









Preview text:
Situation Analysis for Trung Nguyen Coffee by Nguyen Viet Su International Strategy RMIT University Vietnam CONTENTS
ABOUT TRUNG NGUYEN .......................................................................................... 1
PEST ANALYSIS ........................................................................................................ 2
ECONOMIC ............................................................................................................. 2
POLITICAL .............................................................................................................. 7
SOCIAL ................................................................................................................... 8
TECHNOLOGY ........................................................................................................ 8
SWOT ...................................................................................................................... 9
STRENGTHS ............................................................................................................ 9
WEAKNESSES ....................................................................................................... 10
OPPORTUNITIES ................................................................................................... 12
THREATS .............................................................................................................. 12
REFERENCES .......................................................................................................... 14 ABOUT TRUNG NGUYEN
Trung Nguyen Corp is a privately owned company established in 1996 that specializes in
both fresh and instant coffee. Its products are distributed to about 60 countries worldwide and
this Vietnamese brand also operates cafés in Vietnam, Japan and Singapore, amongst other countries.
“Ready to leave no stone unturned to create the finest gourmet coffee
products, specializing in providing the creative energy for glorious
success” Dang Le Nguyen Vu – Chairman, Trung Nguyen Group
According to Euromonitor International 2016c, Trung Nguyen JSC offers four product
categories, which are hot drinks (7.5% value share and 4th ranking), coffee (17.8% value share
and 3rd ranking), tea and other hot drinks. It has six subsidiaries, being Trung Nguyen
Corporation, Trung Nguyen Instant Coffee Company, Trung Nguyen Coffee, G7 Commercial
Services Company, Ðang Le Tourism Company, Trung Nguyen Franchising Company and G7
Ministop Joint Venture Company. 1 PEST ANALYSIS ECONOMIC
According to Fairtrade (2012), coffee provides a livelihood for 125mil people globally,
generates cash returns in subsistence economies, and provides much-needed rural employment in
the labour-intensive production and harvesting processes.
A general outlook of Vietnam reveals it still depends heavily on agriculture exports to
grow its economy while the agricultural value-added as a share of GDP has been declining since
1985. Nonetheless, its economic development has been successful given the strong growth
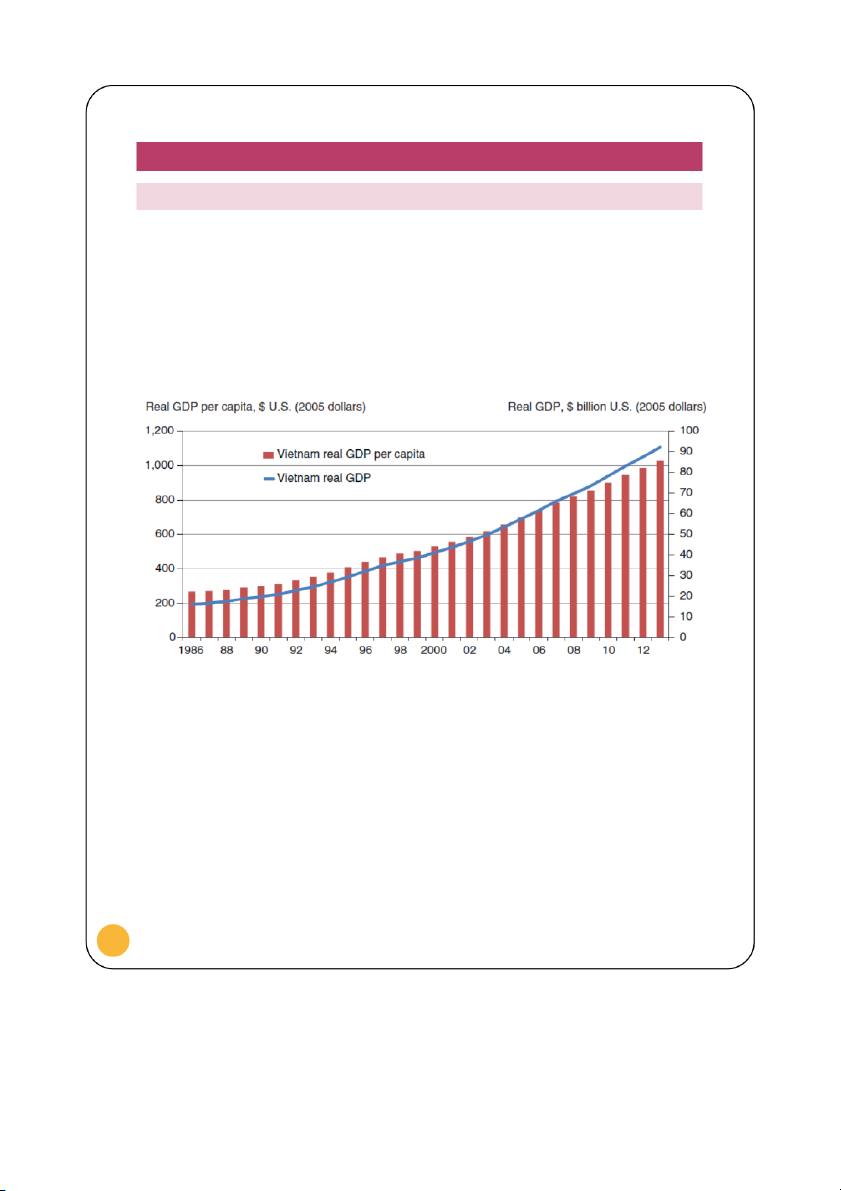
following 2008 financial crisis as indicated in Figure 1.
Vietnam real GDP per capita and real GDP, 1986-2013
Figure 1. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014
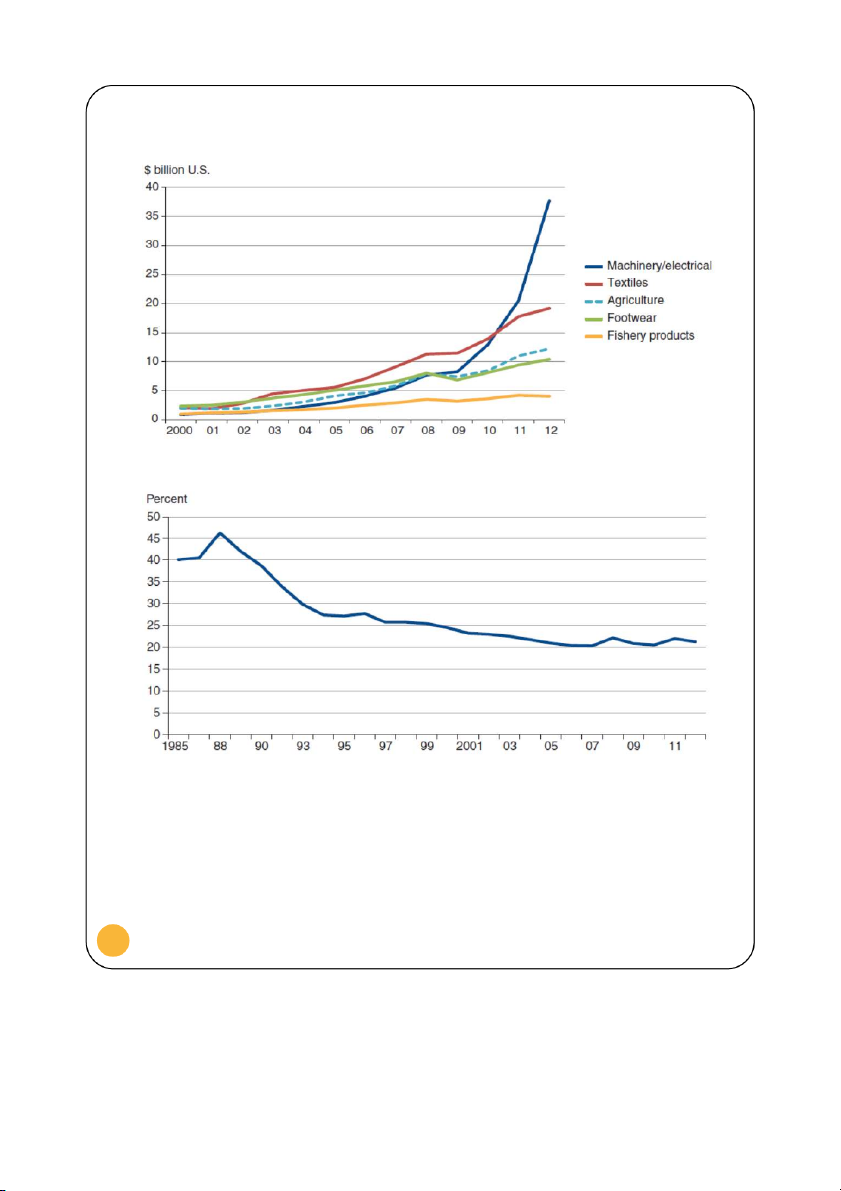
Figure 2 shows Vietnam mainly relies on machinery/electrical, textiles, agriculture,
footwear, and fishery products in its Agri-Food export sector. 2
Vietnamese exports to the world, selected sectors, 2000-12
Figure 2. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014
Vietnamese agricultural value-added as a share of GDP, 1985-2012
Figure 3. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014 3
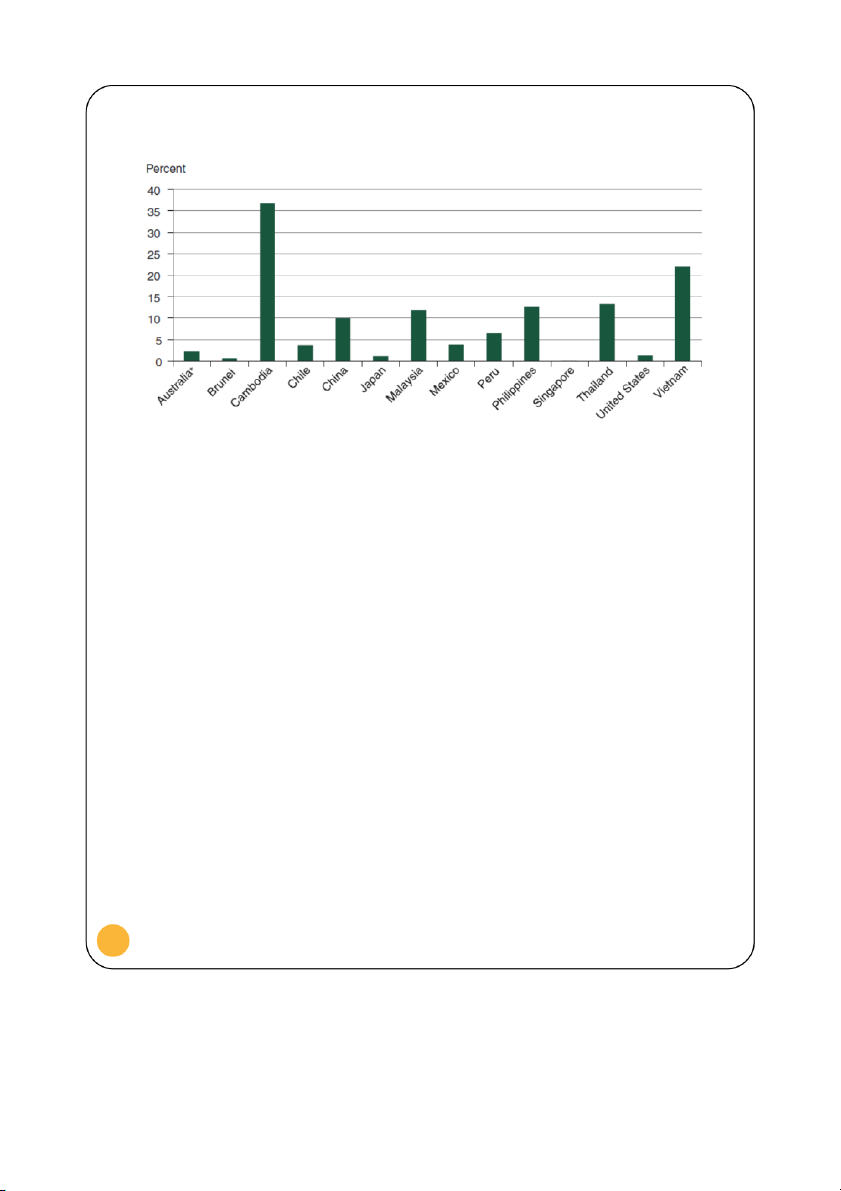
Agricultural value-added as a share of GDP for selected countries, 2011
Figure 4. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014
Figure 3 and Figure 4 indicate Vietnam’s agricultural value-added as a share of GDP
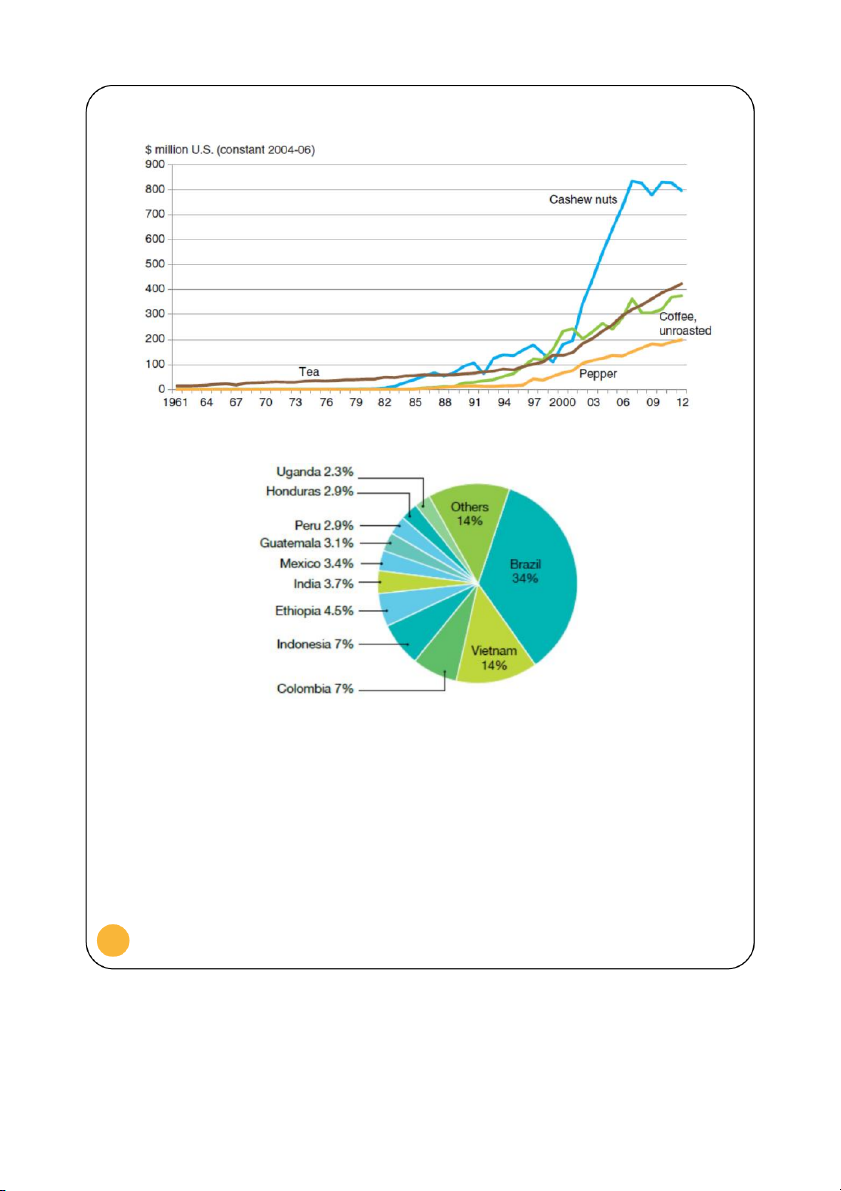
(1985-2012) has been falling to around 22% in 2011. Nonetheless, the production and export of
unroasted coffee are on the rise annually in Figure .
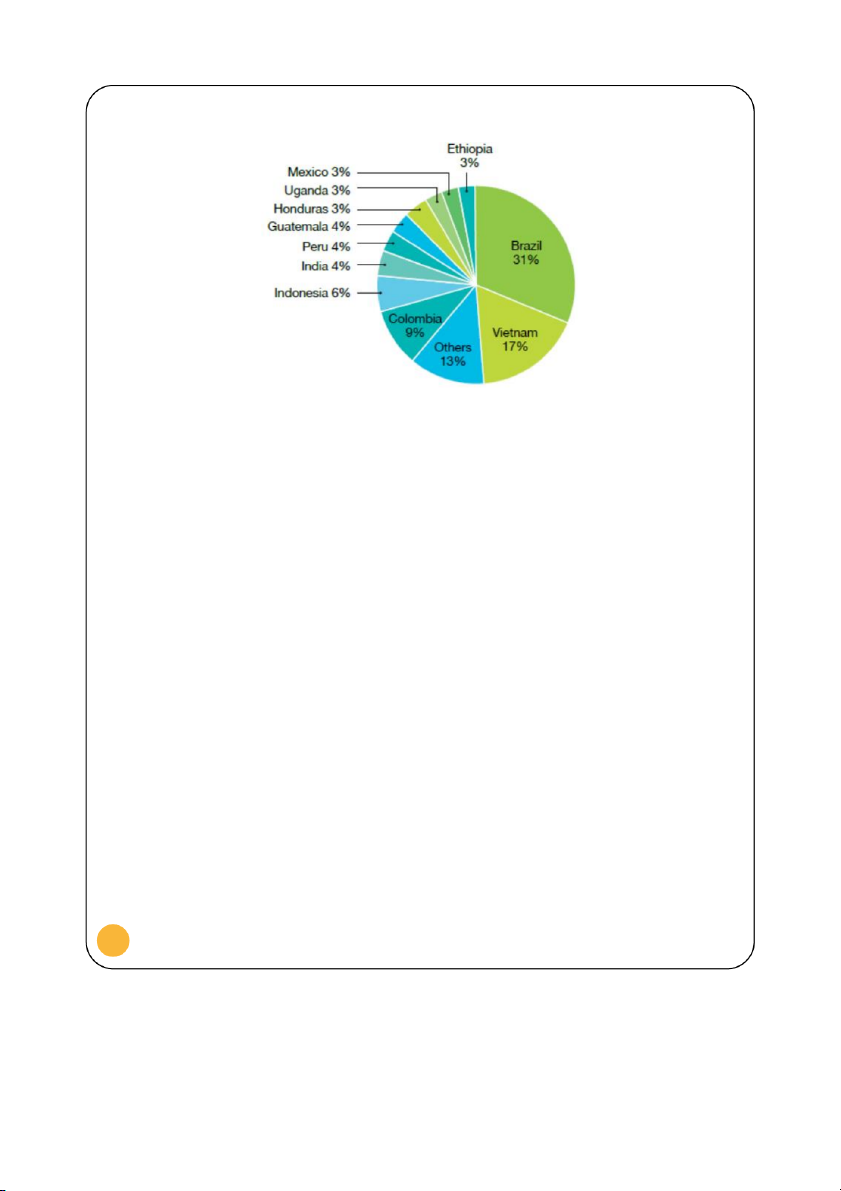
5 In fact, Vietnam is the second largest
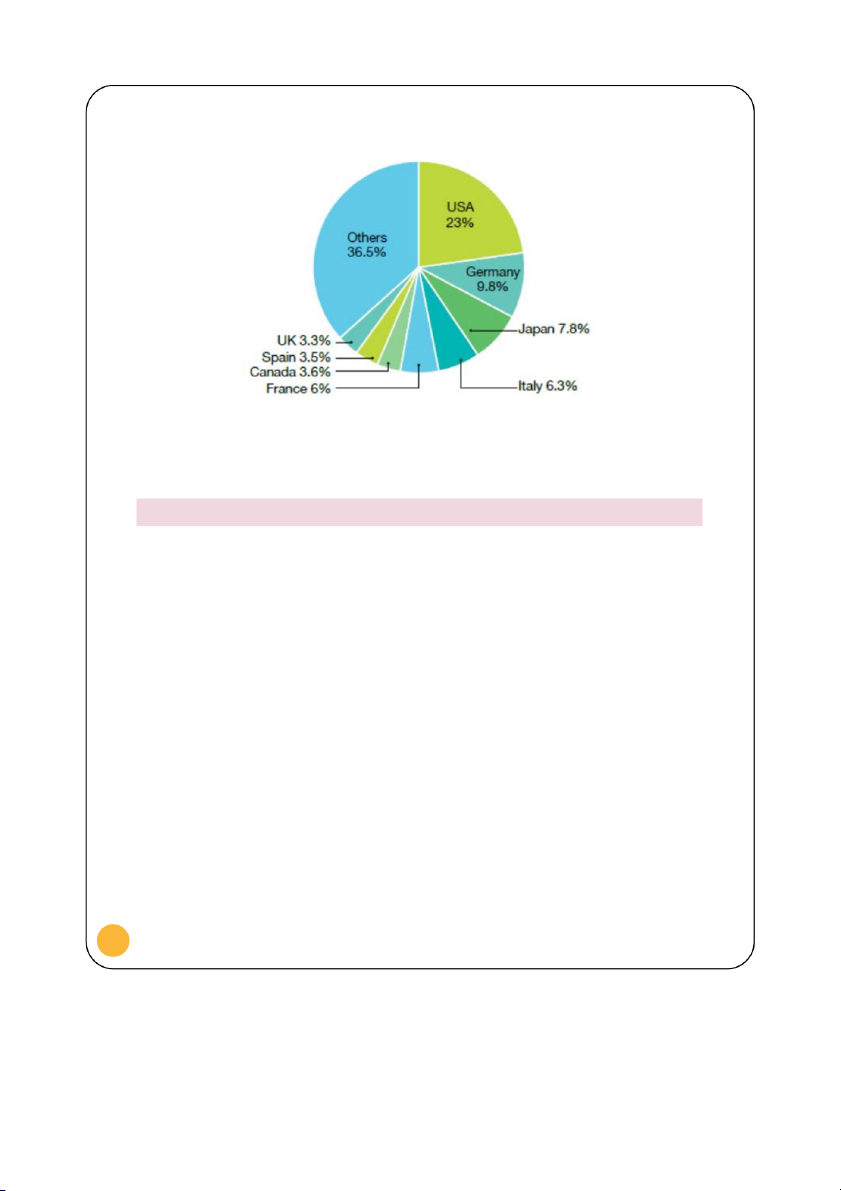
producer (14%) and exporter (17%) of coffee in the world mainly to USA (Figure 6, Figure 7, and Figure 8)
. The US economy grew 2.4% in 2015 (World Bank 2016), indicating a good sign
to export commodities to the US, but US importers have economic power with strong financial
power to bargain for coffee prices, meaning coffee producers trade unroasted coffee in a fickle priced global market.
Vietnam’s production of selected export crops, 1961-2012 4
Figure 5. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014
Largest producers of coffee as % of world production, 2007-11
Figure 6. Reproduced from: Fairtrade 2012
Largest exporters of coffee as % of world exports, 2007-11 5
Figure 7. Reproduced from: Fairtrade 2012 6
Largest importers of coffee as % of world total 2006-10
Figure 8. Reproduced from: Fairtrade 2012
Furthermore, cafés/bars are projected to grow with a constant 2015 price value CAGR of
4%, but the projected sales per outlet growth is higher (Euromonitor International 2016a). This
declined percentage from previous year means slower growth thanks to rising competition. POLITICAL
The government has been assisting coffee farmers by interfering to decrease interest
costs on loans from the Vietnamese banks to coffee farmers, and offered value-added 5% tax
exemptions on coffee and other agricultural products with regards to exporting (Arita & Dyck
2014). They also benefit from marketing coordination from Vicofe, a state-own enterprise.
Vietnam’s formal institutional framework restricts foreign-invested business in a way
that forces them to adopt franchising when opening a store (Euromonitor International 2016a).
The success of Starbucks has inspired Viet Idea Food and Beverages to embrace the franchise
model and become the fastest franchisee company.
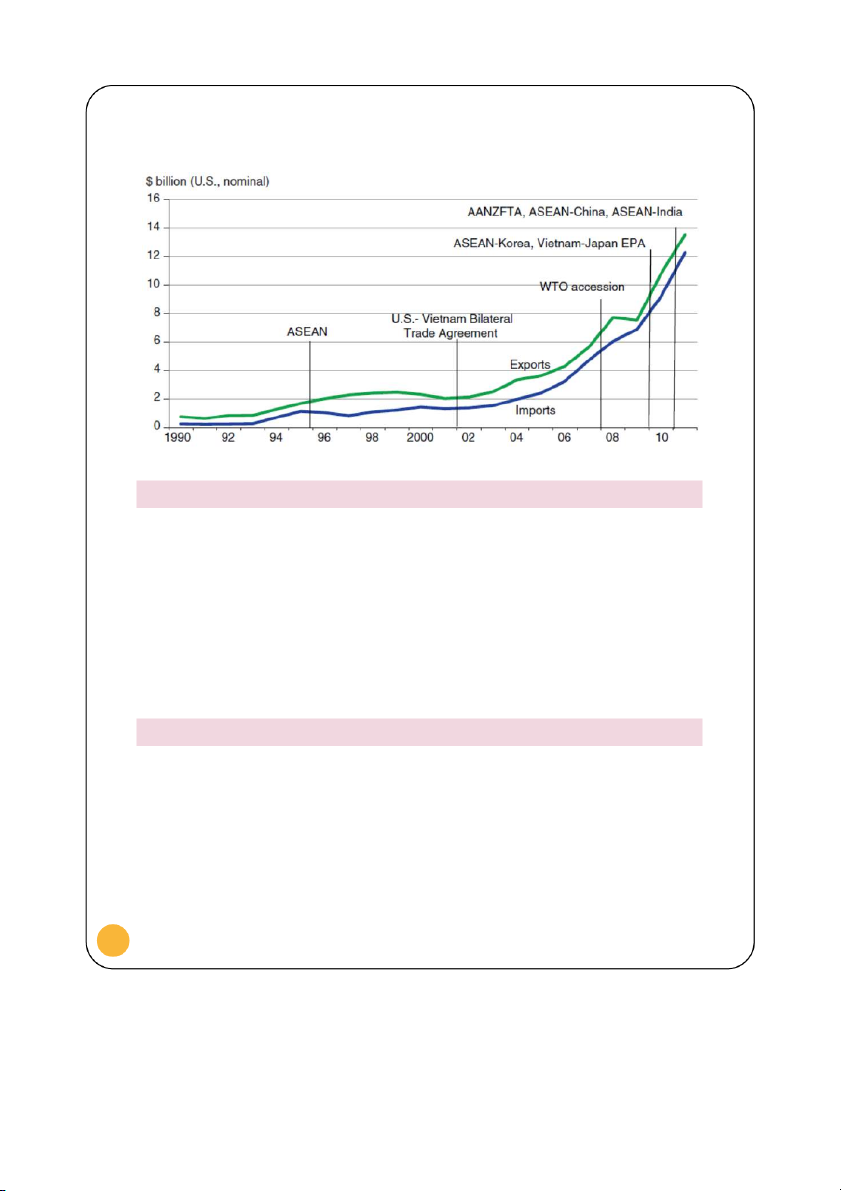
The government has been facilitating open markets in Vietnam through many trade
agreements in Figure 9. 7
Vietnam Agricultural Trade and Trade Agreements (1990-2011)
Figure 9. Reproduced from: Arita & Dyck 2014 SOCIAL
Vietnam’s rising middle class are developing more appetite for coffee and café shop as a
culture. Vietnamese consumer expenditure for coffee, tea and cocoa rises from VND13.2mil in
2010 to VND19.9mil in 2015 (Euromonitor International 2016b). Also, wealthy consumers have
the tendency to experience exotic food, and Trung Nguyen offers a unique yet valued tradition in
its Weasel package to meet such a c
onsumer desire (Trung Nguyen 2015).
Catching on to the latest consumer lifestyle inseparable from smartphones, Trung
Nguyen uses the growing media, internet, and social networks on different platforms to advertise
its brands, increase words-of-mouth, and build reciprocal communities with direct feedback
(Euromonitor International 2016a). TECHNOLOGY
Trung Nguyen implements the Microsoft Dynamics NAV
– LS Retail system, which is
an integrated business system to manage the firm’s POS network using its own in-house IT
resources (NaviWorld Vietnam 2011). This technology allows the firm to become a vertically
integrated business to manage its coffee outlets via real-time information to forecast demand,
streamline supplies, take orders and process transactions using handheld devices, and offer
customer loyalty programs across all locations. 8




