

Preview text:
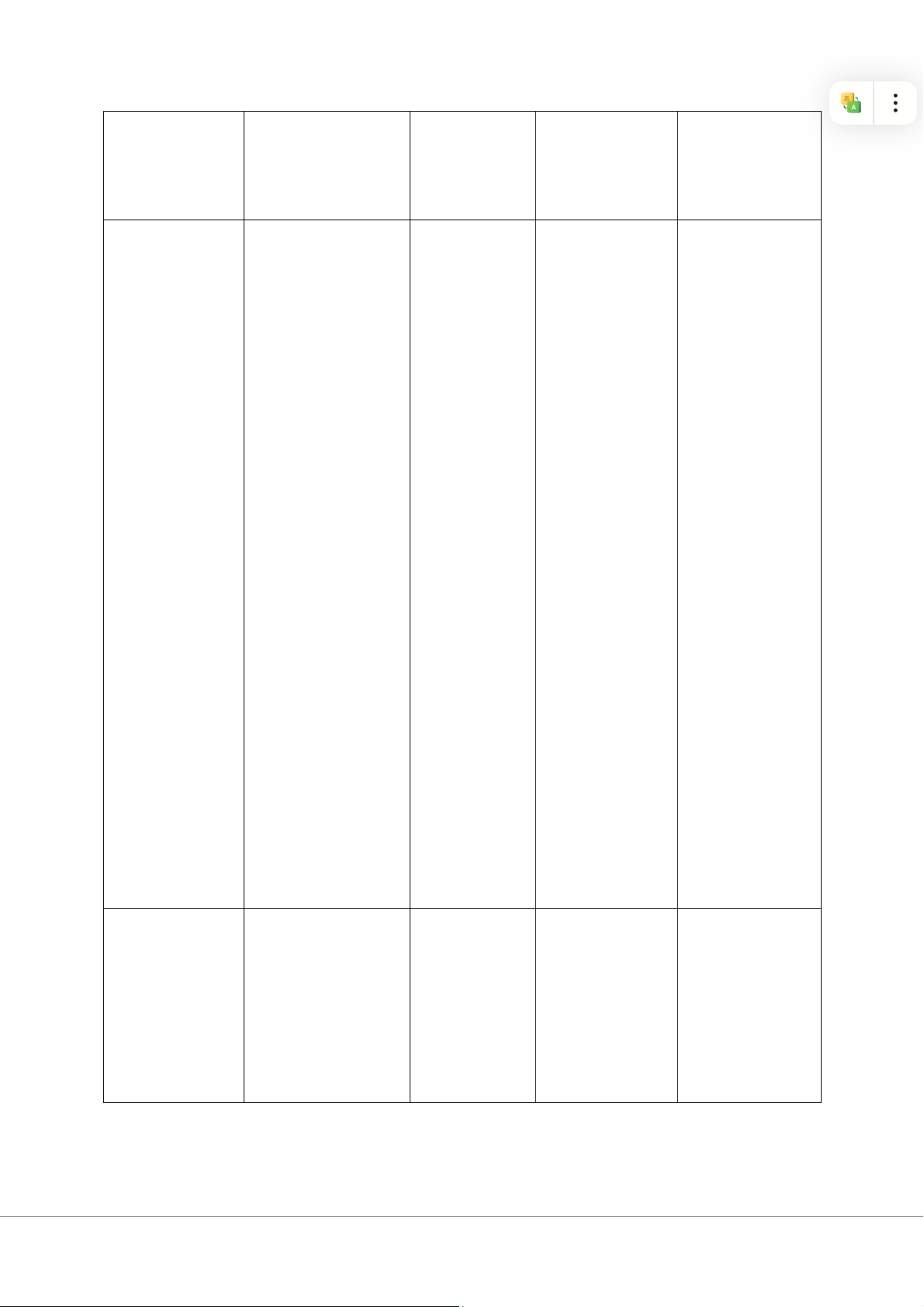
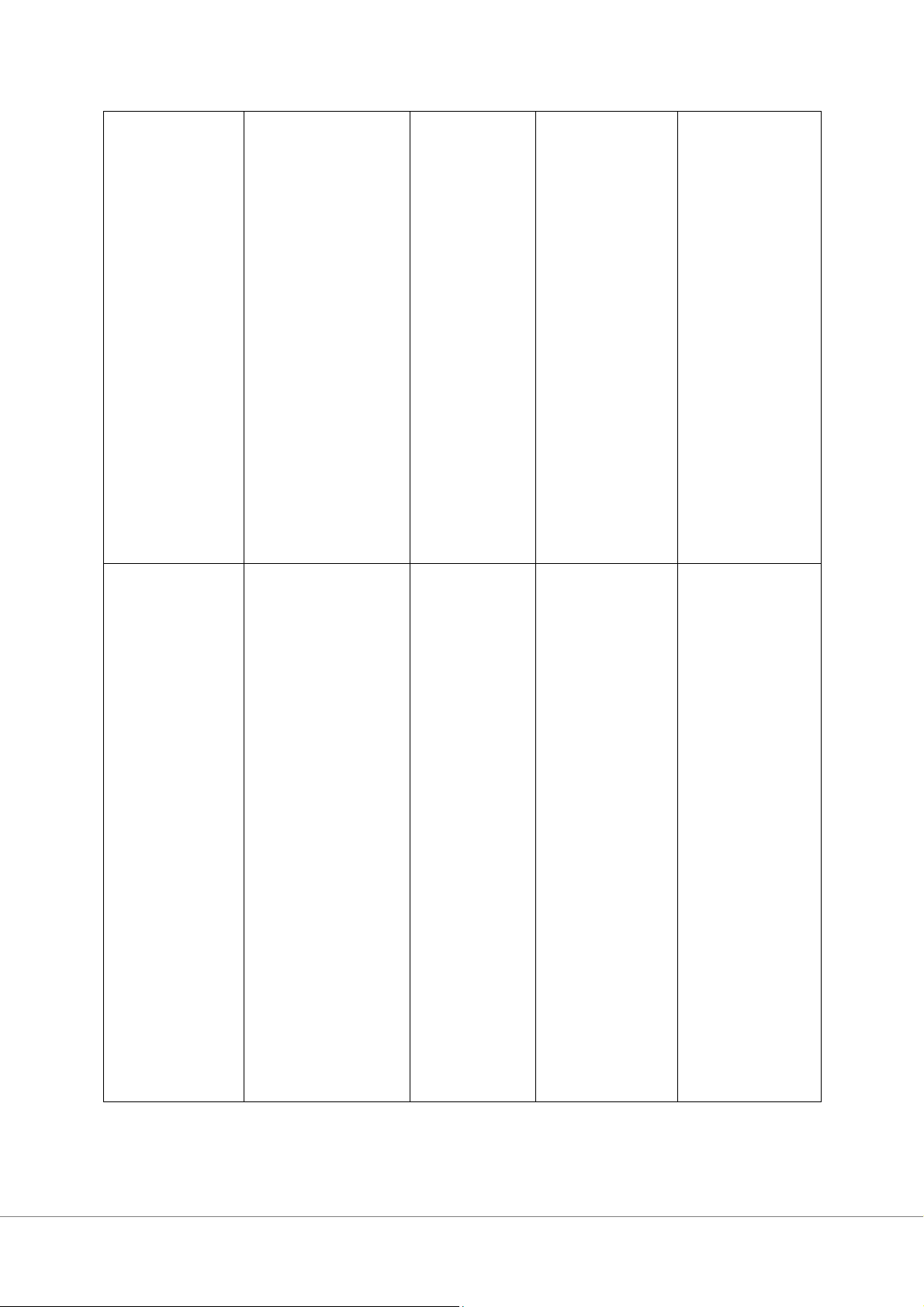
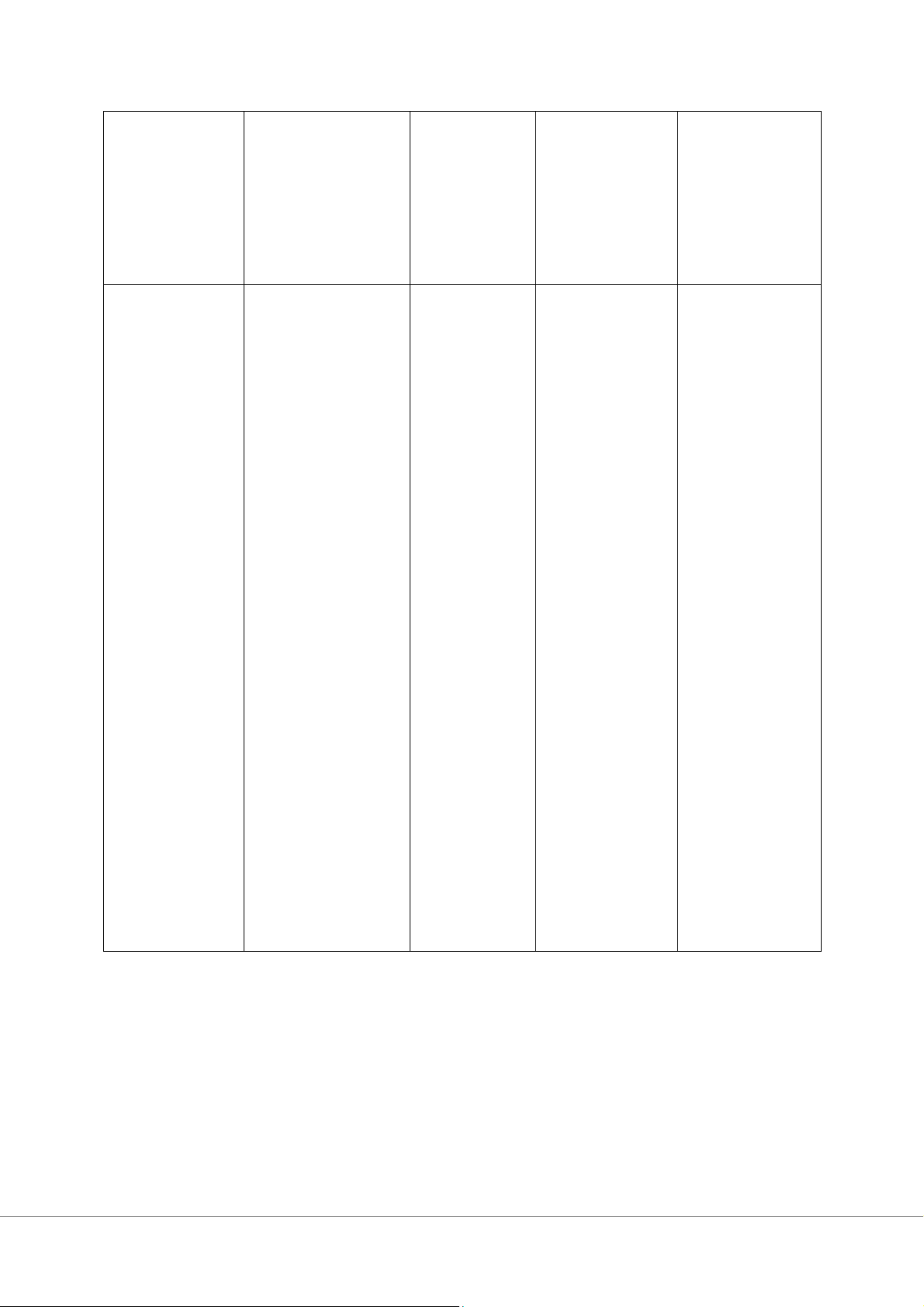
Assumptions / Context What the Employee Beliefs manager behaviour
does (A – changes (B causes) – effects) Maslow’s - Employees are Ms. Trang - Provides - Staff show Hierarchy motivated by a supervises stable up more of Needs hierarchy of a café minimum regularly needs, from where staff monthly because basic needs to feel income and financial higher stressed fair shift stability psychological due to distribution reduces and self- unstable (physiologica stress. fulfillment income, l & safety). - Team needs. lack of - Organizes bonding - Once a lower- teamwork, short after- sessions level need is and no shift increase met, higher- opportuniti gatherings cooperation level needs es for every during busy become growth weekend hours. stronger (social). - Awards motivators. - Creates a boost “Best Service confidence Attitude” and motivate award employees to (esteem). treat - Allows customers passionate better. baristas to - Baristas design new involved in seasonal creating new drink recipes drinks show (self- more actualization) initiative and . creativity during work. 2. - Employees Mr. Khánh - Improves - Employees Alderfer’s can pursue manages a break-room feel ERG Theory multiple needs warehouse facilities and physically (Existence at the same team that provides more – time. feels bottled water comfortable Relatednes - If higher-level discourage during hot and show s – Growth) needs (growth) d because shifts fewer are blocked, career (Existence). complaints. employees may advanceme - Sets up - Team focus back on nt is slow. weekly team discussions lower-level discussions reduce small needs to improve conflicts, (existence, communicati making relatedness). on operations (Relatedness smoother. ). - Job- - Lets shadowing interested opportunities employees reignite shadow motivation, supervisors making to develop employees leadership more skills proactive and (Growth). reducing frustration from slow promotion cycles. 3. - Employees Ms. Thảo - Gives the - The McClelland’ differ in leads a achievement achievement- s Acquired dominant customer -focused driven Needs needs: service employee employee Theory + nAch = center with challenging solves cases achievement staff who cases and faster and + nPow = perform target-based exceeds power differently bonuses targets + nAff = depending (achievemen consistently. afÏliation on their t). - The power- - Matching personalitie - Assigns the driven tasks to the s. power- employee dominant need focused becomes increases employee to more motivation and mentor new confident performance. trainees and and lead weekly organized, briefings improving (power). team - Pairs the discipline. afÏliation- - The focused afÏliation- employee to driven handle employee customer maintains satisfaction warm calls and communicati follow-ups on with (afÏliation). customers, boosting satisfaction ratings. 4. - Hygiene Mr. Quân - Updates - Complaints Herzberg’s factors prevent manages a design about Two-Factor dissatisfaction small software and equipment Theory but do not graphic clarifies and workflow (Hygiene create true design workload decrease Factors & motivation. team that policies to immediately. Motivators) - Motivators recently reduce - Designers (achievement, complained complaints become recognition, about (hygiene). more responsibility) outdated - Assigns engaged and generate higher software designers to enthusiastic satisfaction and and different due to varied better repetitive types of assignments. performance. tasks. creative - Recognition projects and boosts pride, highlights leading to outstanding more designs in innovative monthly and higher- meetings quality (motivators). design work. - Lets senior - utonomy designers strengthens propose new commitment design and guidelines for encourages upcoming designers to campaigns, contribute giving them new ideas. autonomy.




