








Preview text:
Lecture 6
Telecommunications and Networking Objectives
• Compare and contrast the major types of networks.
• Describe the wireline communications media and transmission technologies.
• Describe the most common methods for accessing the Internet. • Ref.: Chapter 6 - 8
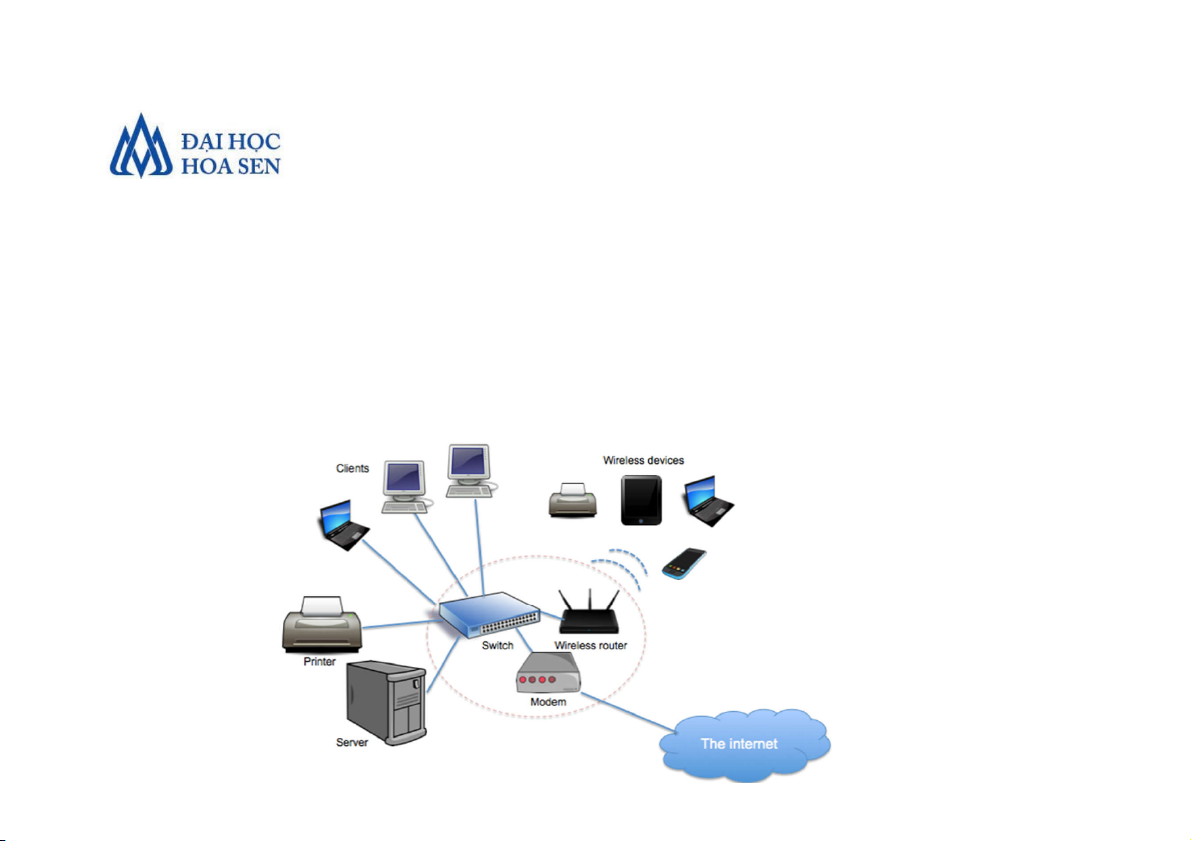
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 2 Computer Network
• A computer network is a system that connects
computers and other devices (e.g., printers) via
communications media so that data and
information can be transmitted among them.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 3
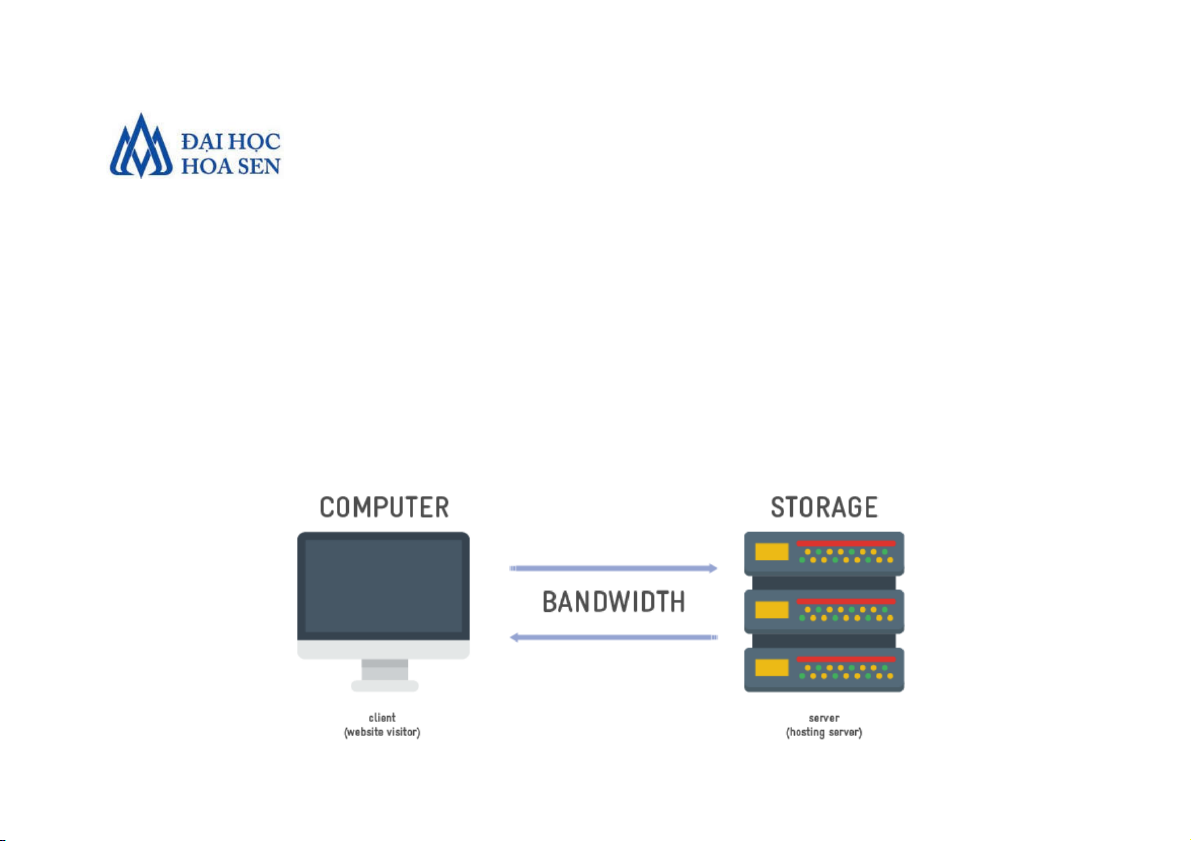
• Bandwidth refers to the transmission capacity of
a network; it is stated in bits per second.
Bandwidth ranges from narrowband (relatively
low transmission capacity) to broadband
(relatively high network capacity)
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 4
• Broadband is wide bandwidth data transmission which
transports multiple signals and traffic types. The medium
can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, radio or twisted pair (25
Mbps for download - 4 Mbps for upload – DSL(digital
subscriber line), ADSL(Asymmetric digital subscriber line))
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 5
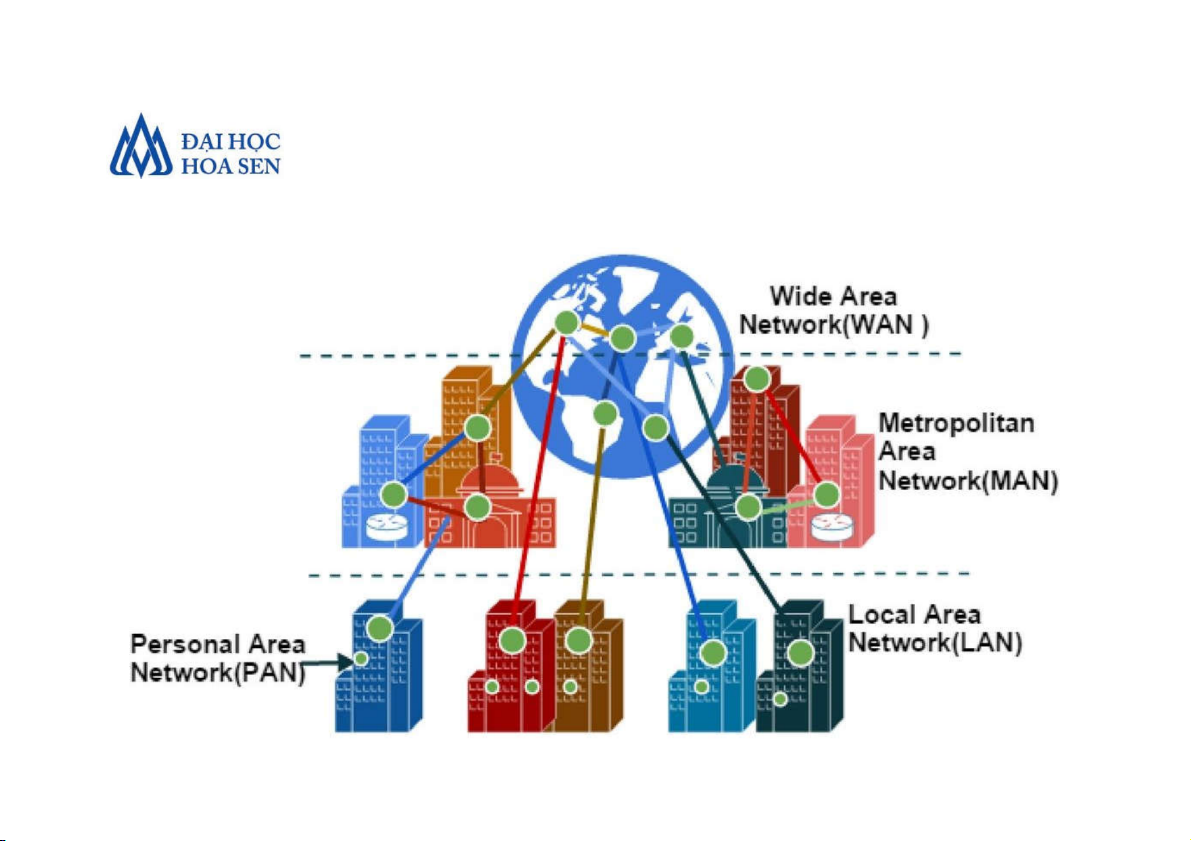
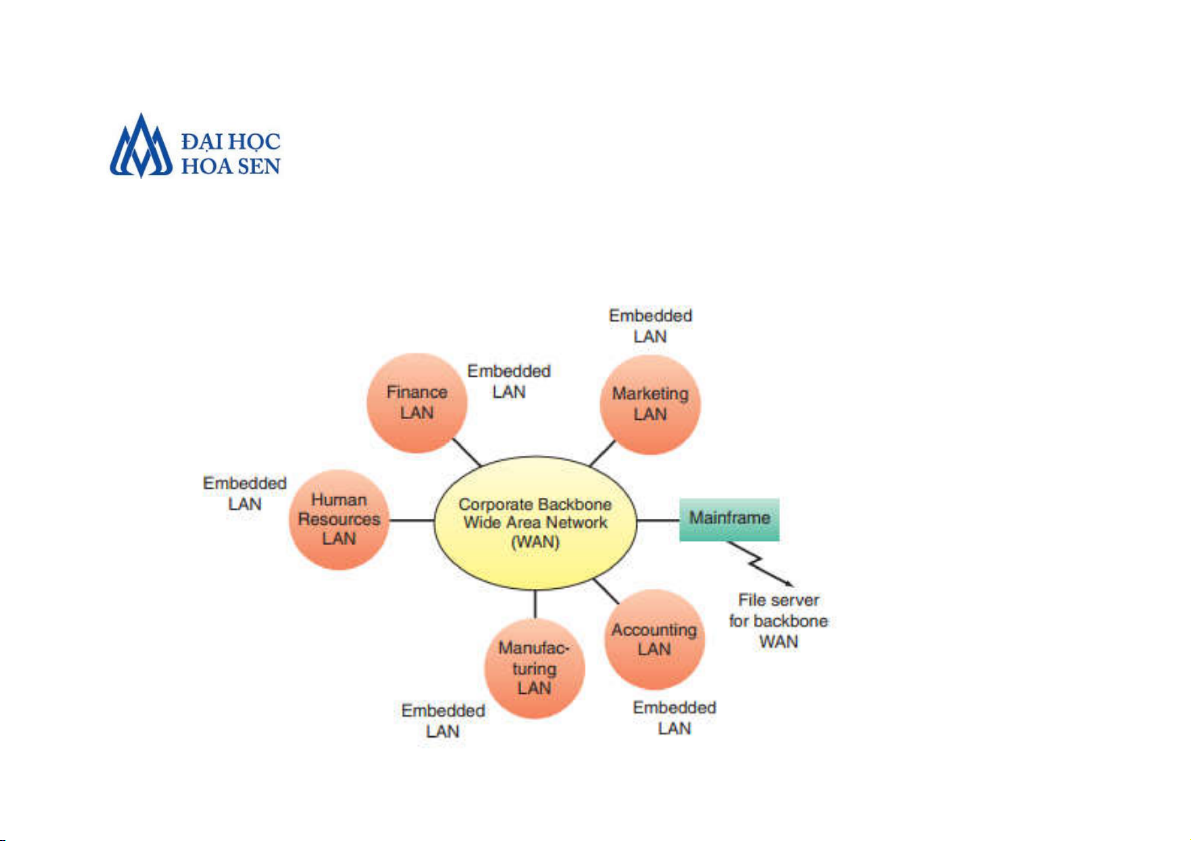
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 6 • Enterprise Networks
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 7 Network Fundamentals
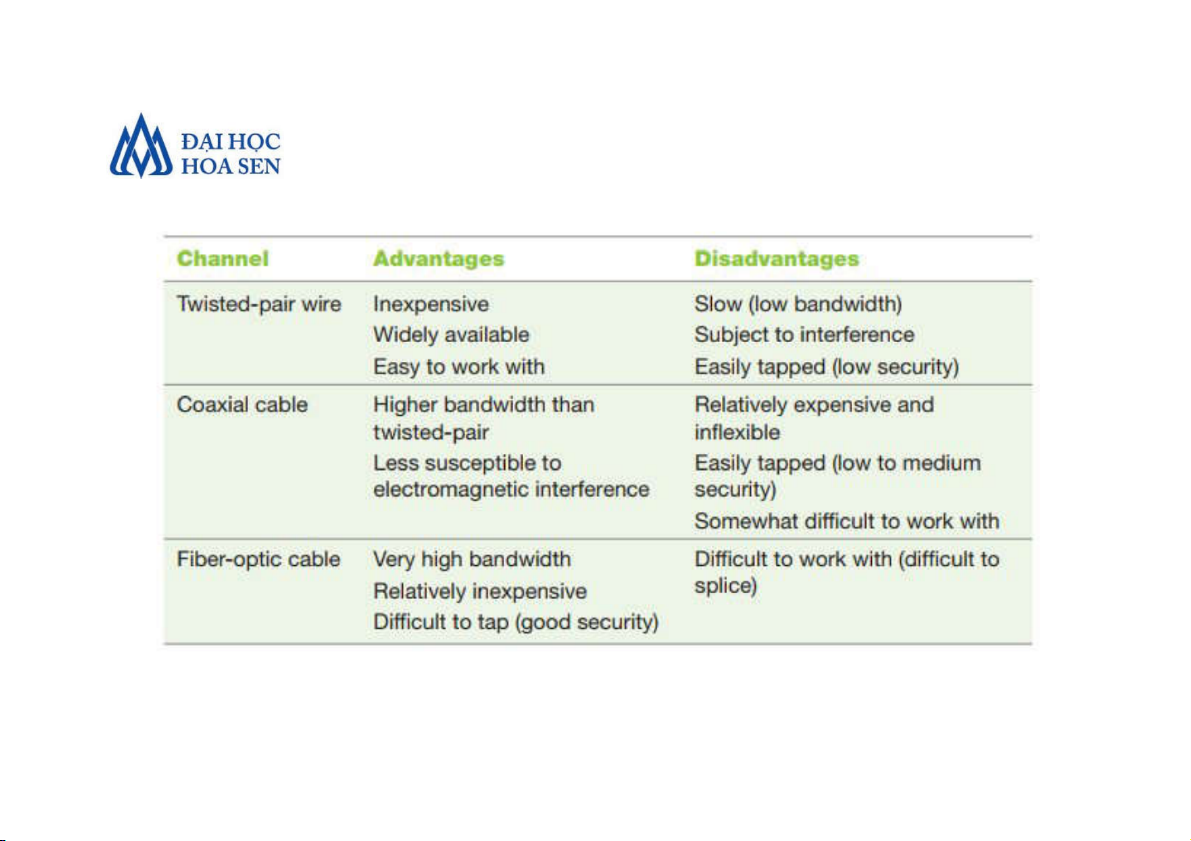
• A communications channel is such a pathway.
It is comprised of two types of media: cable
(twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, or fiber-optic
cable) and broadcast (microwave, satellite, radio, or infrared)
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 8
• Wireline media or cable media use physical
wires or cables to transmit data and information.
Twisted-pair wire and coaxial cables are made of
copper, and fiber-optic cable is made of glass.
The alternative is communication over broadcast media or wireless media.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 9
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 10