






Preview text:
Chap 1: Operation and productivity 1/ 10 decisions 2/ Productivity
Chap 2: Operations strategy in global environment 1/ 6 reasons to globalize
+Improve supply chain: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
+Reduce cost (labor, taxes, tarrifs,...): (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
+Improve product: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
+Improve operations: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty) 2/ 3 competitive advantages
+Competing on Differentiation: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
+Competing on Cost Leadership: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
+Competing on Response: (definition + Vd: 1 công ty)
Chap 5: Design of products & sevices (200=> 203)
+ Product development teams: Teams charged with moving from market requirements
for a product to achieving product success.
+ Concurrent engineering: Use of cross-functional teams in product design and
preproduction manufacturing. (known as a cross-functional team)
+ Manufacturability and value engineering: Activities that help improve a product’s
design, production, maintainability, and use.
+ Robust design: A design that can be produced to requirements even with unfavorable
conditions in the production process.
+ Modular design: A design in which parts or components of a product are subdivided
into modules that are easily interchanged or replaced.
+ Computer-aided design (CAD): Interactive use of a computer to develop and document a product.
+ Design for manufacture and assembly (DFMA): Software that allows designers to
look at the effect of design on manufacturing of the product.
+ Standard for the exchange of product data (STEP): A standard that provides a
format allowing the electronic transmission of three-dimensional data.
+ Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM): The use of information technology to control machinery.
+ 3-D printing: An extension of CAD that builds prototypes and small lots.
+ Virtual reality: A visual form of communication in which images substitute for reality
and typically allow the user to respond interactively.
+ Value analysis: A review of successful products that takes place during the production process.
+ Time-based competition: Competition based on time; rapidly developing products and moving them to market.
1/ Defining a product: (205-206)
+ Engineering drawing: A drawing that shows the dimensions, tolerances, materials, and finishes of a component.
+ Bill of material (BOM): A list of the hierarchy of components, their description, and
the quantity of each required to make one unit of a product.
2/ Documents for Production (208)
+An assembly drawing is usually a three-dimensional drawing, known as an isometric
drawing; the relative locations of components are drawn in relation to each other to show how to assemble the unit.
+ Assembly chart: A graphic means of identifying how components flow into
subassemblies and final products.
+ Route sheet: A listing of the operations necessary to produce a component with the
material specified in the bill of material.
+ Work order: An instruction to make a given quantity of a particular item.
+ Engineering change notice (ECN): A correction or modification of an engineering drawing or bill of material.
+ Configuration management: A system by which a product’s planned and changing
components are accurately identified.
+ Product life-cycle management (PLM): Software programs that tie together many
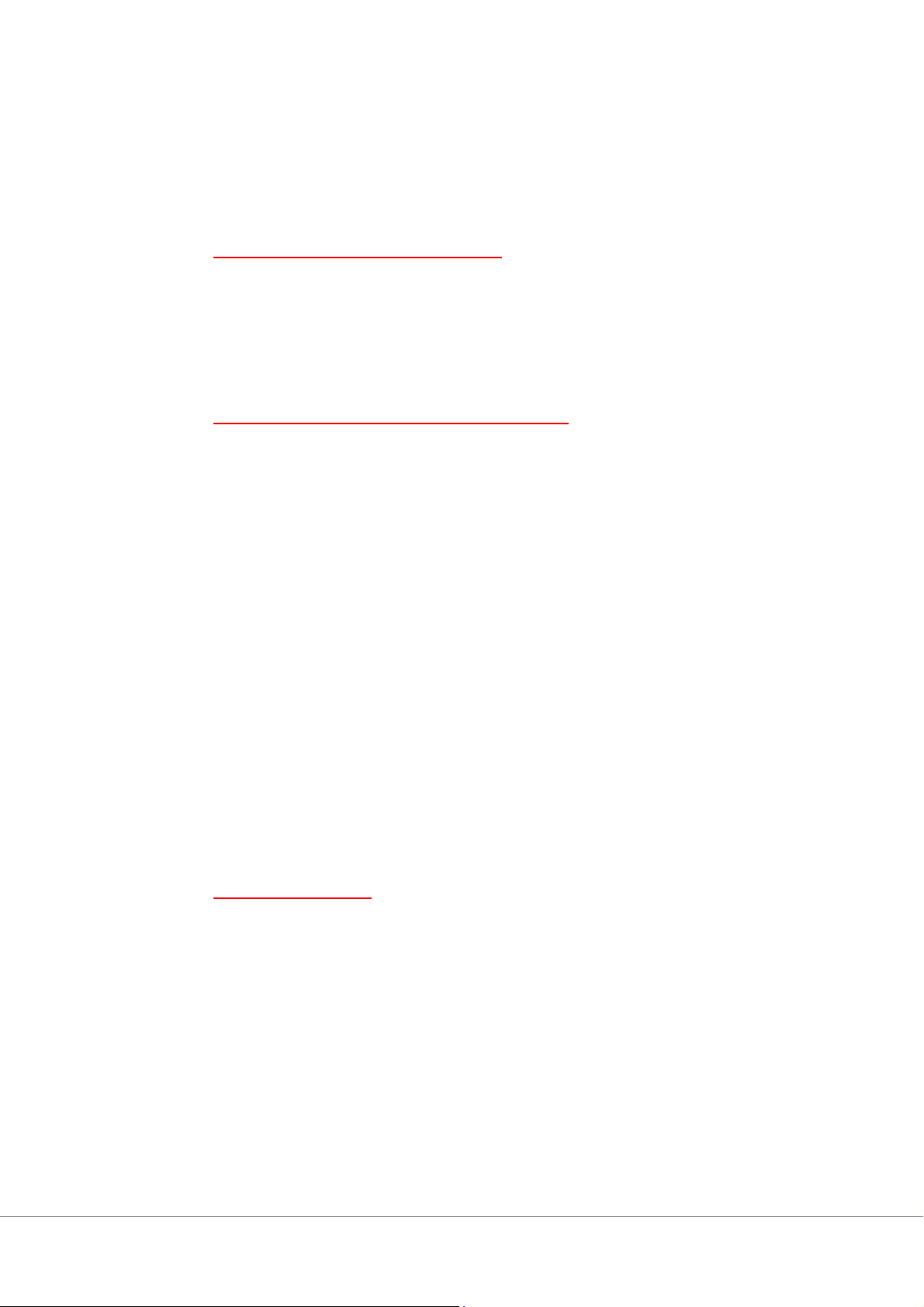
phases of product design and manufacture. 3/ Decision tree *Tính EMV + Kết luận
EMV (Low tech) = 0.2*155,000+0.5*145,000+0.3*135,000 = $144,000
EMV (Sub-contract) = 0.7*155,000+0.2*145,000+0.1*135,000 = $151,000
EMV (high-tech) = 0.9*155,000+0.1*145,000 = $154,000
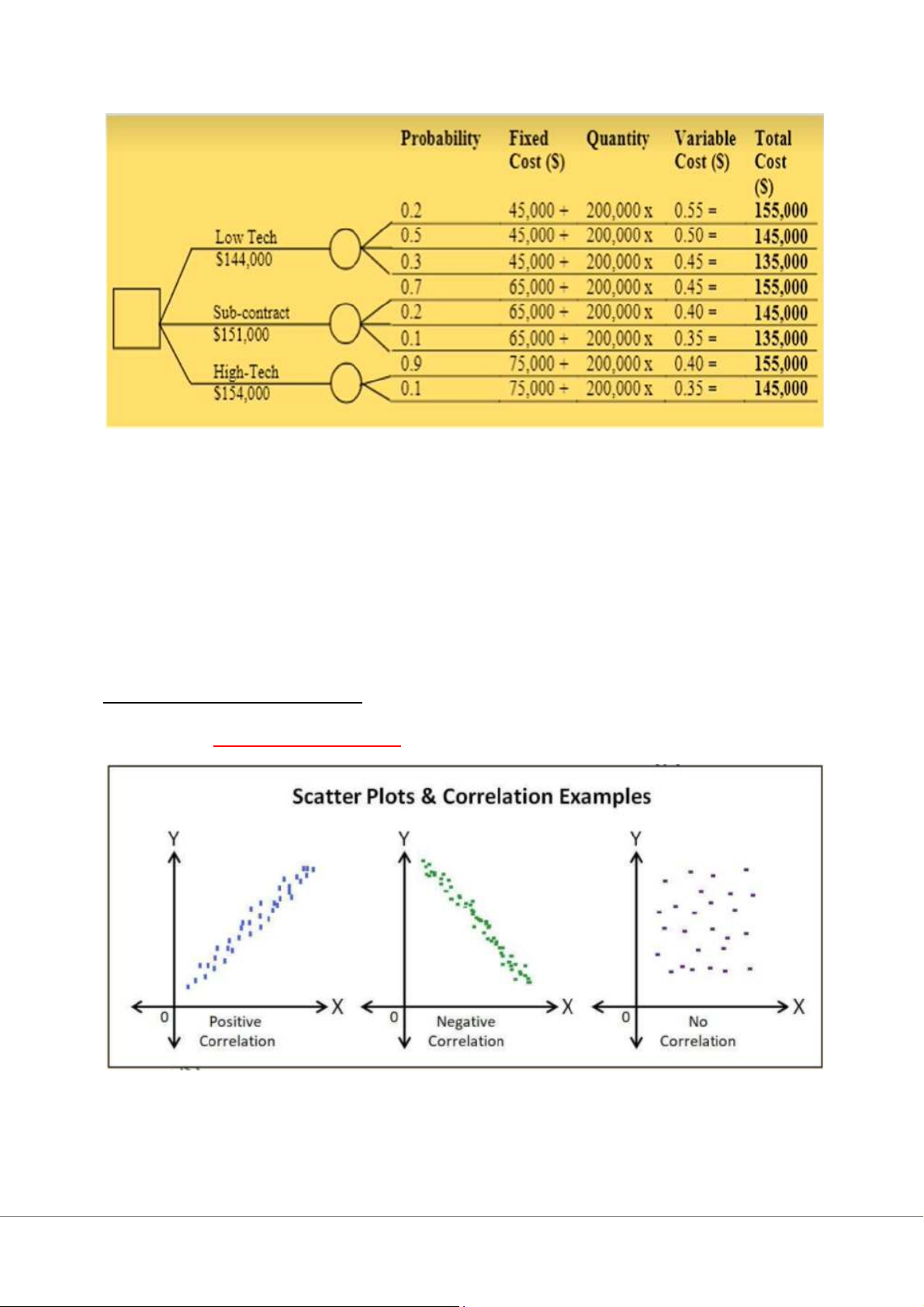
Conclusion: A should choose option Low-tech with the lowest EMV of $144,000 Chap 6: Manage Quality 1/ Scatter diagram 2/ Flow Chart 3/ Cause & Effect Diagram 4/ Pareto chart
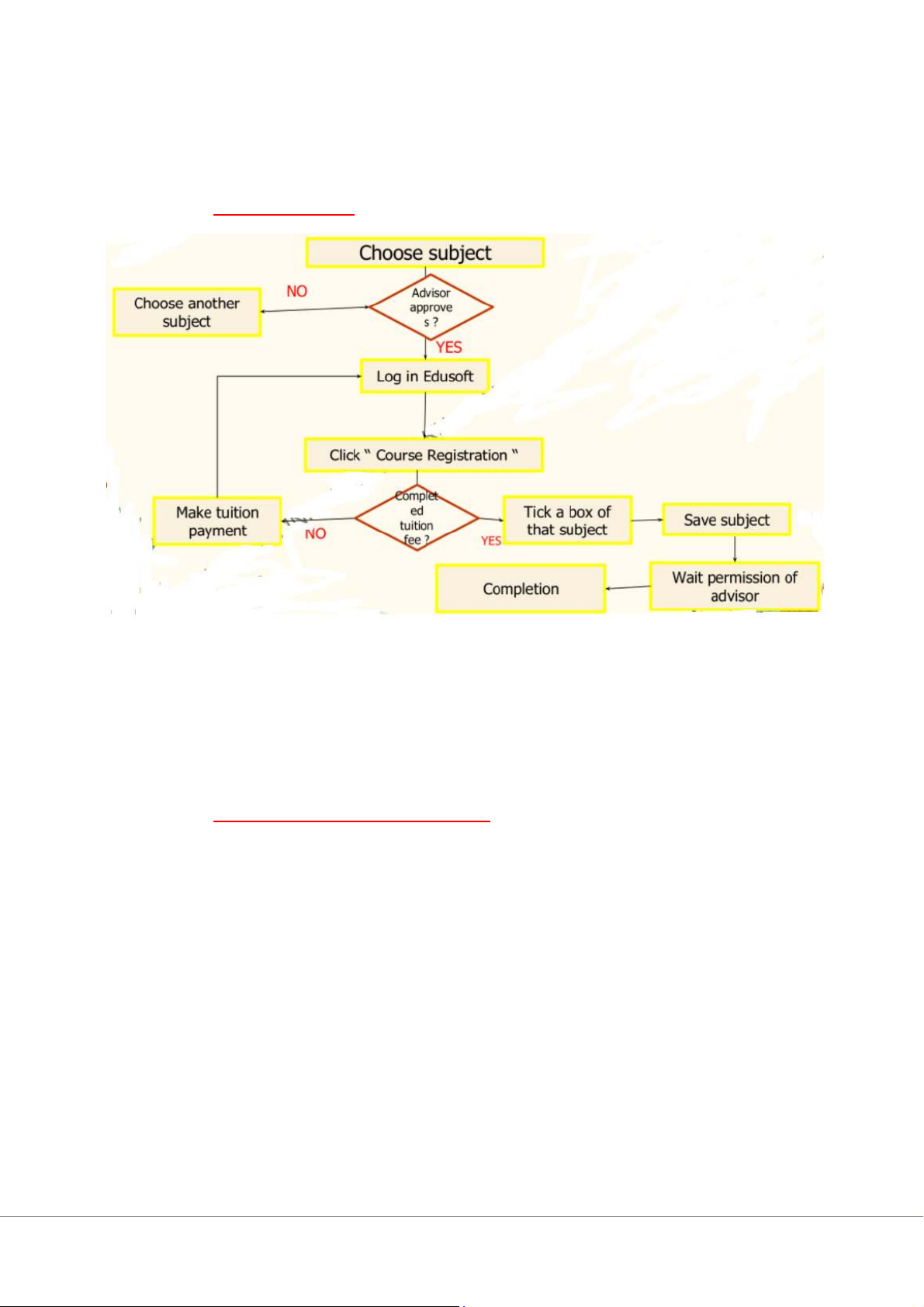
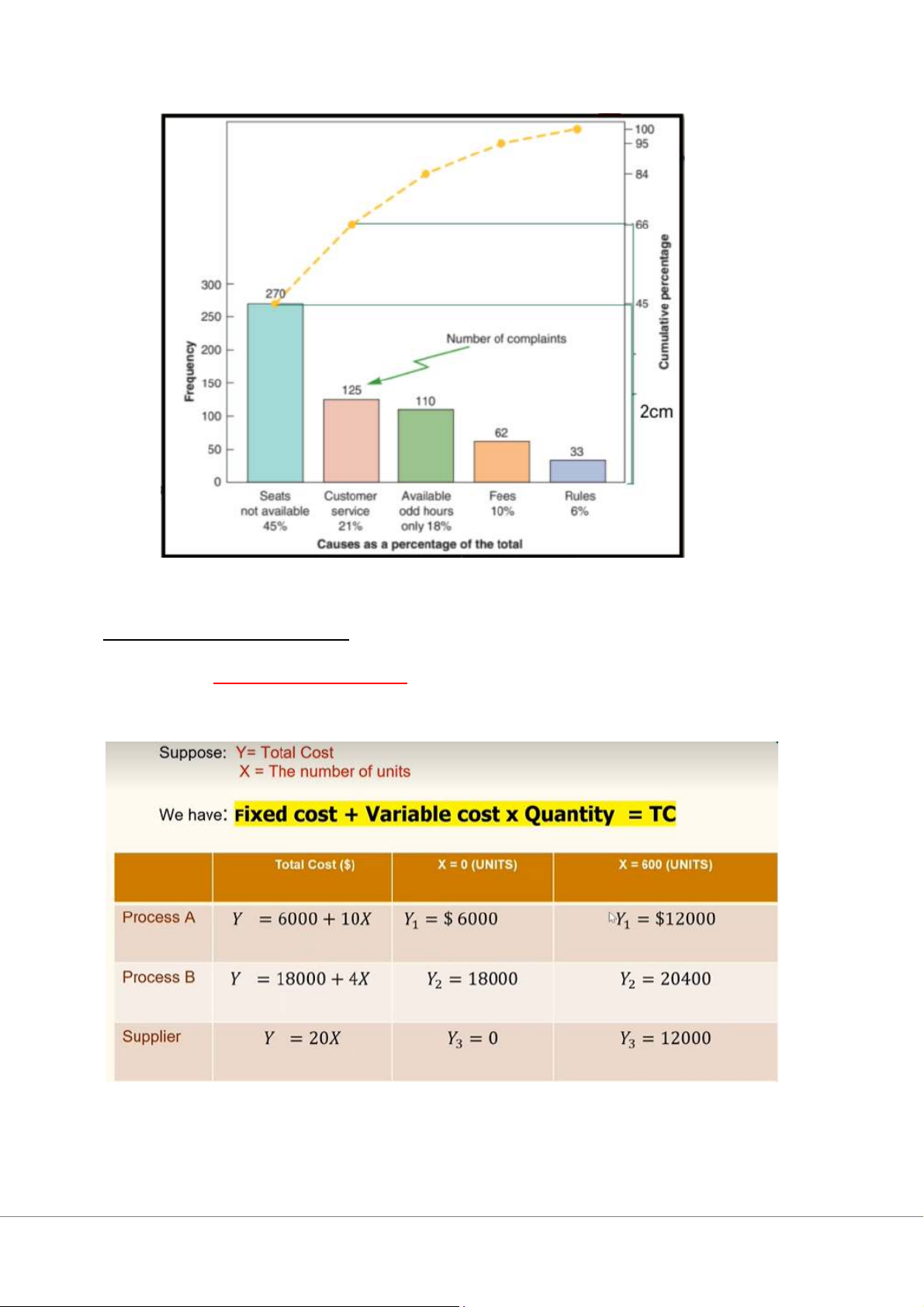
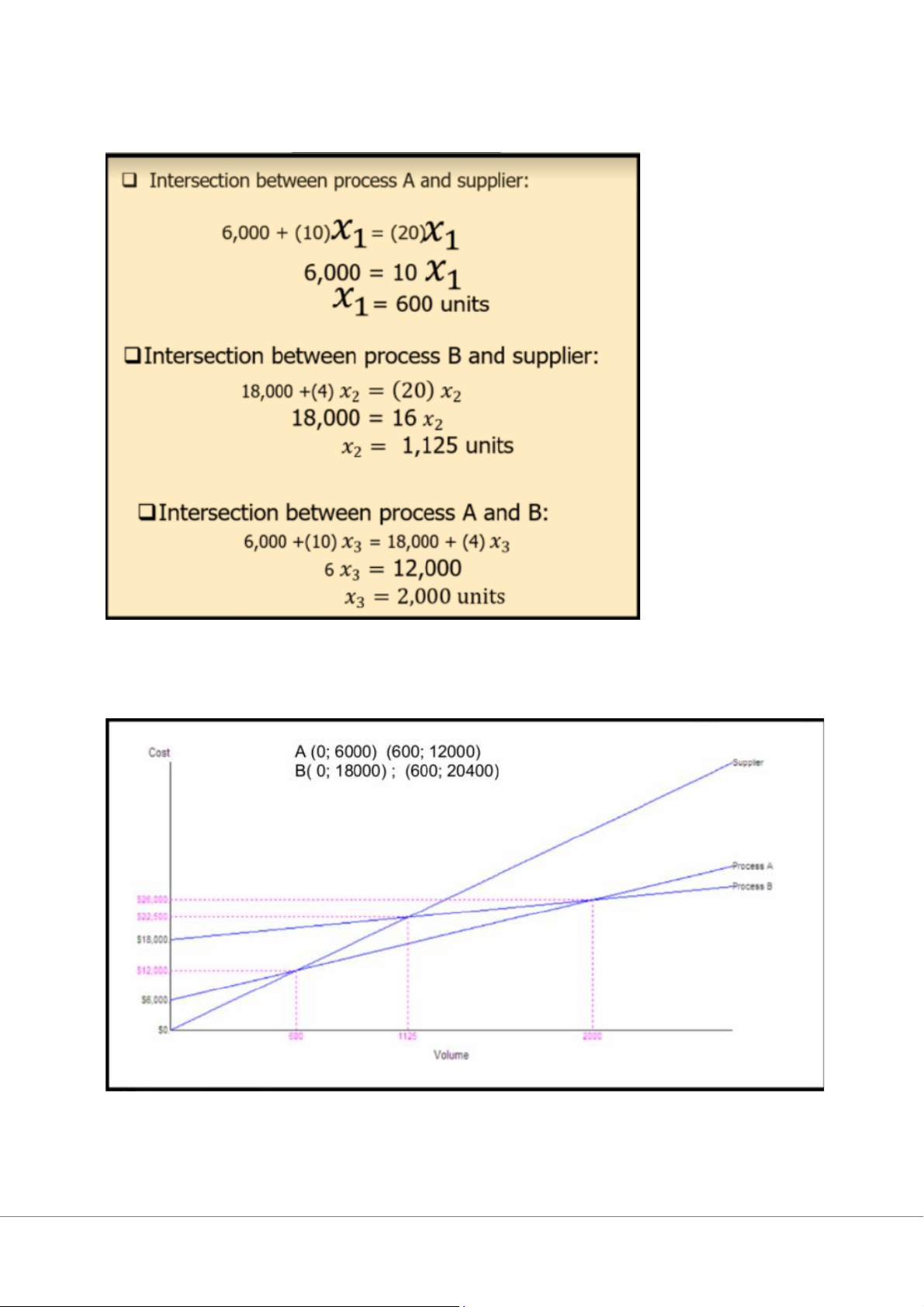
Step 1: (*Frequency phải xếp từ cao xuống thấp) Sept 2: Chap 7: Process Design 1/ Cross-over chart Step 1: Step 2:
(Suy ra con Y nun + Đề cập 2 điểm sẽ vẽ từng đth) Step 3: Step 4: Kết luận: Chap 7s: Capacity Planning
1/ Utilization & Efficiency 2/ Bottleneck time
+Bottleneck time: is the time of the lowest workstation (đv: thời gian).
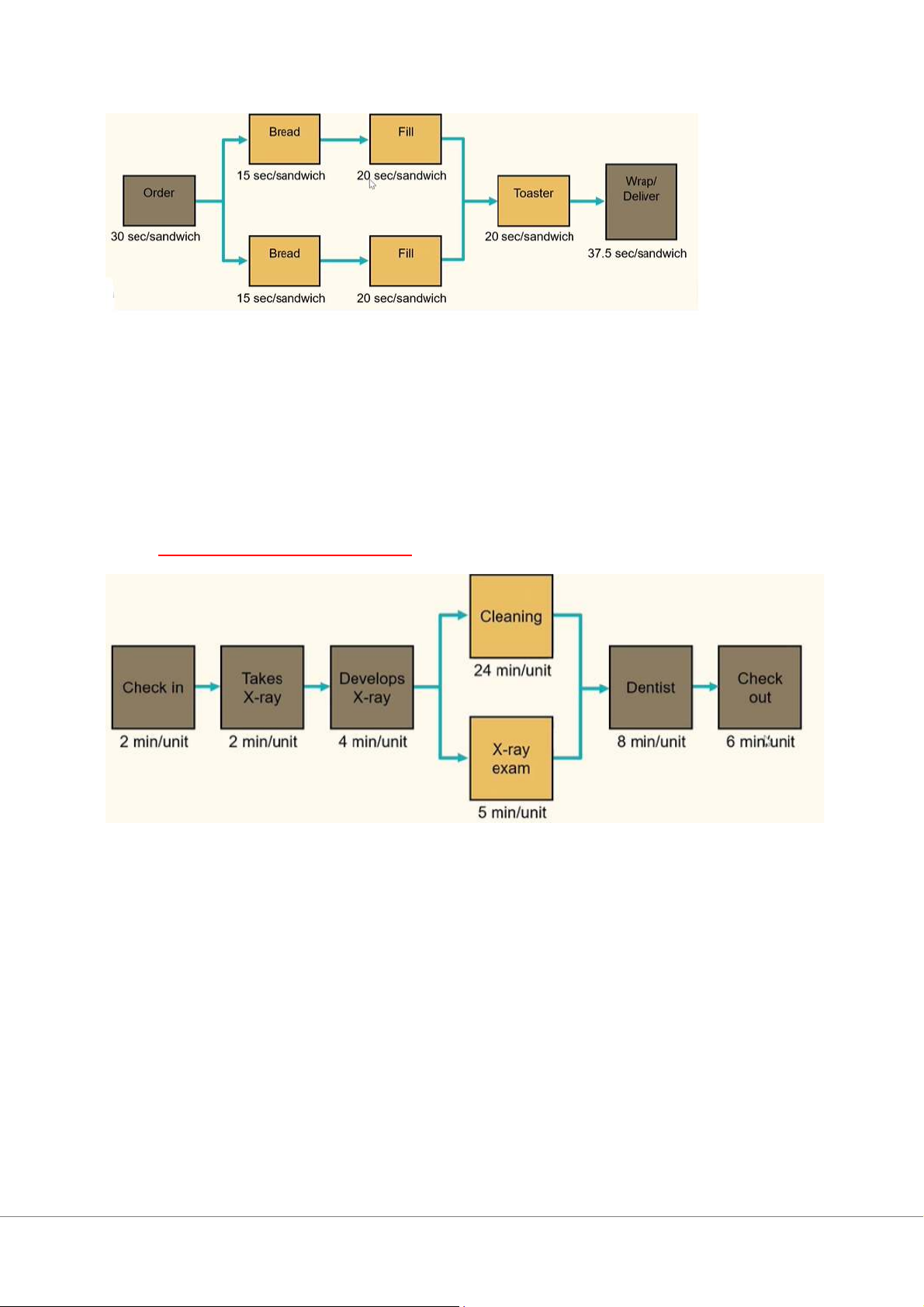
+Throughput time: is the time from start to end (đv: thời gian). 2.1/ Parallel process:
(*Lưu ý: Khi đề cho units/hour thì phải đổi qua hours/unit)
+At 37.5 seconds, wrapping and delivery has the longest processing time and is the bottleneck time.
+ Capacity per hour of wrapping and delivery = 3600 sec/ 37.5 sec = 96 units/hour
+Throughput time is 30 + 15 + 20 + 20 + 37.5 = 122.5 seconds/sandwich. 2.2/ Simultaneously process:
+At 24 minutes, Cleaning has the longest processing time and is the bottleneck time.
+Hourly capacity of Cleaning = 60 min/24 min = 2.5 units/ hour. (phải đổi từ hour ra…)
+Path containing Cleaning = 2+2+4+24+8+6 = 46 mins/unit.
+Path containing X-ray exam = 2+2+4+5+8+6 = 27 mins/unit
⇨Nhánh nào có thời gian nhiều hơn là throughput time => Cleaning path 3/ Break-even point: Sept 1: Assume x = number of units produced
BEP(x) = break-even point per units TR = total revenue = P*x
BEP($) = Break-even point per dollar F = Fixed costs
P = price per unit (after all discounts) V = variable cost per unit TC = total costs = F + V*x Step 2: Computing Break-even point occurs when +BEP(x) = F/(P-V) = …..units
+BEP($) = BEP(x) * P =…… dollars
+Profit = TR – TC = P*x – (F + V*x) = (P-V)*x – F = ……dollars
4/ EMV of capacity decision (Giống decision tree)




