Preview text:
PRE-TEST (EC)
PART 1: VOC AND GRAMMAR (20 pts)
Task 1: Choose the correct answer by circling A, B, C or D.(10pts)
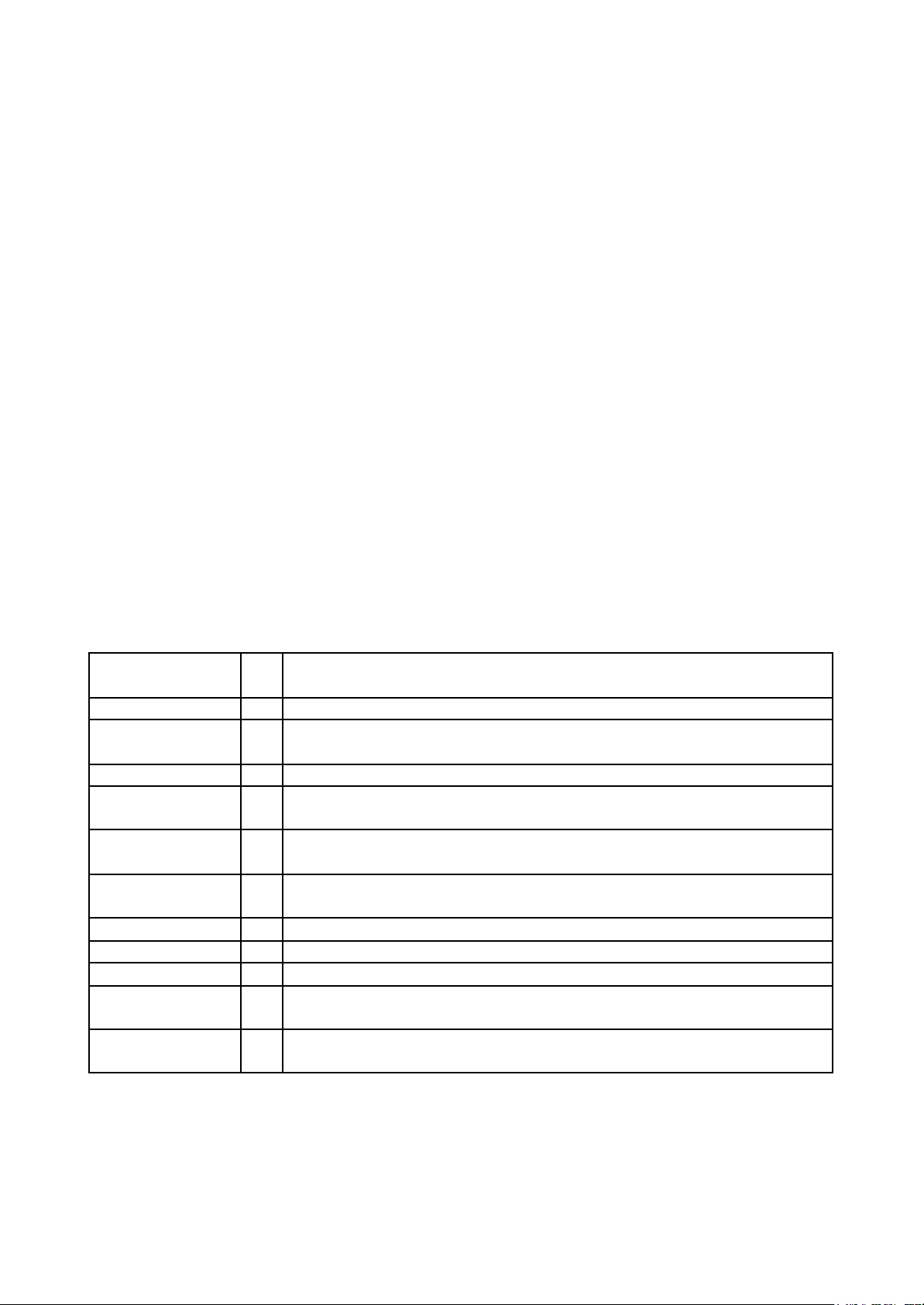
1. Walls________ made up of blocks both support the building and divide the space in the building. A. which is B. that are C. which was D. that were
2. Navvies are usually the first men employed on a building site________ the building will take place. A. which B. where C. whose D. that
3. Beam is one of the basic structural elements ____ are capable of withstanding load primarily by resisting bending force. A. which B. whose C. who D. x
4. Rod materials which ________for structural support but not for dividing spaces are timber, steel and concrete. A. can be used . B. can to be use C. were able to use D. was able be used
5. These floors ________ generally________ up of reinforced or prestressed concrete. A. is/ made B. are/ maked C. are/ made D. is / maked
6. Bridges ________ by different kinds of material. A. can to be built B. can be built C. were able to build D. were able built
7. Cement ________ at or near the construction site with sand, aggregate and water to make concrete. A. are mixed B. is mixed C. was mixed D. mixes
8. It ________in mind that the foundation system is likely________ again.
A. must to be kept/ will be fully exposed
B. must keep/ will be fully exposed
C. must be kept/ will be fully exposed
D. must be kept/ will be fully expose
9. The load can be spread over a large area or carried to________.
A. soil stronger B. soil strong C. stronger soil D. strongs soil
10. Sheet materials are used to form walls which act as the ________and structural support. A. space-dividers B. spaces-divider C. dividers space D. space-deviders
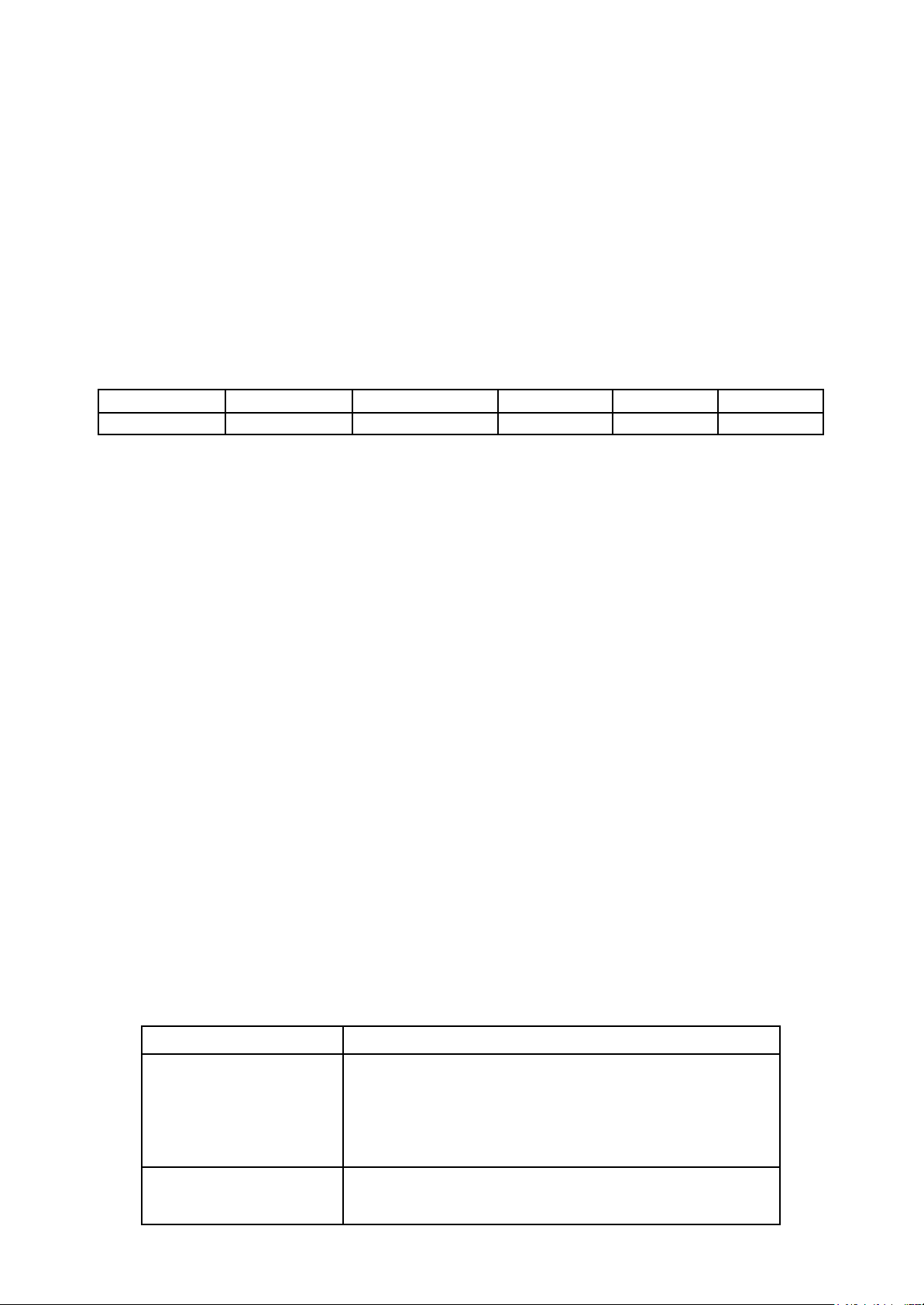
Task 2: Match a number on the left with a letter on the right. (10pts) 11. Concrete
A. are usually used in construction of bridge piers and other structures
where the foundation is under water. 12. Fatigue
B. takes the load from a structure and transmits it safely to the ground. 13. Compression
C. are used when there are weak soils near the surface or when loads are
very high, such as very large skyscrapers. 14. Tension
D. is built vertically to transmit the weight of the structure. 15. A structure E.
The tendency of a material to weaken because of continual changes in stress. 16. A column F.
A masonry material made of a mixture of cement, aggregate, sand and water. 17. Deep
G. A material such as small stones, gravel, or crushed rock used for foundations construction. 18. Aggregate
H. The force that presses or pushes a material together. 19. A foundation I
is the part of a building that carries its weight. 20. Caissons J
The force that stretches or pulls apart a material K
is kind of concrete which wire mesh or steel bar embedded to increase its tensile strength L
are people who prepare drawings, specifications, construction costs to implement the projects.
PART II: READING COMPREHENSION (20 pts)
Part 1: Read the text and decide if the following statements are true (T) or False (F). (10pts)
Today, however, the engineer has the advantage not only of empirical information, but also of scientific data that
permit him to make careful calculations in advance. When a modern engineer plans a structure, he takes into
account the total weight of all its component materials. This is known as the dead load, which is the weight of Midterm-M.10 1
the structure itself. He must also consider the live load, the weight of all the people, cars, furniture, machines,
and so on that the structure will support when it is in use. In structures such as bridges that will handle fast
automobile traffic, he must consider the impact, the force at which the live load will be exerted on the structure.
He must also determine the safety factor, that is, an additional capability to make the structure stronger than the
combination of the three other factors.
The modern engineer must also understand the different stresses to which the materials in a structure are
subject. These include the opposite forces of compression and tension. In compression the material is pressed or
pushed together; in tension the material is pulled apart or stretched, like a rubber band. In the diagram alongside,
the top surface is concaved, or bent inward, and the material in it is in compression. The bottom surface is
convex, or bent outward, and the material in it is in tension.
21. A modern engineer calculates the total weight of all its component materials when he plans a structure
22. The dead load is the weight of the structure itself
23. One example of the “live load” is the weight of the vehicles moving on the road
24. Compression and tension are different stresses
25. When the material is in compression, the bottom surface is bent inward.
Part 2: Fill in the gaps with the words provided. (10pts) length which of cement Concrete are is regularly independent spread other reinforced
There are a lot of types of foundations in construction. The main types of 26 _______ foundations are
“independent”, “raft” and “pile”. For bridge building and 27 ______ heavy engineering structures “caisson”
foundations 28 ________ used. Independent foundations are used to support columns or piers, 29 ______ are
unevenly spaced and unequally loaded. A pad of concrete, plain or 30 _____, is placed under each column or
pier, the base of the pad extending far enough in all directions to 31_____ the load evenly over the ground. Strip
foundations are used when a row 32 _____ columns is so closely spaced that 33 _____ foundation would nearly
meet. When the columns are both near together and 34 ______ spaced, and carry nearly equal loads, raft
(sometimes called “slab”) foundations, extending the whole 35 ____ and breadth of a building, are used instead of strip foundation.
PART III: WRITING (20 pts)
Part 1: Rewrite these sentences as indicated. (10pts)
36.People can make timber, concrete and some plastic into large rigid sheets and fix them together to form a building. Timber ………………….
37. They still used mat foundations although the soil bearing capacity in this area is high.
In spite of ……………….
38. Thin-shell structures are fuselages of aeroplanes, boat hulls and roofs in some buildings. These structures are
usually made of steel or high-compacted plastic.
The thin-shell structures……………………….
39. As concrete has a rather low tensile strength, it is generally strengthened by steel rods.
Because of ……………………………
40. This concrete is not strong enough as it is not in good curing
= this concrete is too ………………… Part 2: (10pts)
Write a paragraph of about 80 – 100 words to describe these kinds of concrete, using all the following given details Types of Properties ● Support any applied loads ● Allow longer spans. Pre-stressed concrete
● Reduced structural thicknesses. ● Material savings.
● Good bond between the tendon and concrete. Pre-tensioned concrete
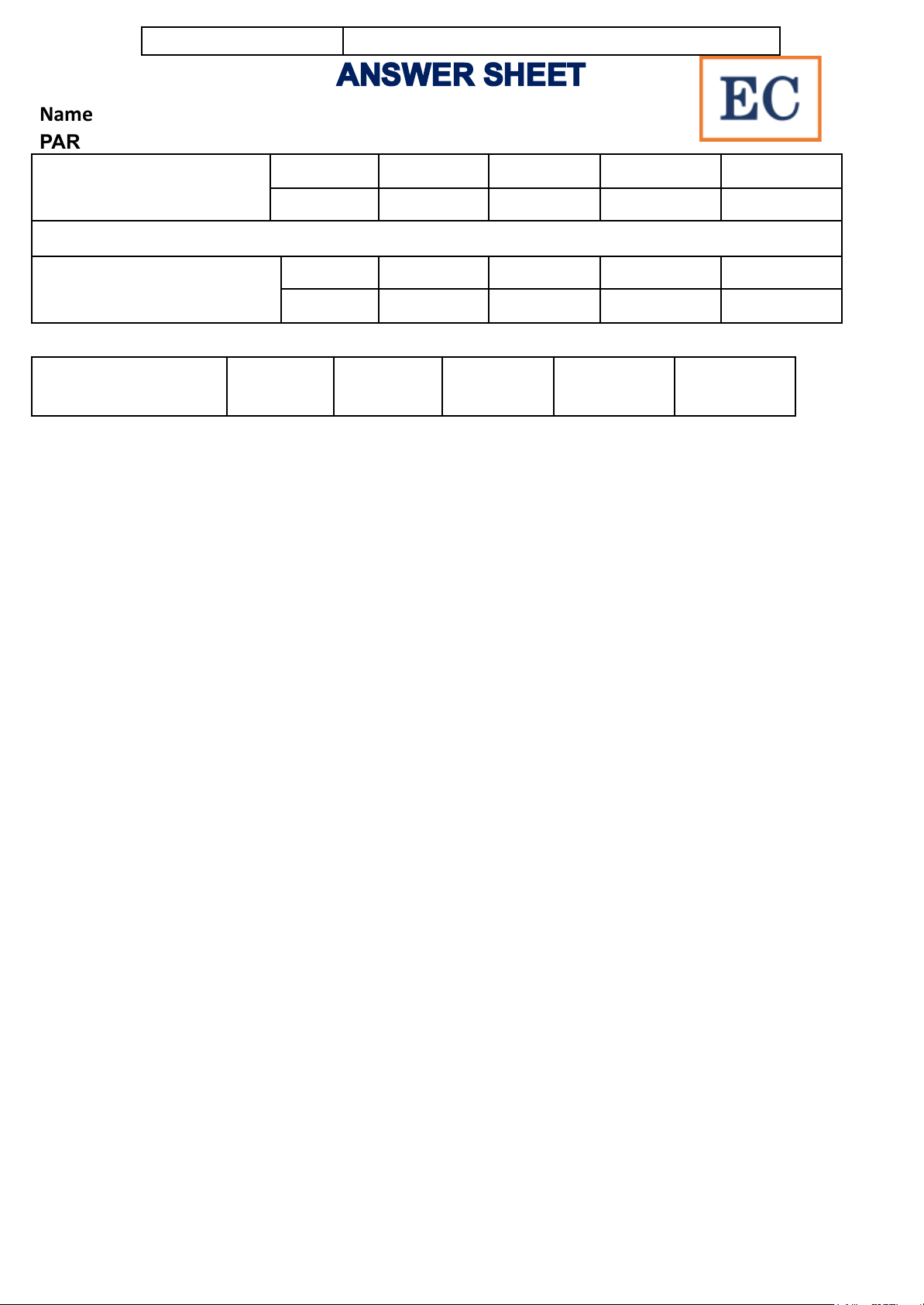
● Prefabricated in a factory. Midterm-M.10 2 ● Limit their sizes. ANSWER SHEET Name:
PART I. GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY (20 pts) Task 1: 1............. 2............. 3.............. 4.............. 5...............
Multiple choice (10 pts) 6............. 7............. 8.............. 9.............. 10.............
Task 2: Column matching 11........... 12........... 13............ 14............ 15............. (10 pts)
16........... 17........... 18............ 19............ 20.............
PART II. READING COMPREHENSION (20 pts) Task 1:
21............ 22............ 23............ 24............ 25............ True or False Task 2: Gap-fil ing 26. 31. 27. 32. 28. 33. 29. 34. 30. 35.
PART III. WRITING (20 pts) 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Midterm-M.10 3
Document Outline
- ANSWER SHEET



