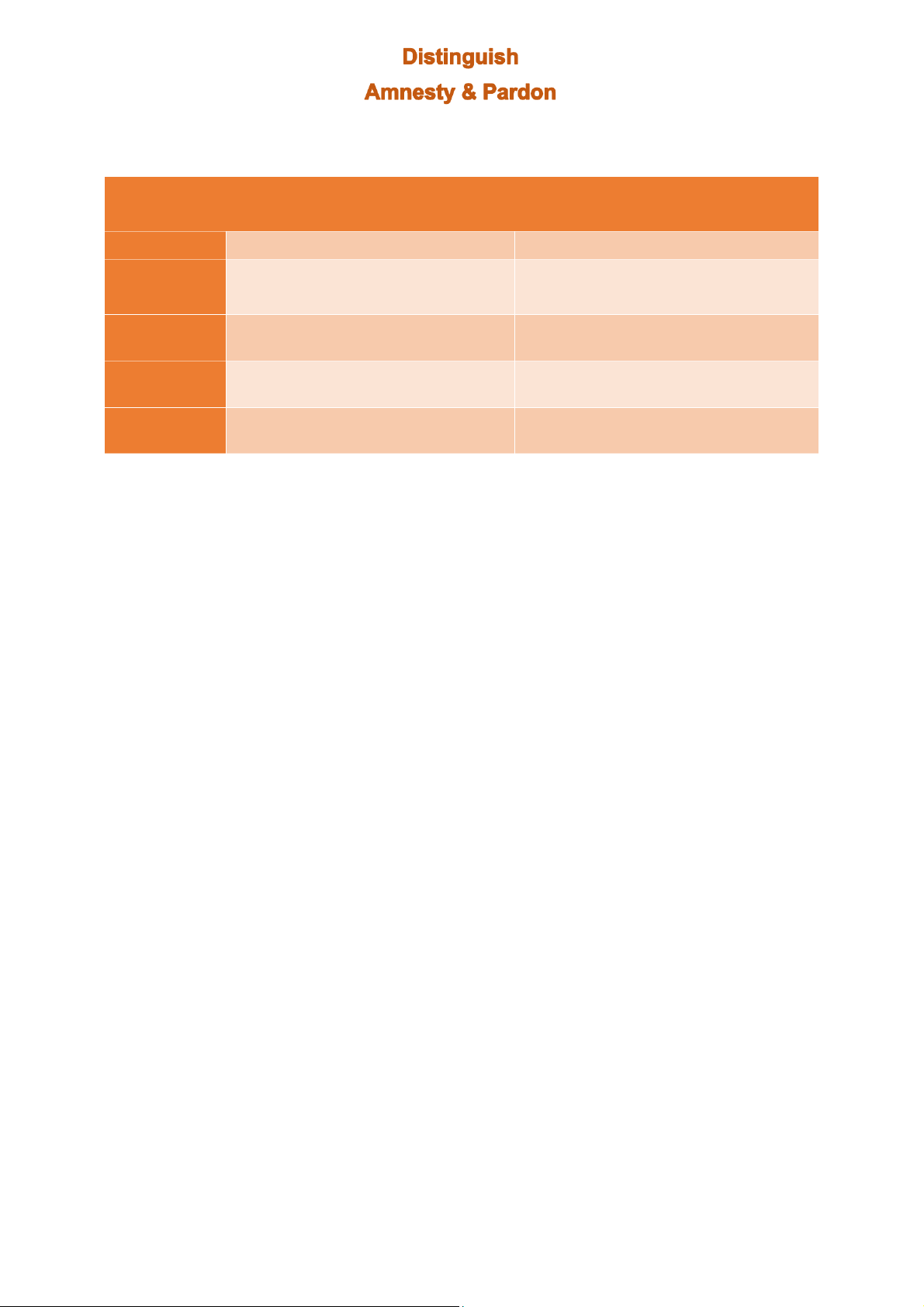
chinh quyền lực của bản thân họ) Pham Nhat Khanh Chi Amnesty Pardon (General amnesty) (Special amnesty) Authority National Assembly National President Subject Group of crimes Specific individuals
(al individuals in that group) When granted
Before or after convicted by a final
After convicted by a final judgement judgement Legal outcome
Individuals wil no longer be criminals and Criminal record of individuals wil not be have no criminal records wiped Nature
Absolution and forgetfulness of an
Release from prisons ahead of time offence
people serving imprisonment penalty Pham Nhat Khanh Chi 18 Ministers or
4 head of ministerial level agencies
• Ministry of National Defense • Government Inspectorate
• Ministry of Public Security (bộ công an) (Thanh tra chính phủ)
• Ministry of Foreign Affairs • State Bank of Viet Nam (Ngân hàng nhà nước VN) • Ministry of Justice • Ministry of Finance
• Committee on Ethnic Minority Affairs (Uỷ ban dân tộc) • Ministry of Transport • Government Office • Ministry of Construction (Văn phòng chính phủ)
• Ministry of Education and Training
• Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
• Ministry of Industry and Trade
• Ministry of Planning and Investment • Ministry of Health
• Ministry of Science and Technology
• Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment
• Ministry of Information and Communications • Ministry of Home Affairs
• Ministry of Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs
• Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
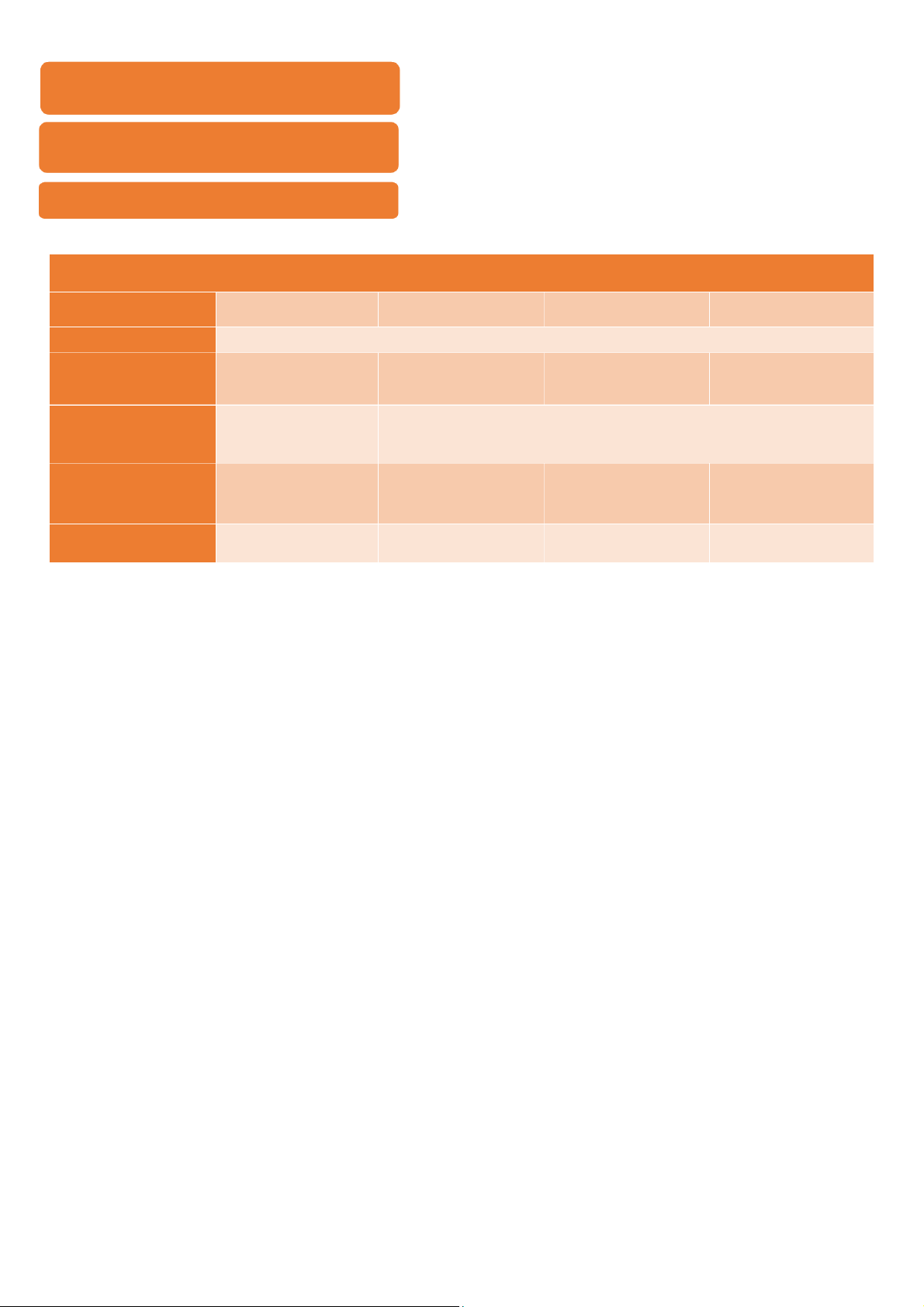
Organs have the right to issue legal documents State bodies Legal documents National assembly
Constitution, Act, Resolution (hiến pháp, luật, nghị quyết)
Standing committee of the national assembly
Ordinance, Resolution (pháp lệnh, nghị quyết) National president
Order, Decision (lệnh, quyết định) Government(cabinet) Decree (nghị định) Prime minister Decision
Ministers and head of ministry – level bodies Circular (thông tư)
(Bộ trưởng, Thủ trưởng cơ quan ngang bộ)
Justice council of the supreme people’s court Resolution
(Hội đồng thẩm phán TANDTC)
Chief justice of the supreme people’s court & Circular
Chief of the supreme people’s procuracy
(Chánh án TANDTC & Viện trưởng VKSNDTC) State auditor general Decision
(Tổng kiểm toán nhà nước) People’s council Resolution People’s Committee Decision Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
1. Which of the fol owing organ has the highest state power? A. Communist party B. National presient C. National assembly D. Prime minister
2. Which of the fol owing is an administrative organ?
A. The office of Ho Chi Minh People’s Committee
B. The office of Ho Chi Minh City People’s council
C. The office of Ho Chi Minh people’s court D. Al of the above
3. According to the constitution 2013, who of the following can vote for the delegates of the people’s councils
A. An 18 year old and above local person
B. An 18 year old and above local Vietnamese citizen
C. A 21 year old and above local Vietnamese citizen D. None of the above
4. In order to amend criminal codes, the National assembly needs at least approvals of____________. A. More than half of deputies
B. More than half of attending deputies C. 2/3 deputies D. 2/3 attending deputies
5. Which of the fol owing organs have the right to issue legal documents? A. Government B. National Assembly
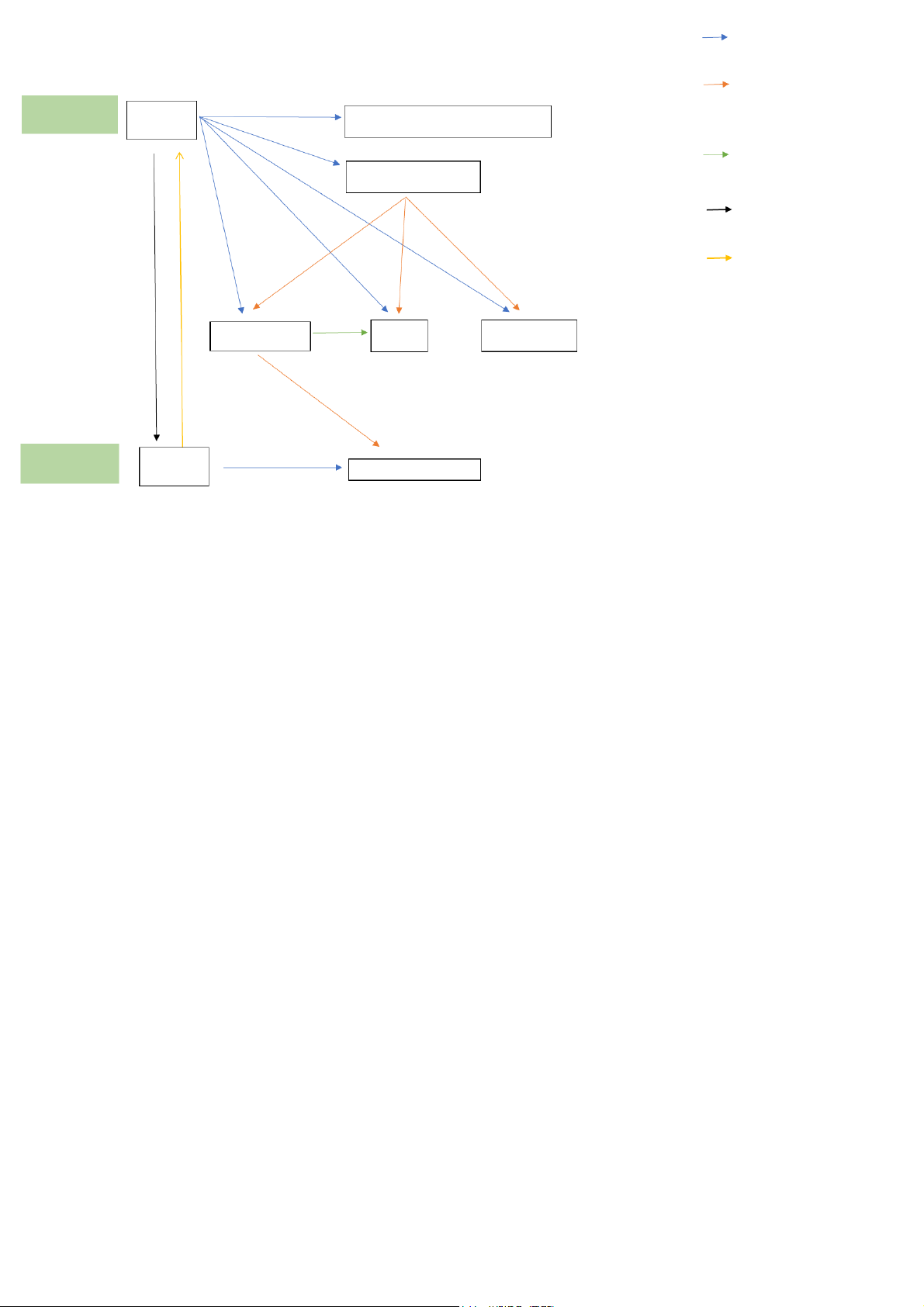
C. National Assembly’s standing committees D. Al of the above =EXCUTIVE LAW One site has state power
• State organ – State organ ( Gov- People’s committees) ADMINISTRATIVE Only govern
• State organ – People (administrative organs - citizens) Administrative Content: State administrative LAW
• Inside state organ (prime minister- ministry of transport) management activities Relations Nature: Command - obedient
Fail to perform administrative law Organization Al violation (not a crime) Handle Administrative
Liability capacity: Age + Cognition Individual Cognition: no mental issues Viola tion A ge:
>=12- <14: violation related to security, At fault
Be aware or have to be aware of your acts safety, order
>=14 - <16: intentional fault >=16: al violation Bear Liability Administrative violation Circumstences • Emergency: violate la
w to prevent damages threatening
Not fal under exceptional cases
• Unexpected event: sudden event caused violations
• Force majeure event: happened event, violate to save your time NO harm Sanctions • Legitimate defence v Administrative sanctions
Administrative handling measures(*) • Caution Principle (for Vietnamese people only) • Fine >= 16 Remedial measures • Deprive license • Confiscate vehicles Principle/additional • Expulsion: foreigners Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
Principles of applying administrative sanctions One violation wil have applied only one principal sanction
One or several additional sanctions can be applied for one violation
One violation is only sanctioned once
ADMINISTRATIVE HANDLING MEASURES(*) Forms Education At Reformatory Center
Compulsory Education Detoxification Centers Commune Principle
apply for individuals violating legal regulations on security, order and social safety Subject ≥ 12 ≥12 - <18 Woman: ≥18-<=55, ≥ 18 Man: >=18-<=60 Exception N/A
- Mental problems or unable to cognize - Pregnant women
- Women or persons who are alone, nursing under 36-month child How long wil 3 – 6 months 6 – 24 months 6 - 24 months 12 – 24 months punishment be applied for Time Limit for 03 – 12 months 06 – 12 months 1 year 03 months Applying Pham Nhat Khanh Chi
An was stopped by a policeman because he drove a motorbike without wearing a helmet. The policeman recorded
and applied sanctions on the violation. A few hours later, on the way to the state treasury to pay the fine, An was
stopped by another policeman for driving without wearing a helmet.
a. An wil not have to pay the fine again as an administrative violation is only sanctioned once
b. An wil not have to pay the fine again as an administrative violation was committed due to force majeure events
c. An wil have to pay the fine again because he made a various violation
d. An wil have to pay the fine again because the violation is considered as a new
Which of the fol owing administrative violator wil not bear liability due to force majeure events?
A. Due to fire, a company trading in petrol lost al VAT input and output invoices
B. In order to avoid a motorbike suddenly joining the main road, a car drove into a motorbike lane
C. In order to catch a person who squandered someone s bag by snatching, Thien drove over speed limit. D. Al of above
Which of the fol owing is an administrative violation?
A. A 10-year-old boy drove a car to his school
B. A 22-year-old student sold drugs at his school
C. A 71-year-old threw rubbish to his neighbor D. Al of the above Case:
On 12th August 2016, Huyen, 16 years old, drove her motorbike with the registered number 61B5 – 3981 from Thu Dau
to Di An, Binh Duong. In front of Ong Cu temple, Thanh who drove an electric bicycle col ided with Huyen when he tried to
overtake her. The col apse caused Thanh spinal cord injuries (equal to 8% of health damages) and caused Huyen’s
motorbike to knock on another motorbike nearby within 1 meter which was droved by Khanh, 21 years old. On 12th
December 2016, the head of Di An police station issued a decision to apply administrative sanctions on Huyen since she
caused the accident with Khanh. As is not happy with the decision, Huyen sued the Di An police station to Di An people’s court
1. Which of the fol owing relations wil be governed by administrative law?
a. Thanh drove into Huyen’s motorbike
b. The head of Di An police station issued a decision to apply administrative sanctions on Huyen
c. Di An people’s court settled Huyen’s lawsuit petition d. Al of the above
2. Which kind of fault does Huyen commit when she drove her motorbike into Khanh? a. Direct intentional fault b. Indirect intentional fault
c. Unintentional fault due to overconfidence
d. Unintentional fault due to negligence
3. Which of the fol owing sanctions may Huyen face for her administrative violations? a. Caution b. Fine c. Expulsion d. None of the above




