










Preview text:
Review - Final Exam - Restructuring and Evaluation Class - 22.1A
Part 1: Multiple Choices
1. The restructuring of a corporation should be undertaken if
a. restructuring can prevent an unwanted takeover.
b. restructuring is expected to create value for shareholders.
c. restructuring is expected to increase the firm's revenue.
d. the interests of bondholders are not negatively affected.
2. In the long run, a successful acquisition is one that:
a. enables the acquirer to make an all-equity purchase, thereby
avoiding additional financial leverage.
b. enables the acquirer to diversify its asset base.
c. increases the market price of the acquirer's stock over
what it would have been without the acquisition.
d. increases financial leverage.
3. The public sale of common stock in a subsidiary in which the parent
usually retains majority control is called a. a pure play. b. a spin-off. c. a partial sell-off. d. an equity carve-out.
4. One means for a company to "go private" is a. divestiture. b. the pure play.
c. the leveraged buyout (LBO).
d. the prepackaged reorganization.
5. The supply chain is a representation of: a.
the sequence of events required to convert raw materials into finished goods. b.
the static risks involved in each stage of production. c.
the contractual arrangements for procurement. d.
organizational communication systems.
6. Typical indicators of likely cultural problems during subsequent
mergers or acquisitions include: I. high staff turnover. II.
difficulty in keeping hold of key staff. III.
increasing assertion of harassment. IV.
decreasing employee motivation, energy and commitment.
Which of the above is/are true? a. I only. b. I and II. c. I, II and III. d. I, II, III and IV.
7. Mergers and acquisitions conducted under the strategic rationale are
usually carried out with the objective of: I.
adding long-term competitive advantage. II.
increasing the value of the target with the intention of future resale. III.
responding to the demands of immediate financial shortcomings. IV.
complying with regulatory requirements.
Which of the above is/are true? a. I only. b. I and II. c. I, III and IV. d. I, II, III and IV.
8. Which of the following is correct? The net advantage of merging (NAM) is: a.
the value of the combined firms less the value of the two
independent firms as stand-alone entities less the costs of acquisition. b.
the value of the combined firms less the value of the net
difference between the two firms as stand-alone entities. c.
the value of the combined firms less the value gain to the target firm’s shareholders. d.
the value of the combined firms less the expenses of merging
plus the value gain to the acquiring firm’s shareholders.
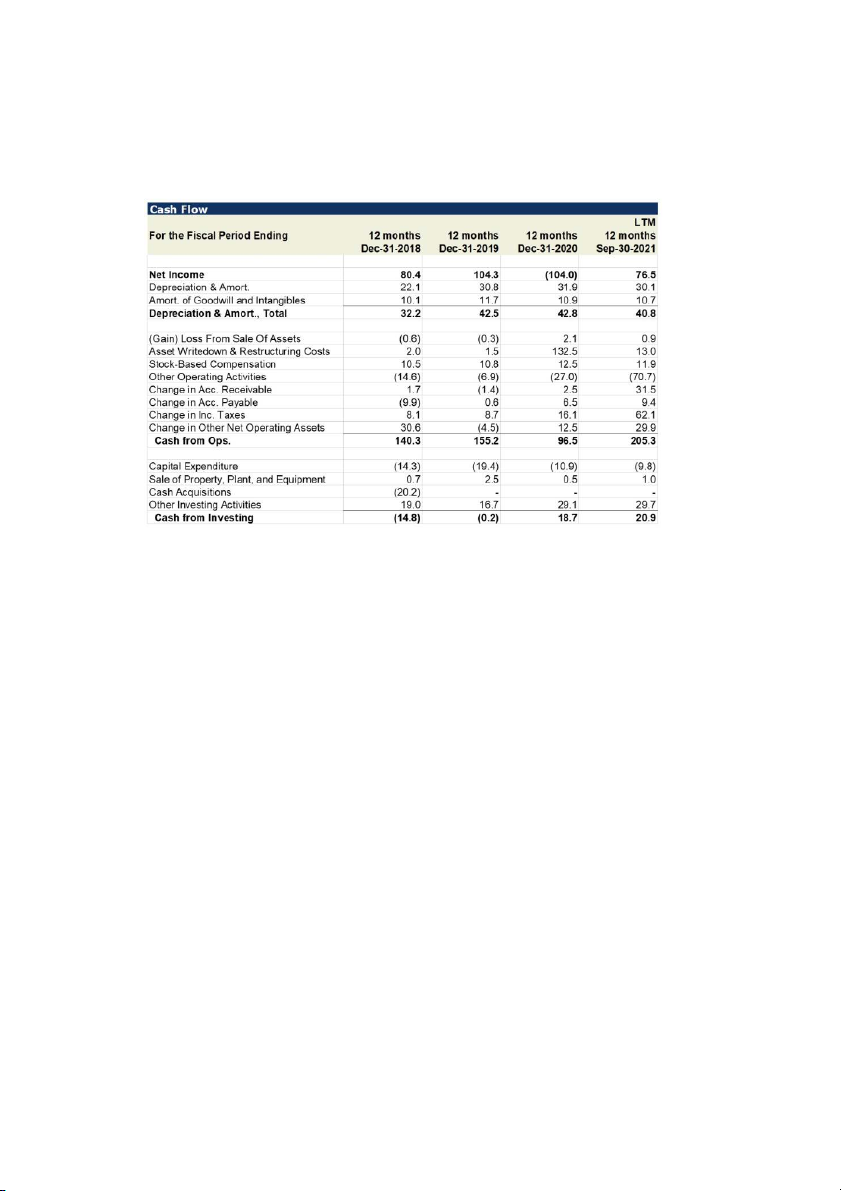
9. This question is based on the cash flow statement for Company X below:
Which of the following options is NOT correct?
a. Sale of property plant and equipment is likely to be a business
(dis)investment and should be included in investment forecasts.
b. Changes in accounts receivable are not a relevant investment
and should be ignored when forecasting future investments.
c. To forecast required long-term investments beyond 2020, it would be
reasonable to ignore the cash acquisition that this company executed in 2018.
d. The asset writedown of 132.5 in 2020 is a one-time item and should be
ignored when forecasting investments.
10. Which of the following is NOT true regarding free cash flows?
a. Free cash flows are affected by changes in EBITDA in the income statement.
b. An increase in interest payments reduces free cash flow.
c. An increase in R&D expenses reduces current free cash flow.
d. An increase in required short-term investments such as inventory has
an immediate negative impact on free cash flows.
11. Suppose in Country X, the average annual historical return on the
stock market (last 100 years) was 12%, while the average annual
historical return on a 10-year government bond was 9%. The most
current 10-year government bond yield is 4%.
Which of the following options is NOT correct?
a. The 10-year yield of 4% is a good estimate of the risk-free rate
despite being much lower than the historical yield.
b. Using historical data, the best estimate for the current required
return to invest in the stock market is 7%.
c. The historical market risk premium is 3%.
d. Using historical data, the best estimate for the current
required return to invest in the stock market is 12%.
12. The current 5-year Beta for a company is 1.4. Using a risk-free rate of
3% and a risk premium of 5%, the CAPM estimate for the company’s required return on equity is: a. 10.0% b. 5.95% c. 12.9% d. 3.00%
13. The long-term bond yield (30-year bond) for Company Y is 4.5%. If you
assume that the 10-year cumulative default probability for Charter is
6.5% and the recovery rate is 40%, then the expected annual return on long-term debt for Charter is: a. 3.62% b. 4.08% c. 4.50% d. 6.50%
14. Suppose that the market price of Company X is $45 per share and that
of Company Y is $30. If X offers three-fourths a share of common stock
for each share of Y, the ratio of exchange of market prices would be: a. 0.667 b. 1.0 c. 1.125 d. 1.5 34 = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 �
=> 34�� = 0.7530*45 = 1. 125 Part 2: Practice Questions Question 1:
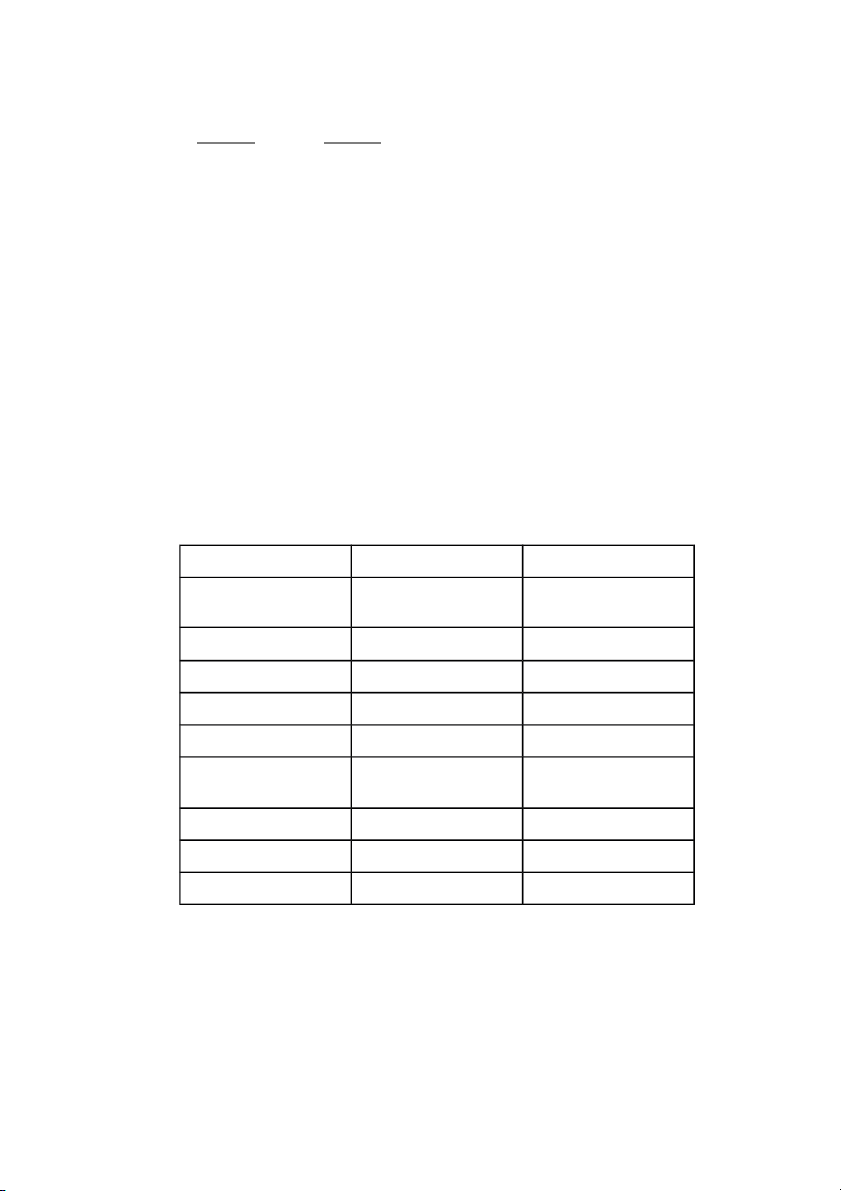
Abbreviated financial statements are given for Hitachi Corporation in
the following table. Year-end working capital in 2021 was $150 million,
and the firm’s marginal tax rate was 40% in both 2022 and 2023.
Estimate the following for 2022 and 2023:
Abbreviated Financial Statements for Hitachi Corporation ($ million) 2022 202 3 Revenues $800 $99 0 Operating expenses 520 60 0 Depreciation 15 19
Earnings before interest and taxes 265 37 1 Less interest expense 19 19 Less taxes 98.4 140. 8 Equals: net income 147.6 211. 2 Addendum Year-end working capital 190 2 9 0 Principal repayment 35 35 Capital expenditures 30 20
a. Calculate Free cash flow to equity in 2022 and 2023
Hint: FCFE = EBIT - Taxes + Depreciation - Capex - change in WC
- (Debt repayment +interest expense) Answer:
FCFE 2022 = EBIT - Taxes + Depreciation - Capex - change in WC -
(Debt repayment +interest expense) = 265 - 98.4 + 15 - 30 - 40 - (35+19) = 57.6 mil
FCFE 2023 = 371 - 140.8 +19 -20 -100 - (35 +19) = 75.2 mil
b. Calculate Free cash flow to the firm in 2022 and 2023
Hint: FCFF = EBIT + Depreciation - Capex - change in WC - tax rate * EBIT Answer:
FCFF 2022 = EBIT + Depreciation - Capex - change in WC - tax rate * EBIT
= 265 + 15 - 30 - 40 - 40%*265 =
104 mil FCFF 2023 = 371 + 19 - 20 - 100 - 40%*371 = 121.6 mil Question 2:
ABC Incorporated shares are currently trading for $32 per share. The
firm has 1.13 billion shares outstanding. In addition, the market value
of the firm’s outstanding debt is $2 billion.
The ten-year Treasury bond rate is 6.25%. ABC has an outstanding
credit record and earned a AAA rating from the major credit rating
agencies. The current interest rate on AAA corporate bonds is 6.45%.
The historical risk premium over the risk-free rate of return is 5.5
percentage points. The firm’s beta is estimated to be 1.1, and its
marginal tax rate, including federal, state, and local taxes, is 40%. a. What is the cost of equity? Answer:
CAPM: Re = Rf +beta (Rm - Rf) = 6.25% + 1.1*(5.5%) = 12.3%
b. What is the after-tax cost of debt? Answer:
after tax cost of debt = (1 - tax rate) * cost of debt = 6.45%*(1-40%) = 3.9%
c. What is the weighted average cost of capital? Answer:
WACC = after tax cost of debt * ����� ����
+ cost of equity * ����������� = 3.9%*Question 3:2 12.3%* *1.13 +
2+3232*1*1.13.13 = 3.9%*5.24% +
12.3%*94.76% = 11.9% 2 +32
In 2021, No Growth Incorporated had operating income before interest
and taxes of $220 million. The firm was expected to generate this level
of operating income indefinitely. The firm had a depreciation expense
of $10 million that year. Capital spending totaled $20 million during
2021. At the end of 2020 and 2021, working capital totaled $70 million
and $80 million, respectively. The firm’s combined marginal state,
local, and federal tax rate was 40%, and its outstanding debt had a
market value of $1.2 billion. The ten-year Treasury bond rate is 5%,
and the borrowing rate for companies exhibiting levels of
creditworthiness similar to No Growth is 7%. The historical risk
premium for stocks over the risk-free rate of return is 5.5%. No
Growth’s beta was estimated to be 1.0. The firm had 2.5 million
common shares outstanding at the end of 2021. No Growth’s target
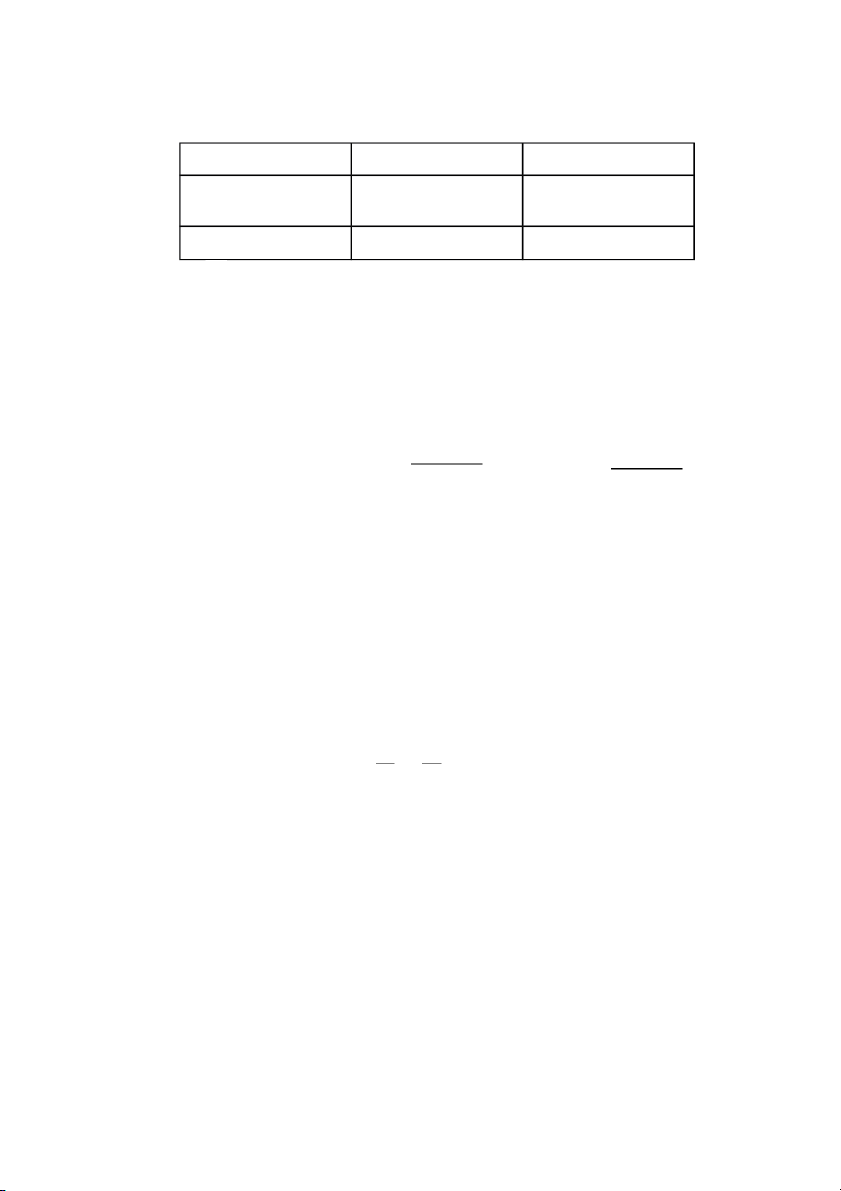
debt–to–total capital ratio is 30%. Summarized information table: 2010 2011 (mil) 330 Operating income before interest and taxes (EBIT) Depreciation 10 Capex 20 Working Capital 70 80 tax rate 40% 1.2 bil = 1200 mil outstanding debt had a market value Rf 5% cost of debt 7% Rm - Rf = risk premium 5.5% beta 1.0 2.5 No. of common shares outstanding
debt–to–total capital ratio 30%
a. Estimate free cash flow to the firm in 2011. Answer:
FCF 2011 = EBIT + Depreciation - Capex - change in WC - tax rate * EBIT
= 330 + 10 - 20 - 10 - 40%*330 = 178 mil
b. Estimate the firm’s weighted average cost of capital. Answer: = � + β * = 5% + 1. 0 * 5. 5% = 10. 5% = (1 − �� ) �� * ���� + ������ * + ���� * + = (1 − 40c.%)Estimate the
enterprise value of the firm at the end of 2011, assuming that it will* 7% *
30% + 10. 5% * (1 − 30%) = 8. 61%
generate the value of free cash flow estimated in sentence a. indefinitely.
����������d.
Estimate the value of the equity of the firm at the end of 2011. =
� ��� � �� = 8178.61% = 2, 067. 36 e. Estimate
the value per share at the end of 2011. ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ = − = $867. 36 ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ = ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ . ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ ℎ = $8672.5.3 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 = $346. 95
Part 3: Theory Questions
1. Why is it important to think of an acquisition or merger in the context
of a process rather than as a series of semi-related, discrete events? (Chapter 4 - Textbook 1)
It is important to think of an acquisition or merger in the context of
a process rather than as a series of semi-related, discrete events
because it helps to ensure that the integration of the two companies is
successful. By thinking of it as a process, you can identify the key steps
that need to be taken to ensure that the integration is successful. This
includes things like identifying the key stakeholders, developing a
communication plan, and creating a timeline for the integration.
In addition, thinking of an acquisition or merger as a process helps
to ensure that everyone involved is on the same page. This can help to
reduce confusion and ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
Finally, thinking of an acquisition or merger as a process can help to
ensure that the integration is successful in the long term. By taking a
strategic approach and thinking about the long-term implications of the
merger or acquisition, you can help to ensure that it is successful over the long term.
Điều quan trọng là phải nghĩ về việc mua lại hoặc sáp nhập trong bối
cảnh của một quá trình chứ không phải là một loạt các sự kiện rời rạc,
bán liên quan vì nó giúp đảm bảo rằng sự hợp nhất của hai công ty
thành công. Bằng cách nghĩ về nó như một quá trình, bạn có thể xác
định các bước chính cần được thực hiện để đảm bảo rằng việc tích hợp
thành công. Điều này bao gồm những thứ như xác định các bên liên
quan chính, phát triển kế hoạch truyền thông và tạo dòng thời gian cho việc tích hợp.
Ngoài ra, suy nghĩ về việc mua lại hoặc sáp nhập như một quá trình
giúp đảm bảo rằng mọi người liên quan đều ở trên cùng một
trang. Điều này có thể giúp giảm sự nhầm lẫn và đảm bảo rằng mọi
người đang làm việc hướng tới cùng một mục tiêu.




