Preview text:
HANOI NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION FINAL EXAM
Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics Math Softwares (MATH 245E) Duration: 90 minutes
Problem 1. Let f and g denote functions defined on some set A. Prove that
sup (f (x) + g(x)) ≤ sup f (x) + sup g(x). x∈A x∈A x∈A
Problem 2. Sketch the graph of the function x2 y = f (x) = . x2 − 1
Make sure that your graph clearly indicates the following:
The domain of definition of f (x).
The behaviour of f (x) near the points where it is not defined (if any) and as x → ±∞.
The exact coordinates of x- and y- intercepts and all minimas and maximas of f (x).
Problem 3. Compute the following integral: Z 1 x2 + 1 I = dx. x + 1 0
Solution. By long division of polynomials, x2 + 1 = (x + 1)(x − 1) + 2. Thus we can rewrite
our integral as a sum of two terms as follows: Z 1 (x + 1)(x − 1) Z 1 2 Z 1 Z 1 1 I = dx + dx = (x − 1)dx + 2 dx x + 1 x + 1 x + 1 0 0 0 0 1
= x2 − x + 2 ln(x + 1) = 2 ln 2. 0
Problem 4. Use Geogebra to draw the diagram for the following problem:
Consider the circle (C), and let KL and KN be tangents to the circle, with L and N lying on
the circle. Take a point M anywhere on the line KN (M and K on different sides of N ).
Assume that the circle (C) intersects the circumcircle of triangle KLM at a second point P .
Let Q be the foot of the perpendicular dropped from N onto M L. Prove that \ M P Q = 2 \ KM L.
Problem 5. For each of the piecewise-defined functions, (a) sketch the graph, and (b) evaluate
at the given values of the independent variable. x2 − 3 x ≤ 0 f (x) = . Find f (−4), f (0), f (2). 4x − 3 x > 0 x + 1 x ≤ 5 g(x) = . Find g(0), g(π), g(5). 4 x > 5
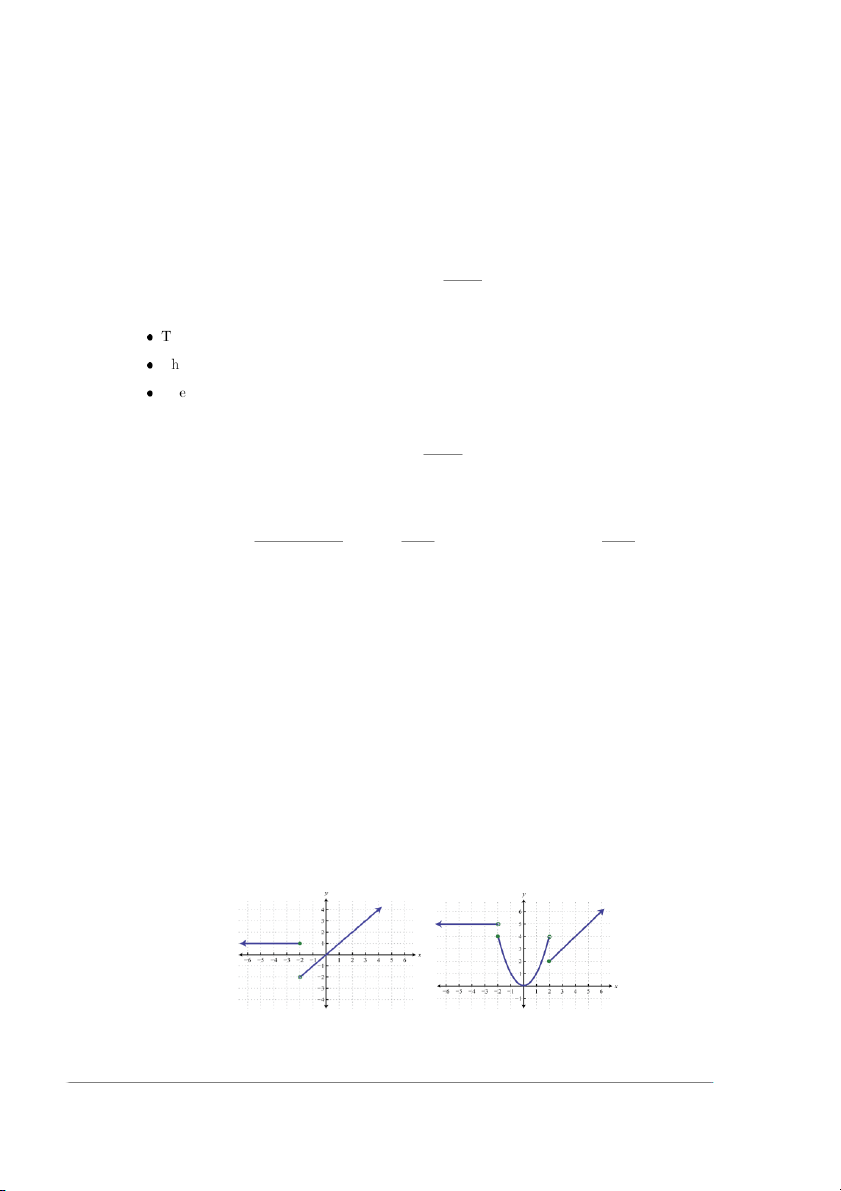
Problem 6. (a) Evaluate piecewise function values from a graph. (b) Construct a piecewise
function corresponding to the graph. Find f (−4), f (−2), f (0) Find g(−3), g(−2), g(2) 1




