
Preview text:
Lecture 3 Data and Knowledge Management Objectives
• Discuss ways that common challenges in managing data can
be addressed using data governance.
• Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of relational databases.
• Define Big Data, and discuss its basic characteristics.
• Explain the elements necessary to successfully implement and maintain data warehouses.
• Describe the benefits and challenges of implementing
knowledge management systems in organizations.
• Understand the processes of querying a relational database,
entity-relationship modeling, and normalization and joins. • Ref.: Chapter 5
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 2 Managing Data
• All IT applications require data.
• These data should be of high quality, meaning
that they should be accurate, complete, timely,
consistent, accessible, relevant, and concise
• The process of acquiring, keeping, and managing
data is becoming increasingly difficult
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 3
• The Difficulties of Managing Data
• The amount of data increases exponentially with time
• Data are also scattered throughout organizations,
and they are collected by many individuals using various methods and devices.
• Data are generated from multiple sources
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 4
• Two other factors complicate data management • Federal regulations
• Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002: how they are managing information
• Public companies evaluate and disclose the
effectiveness of their internal financial controls and
• Independent auditors for these companies agree to this disclosure
• Companies are drowning in data
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 5 • Data Governance
• Is an approach to managing information across an entire organization
• Involves a formal set of business processes and
policies that are designed to ensure that data are
handled in a certain, well-defined fashion
make information available, transparent, and
useful for the people who are authorized to access
it, from the moment it enters an organization until it is outdated and deleted.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 6
• Master data: set of core data, such as customer,
product, employee, vendor, geographic location,
and so on, that span an enterprise’s information systems.
• Master data management: process that provides
companies with the ability to store, maintain,
exchange, and synchronize a consistent,
accurate, and timely “single version of the truth”
for the company’s core master data.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 7 The Database Approach
• Database systems minimize the following problems:
• Data redundancy: The same data are stored in multiple locations.
• Data isolation: Applications cannot access data
associated with other applications.
• Data inconsistency: Various copies of the data do not agree.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 8
• In addition, database systems maximize the following:
• Data security: databases must have extremely high
security measures in place to minimize mistakes and deter attacks.
• Data integrity: Data meet certain constraints
• Data independence: Applications and data are
independent of one another; that is, applications
and data are not linked to each other, so all
applications are able to access the same data
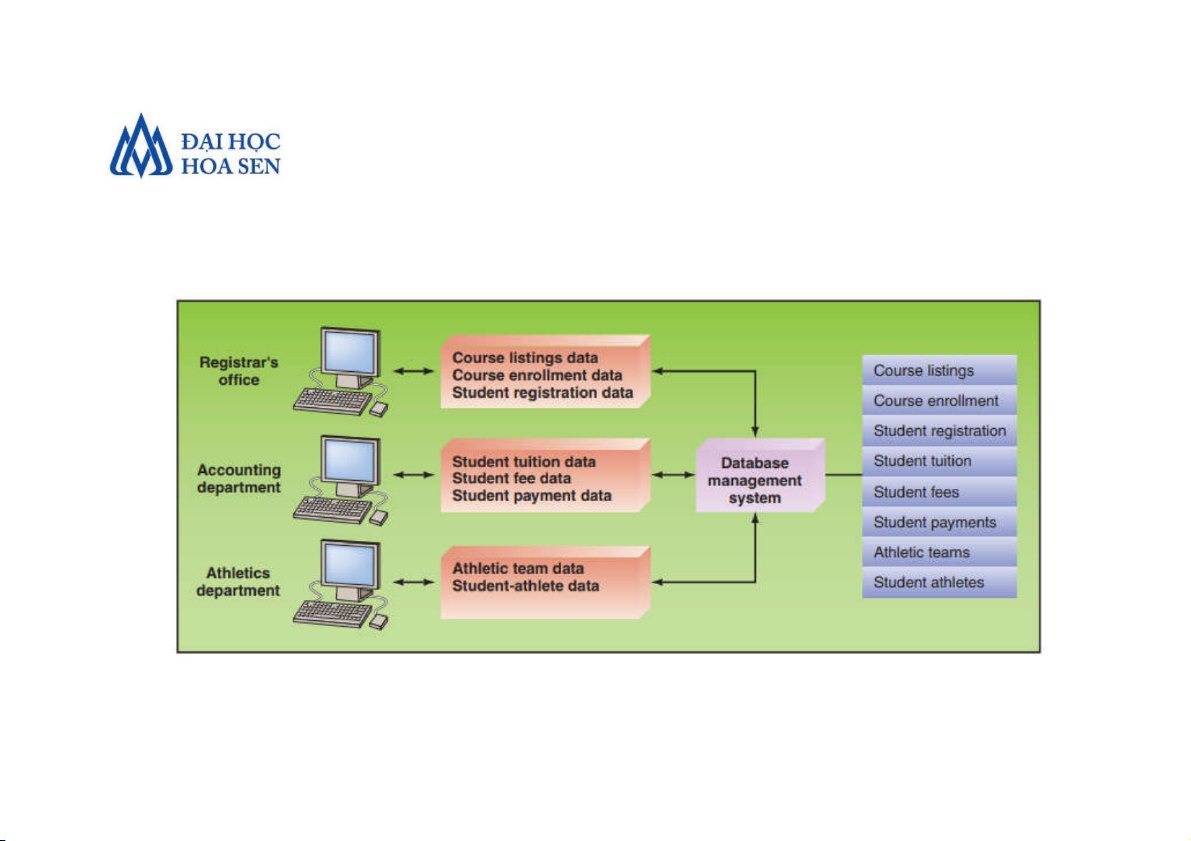
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 9 • A university database
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 10