









Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW ON ECONOMICS OF INVESTMENT CHAPTER 2:
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ON INVESTMENT AND ECONOMICS OF INVESTMENT
Concept And Classification Of Investment Concept: o The sacrifice of current
consumption to increase future consumption (for profit generating projects only)
o The output accumulated to increase production capacity in the later period of the economy o Classification:
o Private Investment (I): equipment, factory, new ofÏce, inventory
(profit seeking) o Government Investment (Gi): government spending, government
expenditure or perodic government payments to supply public good (social + profit)
Investment is the use of capital to gain profits and/or socio-economic benefits o Private
Investment: profit, sales, market share
o Public Investment: economic-social efÏciency (employment, new asset, tax or income distribution,....) Classification
- Based on the nature of object o Fixed capital formation (new factoies,
machineries,..) o Financial Assets o Intangible Assets
- Based on sector of investment: Investment in business operation, investment on Tech/R&D
- Based on the feature of investment target o Basic investment to reproduce
fixed assets o Operational investment to create current assets
- Based on investment for social reproduction process o Investment for
commerce o Investment for production
- Based on time duration o Short term investment (<1 year) o Longterm investment (>5 year)
- Based on the relationship among investors:
o Indirect Investment: investors don’t manage or supervise the project
o Direct Investment: investors manage or supervise the project
M&A: not new asset formaetion Investment for development
- Based on the result of investment for development o Increasing tangible
assets: factories, equipment o Increasing intellectual capital: expertise o
Increasing intangible asset: copyright
- Based on national scale o Investment by domestic capital (focus on this for sustainable developement)
o Investment by foreign capital lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
Objectives of Investment - For investors:
o Private Investors: Profit, market share, development etc o State agencies: profit anf social economic targets - For the government:
o Economic targets (collect more taxes from new businesses, increase budget)
o Social targets (invest in human resources to increase productivity and value added)
o Environmental targets (too costly but have to achieve to obtain the 2 above) (cptpp and
eudr) (restrict all fields)(too costly doanh nghiệp dùng ít tiền hơn trong việc sản xuất) Features:
- Capital: Tangible and Intangible
- Profitability: the main target
- Risk: Investment may be implemented in long term - Time duration
- Being implrmented via the formation of projects
Return of Individual Investment - Profit and business - Profit from hiring property - Income from copyright
- Return from financial assets - Income from KOL
Impact Of Investment For Development On Economic Growth And Development
- Investment adds to the stock of capital
- The available capital is the determinant of production factor
Investment is the source of economic growth Y = L* x K* x A Sp: Saving in Private sector Ảnh 2 Ảnh vvv
Incremental Capital Output Ratio ICOR
- Incremental capital-output ratio (used for a country, while ROI used for a project) o ICOR: an
additional unit of capital or investment needed to produce an additional unit of output k o For
a given year: ICOR=g, k is the growth rate in capital; g is the growth in economics (GDP) o K is
like stock, I is a flow of money lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 ICOR=
Kt−Kt−1 = It =(¿:GDPt)/¿ GDPt−GDPt−1 ∆GDPt o For a period: n ICOR=∑t=1 GDPn−¿GDP0
o Application to economic forecast: Economic growth rate
Demand for investment capital
Economic growth and measures
- Economic growth is the increase in output/value of commodity and service produced by
an economy in a given period - Measures: o GDP:
o GNI: is product produced by enterprises owned by a country’s citizens
o PPPs: the rates of currency conversion that equalize the purchasing power of different
currencies by eliminating the differences in price levels between countries
o GDP or GNI per capita o Economic growth rate: Y t−Y t−1 ¿= x100% Y t−1 Y: norminal GDP Gt: o GDP per capita:
o Income per capita and Income disparity INVESTMENT THEORIES Classical Mercantilist
- Chủ nghĩa trọng thương
- The national output was measured by the supply of money generated, in terms of gold
Gov encourage increase export and reduce imports.
- The goal of these policies was, supposedly, to achieve a “favorable” balance of trade that
would bring gold and silver into the country and also to maintain domestic employment.
- The relationship between the government and merchants was rather complicated o
Governments levied tax for armies and battles among capitalist nations.
o Merchants needed the guarantee of governments to protect them against competition A.Smith ideas
- Free trade benefits both parties lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
- The collusive relationship between government and industry was harmful to the general population
- Three aspects that correlate the division of labor with the increase in productivity, finally
improve economic growth: o Capital accumulation -> the expansion of the market: labor is
specialized actions and wages can increase above the subsistence level with more capital
o The increase in the number + efÏciency of worker
- Investment should be directed towards productive activities -> capital accumulation depends
on allocation between consumption and investment
- The manufacturing sector was a generator of surplus and played a major role, although
agriculture was still of vital importance
Ricardo doctrine
- Growth of agricultural output reinvestment of profit capital accumulation economic growth
- Unluckily, agricultural output faced diminishing return: food price increasing -> grade up salary
that harmed profit of entrepreneurs: o Income division: land rent + wages + profit
- Wages were determined by minimum subsistence level of the workers
- Industrial sector pursued constant return: stock of fixed capital plays an important role in the
growth of output and employment, which are constrained by the operation of diminishing returns in agriculture
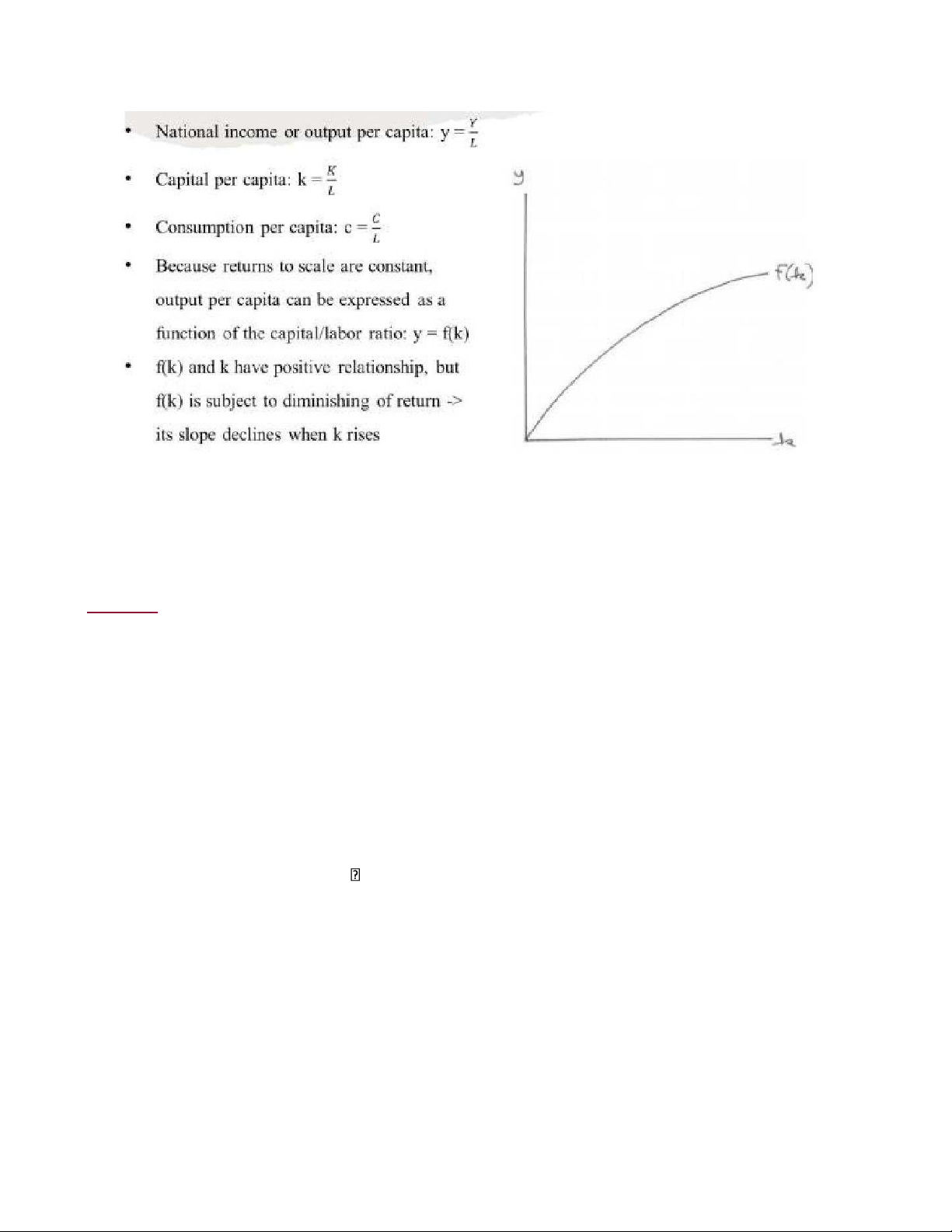
Neo Classical Solow Model - Assumption:
o Full employment, minimal capital stock only 2 factors: labor L and capital K
o All capital and labor are ultilizes in production no redundancy o Capital is subject to
diminisihing returns in a closed economy o (Net) Capital accumulation = saving
accumulation – depreciation o Consumption increase in association with capital
increase until steady state (saturated consumption) K -
National income or outcome per capita = y= L K - Capital per capita: k= L
- y = f(k) là đạo hàm của y = f(K,L) lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
CHAPTER 6: STATE MANAGEMENT ON INVESTMENT CHAPTER 3: INVESTMENT CAPITAL
CONCEPT AND NATURE OF INVESTMENT RESOURCES Concepts
- Capital iss the accumulation in terms of value for investment to adapt the requirements of social development
- Investment resources are capital mobilization and distribution for investment to adapt the
requirements of social development Nature - Idea of A.Smith:
o Savings is direct source for capital acceleration. Labor creates products for saving
acceleration to improve investment
o New value created must be higher than products made in the sector producing
consumer products promoting production
materials and saving in both sectors - Idea of Keynes:
o In closed economy: Saving = Investment
o In open economy: Disposable consumption = C + Sp (private saving) Y – T = C + Sp Y = C + Sp + T Y = C + I + G + X – IM Sp + T = I + G + X – IM lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
I = Sp + T – G – (X-IM) = Sp + Sg – NX (
Investment = Saving + Inflow Capital (IM – X) Investment depends on
foreign sector and net export Implications:
o If Y is near to Yp (potential), Sp and Sg is constant, thus to reduce budget deficit:
Reduce investment (crowding out effect)
NX deterioration (trade deficit) o G increase T to increase Sg, however
reduce income in private sector reduce Sp CLASSIFICATION - FDI:
CHAPTER 4: PLANNING AND MANAGING INVESTMENT PROJECT
Overview of investment project management Concepts:
- A project is a sequence of unique, complex, and connected activities that have one goal
or purpose and that must be completed by a specific time, within budget, and according
to specification o Sequence of activities: activities must be completed in a specified
order with technical requirement - Characteristics:
o Specified goal o Unique and unrepeated o Human’s proactive interference o
Risk and uncertainty o Budget/cost and time constraint - Requirements: o Legal status
o Scientific and systematic requirements o Practical requirement o Standardized
requirement o Estimation - Classification: o According to the investor Private Project
Collective Project: having to satisfy all stakeholders National
International o According to the nature Production project
Infrastructure, social projects
- Scope: Project scoping o Based on demand: market demand for project's products, demand prospect
o Based on supplier: current suppliers and the threat of output increase
o Based on participants: the competences of participants
• Note: the compatible project with investor's strategy - Participants:o Clients
o Project managers and core members o Facilitators - Plan: o Requirement
The project fits social-economic development policy
Promising market for project’s output and low competition
High financial and social-economic efÏciency Investor’s affordability lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 High feasibilty o Benefits: Reduction of uncertainty Increase of understanding
EfÏciency improvement o Building work breakdown structure WBS
o Estimating: time duration, cost, resource requirement, and task duration
o Constructing the project network diagram o Writing an effective project approval Executive summary Background Objectives Approach to be taken
Detailed statement of the work
Time and cost summary o Launch project
Recruiting project team members
Developing team deployment strategy
Conducting the project kick-off meeting
Establishing rules of team operation Managing scope changes Managing team communication Assigning tasks -
Monitoring and controlling project o
Establishing progress reporitng system o
Applying graphical reporting tools (Gantt chart,..) o Building the scope bank
o Building and maintaining the issues logs
Project Constraint (ảnh) Project Evaluation 1. Investors - Name - Representatives - Head ofÏce - Product line
- Enterprise establishment license
2. Application for business registration - Law 3. Product
- Product: name, trademark, specifications, output - Market:
o Supply-demand Survey and market forecast lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
o Comparisons among similar products (in terms of function) sold in the market or on- production o Cross border trading Output and market
5. Technology, machinery and environment 6. Production demand
7. Sites and location, construction
8. Organizational structure, management and salary
9. Project implementation progress
10. Investment capital structure by year 11. Financial analysis 12. Social-economic outcomes
13. Self-evaluation and recommendations Important Decisions - Investment decisions - Financing decision
- Asset management decision o Cash management o Inventory management o Receivables management
Determining capital resources for investment project
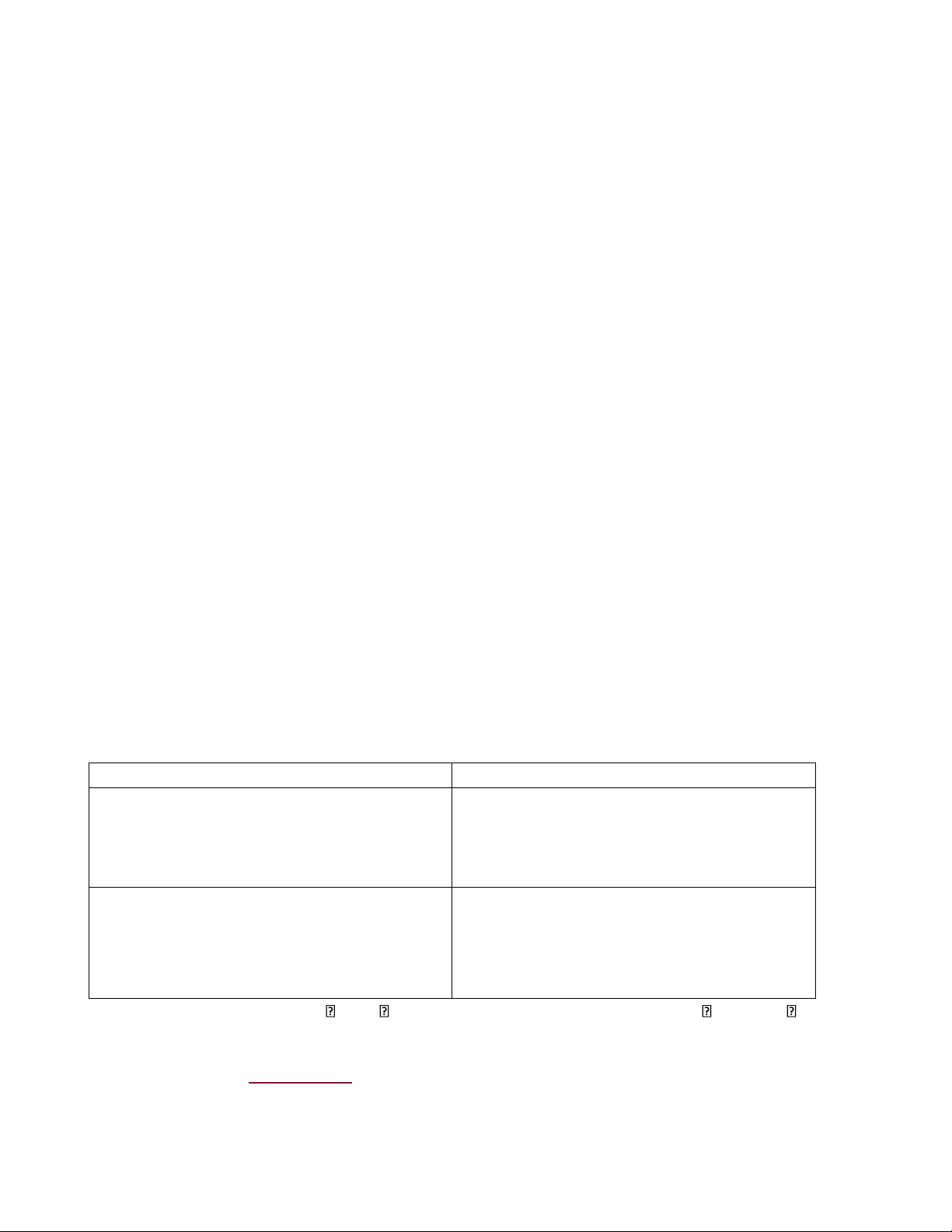
Investment capital is resources used in business and production for investor’s profit-seeking and/or social development target Assets Liabilities and equity Current assets: Owner equity - Inventory - Cash - Recievables Fixed Assets Liabilities: - Tangible - Payables - Intangible - Shortterm liabilities - Financial
- Medium and long-term liabilities
Cash inflows + Sold receivables Cash Cash outflows, Pays (materials, salary,...) Products Cash inflows,...
Investment Capital Components: lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
- Opinion 1: fixed capital and working capital o Fixed capital: is fixed assets of the project in
terms of money o Working capital: is current asset of the project in terns of money o Asset features: Being controlled by enterpol Gonaruting future benefit
Bring con calcalation o Distinguishing fixed and working capital
- Opinion 2: Fixed capital and demand for working capital
Working capital requirement = Inventory + Receivables – Payables
Determination of investment capital
- Owner equity: capital stock (common share, preferential share) and retained profit
- Share issuance: with diversified types (IPO, priority to buy shares, dividend in form of share)
- Credit: corporate bond issuance, commercial borrowings
- Leasing (thuê tài sản) - Note:
o Selecting investment capital resource depends on: risk, ownership, futare cash flow,
possibility of capital mobilization CASH FLOW
Based on P&L statement, balance sheet, financial statement etc., cash flow can be calculated as: Initial investment: - Buying fixed asset (-)
- Financing working capital (-) - Other expenditures (+, -) Business operation - Revenue (+)
- Cost (-), corporate income tax (-)
- Depreciation (+), interest payment (+) because cost covers both Depreciation and interest
payment, thus, in the cash flow they are not included
- A Working capital requirement (±) - Net profit (+) Project closing:
- Liquidation of fixed asset (+) (thanh lý fixed assets)
- Payback of working capital requirement (+)
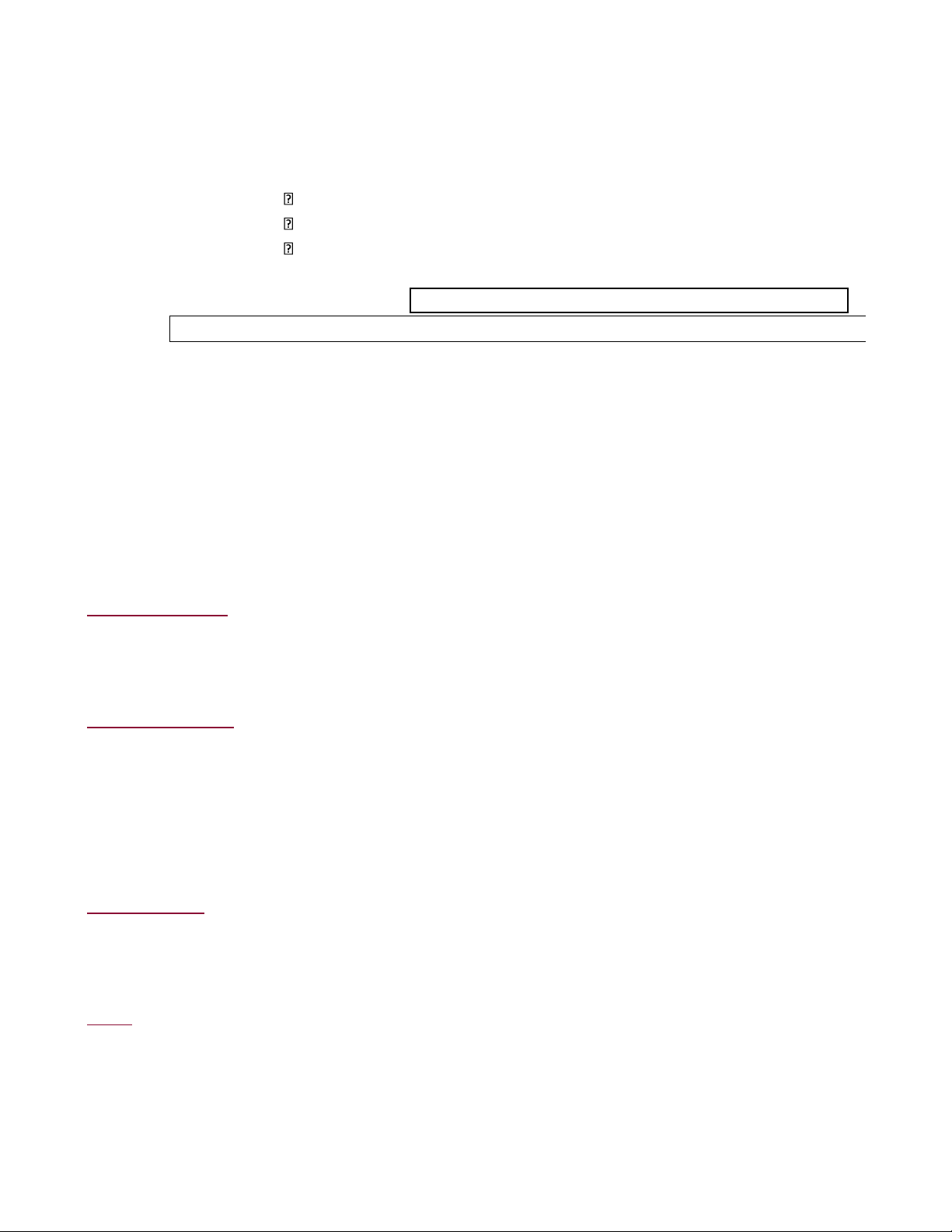
- Other expenditure and incomes (±) Ví dụ:
Tổng vốn đầu tư của DN A là 40.000 USD, trong đó 30.000 USD đầu tư mua sắm tài sản cố định, còn lại
để trang trải nhu cầu vốn lưu động. Dự kiến dự án tiến hành trong 5 năm. Tài sản cố định của dự án
được khấu hao đều và khấu hao hết trong 5 năm. Doanh thu hàng năm của dự án là 50.000 USD, tổng lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
chi phí hàng năm (chưa kể chi phí khấu hao) là 20.000 USD. Thuế thu nhập doanh nghiệp mà công ty
phải nộp sẽ có thuế suất là 20%. Hãy lập dòng tiền hàng năm của dự án này. Ví dụ 2:
A purchase of fixed capital valued up to VND 800 million (in pre-investment period and even
depreciation within 10 years, after 10 years it can be sold with the price of VND 100 million). Working
capital requirement is equal to 10% of revenue (must be prepare in previous year):
Revenue: 1000; 1200;1400; 1600; 1200; 1200; 1200; 1200; 1200; 1200.
Yearly estimated cost (including Depreciation): is equal to 80% of yearly revenue Corporate income tax: 20%
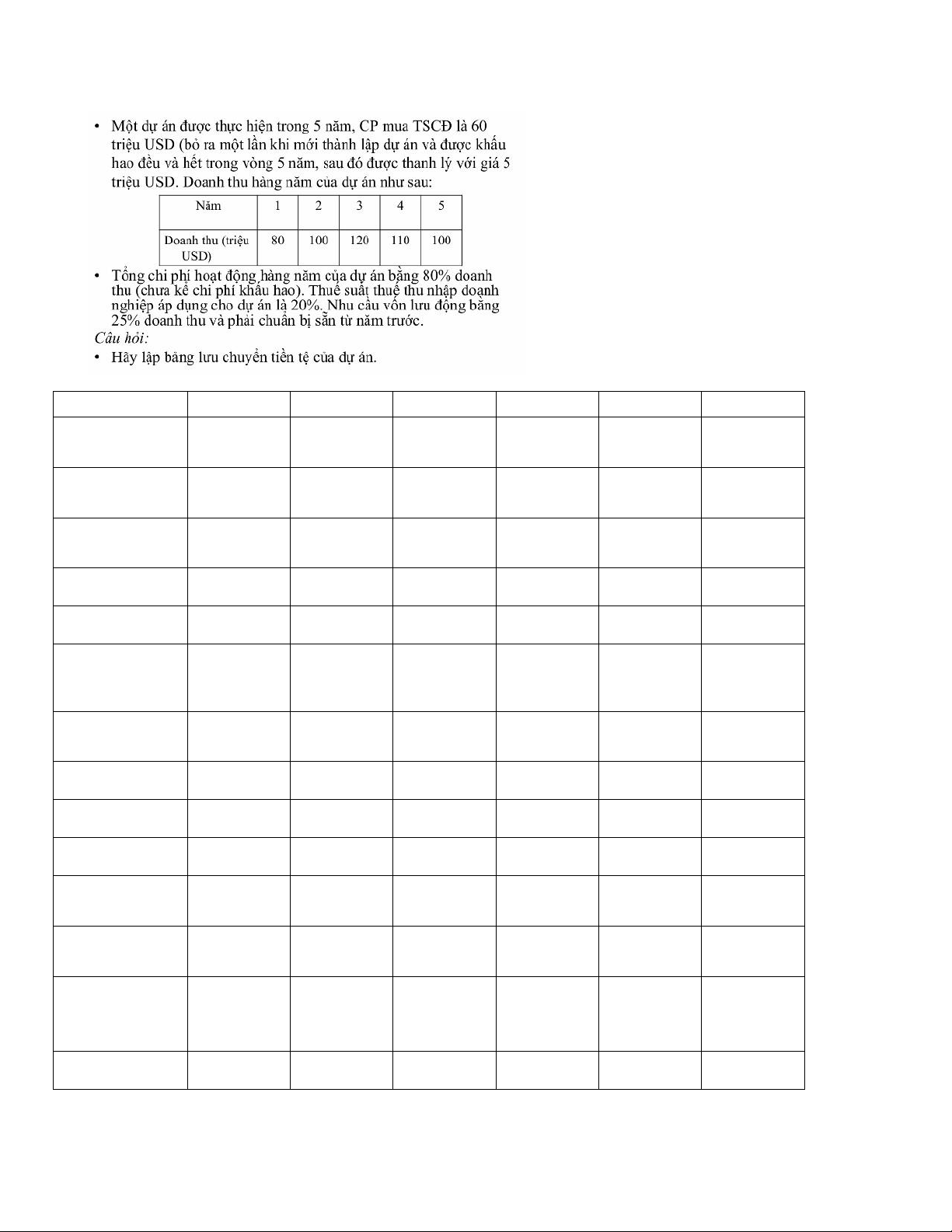
1. Estimate cash flow statement Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Pre-investment Buying fixed -800 assets Financing WCR Other expenditu re Project deployment lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 + 10 120 140 160 120 120 120 120 120 1200 Revenue 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 + Cost - -960 - - -960 -960 -960 -960 -960 -960 80 112 128 0 0 0 + Depreciat +8 +80 +80 +80 +80 +80 +80 +80 +80 +80 ion 0 Profit 20 240 before tax 0 +Tax -40 -48 -56 -64 -48 -48 -48 -48 -48 -48 WCR -100 - -140 -160 -120 -120 -120 -120 -120 -120 12 0 Net WCR -100 -20 -20 -20 40 0 0 0 0 0 Closing Fixed Asset 100 liquidatio n Payback of 120 WCR Tax on -20 Fixed Asset liquidatio n CF -900 22 252 284 376 272 272 272 272 272 472 0 Example 3: lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 Buying fixed assets Financing WCR Other expenditure + Revenue + Cost + Depreciatio n Profit before tax +Tax WCR Net WCR Fixed Asset liquidation Payback of WCR Tax on Fixed Asset liquidation CF lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
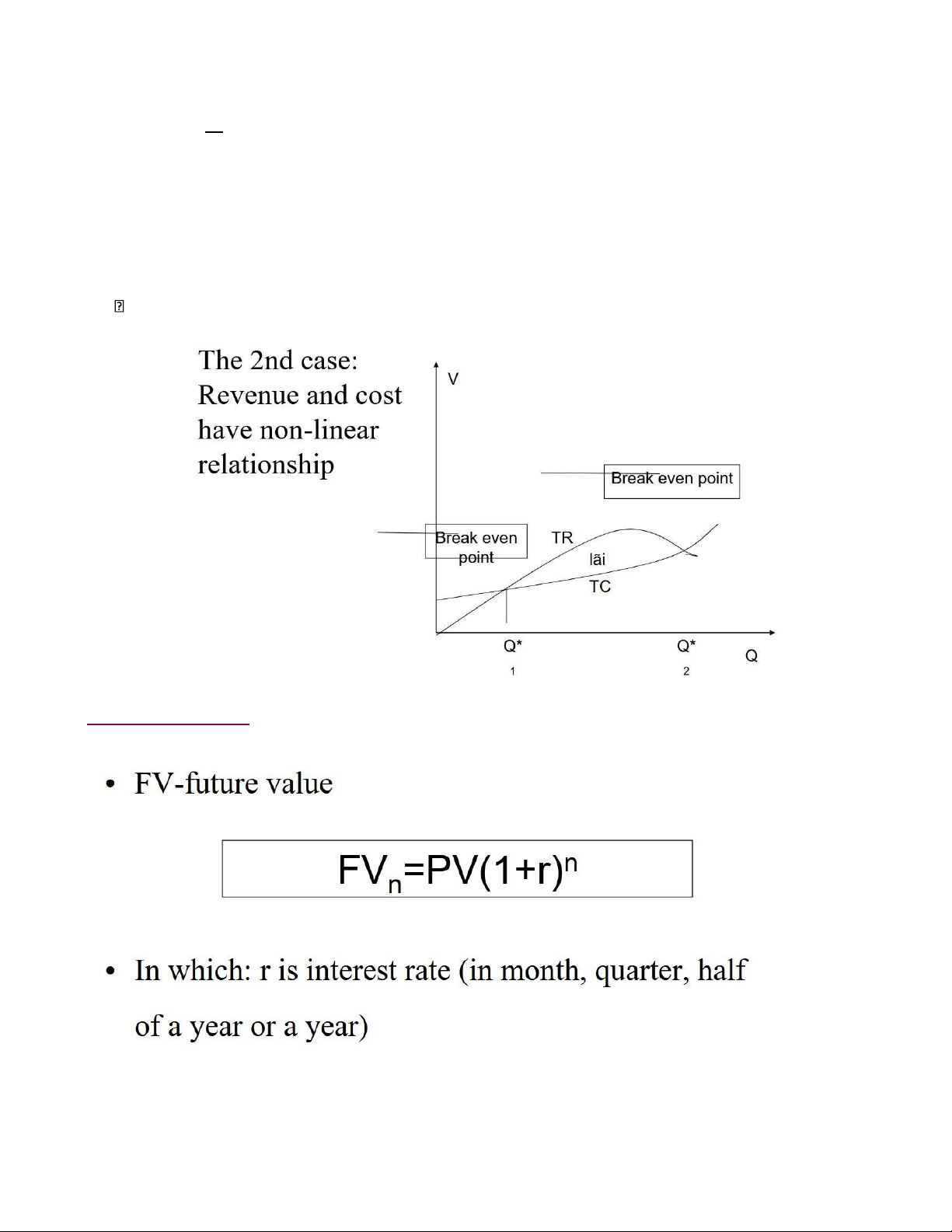
CHAPTER 5: INVESTMENT EFFICIENCY
Concept of investment efÏciency
- Investment efÏciency or project efÏciency is the net outcome measured by
investment’s gain and cost - 2 approaches:
+ Private sector: Financial effciency, sometimes social-economic efÏciency
+ Public sector: social-economic efÏciency Financial efÏciency Non-discounted cash flow lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 Case study
The value of a project is up to USD 30 million, USD 20 million of which is for fixed asset being evenly
and fully depreciated in 10 years (the duration of project operation). Expected net profit is USD 6
million yearly. Assume that there is no credit for the project.
1. Estimate payback period for this project.
2. If there is a change in the depreciation of fixed asset as follow:
USD 2 million are depreciated by 50% per year, USD 10 million is evenly and fully depreciated in 5 years.
The remain of fixed asset will be evenly and fully depreciated in 10 years.
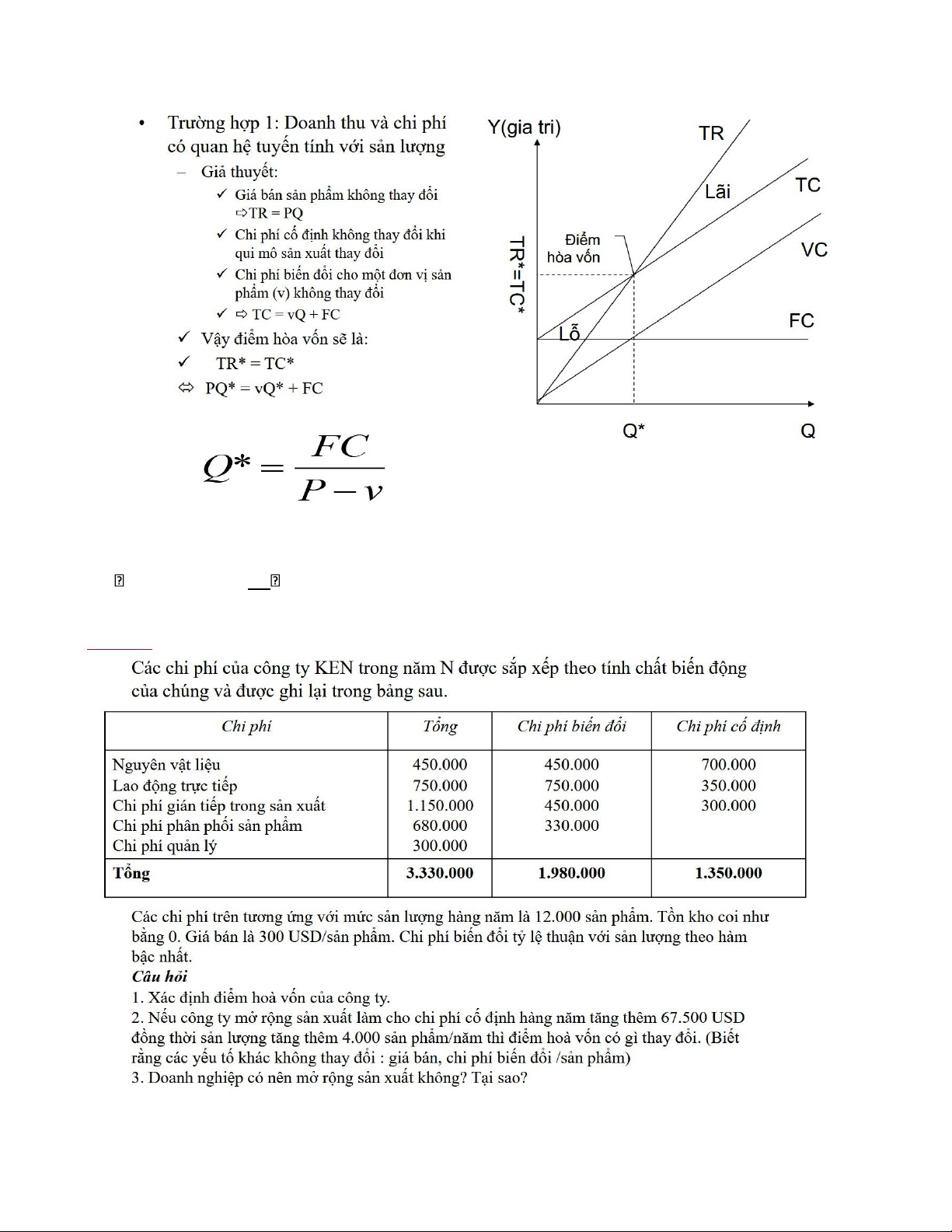
Estimate payback period for this project? Is there any changes in the 2 cases? lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 Break-even point: TC = TR PxQ*=vQ* + FC FC Q*= P−v Example lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 FC
1. Q* = = 1350000/(300- (1980000/12000)) = 10.000 P−v
2. Q* = 1417500/(300-165) = 10.500
Profit ban đầu = TR – TC = 12.000 x 300 – 3.330.000 = 270.000
Profit sau khi mở rộng: TR – TC = 16000 x 300 – (1417500+ 165x16000) = 742.500
Tăng 33.33% sản lượng -> tăng 175% lợi nhuận (bỏ qua) Discounted net flows
Net present value and future value lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 PV = 200 FV = 200 x (1+10%)^5 = 322 Profit = 122 FV = 200 x (1+10%)^5 = 352 Profit = 152
Tổng gốc lãi = 150 x (1+8%)^2 x (1+9%)^3 + (1+11%)^4 = 343.96 Lãi suất trung bình = (8%x2+9%*3+11%*4)/9 = 9.66% lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065
N = 10 periods (tính theo quý) R = 12%/3 = 0.04 FV = 30*(1+0.04)^10 – 44.4
Future value of Annuity (r+1)n−1 FVa=Ax( ) r
Present value of an annuity (r+1)n−1 lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065 PVa=Ax( )
r x(r+1)n
Trả ngay: 55.000 USD Trả góp:
PV = 15000/(1+10%) + 15000/(1+10%)^2 + 15000/(1+10%)^3 +
15000/(1+10%)^4 + 15000/(1+10%)^5 = Investment EfÏciency NPV
NPV as an indicator for investment decision making:
- Independent project : NPV and 0
- Mutually exclusive projects: NPV max
- Budget constraint: Selecting group of projects with highest NPV lOMoAR cPSD| 58540065



