






Preview text:
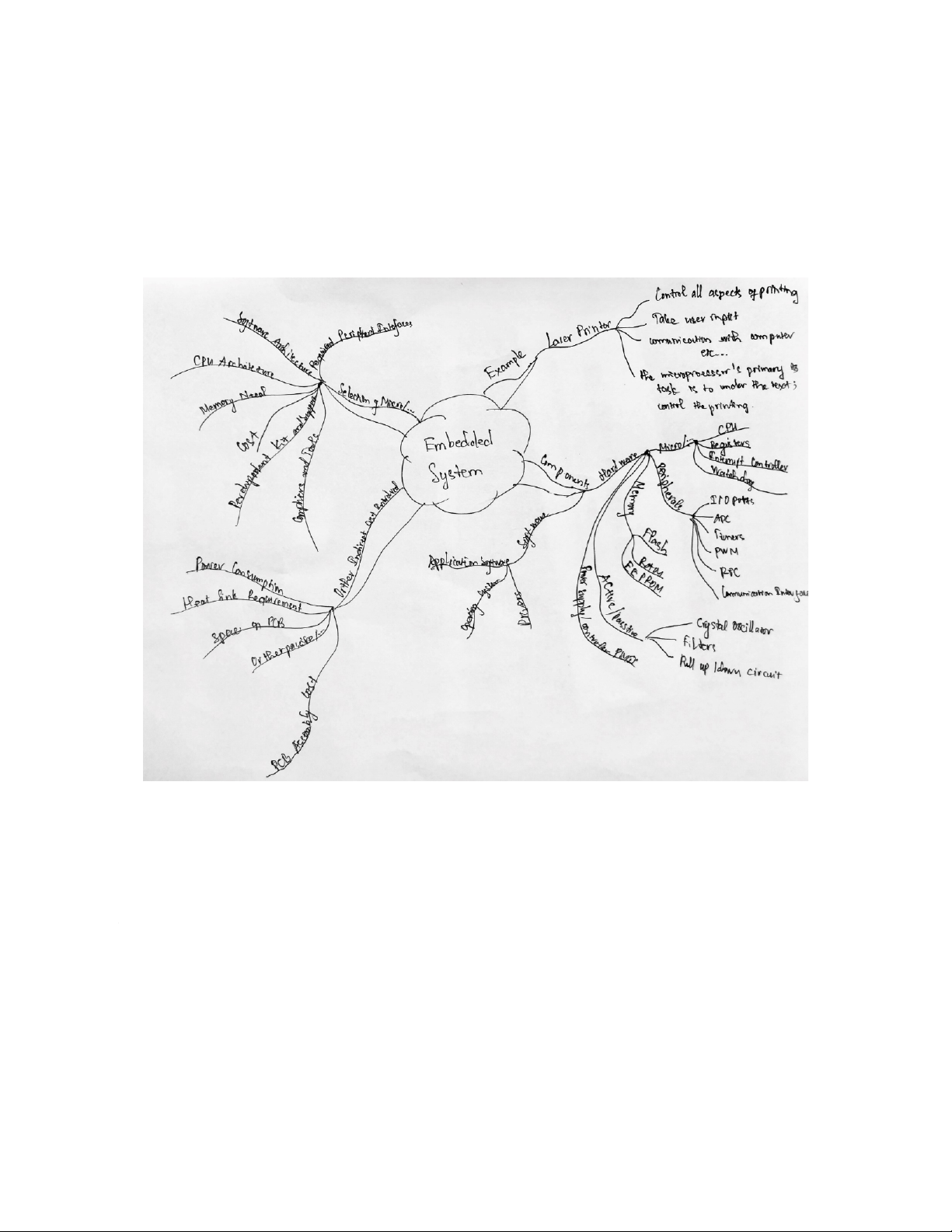
Nguyen Anh Tuan – 20203630 Example of an Embedded System Laser Printer
Laser Printers have a notable amount of embedded systems in them
to control all aspects of printing. Along with the primary job of
printing it has to take user inputs, handle communication with the
computer, sensing paper jams, handling faults, sensing papers left on the tray, etc.
Máy in Laser là một lượng đáng kể các hệ thống nhúng để điều
khiển tất cả các khía cạnh của quá trình in ấn. Bên cạnh nhiệm vụ
chính là in ấn, nó còn phải xử lý đầu vào từ người dùng, điều khiển
giao tiếp với máy tính, phát hiện giấy kẹt, xử lý lỗi, phát hiện giấy còn lại trên khay. Vv
The microprocessor’s primary task is to understand the text and
control the printing head such that it discharges ink where it is
needed. To do so it has to decode the different files given to it and
understand the font and graphics. It takes a significant CPU time to
process the data as well as it has to control motors, take user inputs,
etc so you can imagine that it takes quite an effort to design and program an embedded system.
Nhiệm vụ chính của vi xử lý là hiểu văn bản và điều khiển đầu in để
phát ra mực đúng chỗ cần in. Để làm được điều đó, nó phải giải mã
các tệp tin khác nhau và hiểu các kiểu chữ và đồ họa. Việc xử lý dữ
liệu cũng như việc điều khiển động cơ, nhận đầu vào từ người
dùng,vv đòi hỏi một lượng thời gian CPU đáng kể, vì vậy ta có thể
tưởng tượng rằng nó đòi hỏi rất nhiều công sức để thiết kế và lập
trình một hệ thống nhúng. Embedded System Components
Superficially the components of a general embedded system can be classified as :
Tổng quát, các thành phần của một hệ thống nhúng có thể được phân loại như sau: Hardware (Phần cứng)
oMicroprocessor / Microcontroller (Vi xử lý/mạch điều khiển nhúng) CPU Registers (Thanh ghi)
Interrupt Controller (Bộ điều khiển ngắt) Watchdog (Bộ định thời)
oPeripherals (Các linh kiện ngoại vi)
I/O Ports (Các cổng ra vào)
ADC – Analog to Digital Converter (Bộ chuyển đổi tín hiệu tương tự - số) Timers (Bộ định thời) PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) RTC – Real Time Clock
Communication Interfaces (Các giao diện truyền thông) UART SPI I2C CAN LIN I2S USB Ethernet oMemories (Bộ nhớ) Flash RAM EEPROM
oActive / Passive Components (Các thành phần hoạt động)
Crystal Oscillator (Dao động tinh thể) Filters
Pull Up / Down Circuit (Mạch kéo lên/xuống)
oPower Supply and Controller PMIC (Nguồn cấp và bộ điều khiển nguồn điện) Software
oApplication Software (Phần mềm ứng dụng)
oOperating System (Hệ điều hành)
oDrivers (Các trình điều khiển)
Selection of Microprocessor / Microcontroller
The selection of a Microcontroller or Microprocessor depends on
many factors. Some of the important factors are :
Việc lựa chọn một vi xử lý hoặc mạch điều khiển nhúng phụ thuộc
vào nhiều yếu tố. Mốt số yếu tố quan trọng bao gồm:
Required Peripheral Interfaces (Các giao diện ngoại vi cần thiết)
oDepending on the application of the microcontroller the
need for different peripherals will change as well as the
specifications for the peripherals will change. Ex – an
application may need only USB1.0 interface so there will
be no need to go for an expensive MCU with USB2.0 / 3.0.
Tùy thuộc vào ứng dụng của vi điều khiển nhúng, nhu cầu
cho các bộ quận ngoại vi sẽ thay đổi cũng như các thông
số kỹ thuật cho các bộ phận ngoại vi sẽ thay đổi. Ví dụ:
một ứng dụng có thể chỉ cần giao diện ÚB 1.0, do đó sẽ
không cần phải chọn MCU đắt tiền với USB 2.0/3.0
Software Architecture (Kiến trúc phần mềm)
oThe Software going to run on the system may demand
specific CPU requirements. Ex – You may need an FPU or
DSP Instruction Set enabled CPU if you need to do any
heavy mathematical computation or signal processing
application. Based on your application you have to choose a 16MIPS AVR or a 300MIPS ARM.
Phần mềm sẽ chạy trên hệ thống có thể yêu cầu các yêu
cầu CPU cụ thể. Ví dụ: Bạn có thể cần một CPU có FPU
hoặc bộ lệnh DSP nếu bạn thực hiện bất kỳ tính toán toán
học nặng hoặc ứng dụng xử lý tín hiệu nào. Dựa trên ứng
dụng của bạn, bạn phải chọn một AVR 16MIPS hoặc ẢM 300MIPS.
CPU Architecture (Kiến trúc CPU)
oBased on the previous two steps you have to choose the
CPU Architecture most suitable for the kind of software
application you want to run on the device. Some small
applications may work well with 8-bit CPUs but
Applications like motion processing will demand a 32-bit or 64-bit CPU.
Dựa trên hai bước trước đó, bạn phải chọn Kiến trúc CPU
phù hợp nhất cho loại phần mềm ứng dụng bạn muốn
chạy trên thiết bị. Một số ứng dụng nhỏ có thể hoạt động
tốt với CPU 8 bit nhưng ứng dụng xử lý chuyển động sẽ
yêu cầu CPU 32 bit hoặc 64 bit.
Memory Need (Nhu cầu bộ nhớ)
oThis also depends on the size of the software you want to
run. Memory need includes Internal or External Flash,
RAM, EEPROM or any special memory. Based on the
peripherals and application software it can be calculated
how much memory resources are needed. You also have
to keep some extra memory for future improvements and versions.
Điều này cũng phụ thuộc vào kích thước phần mềm bạn
muốn chạy. Nhu cầu bộ nhớ bao gồm bộ nhớ Flash, RAM,
EEPROM hoặc bất kỳ bộ nhớ đặc biệt nào khác. Dựa trên
các bộ phận ngoại vi và phần mềm ứng dụng, bạn có thể
tính toán được bao nhiêu tài nguyên bộ nhớ cần thiết. Bạn
cũng phải giữ một số bộ nhớ dự phòng cho các cải tiến và
phiên bản trong tương lai. Cost
oCost is an important factor when you are planning to
make an end product. Every penny is important when a
product will be manufactured in large quantities like in tens of thousands.
Chi phí là yếu tố quan trọng khi bạn dự định tạo ra một
sản phẩm cuối. Mỗi xu là quan trọng khi một sản phẩm sẽ
được sản xuất hàng loạt như trong hàng chục ngàn. Availability and Supply
oWhen a product is planned for long production cycle. It is
important to note parameters like lead time, availability,
long-term support. Every MCU manufacturer will let you
know when they will stop supplying the IC. You have to
choose the Microcontroller accordingly otherwise you
have to stop production after a couple of years and again invest in development.
Khi một sản phẩm được lên kế hoạch cho chu kỳ sản xuất
dài. Quan trọng là lưu ý các tham số như thời gian dẫn
đầu, sự sẵn có và hỗ trợ dài hạn. Mỗi nhà sản xuất MCU sẽ
cho bạn biết khi họ sẽ ngừng cung cấp IC. Bạn phải chọn
vi điều khiển phù hợp nếu không, sau vài năm bạn sẽ phải
dừng sản xuất và đầu tư vào phát triển lại. Development Kit and Support
oIt is always advisable to get a development board from
the supplier to help you develop and test the software
before your hardware is built. This will ensure the first
four points are correctly chosen. Even support from the
supplier can cost you money, so it advisable to make sure
you have a proper deal with the MCU Supplier.
Luôn luôn khuyến khích lấy một bo mạch phát triển từ
nhà cung cấp để giúp bạn phát triển và kiểm tra phần
mềm trước khi phần cứng của bạn được xây dựng. Điều
này sẽ đảm bảo rằng bốn điểm đầu tiên được chọn đúng.
Thậm chí hỗ trợ từ nhà cung cấp cũng có thể tốn tiền của
bạn, vì vậy nó nên được đảm bảo là có thỏa thuận hợp lý với nhà cung cấp MCU. Compilers and Tools
oCompilers, Debuggers and other tools may cost you
separate money due to license. Make sure you consider this while selecting
Trình biên dịch, bộ gỡ lỗi và các công cụ khác có thể tổn
tiền riêng cho giấy phép. Đảm bỏa bạn xem xét điều này khi chọn MCU.
Other Indirect Cost Involved in Selecting a MCU
Power Consumption (Tiêu thụ điện năng)
Heat Sink Requirement (Yêu cầu tản nhiệt)
Space on PCB (Không gian trên PCB)
Other passive and active support components (Các linh kiện hỗ
trợ chủ động và bị động khác)
PCB Assembly Cost (Chi phí lắp ráp PCB)




