
Preview text:
MOCK TEST FOR MIDTERM EXAMINATION
Subject: CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEERING Duration: 90 minutes
PART 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE (40 question – 80 pts) Q.1. Identify a liquid.
A) definite volume and definite shape
B) definite volume and no definite shape
C) definite shape and no definite volume
D) no definite shape and no definite volume
Q.2. Molecules can be described as
A) mixtures of two or more pure substances
B) mixtures of two or more elements that has a specific ratio between components
C) two or more atoms chemically joined together D) heterogeneous mixtures
Q.3. A substance that can’t be chemically broken down into simpler substances is A) a homogeneous mixture B) an element C) a heterogeneous mixture D) a compound
Q.4. Which of the following are examples of a chemical change? A) coffee brewing B) water boiling
C) leaves turning color in the fall D) sugar dissolves in water
Q.5. Which of the following are examples of physical change?
A) Dew forms on a blade of grass.
B) A Halloween light stick glows after shaking. C) browning meat
D) An oxygen balloon explodes when contacted with a flame.
Q.6. The correct result (indicating the proper number of significant figures) of the following problem is (0.002843 x 12.80184)/0.00032 A) 113.73635 B) 113.736 C) 113.74 D) 1.1 x 102
Q.7. How many significant figures are there in the answer to the following problem? (9.992 x 3.200) + 0.610 A) one B) two C) three D) four Q.8. Distillation is
A) a process in which the more volatile liquid is boiled off.
B) dissolving a solid into a liquid.
C) separating a solid from a liquid by pouring off the liquid.
D) pouring a mixture through a filter paper to separate the solid from the liquid. Q.9. A physical change A) occurs when iron rusts.
B) occurs when sugar is heated into caramel.
C) occurs when glucose is converted into energy within your cells.
D) occurs when water is evaporated.
Q.10. What does "X" represent in the following symbol? A) silicon B) sulfur C) zinc D) ruthenium
Q.11. What element is defined by the following information? p+ = 17 n° = 20 e- = 17 A) calcium B) rubidium C) chlorine D) neon
Q.12. Which of the following statements about isotopes is TRUE?
A) Isotopes of the same element differ only in the number of electrons they contain.
B) Isotopes of the same element have the same mass.
C) Isotopes of the same element don't usually have the same properties.
D) Some elements have three or more naturally occurring isotopes.
Q.13. Calculate the atomic mass of silver if silver has 2 naturally occurring isotopes with the following
masses and natural abundances: Ag-107 106.90509 amu 51.84% Ag-109 108.90476 amu 48.46% A) 107.90 amu B) 108.00 amu C) 107.79 amu D) 108.19 amu
Q.14. Iodine belongs to the______ group of the periodic table A) alkaki metal B) metal C) halogen D) noble gas
Q.15. An ion has 26 protons, 29 neutrons, and 23 electrons. The symbol for the ion is A) 55Fe3+ B) 55Fe3- C) 52Cu3+ D) 52Cu3-
Q.16. An atom that has an atomic number of 38 and a mass number of 88 is an isotope of an atom that has
A) an atomic number of 39 and a mass number of 88.
B) an atomic number of 38 and a mass number of 86.
C) 50 neutrons and 38 protons.
D) 50 protons and 38 neutrons.
Q.17. Give the ground state electron configuration for Pb A) [Xe]6s2 . 2 6p B) [Xe]6s2 10 . 2 5d 6p C) [Xe]6s2 14 10 . 2 5f 6d 6p D) [Xe]6s2 14 10 . 2 4f 5d 6p
Q.18. A covalent bond is best described as
A) the sharing of electrons between atoms B) the transfer of electrons
C) a bond between a metal and a nonmetal
D) a bond between a metal and a polyatomic ion
Q.19. For a particular element, identify the species that has smallest radius A) cation B) anion C) neutral D) radical
Q.20. Which ionization process requires the most energy? A) C (g) → C+ (g) + e- B) C+ (g) → C2+ (g) + e- C) C2+ (g) → C3+ (g) + e- D) C3+ (g) → C4+ (g) + e-
Q.21. Place the following in order of decreasing metallic character. A) P > As > K B) As > P > K C) K > P > As D) K > As > P
Q.22. Of the following, which atom has the largest atomic radius? A) Li B) F C) Na D) Cl
Q.23. Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for N? A) B) C) D)
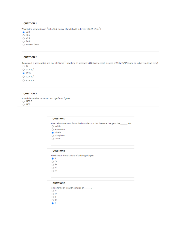
Q.24. Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Br⁻? A) B) C) D)
Q.25. Identify the shortest bond. A) single covalent bond B) double covalent bond C) triple covalent bond
D) all of the above bonds are the same length
Q.26. What is the name of Ca(ClO4)2? A) Calcium chlorate B) Calcium chlorite
C) Calcium perchlorate D)Calcium hypochlorite
Q.27. According to VSEPR theory, repulsion between electron pairs in a valence shell decreases in the order:
A) lone-pair – lone-pair > lone-pair – bond-pair > bond-pair – bond-pair
B) bond-pair – bond-pair > lone-pair – bond-pair > lone-pair – lone-pair
C) lone-pair – lone-pair > bond-pair – bond-pair > lone-pair – bond-pair
D) bond-pair – bond-pair > lone-pair – lone-pair > lone-pair – bond-pair
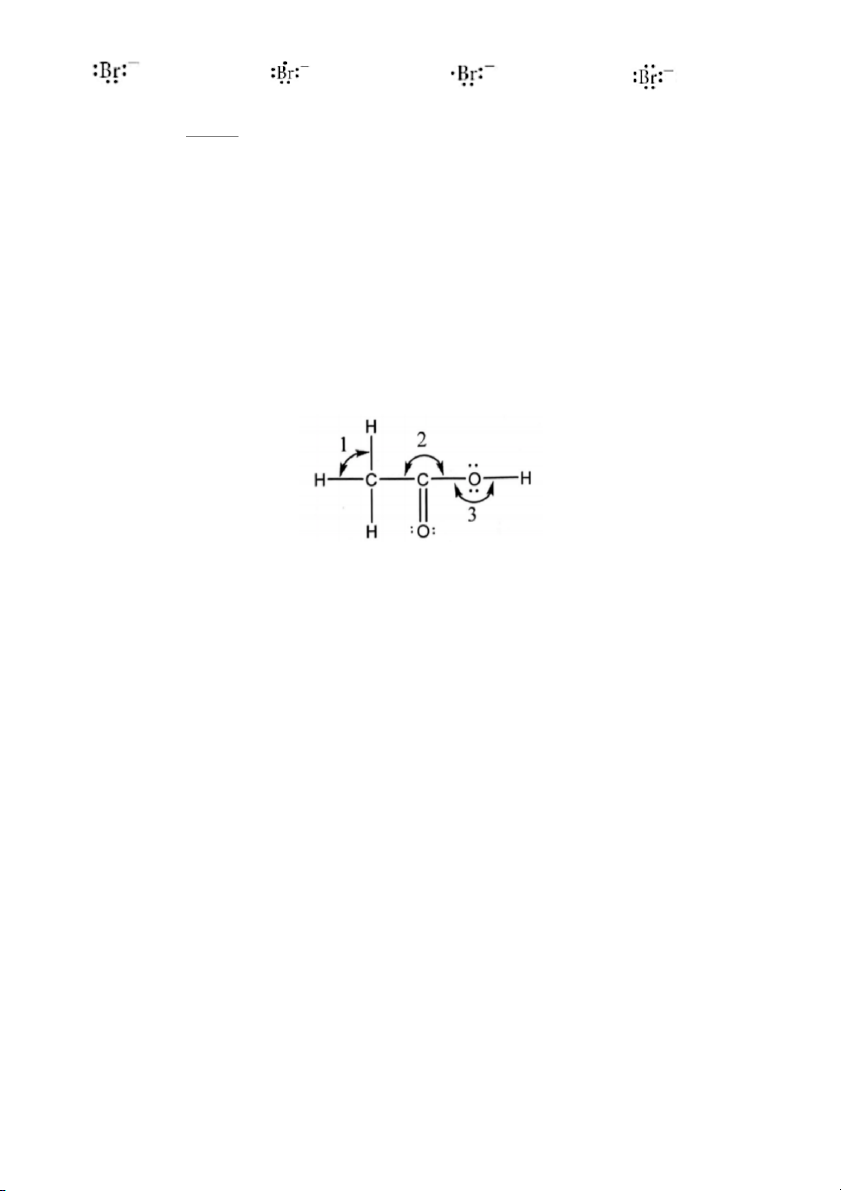
Q.28. A molecule has the Lewis structure given below:
What are the ideal values of the bond angles labeled 1, 2, and 3? A) 109.5°, 120°, 120° B) 109.5°, 109.5°, 120° C) 109.5°, 120°, 109.5° D) 120°, 109.5°, 120°
----------TO BE CONTINUED----------
PART 2: CONSTRUCTED ANSWER QUESTION (20 pts) A. (10 pts)
a) (4 pts) Complete the following table (all empty) in both rows: Symbol Number of Number of Number of atomic mass number protons electrons neutrons number 46 60 K+ 18 20 2 2 4 13 10 14
b) (3 pts) Give the full electron configurations of the following elements and ions: Seq. Atom/ion Full electron configurations 1) Ti2+ 2) S 3) I-
c) (3 pts) An element has four naturally occurring isotopes with the masses and natural abundances given
here. What is the atomic mass of this element? Isotope Mass number Mass (amu) Natural Abundance (%) 1 54 53.9396127 5.845 2 56 55.9349393 91.754 3 57 56.9353958 2.119 4 58 57.9332773 0.0282
Mass = 53.9396127x0.05845 + 55.9349393x0.91754 + 56.9353958x0.02119 + 57.9332773x0.000282
= 3.153 + 51.323 + 1.206 + 0.0163 = 55.698 amu B. (10 pts)
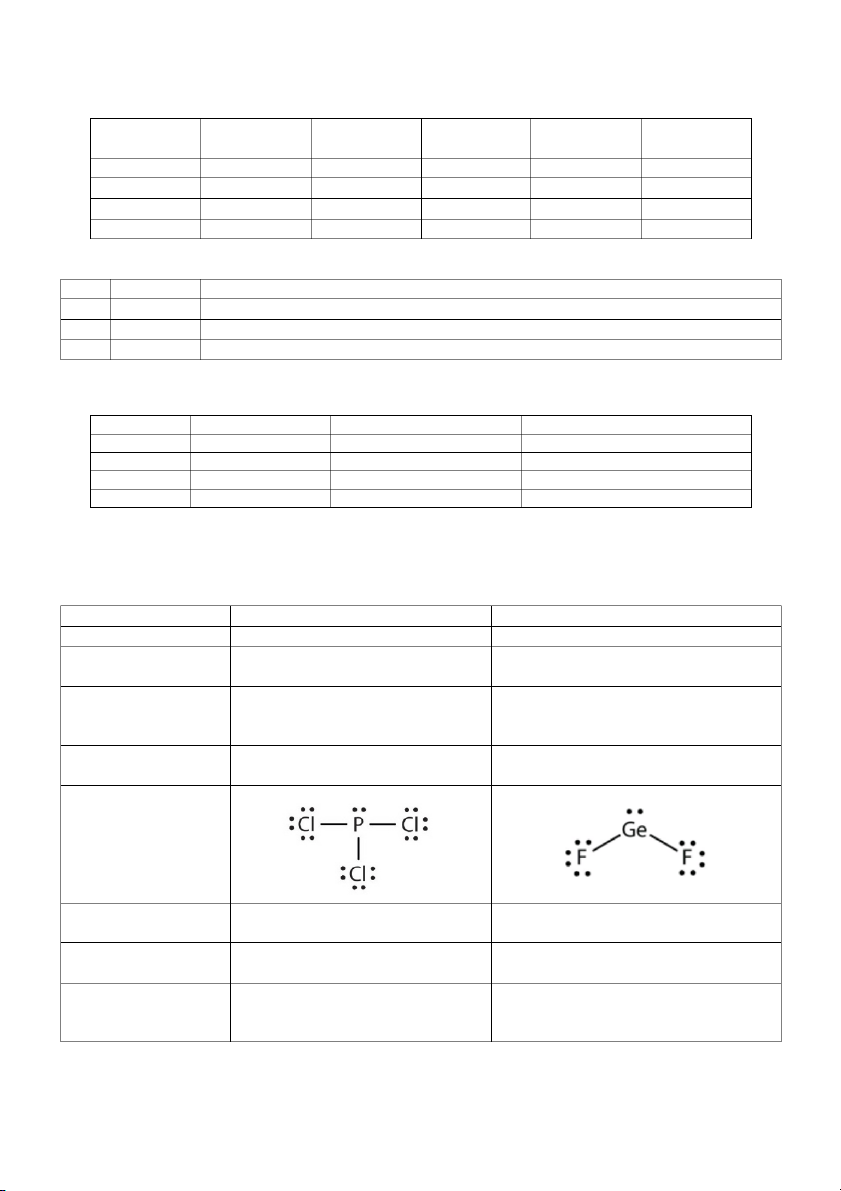
a. (8 pts) Complete the empty box to draw structure of PCl3 and GeF2 Chemical Formula: PCl3 GeF2 Central atom (1pt) P Ge Total number of 26 18 valance electron (1 pt) Total number of electron pairs (electron 8 6 domains) (1 pt) Total number of lone 1 1 pairs (1 pt) Lewis structure (1 pt) Molecular geometry Trigonal pyramidal Bent (1 pt) Molecular polarity Yes Yes (yes/no) (1 pt) Ideal bond angle of Cl-P-Cl or F-Ge-F (1 109.5° 120° pt)
b. (2pts) Is bond angle of Cl-P-Cl smaller or larger than ideal bond angle? Explain?
The bond angle of Cl-P-Cl will be smaller than ideal bond angle. This is because in PCl3 the lone pair on
the phosphorus pushes the P-Cl bonding electrons away from itself. This lone pair electron is more spread
out in space than a bonding electron pair because a lone pair is attracted to only one nucleus while a bonding
pair is attracted to two. The lone pair occupies more of the angular space around a nucleus, exerting a
greater repulsive force on neighboring electrons and compressing the P-Cl bond angles. Hence, actual bond
angle of Cl-P-Cl is smaller 109.5° angle.
C. Consider these elements: K, Cl, P, Ca, Si.
a. (2 pts) Write the electron configuration for each element.
b. (2 pts) Arrange the elements in order of decreasing atomic radius. Explain!
c. (2 pts) Arrange the elements in order of increasing ionization energy. Explain!
d. (4 pts) Use the electron configurations in part A to explain the differences between your answers to parts B and C. b.
In order of decreasing atomic radius: K > Ca > Si > P > Cl. Explain: atomic radius decreases across a
Period, and increases down a Group. c.
In order of increasing ionization energy: K < Ca < Si < P < Cl . Explain: The ionization energy increases
across a period but decreases down a group. d.
Atoms that have different numbers of electron shells:
According to Coulomb’s law, the larger distance the higher the attraction force. Therefore, the atom which
has a bigger radius (more electron shells) requires smaller energy to remove an electron. In other words, it has lower ionization energy.
Atoms that have the same number of electron shells:
According to Coulomb’s law, the greater the nuclear charge the stronger the attraction between the nucleus
and the electron. Therefore, in a period, the atoms that have more valance election require higher energy to
remove an electron. In other words, it has higher ionization energy. END.