
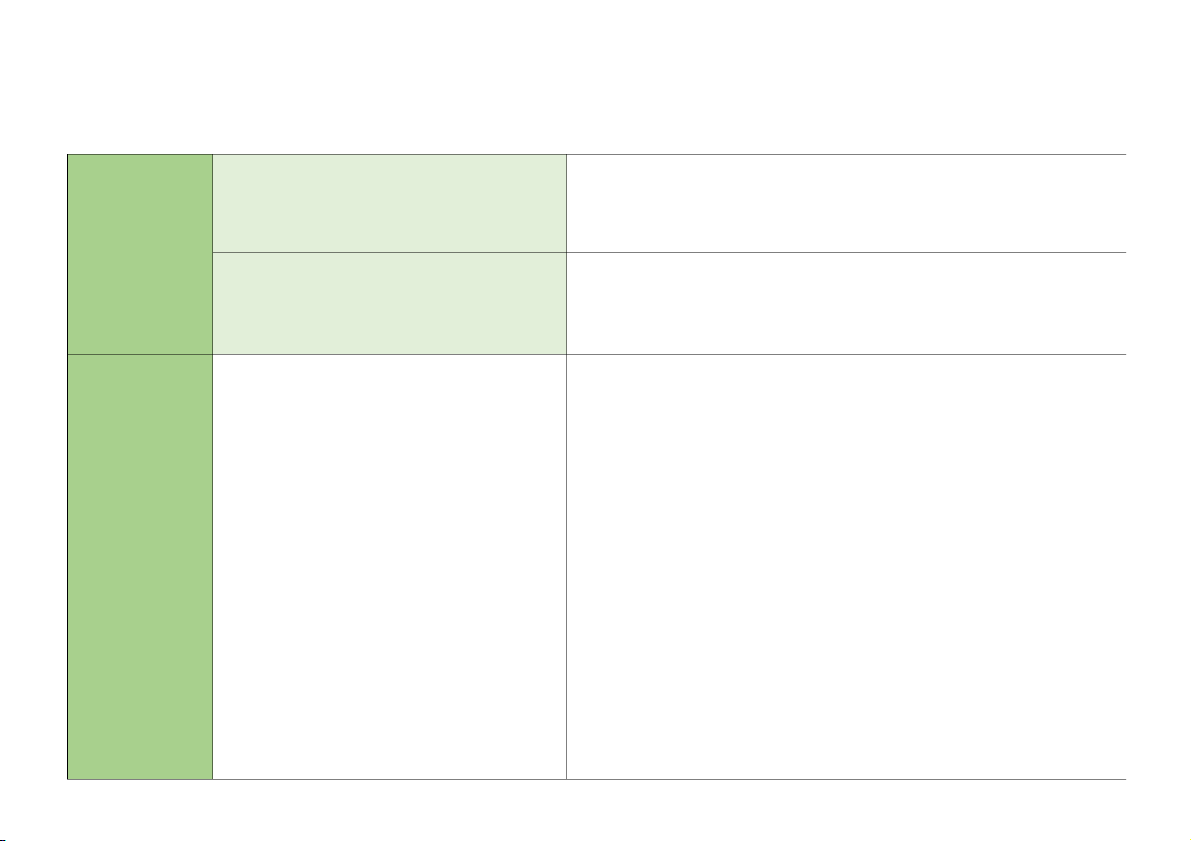











Preview text:
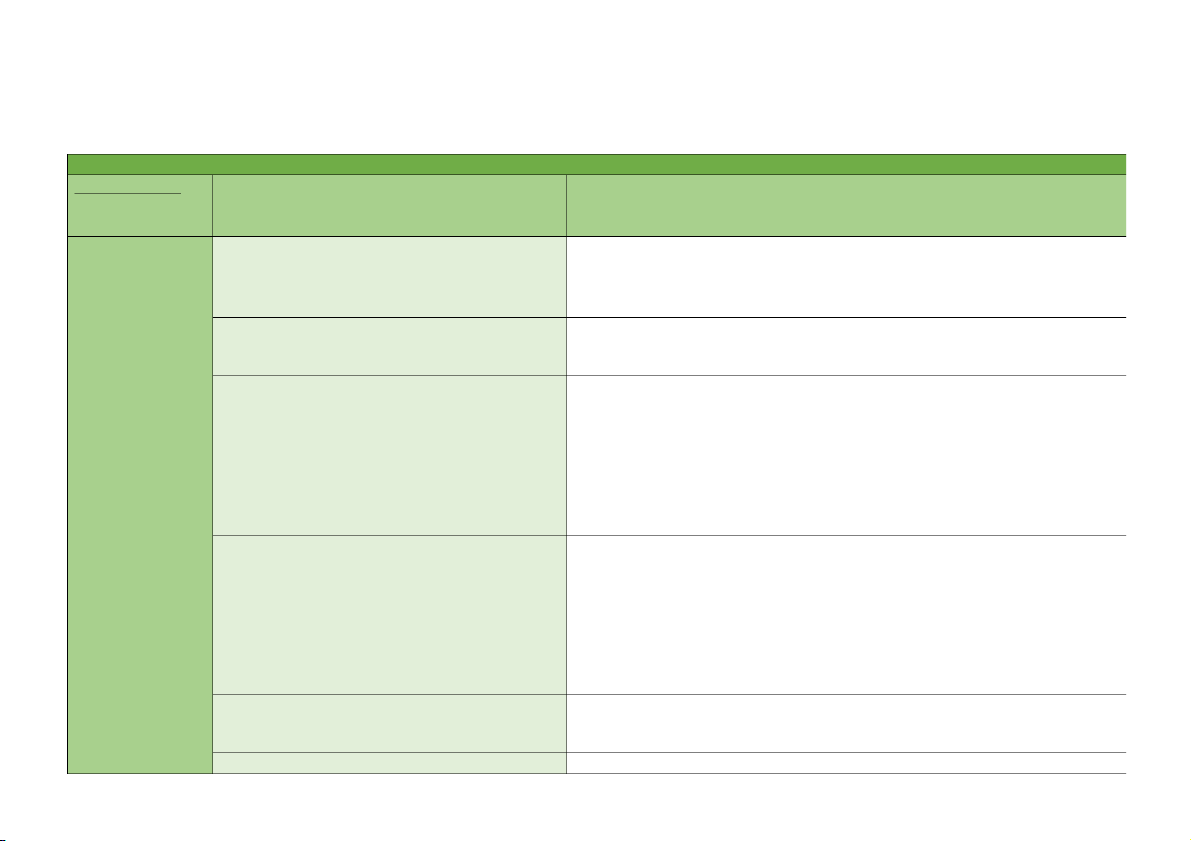
INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM I.Components Elements Characteristic (Các thành
(Các yếu tố của thành phần đó) (Đặc điểm) phần)
Communication and enforcement of integrity NQT cần thiết lập những tiêu chuẩn ứng xử và giá trị đạo đức, đồng thời tôn and ethical value
trọng và gương mẫu => Ethic, standard, respect…
Truyền đạt thông tin và yêu cầu về tính chính
trực và giá trị đạo đức
Commitment to competence
NQT cần xác định những kỹ năng và kiến thức cần thiết để thực hiện công Cam kết về năng lực
việc => Skill, knowledge… 1.Control environment
Participation by those charged with
-Independence and ability to evaluate Môi trường kiểm governance
Sự độc lập và khả năng đánh giá hoạt động của BGĐ soát (7)
Sự tham gia của ban kiểm soát
-Understanding of enity business transactions
Hiểu biết về nghiệp vụ kinh doanh của đơn vị
-Evaluation of the appropriateness of FS in accordance with applicable reporting framework
Mức độ đánh giá về tính phù hợp của BCTC với khuôn khổ và quy định
Management’s philosophy and operating
-Approach to taking and managing business risk style
Cách tiếp cận đối với việc quản lý và chấp nhận rủi ro
Triết lý và phong cách điều hành của nhà quản
-Attitudes and actions towards FS trị
Quan điểm lập và hành động đối với việc lập và trình bày BCTC
-Attitudes towards information processing and accounting functions and personnel
Quan điểm đối với việc xử lý thông tin, công việc kế toán và nhân sự
Organizational structure
Sự phân chia quyền hạn, trách nhiệm và nhiệm vụ giữa các bộ phận, phòng Cơ cấu tổ chức
ban tổ chức. Phụ thuộc vào quy mô, bản chất hoạt động của DN
Assignment of authority and responsibility
-How authority and responsibility for operating activities are assigned
Phân công quyền hạn và trách nhiệm
Cách thức phân công quyền hạn và trách nhiệm đối với các hoạt động
-How reporting relationships and authorization hierarchies are established
Cách thức thiết lập trình tự hệ thống báo cáo và sự phân chia quyền hạn và
trách nhiệm giữa các cấp
Human resource policies and practices
Includes recruitment, orientation, training, evaluating, counseling,
Các chính sách và thông lệ về nhân sự
promoting, compensation and remedial actions
Gồm toàn bộ các phương pháp quản lý nhân sự và các chế độ của đơn vị đối
với việc tuyển dụng, huấn luyện, đánh giá, đề bạt, khen thưởng và kỷ luật nhân viên 2. Risk
Process risk assessment:
Risk could be high (situation): assessment
- Changes in business environment Đánh giá rủi ro
1.Risk identification: Xác định RRKD liên
Những thay đổi trong môi trường hoạt động quan lập BCTC - New personnel
2.Estimating the significance: Ưóc tính mức Thay đổi nhân sự độ rủi ro
- New or amended information system
3.Assessing the likelihood: Đánh giá khả năng HTTT mới hoặc được chỉnh sửa xảy ra rủi ro - High growth
4. Actions: Quyết định các hành động đối với Tăng trưởng nhanh RR - New technology
=> Tạo cơ sở đến BGĐ xác định các RR cần Công nghệ mới quản lý
- New products or business model
Hoạt động, sản phẩm hay mô hình kinh doanh mới ↔ Organizational restructing Tái cơ cấu tổ chức ↔ Expanding overseas
Mở rộng các hoạt động ở nước ngoài
↔ Applying new accounting standards
Áp dụng các đơn vị kế toán mới
=> Nhận dạng và đánh giá rủi ro ảnh hưởng đến việc đạt mục tiêu để có các
biện pháp kiểm soát rủi ro. Để đánh giá thì phải xác định mục tiêu của đơn vị
=> nhận dạng RR từ mục tiêu đó => xác định tầm quan trọng của RR => đưa
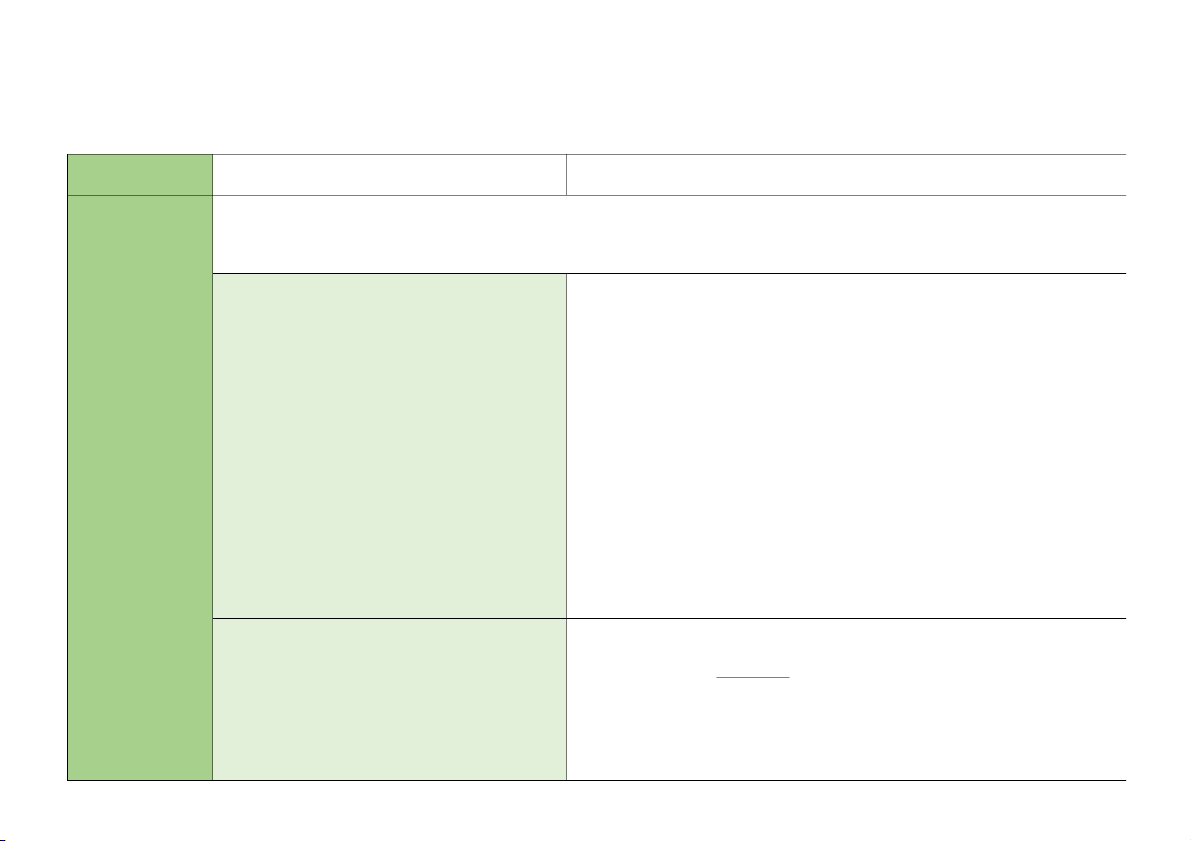
ra phương pháp kiểm soát RR 3. Control Definition: activities
Are actions established by the policies & procedures to help ensure that management directives to mitigate risks to the Hoạt động kiểm
achievement of objectives are carried out soát (5)
1.Adequate separation of duties
Means many people involve in the accouting access
Phân chia trách nhiệm thích hợp
Impact: ↓ risk of fraud & errors
Segregation principles: Các nguyên tắc phân chia
+Segregaton of functon: carrying out, recording, maintaining asset
Phân tách chức năng: thực hiện, ghi chép và bảo quản tài sản
+Segregation of various steps in carrying out a transaction
Phân chia giữa các bước trong 1 quy trình nghiệp vụ
+The carrying out of various accounting operation should be segregated
Việc thực hiện các hđ kế toán khác nhau cần được tách biệt Example:
- Custody ∞ Accounting (Lưu giữ TS ∞ Kế toán)
- Authorization of transaction ∞ Custody of related assets
Phê duyệt ∞ Giám sát TS
- Operational responsibility ∞ Record-Keeping responsibility
Vận hành ∞ Lưu giữ hồ sơ
- IT Duties ∞ User Departments CNTT ∞ Người dùng
2.Proper authorization of transactions and
-Transactions should be approved by an appropriate person before being activities carried out
Các thủ tục phê chuẩn đúng đắng -Authorization may be include:
+General authorization: approval for general policies for transactions
being carried out. And when carried out, no need approval again.
=> Đưa ra chính sách chung để cấp dưới thực hiện và khi thực hiện thì ko cần duyệt lại
+Specific authorization: relates to individual transaction in these situation: E
xtraordinary circumstances are not included in the general policy
Trường hợp bất thường không có trong chính sách chung
Regular operations but beyond the allowed limit in general policy
Nghiệp vụ thường xuyên nhưng vượt khỏi giới hạn cho phép trong chính sách chung
3.Adequate documents and records
Đảm bảo chứng từ và sổ sách được thiết kế phù hợp, lập đầy đủ và lưu trữ
Chứng từ và sổ sách đầy đủ khoa học
4.Physical control over assets and records - Physical security Kiểm soát vật chất
Các phương tiện bảo vệ vật chất
- Limiting access to the computer programme and data files
Hạn chế quyền truy cập vào chương trình máy tính và dữ liệu
- Limiting physical access to assets and records
Hạn chế tiếp cận tài sản và hồ sơ
5.Independent checks on performance
Xem xét lại 1 cách độc lập các thủ tục kiểm soát để các thủ tục kiểm soát Kiểm tra độc lập
thường xuyên được thực hiện 4. Information system
HTTT related FS: relevant business
Necessary to carry out IC responsibilities in support of the Hệ thống thông process, information exchange achievement of its objective tin Information system
Communication & provides for organization to carry out Quality of in4 will influence day-to-day IC activities
management’s decision in relation to management and controlling
Communication help personnel understand IC
business activities and reliable FS
responibilities & their importance to the achievement of objectives
Are policies and procedures that relate to many applications and support the effective functioning of application control General control
Including: control over data centre, system (software & access security)
Either manual or automated and typical y operate at the business process level and apply to the processing of transaction
Application control Ensure the security of accounting data 5. Monitoring of Definition Classification controls
-Monitoring ensures that IC continues to
- Ongoing evaluation: are built into the routine operations and are performed Giám sát kiểm operate effectively on a real-time basis soát
-This process involves assessment by
Giám sát thường xuyên: thường diễn ra trong quá trình hoạt động, do các nhà
appropriate personnel of the design and
quản lý và nhân viên thực hiện trách nhiệm của mình
operation of controls on a suitably timely basis
- A separate evaluation: is conducted periodically by objective management
and the taking of necessary actions
personnel, internal or external audit
Giám sát định kỳ: thường được thực hiện thông qua các cuộc kiểm định kỳ
do KTV nội bộ hoặc độc lập
II.Understanding and evaluating Internal control 1. The need for ISA 315: assessment of IC
- Objective: obtain an understanding of entity and entity’s environment, included IC
Yêu cầu về chuẩn + Provide the auditor with a basis for planning the audit and exercising professional judgment throughout the audit mực process.
Thu thập những hiểu biết về đơn vị và môi trường của đơn vị, trong đó có KSNB =>cung cấp cho KTV cơ sở để lập kế hoạch
kiểm toán và đưa ra các xét đoán chuyên môn trong quá trình kiểm toán
+ Help the auditor indentify:
Business risk relevant to FS objectives: Rủi ro kinh doanh liên quan đến mục tiêu BCTC (1)
Types of potential (inherent) error, factors affecting the risk of material misstatement
Xác định các loại sai sót tiềm tàng, các yếu tố ảnh hưởng RRSSTY
Estimating the significance of the risk
Ước tính tầm quan trọng của rủi ro (2)
Assessing the likelihood of their occurrence
Đánh giá khả năng xảy ra của chúng (3)
Deciding upon actions to address those risk
Quyết định hành động để giải quyết những rủi ro đó (4)
Determine the nature, timing and extent of subsequent audit procedures
Xác định nội dung, lịch trình và phạm vi của cuộc kiểm toán tiếp theo
Auditor’s responsibility:
(1) (2) (3) (4) & must evaluate the design of controls and determine whether these controls have been implemented at the
entity. KTV phải đánh giá về mặt thiết kế của các kiểm soát và xác định xem các biện pháp kiểm soát này đã được thực hiện tại đơn vị chưa
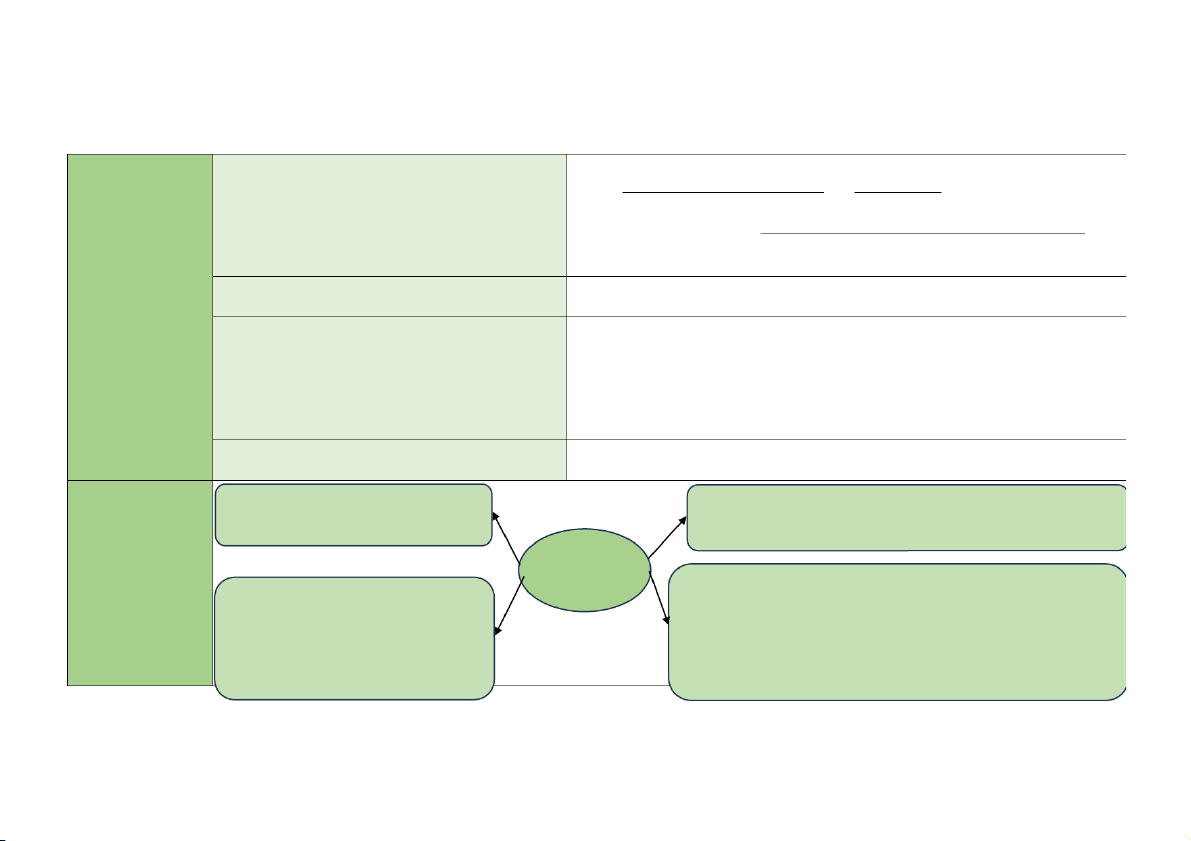
Process for Understanding IC and Assessing control risk
B1: Obtain and document understanding of IC design and operation B2: Assess control risk
B3: Design, perform and evaluate test of controls
B4: Design planned detection risk and substantive tests 2. Method to
Narrative notes (Bản tường thuật): is a written document Advantages: obtain and to describe the IC, include:
Simple to use & suitable for recording of simple IC system document an
The origination of all books and documents in the
Dễ sử dụng và thích hợp với những đơn vị có HTKS đơn giản understanding of system Disadvantages: IC
Nguồn gốc mọi chứng từ, sổ sách
Not suitable for entity whose IC system are in a complex Phương pháp để The processes structure
thu thập và mô tả Tất cả quá trình đã xảy ra những hiểu biết The flow of each document về KSNB
Sự luân chuyển chứng từ, sổ sách
Necessary control activities
Các HĐKS cần thiết giúp cho quá trình đánh giá RRKS
Questionnares (Bảng hỏi): is a list of questions on IC Advantages:
system whether control exist which meet specific control
-If drafted thoroughly, the can ensure all controls are considered
objectives (ICQs) or to determine whether there are controls -Quick to prepare
which prevent or detect specified errors or omissions -Easy to use and control (ICEQs) Disadvantages:
Là bảng liệt kê những câu hỏi đã được chuẩn bị
May not include unusual control, which are nevertheless
trước về HTKSNB để xác định sự tồn tại của các
effective in particular circumstances
kiểm soát trong việc đáp ứng các mục tiêu kiểm soát
Có thể không bao gồm các kiểm soát đặc thù, tuy nhiên vẫn có
(ICQs) hoặc để ngăn ngừa và phát hiện các sai sót
hiệu quả trong các trường hợp cụ thể cụ thể (ICEQs) hay không?
Flow chart (Lưu đồ): is a type of diagram that represents a Advantages:
workflow or process, showing the steps and their order by
Fairly easy to follow & review connecting them with arrows:
Can help auditor to highlight the salient points of control (điểm
Loại biểu đồ trình bày quá trình, quy trình làm việc; các
KS nổi bật) and any weakness in the system (bất kỳ điểm yếu
bước và thứ tự được nối bằng mũi tên nào trong hệ thống)
Horizontal flow chart: highlight (chỉ ra) the Disadvantages:
participation of people/function in a process Time-consuming
Vertical flow chart: highlight (chỉ ra) the order of
Mất nhiều thời gian có khi không cho phép xác định điểm yếu steps in a process của KSNB 3. Test of Definition: control:
Audit evidence is used as the basis for auditor to provide an audit opinion. Audit evidence is obtained through: p p g Thiết kế các thử + Risk assessment nghiệm kiểm soát
+ Carrying out further audit procedures which include:
Control test (Thử nghiệm kiểm soát)
Substantive test (Thử nghiệm cơ bản) Objective:
An audit procedure is designed to evaluate the operating effectiveness of control in preventing, or detecting and correcting,
material misstatement at the assertion level
Một thủ tục kiểm toán được thiết kế để đánh giá sự hữu hiệu của HĐKD trong việc ngăn ngừa, hoặc phát hiện và sửa chữa
những sai sót trọng yếu ở cấp độ cơ sở dẫn liệu
An auditor must obtain evidence as to (about):
- How the controls were applied at relevant times during the period under audit
Cách thức áp dụng các biện pháp kiểm soát vào thời điểm thích hợp trong quá trình kiểm toán
- The consistency with which they were applied
Tính nhất quán trong việc áp dụng biện pháp kiểm soát
- By whom or by what means they were applied
Biện pháp kiểm soát được áp dụng bởi ai và bằng phương tiện gì
Internal control evaluation process: RRKS thấp RRKS là tối đa
The nature of a test of control can be: Thử nghiệm kiểm soát có thể là 1. Inspection (Kiểm tra)
- Definition: “inspection” is an audit procedure to gain audit evidence that IC have operated properly, verifying that a
transaction has been authorized
Thủ tục kiểm tra trong thử nghiệm kiểm soát là kiểm tra tài liệu, sổ kế toán và chứng từ, thường để thu thập bằng chứng về việc
tuân thủ các quy định và việc phê chuẩn đúng thẩm quyền - Gồm:
+ Kiểm tra tài liệu, sổ kế toán hoặc chứng từ: có thể từ trong hoặc ngoài đơn vị và có thể ở dạng giấy, điện tử hoặc cá dạng thức khác
+ Kiểm tra tài sản hiện vật 2. Observation (Quan sát)
- Auditors will consider the manner in which the control is being operated
KTV quan sát nhân viên của đơn vị thực hiện HĐKS
- Limited to the point in time at which the observation take place
Chỉ giới hạn ở thời điểm quan sát
- The act of being observed may affect how the process or procedure is performed
Hành động quan sát có thể ảnh hưởng cách thức thực hiện quy trình hoặc thủ tục đó
=>Should observe and inquiry 3. Inquiry (Phỏng vấn)
- Definition: inquiry consists of seeking in4 of knowledgeable persons, both financial and nonfinancial, throughout the enity or outside the entity - Object (đối tượng):
+ Director and those responsible for preparing and presenting financial statements;
+ Other individuals and employees at different levels and positions
- Inquiry is used extensively throughout the audit plan and often is complementary to performing other audit procedure
- Questions inquiry include formal written or informal oral. And evaluating responses to inquiries is intergral part of the inquiry process.
4. Re-performance (Thực hiện lại)
Is the auditor’s independent execution of controls that were originally performed as part of the entity’s IC
KTV thực hiện độc lập các thủ tục hoặc các kiểm soát đã được đơn vị thực hiện trước đó như một phần của KSNB
III. Communicating deficiencies in internal control: Trao đổi về KSNB VSA 265
Auditor shall communicate in writing significant deficiencies in IC identified during the audit to those charged with governance on a timely basis
KTV phải trao đổi bằng văn bản một cách kịp thời (VD: thư đề nghị, thư quản lý) với ban quản trị về những khiếm khuyết nghiêm trọng trong
KSNB được phát hiện trong quá trình kiểm toán
Communication content: - The purpose of the audit
- The extent to which audit procedures are carried out in relation to the IC system Phạm vi công việc liên quan đến KSNB
- Identified significant deficiencies Các khiếm khuyết nghiêm trọng đã được phát hiện
Deficiency in internal control:
- A control is designed, implemented or operated in such way that it is unable (cannot) to prevent or detect and correct, misstatements in the FS on a timely basis
- A control necessary to prevent or detect and correct, mistatements in the FS on a timely is missing
Indicators of significant deficiencies in IC:
- Ineffective IC environment MTKS không hữu hiệu
- Absence of a risk assessment process Đơn vị không có quy trình đánh giá rủi ro lẽ ra phải có
- Ineffective entity risk assessment process Quy trình đánh giá rủi ro không hữu hiệu
- Restatement of previously issued FS Điều chỉnh BCTC đã phát hành kỳ trước để phản ánh việc sửa chữa một SSTY / gian lận
- Evidence of management’s inability to oversee the preparation of the FS BGĐ không có khả năng giám sát việc lập và trình bày BCTC
Plan and design an audit approach Perform audit tests
Complete the audit and issue an audit report - Audit contract - Understand IC - Tests of control - Audit completing
- Determine the level of materiality - Substantive Tests and audit risk assessment - Audit report
- Finalise audit strategy and design
RISK ASSESSMENT AND AUDIT PLANNING




