










Preview text:
Lecture 10 Supply Chain Management (SCM) Objectives
• Describe the three components and the three flows of a supply chain.
• Identify popular strategies to solving different challenges of supply chains.
• Explain the utility of each of the three major
technologies that support supply chain management. • Ref.: Chapter 9
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 2 Introduction to Supply Chains
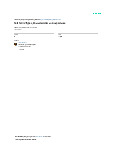
• A supply chain is the flow of materials,
information, money, and services from raw
material suppliers (producer), through factories
and warehouses, to the end customers
• A supply chain also includes the organizations
and processes that create and deliver products,
information, and services to the end customers.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 3
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 4
• Supply chains are a vital component of the overall
strategies of many modern organizations.
• To utilize supply chains efficiently, a business
must be tightly integrated with its suppliers,
business partners, distributors, and customers
• A critical component of this integration is the use
of information systems to facilitate the exchange
of information among the participants in the supply chain.
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 5
The Structure and Components of Supply Chains
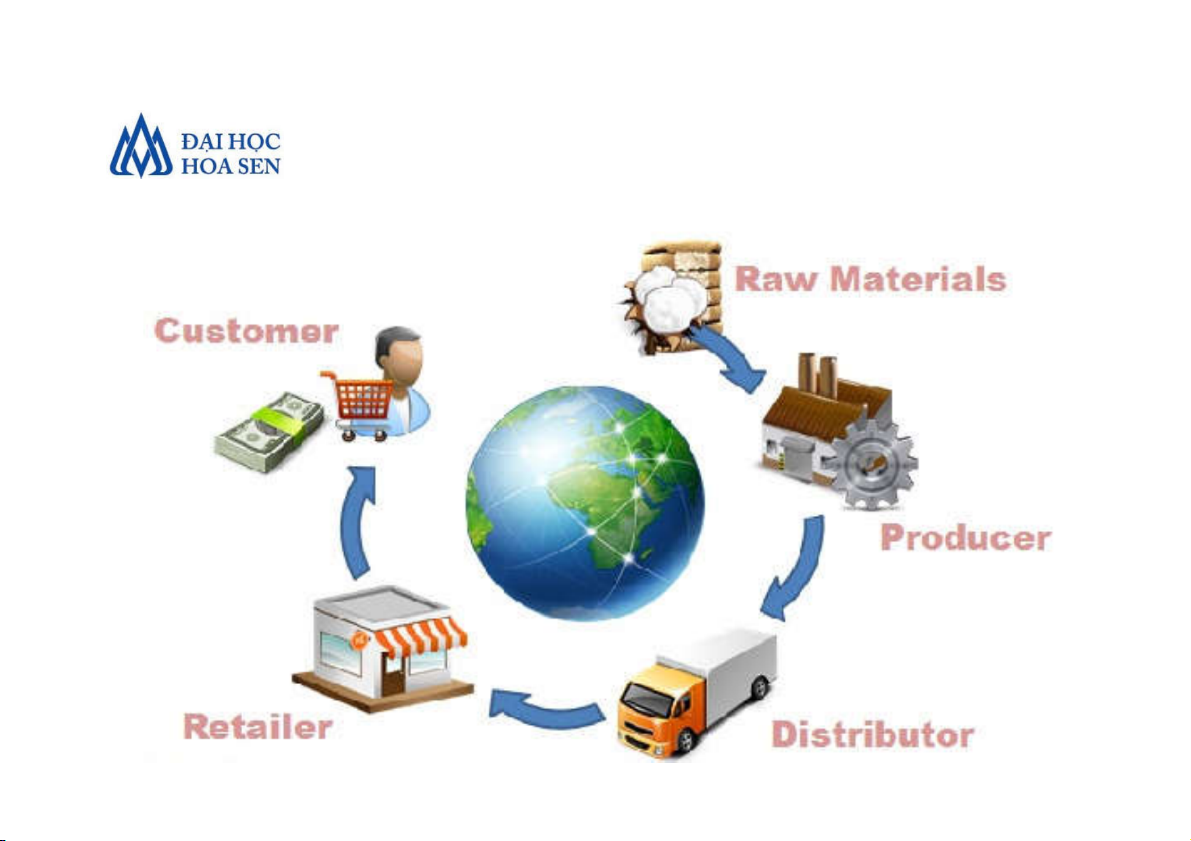
• Three segments of Supply Chains • Upstream:
• Sourcing or procurement from external suppliers occurs
• Select suppliers, develop the pricing, delivery, and payment
• Managing inventory, receiving and verifying
shipments, transfer goods to manufacturing facilities
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 6 • Internal
• Packaging, assembly, or manufacture products
• Schedule activities necessary for production, testing,
packaging, and preparing goods for delivery
• Monitor quality levels, production output, and worker productivity • Downstream
• Receive customer orders, develop a network of
warehouses, select caries, and generate invoices
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 7 • Tiers of suppliers
• A supplier may have one or more sub-supplier(s)
• The sub-supplier may have its own sub-supplier(s)
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 8
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 9
• The Flows in the Supply Chains
• Material flows are the physical products, raw
materials, supplies, and so forth that flow along the chain
• Information flows consist of data related to
demand, shipments, orders, returns, and
schedules, as well as changes in any of these data
• Financial flows involve money transfers,
payments, credit card information and
authorization, payment schedules, e-payments, and credit-related data
Faculty of Information Technology Introduction to MIS 10