
Preview text:
Module Title OPERATION MANAGEMENT Exam FINAL EXAM Date of Exam 30/4/2022 Lecturer Lam Hoang Phuong Class IBP19D02 Student Name Nguyen Ngoc Han ID Number 110319200008 Total number of pages
(in words: ………………… pages) Exams supervisor 1: Exams supervisor 2: Marks: Examiner: In words: Question 1 (5 marks):
What is layout design? Describe the 4 basic layouts used in production. What are the
advantages and disadvantages of each layout design?
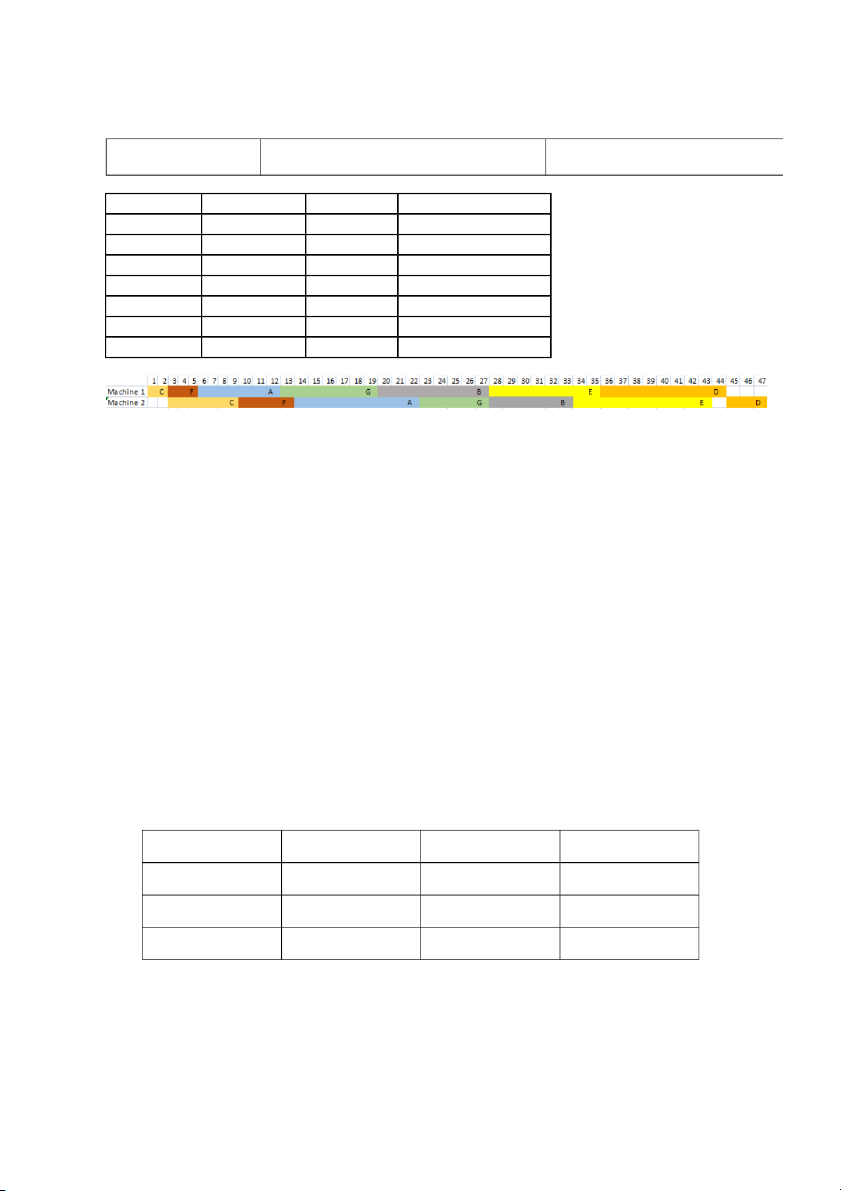
There are 7 items that need to be processed on 2 machines. The time (hours) required for each
item on each machine is as follows: Item Machine 1 Machine 2 A 7 9 B 8 6 C 2 7 D 9 3 E 8 10 F 3 4 G 7 5
Schedule these 7 jobs on 2 machines with the minimum processing time. What is the minimum
processing time for these 7 jobs on 2 machines?
-Layout design: The actual positioning of resources such as equipment and storage facilities is referred
to as layout design. The architecture is intended to make it easier for customers or commodities to
move efficiently through the production or service system.
-There are four basic layout types:
• Fixed-position layout: A fixed-position layout is acceptable for a product that's large or too significant
to transport. Fixed-position layout has high variety, high cost, low volume, high cost of transportation.
So as to form this work, needed resources should be moveable so they will be taken to the work for on-
site execution. Example: doctor performance in the hospital, aircraft manufacturing,..
• Functional layout: In the process layout, all equipment that conduct comparable processes are placed
together. Facilities are classified together based on their functions. Material flow patterns across the
facilities from one functional area to another differ from one product to the next. When the production
volume is insufficient to support a product layout, a process layout is usually employed. Example: baking cake…
• Cell layout: Different machines are grouped in a cellular production arrangement based on the
process requirements for a similar set of products or groups of comparable parts that require similar
processing. This procedure entails identifying pieces with similar characteristics in the context of their
design, such as shape, size, and function.
• Product (line) layout: Product layouts are repetitive assembly. In a product layout, resources are
organized in a sequential order depending on product routing. The line's flow can then be segmented
to ensure that manpower and equipment are used efficiently throughout the process. Line balance is
frequently used to improve product layout efficiency. Type of layout Advantages Disadvantages Functional layout
-Maximum Utilization of Machines
-Higher Material Handling Costs -Changes can be incorporated
-May cause confusion among different group
-The investment in layout can be small
-Capital investment may be high
-Adjustments can be made to meet the
-The time required to finish a job will be
shortage of material or absent of worker longer Fixed-position layout -Allows for more flexibility -Limited Workspace
-The layout requires a small initial cost. -High cost of equipment
-Enhances worker capacities and makes job expansion easier. Cell layout
-Faster processing time, less material handling, -Do not optimize all machines
less work-in-process inventory, and reduced setup time lead to reduce cost
-Long process of training employees
-Allows for the production of small batches, high flexibility
-Work effectively because workers are cross- trained to run every machine Product (line) layout -Produce high-volume
-Less flexibility of physical resources -Highly standardized products
-One part failure will delay the whole process
-Low manufacturing cost per unit - Effective inspection of work
-High investment in specialized machine Item Machine 1 Machine 2 Order C 2 7 1st F 3 4 2nd A 7 9 3rd G 7 5 4th B 8 6 5th E 8 10 6th D 9 3 7th
The minimum processing time for these 7 jobs on 2 machines is 47 Question 2 (5 marks):
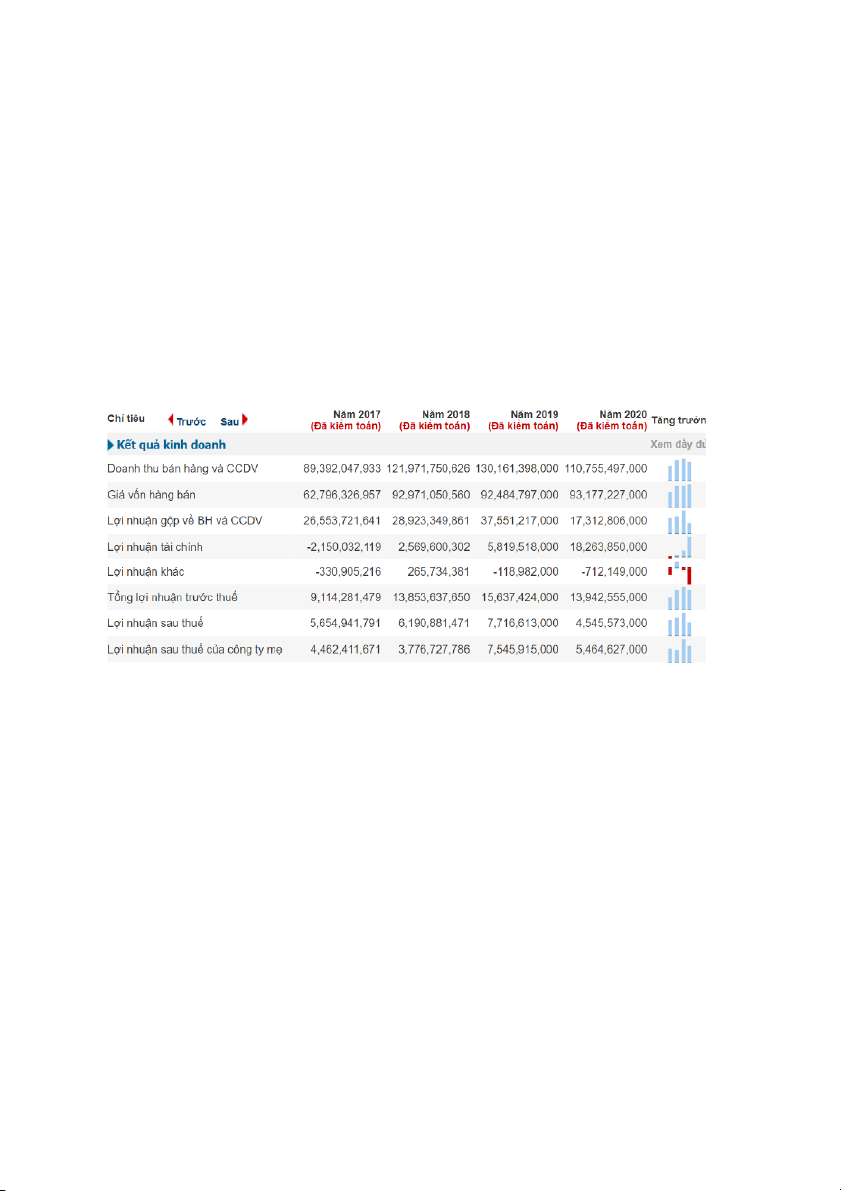
1. Selecting a Vietnamese company listed on HOSE (Ho Chi Minh Stock Exchange). Based on the
annual financial reports of this company from 2017 to 2020, forecasting its revenue in 2021 by using the following method:
a. Simple moving average with n=3
b. Weighted moving average with n=3 and Ht-1=0.6; Ht-2 t-3 =0.3; H =0.1.
c. Exponential smoothing. Given that F1=A1 and Alpha is 0.4.
d. Trend-adjusted exponential smoothing. Given that F1=A1; T1=0 and Alpha is 0.5; Beta is 0.4.
e. Based on the quarterly report in 2020 and forecasted revenue in 2021 (using the simple
moving average method), estimate the revenue of each quarter in 2021.
2. Round up the forecast revenue in 2021 (using the Simple moving average method) to million.
Assuming that the number of products sold is equal to the revenue divided by 10 000 and this
company has 3 factories which can supply 20%; 40% and 40% of total products sold
respectively. The company also has 3 customers that account for 30%; 40% and 30% of the total
products respectively. The delivery cost ($/unit) is as follows: D1 (30%) D2 (40%) D3 (30%) W1(20%) 50 40 30 W2 (40%) 40 50 20 W3 (40%) 30 20 30
a. Find 3 feasible solutions for this transportation problem (using 3 methods).
b. Optimize the solution to find the lowest-cost solution if possible. And what is the lowest cost for delivery?
Instructions: Getting access to the website: cafef.vn. Searching for a company and downloading
the annual financial reports. You are strongly suggested to submit the 4 annual reports from
2017 to 2020 and 4 quarterly reports in 2020 with your assignment as the evidence supporting your data.
1. Vingroup's financial statements
a. Simple moving average with n=3 F2021 = = 120,962,881,875
b. Weighted moving average with n=3 and Ht-1=0.6; Ht-2=0.3; Ht-3=0.1 F2021 = = 117,698,892,663
c. Exponential smoothing. Given that F1=A1 and Alpha is 0.4. F2018 = 89,392,047,933 F2019 = 102,423,929,010 F2020 = 113,518,916,606 F2021 = 112,413,548,764
d. Trend-adjusted exponential smoothing. Given that F1=A1; T1=0 and Alpha is 0.5; Beta is 0.4. F2018 = 89,392,047,933 T2018 = 0 F2019 = 105,681,899,280 T2019 = 16,289,851,347 F2020 = 126,066,574,313 T2020 = 17,927,780,822 F2021 = 127,374,926,067 T2021 = 11,280,009,195 F2021 = 138,654,935,262
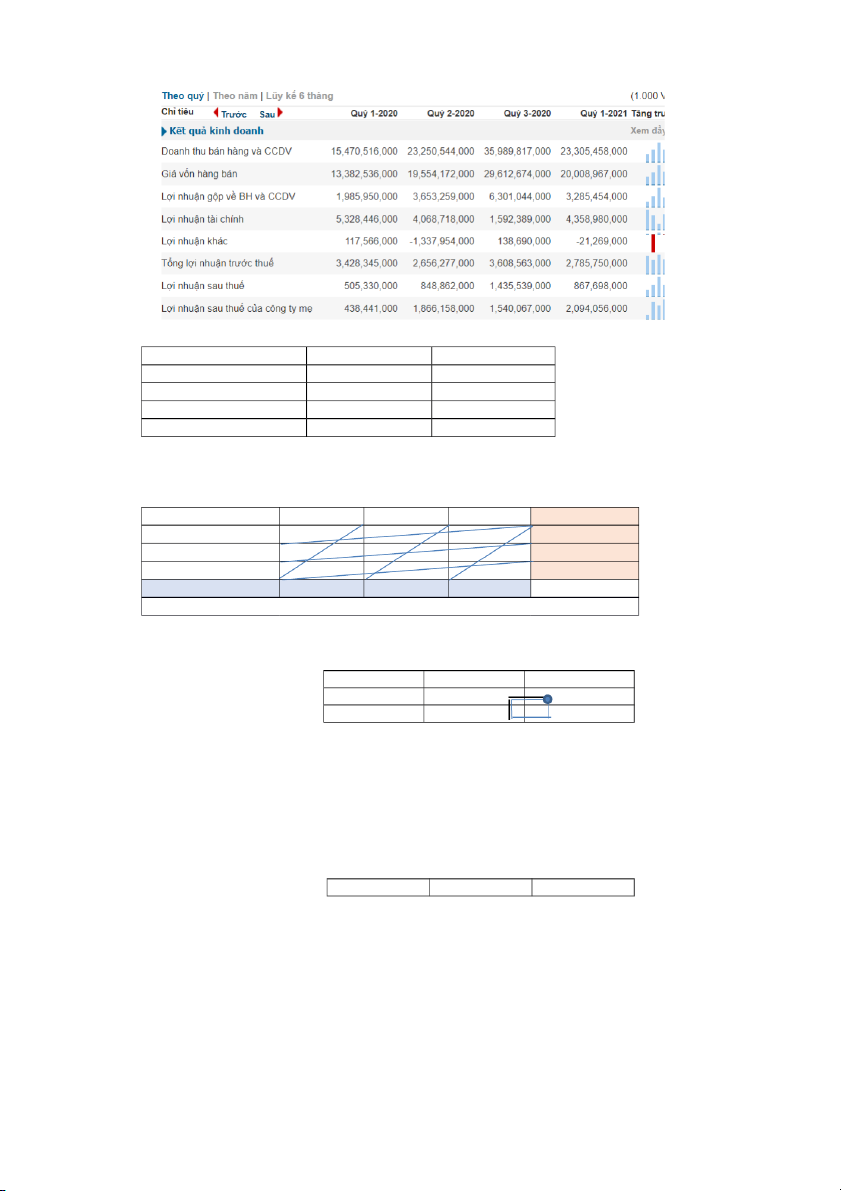
e. Based on the quarterly report in 2020 and forecasted revenue in 2021 (using the simple moving
average method), estimate the revenue of each quarter in 2021. Actual Sales Average Sales
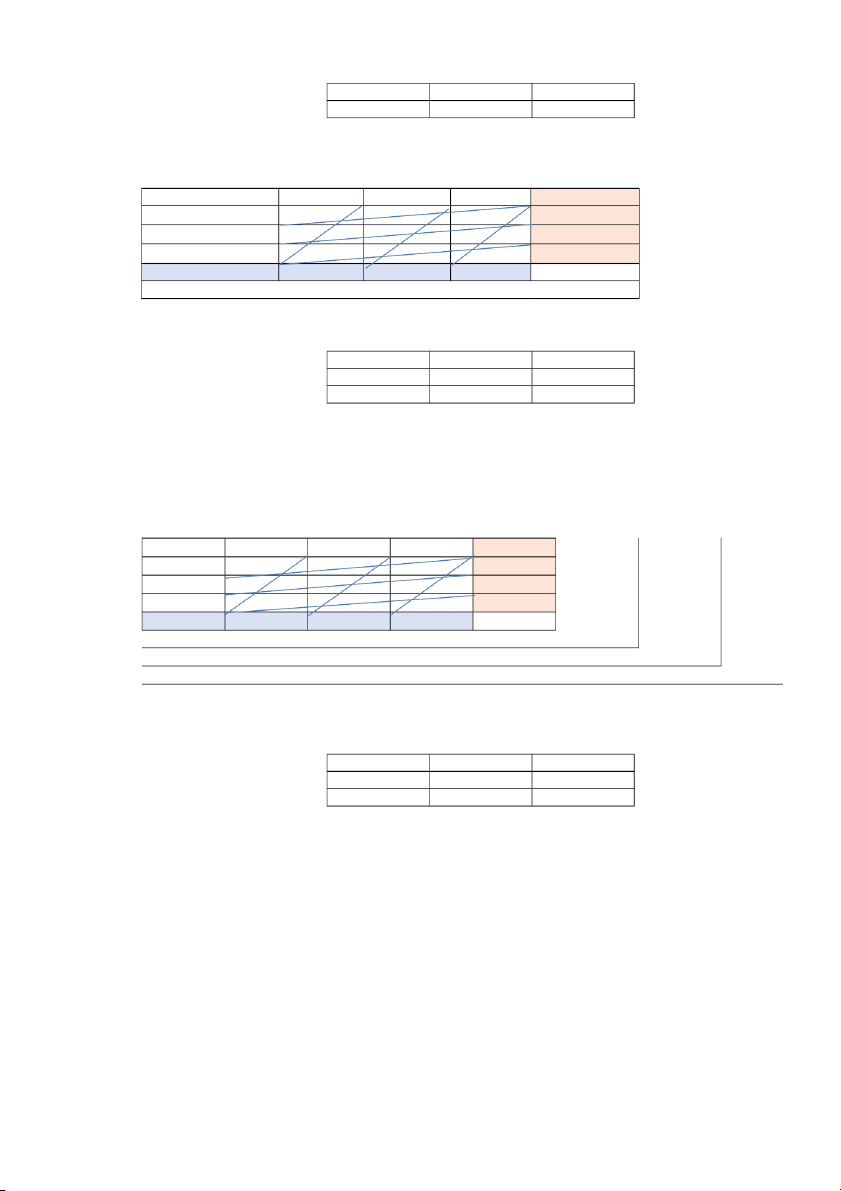
Average Sales Seasonal Index Forecast (2021) (2020) (2020) (2021) 1 15,470,516,000 27,658,574,500 30,240,720,469 0.559 16,914,810,626 2 23,250,544,000 27,658,574,500 30,240,720,469 0.841 25,421,165,572 3 35,989,817,000 27,658,574,500 30,240,720,469 1.301 39,349,750,133 4 35,923,421,000 27,658,574,500 30,240,720,469 1.299 39,277,155,543 Total 110,634,298,000 120,962,881,875 2. Number of product 12,096.3 12,097 Supply (20%) 2419.40 2419 Supply(40%) 4,838.80 4839 Demand ( 30%) 3,629.10 3629 Demand ( 40%) 4,838.80 4839 NorthWest Corner Method D1(30%) D2(40%) D3(30%) Supply W1(20%) (2,419) 50 40 30 2,419 W2( 40%) (1,210) 40 (3,629) 50 20 4,839 W3(40%) 30 (1,210) 20 (3,629) 30 4,839 Demand 3,629 4,839 3,629 12,097 Total value cost is 483,870 V1 = 50 V2= 60 V3= 70 u1 = 0 ( 2,419) 50 40 30 U2 = -10 (1,210) 40 (3,629) 50 - + 20 U3 = -40 30 (1,210) 20 + - (3,629) 30 For C12, P12 = 20 For C13, P13 = 40 For C23, P23 = 40 For C31, P31 = -20 V1 = 50 V2= V3= 30 u1 = 0 ( 2419) 50 40 30 U2 = -10 (1,210) 40 50 (3,629) 20 U3 = 30 (4839) 20 (0) 30 For C13, P13 = 0 Least Cost Cell Method D1 (30%) D2 (40%) D3 (30%) Supply W1(20%) (2,419) 50 40 30 2,419 W2 (40%) (1,210) 40 50 (3,629) 20 4,839 W3 (40%) 30 (4,839) 20 30 4,839 Demand 3,629 4,839 3,629 12,097 Total Value cost is 342,260 V1 = 50 V2= V3= 30 U1 = 0 ( 2,419) 50 40 30 U2 = -10 (1,210) 40 50 (3,629) 20 U3 = 30 (4839) 20 (0) 30 For C13, P13 0 Vogel’s Approximation Method D1 (30%) D2 (40%) D3 (30%) Supply W1(20%) (2,419) 50 40 30 2,419 10 10 W2 (40%) (1,210) 40 50 (3,629) 20 4,839 20 10 W3 (40%) 30 (4,839) 20 30 4,839 10 10 Demand 3,629 4,839 3,629 12,097 10 20 10 10 20 0 10 0 0 Total value 342,260 V1 = 50 V2= V3= 30 U1 = 0 ( 2419) 50 40 30 U2 = -10 (1,210) 40 50 (3,629) 20 U3 = 30 (4839) 20 (0) 30 For C13, P13 0




