

















Preview text:
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION & TRAINING HOA SEN UNOVERSITY FINAL GROUP PROJECT MICROECONOMICS SEMESTER: 2331 TOPIC:
THE MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION IN
THE FITNESS MARKET IN VIET NAM
INSTRUCTOR: PH. S PHUNG THE VINH GROUP: 5 CLASS: 1091 Member Student ID
1. Nguyễn Huỳnh Nhật Châu 22205190 2. Trần Phạm Vân Thanh 22206803 3. Huỳnh Thùy An 22207426 4. Ngô Nguyễn Nhật Nghi 22201458 5. Trần Nguyễn Bảo Trâm 22118001 6. Nguyễn Trường Thọ 22114234
Ho Chi Minh city, November 2023 ABSTRACT 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT MỨC ĐỘ PHÂN CÔNG MEMBER STUDENT ID NHIỆM VỤ HOÀN THÀNH Nhóm trưởng Tổng hợp thông tin Ngô Nguyễn 22201458 Trình bày báo cáo, Nhật Nghi Powepoint 100%
Thuyết trình: Liên hệ với ngành học hiện nay Nguyễn Thụy
Thuyết trình: Khái niệm và 22204956 Thanh Trúc
nội dung hội nhập kinh tế 100% quốc tế
Thuyết trình: Nhận thức
sâu sắc về thời cơ và thách Nguyễn Hải
thức do hội nhập kinh tế 22205920 Đăng
quốc tế; Xây dựng chiến 100%
lược và lộ trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế Trình bày Powerpoint
Thuyết trình: Tác động của Lê Hoàng Thức
hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế 95% 22118807
đến quá trình phát triển của Việt Nam Hứa Quốc Khánh 22207191
Thuyết trình: Vắng mặt 60%
Thuyết trình: Tích cực, chủ
động tham gia vào liên kết
kinh tế quốc tế và thực Nguyễn Hồ Nhật
hiện đầy đủ các cam kết 22012154 90% Minh của Việt Nam trong các
liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và khu vực: Hoàn thiện thể
chế kinh tế và pháp luật 2 TABLE CONTENT
TRÍCH YẾU.......................................................................................................................................... 1
MỤC LỤC............................................................................................................................................. 3
LỜI CẢM ƠN....................................................................................................................................... 5
LỜI MỞ ĐẦU....................................................................................................................................... 6 I.
KHÁI NIỆM VÀ NỘI DUNG HỘI NHẬP KINH TẾ QUỐC TẾ.................................................8 1.
Khái niệm và sự cần thiết khách quan hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế..........................................8
1.1. Khái niệm................................................................................................................................. 8 2.
Nội dung hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế..........................................................................................9
II. TÁC ĐỘNG CỦA HỘI NHẬP KINH TẾ QUÔC TẾ ĐẾN QUÁ TRÌNH PHÁT TRIỂN CỦA
VIỆT NAM......................................................................................................................................... 10 1.
Tác động tích cực của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế...................................................................10 2.
Tác động tiêu cực của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế...................................................................13
III. PHƯƠNG HƯỚNG NÂNG CAO HIỆU QUẢ HỘI NHẬP KINH TẾ QUỐC TẾ TRONG PHÁT
TRIỂN CỦA VIỆT NAM....................................................................................................................15 1.
Nhận thức sâu sắc về thời cơ và thách thức do hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế..........................15 2.
Xây dựng chiến lược và lộ trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế..................................................16 3.
Tích cực, chủ động tham gia vào liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và thực hiện đầy đủ các cam
kết của Việt nam trong các liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và khu vực..............................................17 4.
Hoàn thiện thể chế kinh tế và pháp luật...............................................................................17 5.
Nâng cao năng lực canh tranh quốc tế của nền kinh tế......................................................19 6.
Xây dựng nền kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ của Việt Nam...........................................................20
IV. LIÊN HỆ VỚI NGÀNH HỌC CỦA NHÓM HIỆN NAY...........................................................21 1.
Logistics và Quản lý chuỗi cung ứng..................................................................................21 2.
Marketing..............................................................................................................................22 2.1.
Hiểu và tận dụng thị trường quốc tế:.........................................................................22 2.2.
Xây dựng chiến lược marketing toàn cầu:.................................................................22
2.3. Xây dựng và quản lý thương hiệu:..................................................................................22
2.4. Sử dụng công nghệ và kỹ thuật số:..................................................................................23 3
2.5. Hợp tác và liên kết quốc tế:..............................................................................................23 3.
Quản trị kinh doanh.............................................................................................................23 3.1.
Đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực:...................................................................................23 3.2.
Nắm vững quy định và quy chuẩn quốc tế:...............................................................24 3.3.
Mở rộng mạng lưới kết nối:.........................................................................................24 3.4.
Áp dụng công nghệ và quản lý thông tin:..................................................................24 3.5.
Nghiên cứu thị trường và chiến lược tiếp cận:..........................................................24
KẾT LUẬN.........................................................................................................................................25
TRẢ LỜI CÂU HỎI............................................................................................................................26
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO...................................................................................................................27 4 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
During the process of attending Mr. Phung The Vinh's Microeconomics class, our
group received dedicated support from the school and him. Hereby, Group 5 would
like to express our sincere thanks to: 1.
Mr. Phung The Vinh – master, instructor of Microeconomics. Thank you for
always supporting, guiding our group with experiences, inspiring our group
with the subject.... and always ready to support when the team encounters
difficult problems and give suggestions so that we can successfully complete the subject. 2.
In addition, I would like to express my sincere thanks to the members of group
5 in particular and the students in Mr. Vinh's Microeconomics class in the 2nd
and 2nd grades for creating a professional and successful learning environment.
Finally, the feedback of teachers and students is a valuable source of information for
the team to do better in the future. Thank you very much. 5 I. THEORETICAL BASIC 1.
Content of Monopolistic Competition Marrket
Mononopolistically competition is a market that involves many companies
offering differentiated products (different in quality, and style…) and competing. The
goods or services they provide to customers are similar but not a substitute.
Monopolistic competition is often found in industries such as restaurants, clothing… 2.
Characteristic of Monopolistic Competition Marrket 2.1. Differentiated Products
Each company produces a slightly different product than its competitors, which
makes its product unique. Product differentiation can be based on quality, design, or branding.
This is also the value that helps the company increase its competitive value than
competitors. It only creates value when consumers know and distinguishes it from the products of other company. 2.2. Non-Price Competition
Companies compete on factors other than price, for example, product quality, or
customer service, and aim to attract new customers from competitors. 2.3.
Low barriers to entry and exit
Possessing this characteristic of perfect competition, entering and exiting the
monopolistic competition market does not have too many barriers or difficulties.
Companies and businesses can easily enter the market, and existing firms can exit if they are not profitable.
With the participation of new units, supply will certainly increase, so existing
businesses will only have normal profits. 6 2.4.
Normal Profit in the Long Run
In the long run, companies in monopolistic competition will get a normal profit
because when new firms enter the market the profit you receive will decrease.
Considering that businesses can create super profits in a short time, the profit
will appear when there is competition from competitors. The reason is characteristics
of entry and exit in the market are liberal. 2.5.
Super profits in the short-term
In a monopolistic competition market, businesses can create super profit with the
requirement is take advantage of gaps in the market, when do not have competitors.
However, this is only in a short time. At some point, your competitors will find
this potential opportunity and will definitely take it seriously. 2.6.
The number of buyers and seller is large
Due to the combination of factors, in a monopolistic competition market, the
number of buyers and sellers is not small at all. There will be a large number of
companies and businesses involved but they still control the prices and production of their goods to some extent.
This market also has a large number of buyers. Their needs are being met with
a variety of options. So, each supplier and sales in a monopolistic competitive market
will have an independent pricing policy. 3.
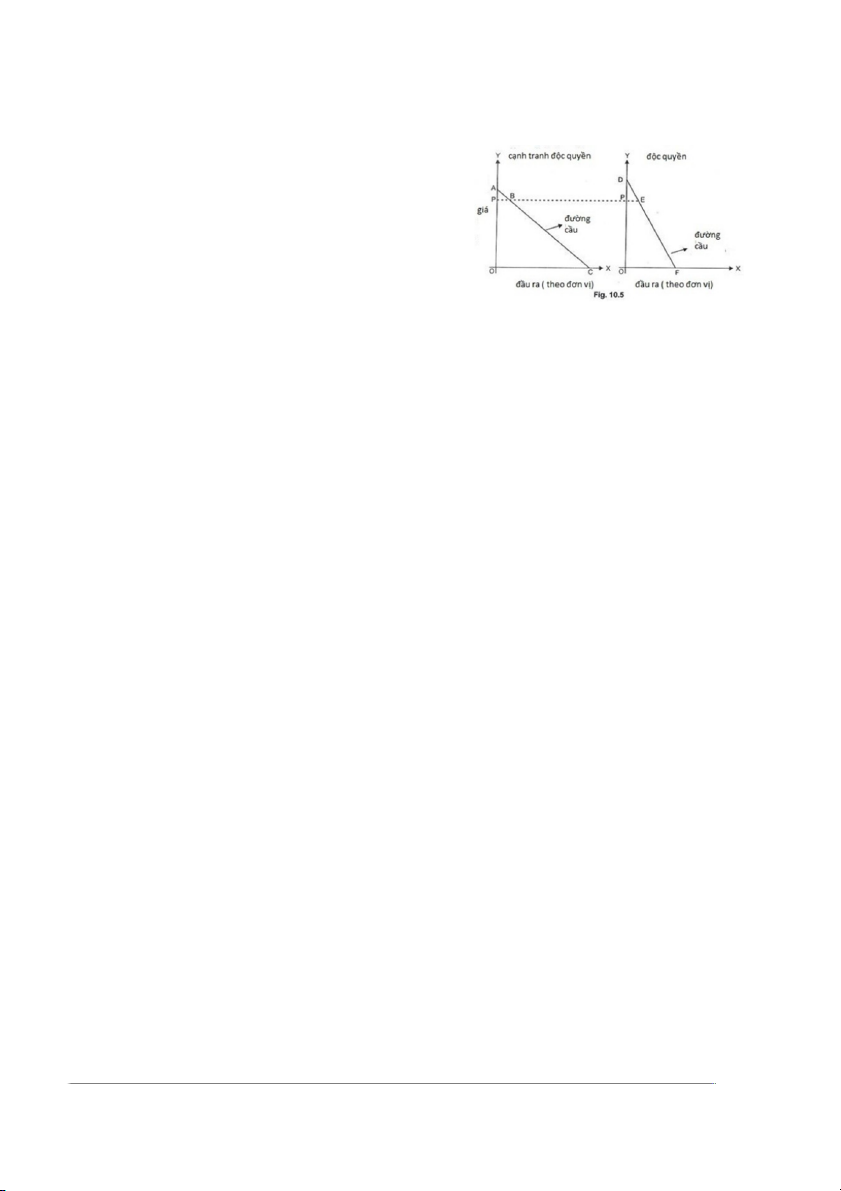
Supply anf Demand in the Monopolistic Competition Marrket
In monopolistic competition, the large
number of firms selling closely related but distinct
products cause the demand curve to slope
downward. This means, that if the company wants
to sell more products, they must reduce the price of their products. 7
The demand curves of the monopolistic
competition market and monopolistic market, the
demand curve of is downward but the demand
curve of the monopolistic competition market has
more elasticity than the monopolistic market. It
means differentiated products under monopolistic
competition have many substitutes, whereas there
are no substitutes in the case of monopolistic. 4.
Supply anf Demand in the Monopolistic Competition Marrket
Monopolistic competition is a fairly common market, so it has a lot of items this
is some examples of monopolistic competitive market: · Restaurant/Hotel · Coffee shop · Clothing · Food/Drink · Service industries II.
DETAILED INFORMATION ABOUT THE FITNESS MARKET 1. Overview of the
2. Tác động tiêu cực của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế
1. Normal Profit in the Long Run
Hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế không chỉ đưa lại những lợi ích, trái lại, nó cũng đặt ra
nhiều rủi ro, bất lợi và thách thức, đó là:
Làm gia tăng sự cạnh tranh gay gắt khiến nhiều doanh nghiệp và ngành kinh tế
nước ta gặp khó khăn trong phát triển, thậm chí là phá sản, gây nhiều hậu quả bất lợi
về mặt kinh tế - xã hội. 8
Hnh 1 - Hai thương hiệu sữa lớn là Milo & Ovaltine luôn cạnh tranh với nhau
Làm gia tăng sự phụ thuộc của nền kinh tế quốc gia vào thị trường bên ngoài,
khiến nền kinh thị trường dễ tác động trước những biến động khôn lường về chính trị,
kinh tế và thị trường quốc tế.
Phân phối không công bằng lợi ích và rủi ro cho các nước và các nhóm khác
nhau trong xã hội, do vậy có nguy cơ làm tăng khoảng cách giàu - nghèo và bất bình
đẳng xã hội.Trong quá trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế, các nước đang phát triển như
nước ta phải đối mặt với nguy cơ chuyển dịch cơ cấu kinh tế tự nhiên bất lợi, do thiên
hướng tập trung vào các ngành sử dụng nhiều tài nguyên, nhiều sức lao động, nhưng
có giá trị gia tăng thấp. Có vị trí bất lợi và thua thiệt trong chuỗi giá trị toàn cầu. Do
vậy, dễ trở thành bãi thải công nghiệp và công nghệ thấp, bị cạn kiệt nguồn tài nguyên
thiên nhiên và hủy hoại môi trường ở mức độ cao.
Tạo ra một số thách thức đối với quyền lực Nhà nước, chủ quyền quốc gia và
phát sinh nhiều vấn đề phức tạp đối với việc duy trì an ninh và ổn định trật tự, an toàn xã hội.
Làm gia tăng nguy cơ bản sắc dân tộc và văn hóa truyền thống Việt Nam bị xói
mòn trước sự “xâm lăng” của văn hóa nước ngoài hay làm tăng nguy cơ gia tăng của
tình trạng khủng bố quốc tế, buôn lậu, tội phạm xuyên quốc gia, dịch bệnh, nhập cư bất hợp pháp… 9
Ví dụ: Sự gia tăng của thương mại và di cư cũng mở ra cơ hội cho các tội phạm
buôn lậu, từ ma túy đến vũ khí và người. Biên giới mở cửa có thể tạo điều kiện thuận
lợi cho hoạt động buôn lậu và các mạng lưới tội phạm xuyên quốc gia. Hay là sự di
chuyển dễ dàng của người và hàng hóa cũng có thể tăng nguy cơ lây nhiễm dịch bệnh.
Nếu một quốc gia không có các biện pháp kiểm soát chặt chẽ, các dịch bệnh có thể
nhanh chóng lan ra các quốc gia khác (đại dịch covid là 1 điển hình). III.
PHƯƠNG HƯỚNG NÂNG CAO HIỆU QUẢ HỘI NHẬP KINH TẾ
QUỐC TẾ TRONG PHÁT TRIỂN CỦA VIỆT NAM
Hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế là một trong những chủ đề kinh tế có tác động tới toàn
bộ tiến trình phát triển kinh tế xã hội của nước ta hiện nay, liên quan trực tiếp đến quá
trình thực hiện định hướng và mục tiêu phát triển đất nước. Với cả những tác động đa
chiều của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế, xuất phát từ thực tiễn đất nước, Việt Nam cần phải
tính toán một cách thức phù hợp để thực hiện hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế thành công.
Nhận thức sâu sắc về thời cơ và thách thức do hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế mang lại
Xây dựng chiến lược và lộ trình hội nhập kinh tế phù hợp
Tích cực chủ động tham gia vào các liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và thực hiện
đầy đủ các cam kết của Việt Nam trong các liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và khu vực
Hoàn thiện thể chế kinh tế và luật pháp
Nâng cao năng lực cạnh tranh quốc tế của nền kinh tế
Xây dựng nền kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ của Việt Nam
1. Nhận thức sâu sắc về thời cơ và thách thức do hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế
Việc Nhà nước và các doanh nghiệp nhận thức được các thời cơ cũng như cơ hội
về hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế ở quốc gia chúng ta có tầm quan trọng và ảnh hưởng to
lớn đến những vấn đề cốt lõi, chúng là những sự nhận thức quy luật vận động khách
quan của lịch sử xã hội; là cơ sở lý luận và thực tiễn quan trọng để xây dựng chủ
trương và chính sách phát triển thích ứng
Trong nhận thức, hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế
Là một thực tiễn khách quan 10
Là xu thế khách quan của thời đại
Các quốc gia trên thế giới không thể quay lưng và né tránh
Việt Nam cũng không thể đứng ngoài dòng chảy của lịch sử, hội nhập quốc tế
không chỉ là “khẩu hiệu thời thượng” mà phải là “phương thức tồn tại và phát triển” của nước ta hiện nay.
Việt Nam đã và đang nỗ lực để tận dụng thời cơ và đối mặt với thách thức của
hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế. Chính phủ và các doanh nghiệp đang thúc đẩy cải cách, đầu
tư vào đào tạo nguồn nhân lực chất lượng cao và tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho doanh
nghiệp phát triển và cạnh tranh trên thị trường quốc tế. Về chủ thể tham gia hội nhập,
nhà nước là một chủ thể quan trọng nhưng không phải là duy nhất. Lực lưỡng nồng
cốt là đội ngũ doanh nhân với các tầng lớp trí thức cao, doanh nghiệp làm lực lưỡng dẫn đầu Thực tế hiện nay
Chủ trương, đường lối, chính sách về hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế của Đảng và nhà
nước có nơi, có lúc chưa được quán triệt kịp thời, đầy đủ và thực hiện nghiêm túc.
Hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế còn bị tác động bởi cách yếu tố ngoại lại nên chưa tận
dụng được các thời cơ và thách thức
2. Xây dựng chiến lược và lộ trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế
Việt Nam đã thực hiện nhiều nỗ lực để xây dựng chiến lược và lộ trình hội nhập
kinh tế quốc tế. Dưới đây là một số điểm chính:
Ký kết các hiệp định thương mại: Việt Nam đã tham gia và ký kết nhiều hiệp
định thương mại quan trọng như Hiệp định Đối tác Toàn diện và Tiến bộ xuyên Thái
Bình Dương (CPTPP), Hiệp định Đối tác Kinh tế Toàn diện (RCEP) và Hiệp định
EVFTA với Liên minh châu Âu. Điều này giúp Việt Nam mở rộng thị trường xuất
khẩu và thu hút đầu tư nước ngoài.
Đẩy mạnh cải cách kinh doanh: Việt Nam đã thực hiện nhiều biện pháp cải cách
kinh doanh nhằm tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho các doanh nghiệp trong và ngoài nước.
Điều này bao gồm việc giảm quy định hành chính, tăng tính minh bạch và giảm thủ tục hành chính. 11
Phát triển cơ sở hạ tầng: Việt Nam đã đầu tư mạnh vào phát triển cơ sở hạ tầng
giao thông, điện lực và viễn thông. Điều này giúp tăng cường kết nối với các thị
trường quốc tế và thu hút đầu tư nước ngoài.
Đào tạo lao động chất lượng cao: Việt Nam đã tăng cường đào tạo lao động chất
lượng cao để đáp ứng nhu cầu của các công ty đa quốc gia và các ngành công nghiệp chủ chốt.
Tăng cường quản lý và thực thi pháp luật: Việt Nam đã nỗ lực để tăng cường
quản lý và thực thi pháp luật, đảm bảo môi trường kinh doanh công bằng và minh bạch.
Tuy nhiên, việc xây dựng chiến lược và lộ trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế là một
quá trình liên tục và đòi hỏi sự cải tiến và thích ứng. Việt Nam cần tiếp tục nỗ lực để
tăng cường cạnh tranh, nâng cao chất lượng sản phẩm và dịch vụ, và thúc đẩy sự đổi
mới công nghệ để đạt được mục tiêu hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế
3. Tích cực, chủ động tham gia vào liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và thực hiện
đầy đủ các cam kết của Việt nam trong các liên kết kinh tế quốc tế và khu vực
Trong tiến trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế, cho đến nay, về hợp tác song phương,
Việt Nam đã thiết lập quan hệ ngoại giao với hơn 170 quốc gia trên thế giới, mở rộng
quan hệ thương mại, xuất khẩu hàng hoá tới trên 230 thị trường của các nước và vùng
lãnh thổ, ký kết trên 90 Hiệp định thương mại song phương, gần 60 Hiệp định khuyến
khích và bảo hộ đầu tư, 54 Hiệp định chống đánh thuế hai lần.
Đặc trưng của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế là sự hình thành các liên kết kinh tế quốc tế
và khu vực để tạo ra sân chơi chung cho các nước.
4. Hoàn thiện thể chế kinh tế và pháp luật
Để nâng cao hiệu quả của hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế, cần hoàn thiện cơ chế thị
trường trên cơ sở đổi mới mạnh mẽ về sở hữu, coi trọng khu vực tư nhân, đổi mới sở
hữu và doanh nghiệp nhà nước; hình thành dồng bộ các loại thị trường; đảm bảo môi
trường cạnh tranh bình đẳng giữa các chủ thể kinh tế...
Nhà nước cần rà soát, hoàn thiện hệ thống pháp luật, nhất là luật pháp liên quan
đến hội nhập kinh tế như: đất đai, đàu tư, thương mại, doanh nghiệp, thuế, tài chính tín
dụng, di chú... Hoàn thiện pháp luật về tương trợ tư pháp phù hợp với pháp luật quốc 12
tế đồng thời phòng ngừa, giảm thiểu các thách thức do tranh chấp quốc tế, nhất là
tranh chấp thương mại, đầu tư quốc tế; xử lý có hiệu quả các tranh chấp, vướng mắc
kinh tế, thương mại nhằm bảo đảm lợi ích của người lao động và doanh nghiệp trong hội nhập.
Dưới đây là một số khía cạnh cần được xem xét trong việc hoàn thiện thể chế
kinh tế và pháp luật để nâng cao việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế ở Việt Nam:
4.1. Đổi mới và cải cách pháp luật: Cần tiến hành cải cách và đổi mới pháp
luật liên quan đến kinh doanh và hội nhập quốc tế. Việc này bao gồm việc đơn giản
hóa quy trình hành chính, tạo ra một môi trường pháp lý ổn định và an toàn cho các
doanh nghiệp, cung cấp các quy định rõ ràng và minh bạch để tạo dựng lòng tin với đối tác quốc tế.
4.2. Bảo vệ quyền sở hữu trí tuệ: Việc bảo vệ quyền sở hữu trí tuệ là một yếu
tố quan trọng để thu hút đầu tư và tăng cường cạnh tranh trong hội nhập kinh tế quốc
tế. Cần tổ chức và thực thi chặt chẽ các quy định về bản quyền, nhãn hiệu và sáng chế
để đảm bảo rằng quyền sở hữu trí tuệ được bảo vệ và đối tác quốc tế có thể tin tưởng
vào việc kinh doanh và đầu tư tại Việt Nam.
4.3. Tăng cường quản lý tài chính và ngân hàng: Việc tăng cường quản lý tài
chính và ngân hàng là một yếu tố quan trọng để đảm bảo sự ổn định và tin cậy của hệ
thống tài chính. Cần tạo ra các quy định và cơ chế giám sát hiệu quả để đảm bảo tính
minh bạch, đúng luật và an toàn của hoạt động tài chính và ngân hàng, khuyến khích
đầu tư và tín dụng quốc tế.
4.4. Xây dựng môi trường kinh doanh công bằng và minh bạch: Một môi
trường kinh doanh công bằng và minh bạch là yếu tố quan trọng để thu hút đầu tư và
tạo dựng lòng tin với đối tác quốc tế. Cần xây dựng các quy định và cơ chế giám sát
để đảm bảo sự cạnh tranh lành mạnh, tránh độc quyền và hạn chế tham nhũng.
4.5. Đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực: Để đáp ứng yêu cầu của hội nhập kinh tế
quốc tế, cần đầu tư vào đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực chất lượng cao, đặc biệt là trong
lĩnh vực pháp luật kinh tế và quản lý kinh doanh quốc tế. Điều này giúp tăng cường
khả năng thực thi pháp luật vàxây dựng nền tảng chuyên môn mạnh mẽ để thúc đẩy
quá trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế. 13
Tóm lại, điều này đòi hỏi sự cải cách pháp luật, bảo vệ quyền sở hữu trí tuệ, tăng
cường quản lý tài chính và ngân hàng, xây dựng môi trường kinh doanh công bằng và
minh bạch, cùng với việc đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực. Bằng cách thúc đẩy những nỗ
lực này, Việt Nam có thể tạo ra một môi trường kinh doanh thuận lợi và hấp dẫn cho
các doanh nghiệp trong quá trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế.
5. Nâng cao năng lực canh tranh quốc tế của nền kinh tế
Nếu Việt Nam chúng ta vẫn ở trạng thái nền công nghệ và hạ tầng yếu kém,
nguồn lao động có chất lượng thấp, quy mô đầu tư nhỏ bé khiến cho khả năng cạnh
tranh với các quốc gia khác trở nên thấp và hạn chế, như vậy các doanh nghiệp nước
nhà rất khó có thể vươn xa ra cường quốc năm châu như lời Bác Hồ từng dặn.
Để nâng cao hiệu quả hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế và củng cố, giữ vững năng lực
cạnh tranh quốc tế của Việt Nam, có một số phương hướng quan trọng mà quốc gia có thể xem xét:
Đàm phán Hiệp định Thương mại tự do (FTA). Ký kết và thực hiện nhiều hơn
các hiệp định thương mại tự do để mở rộng thị trường xuất khẩu và giảm rủi ro thị trường.
Đào tạo và Phát triển Nhân sự, đầu tư vào giáo dục và đào tạo nguồn nhân lực để
nâng cao chất lượng và kỹ năng lao động, đáp ứng đầy đủ nhu cầu của thị trường lao động quốc tế.
Tăng cường Nghiên cứu và Phát triển (R&D). Tăng cường đầu tư vào nghiên
cứu và phát triển để tạo ra sản phẩm và dịch vụ có giá trị gia tăng, làm tăng cường độ cạnh tranh.
Hỗ trợ Doanh nghiệp Tư nhân và Đổi mới. Tạo điều kiện thuận lợi để doanh
nghiệp tư nhân phát triển và đổi mới, đặc biệt là trong lĩnh vực công nghiệp sáng tạo và công nghệ cao.
Cải thiện Môi trường Kinh doanh. Giảm bớt các thủ tục hành chính, tạo điều
kiện thuận lợi cho doanh nghiệp, và cải thiện môi trường kinh doanh nói chung.
Phát triển Hạ tầng Kết nối. Đầu tư vào hạ tầng giao thông và vận tải để nâng cao
khả năng liên kết vùng và tiếp cận thị trường quốc tế.
Chú trọng vào Kinh doanh Xanh. Phát triển và thúc đẩy các ngành công nghiệp
xanh, không chỉ giúp bảo vệ môi trường mà còn tạo ra cơ hội kinh doanh mới. 14
Chính sách Thu hút Đầu tư Nước ngoài (FDI). Tạo ra chính sách thuận lợi để
thu hút đầu tư nước ngoài và tạo điều kiện cho doanh nghiệp FDI phát triển hiệu quả.
Thúc đẩy Xuất khẩu và Đa dạng Hóa Thị trường. Tăng cường nỗ lực quảng bá
thương hiệu quốc gia, thúc đẩy xuất khẩu và đa dạng hóa thị trường để giảm rủi ro thị trường.
Chia sẻ Kinh nghiệm và Học hỏi Liên ngành. Tổ chức các chương trình đào tạo,
hội thảo để chia sẻ kinh nghiệm và kiến thức giữa các doanh nghiệp và ngành công nghiệp khác nhau.
Bằng cách thực hiện những phương hướng này, Việt Nam có thể tăng cường
hiệu suất trong hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế và phát triển năng lực cạnh tranh quốc tế của mình.
6. Xây dựng nền kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ của Việt Nam
Việt Nam, với lịch sử chiến tranh dài dằng và qua quá trình đổi mới, đang xây
dựng một nền kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ nhằm đảm bảo sự bền vững và phát triển bền vững trong thế kỷ 21.
Chính phủ Việt Nam chú trọng vào việc phát triển kinh tế số, thúc đẩy các ngành
công nghiệp 4.0 để nâng cao hiệu suất và tích cực tham gia vào nền kinh tế thế giới.
Xây dựng nền kinh tế tự chủ bắt đầu từ việc đầu tư vào nguồn nhân lực chất lượng và
hệ thống giáo dục hiện đại để tạo ra lực lượng lao động có kỹ năng cao.
Việt Nam đang tăng cường hợp tác kinh tế với nhiều đối tác trên thế giới, không
chỉ giúp mở rộng thị trường xuất khẩu mà còn giảm thiểu rủi ro từ sự phụ thuộc vào
một số ít đối tác. Phát triển nông nghiệp thông minh, hiệu quả với việc áp dụng công
nghệ để nâng cao sản xuất, chất lượng sản phẩm và giảm tác động tiêu cực đến môi
trường. Đầu tư vào các ngành công nghiệp hỗ trợ và chế biến để tạo ra giá trị gia tăng
và làm tăng cường độ cạnh tranh của sản phẩm Việt Nam trên thị trường quốc tế.
Việt Nam cam kết xây dựng nền kinh tế có trách nhiệm với môi trường, thúc đẩy
các giải pháp xanh và phát triển bền vững. Chuyển đổi sang nguồn năng lượng tái tạo
để giảm thiểu phụ thuộc vào nguồn năng lượng truyền thống và giảm lượng khí nhà kính.
Cung cấp môi trường kinh doanh thuận lợi, giảm bớt thủ tục hành chính, và
khuyến khích sự sáng tạo trong doanh nghiệp. 15
Hợp tác Công tư với Tư nhân, khuyến khích sự hợp tác giữa doanh nghiệp tư
nhân và công tư để tận dụng tối đa nguồn lực và kiến thức.
Tăng Cường Nghiên cứu và Đổi mới, đầu tư vào các chương trình nghiên cứu và
phát triển để tạo ra sản phẩm và dịch vụ có giá trị gia tăng.
Khuyến khích Sự Đổi mới trong Doanh nghiệp. Tạo điều kiện để doanh nghiệp
thúc đẩy sự đổi mới và sáng tạo trong sản xuất và quản lý.
Xây dựng nền kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ là một quá trình dài hơi nhưng quan trọng
để đảm bảo sự phát triển bền vững và đáp ứng được thách thức của thị trường quốc tế.
Việt Nam đang đưa ra những bước đi mạnh mẽ, hướng tới mục tiêu trở thành một nền
kinh tế độc lập, tự chủ và phát triển. IV.
LIÊN HỆ VỚI NGÀNH HỌC CỦA NHÓM HIỆN NAY
1. Logistics và Quản lý chuỗi cung ứng
Ngành logistics và quản lý chuỗi cung ứng đóng vai trò quan trọng trong quá
trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế của Việt Nam. Việc phát triển và nâng cao hiệu quả
của hệ thống logistics và quản lý chuỗi cung ứng sẽ tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho việc
vận chuyển hàng hóa, tăng cường khả năng cạnh tranh và thúc đẩy sự phát triển kinh tế của quốc gia.
Việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế đòi hỏi sự liên kết mạnh mẽ giữa các đối tác
trong chuỗi cung ứng, từ nhà sản xuất, nhà cung cấp, nhà vận chuyển cho đến người
tiêu dùng. Điều này đòi hỏi sự chia sẻ thông tin, tương tác và tối ưu hóa quá trình
vận chuyển và lưu trữ hàng hóa. Việt Nam đã thể hiện sự quan tâm và nỗ lực trong
việc phát triển ngành logistics và quản lý chuỗi cung ứng. Quốc gia đã triển khai
nhiều biện pháp nhằm cải thiện cơ sở hạ tầng vận tải, nâng cao năng lực quản lý và
đào tạo nguồn nhân lực trong lĩnh vực này.
Việt Nam cũng đã tham gia vào các hiệp định thương mại tự do và tổ chức khu
vực như Hiệp định Đối tác Toàn diện và Tiến bộ xuyên Thái Bình Dương (CPTPP),
Hiệp định Đối tác Kinh tế Toàn diện Xuyên Thái Bình Dương (RCEP) và Hiệp định
EVFTA với Liên minh châu Âu. Điều này mở ra cơ hội cho các doanh nghiệp
logistics và quản lý chuỗi cung ứng ở Việt Nam để tham gia vào các chuỗi cung ứng
toàn cầu và tận dụng lợi thế từ việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế. 16
Tuy nhiên, vẫn còn nhiều thách thức đặt ra trước ngành logistics và quản lý
chuỗi cung ứng ở Việt Nam. Một số khía cạnh cần được cải thiện bao gồm cơ sở hạ
tầng vận tải, quy trình hải quan, công nghệ thông tin và đào tạo nguồn nhân lực chất
lượng cao.Để liên hệ với việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế của ngành logistics và quản
lý chuỗi cung ứng ở Việt Nam, các doanh nghiệp và cá nhân có thể tìm hiểu về các
tổ chức, liên minh và hiệp hội trong ngành. Tham gia vào các sự kiện, hội thảo và
triển lãm có liên quan cũng là cách tốt để mở rộng mạng lưới kết nối và chia sẻ kinh
nghiệm với các chuyên gia và doanh nghiệp khác trong lĩnh vực logistics và quản lý chuỗi cung ứng.
Ngoài ra, việc nắm vững các quy định, quy chuẩn và tiêu chuẩn quốc tế cũng
rất quan trọng để đáp ứng yêu cầu của các đối tác quốc tế và tăng cường tính cạnh tranh. 2. Marketing
Ngành marketing cũng có vai trò quan trọng trong quá trình hội nhập kinh tế
quốc tế của Việt Nam. Vì đây là yếu tố quan trọng để tăng cường khả năng cạnh
tranh và xây dựng thương hiệu của các doanh nghiệp trong môi trường kinh doanh quốc tế.
2.1. Hiểu và tận dụng thị trường quốc tế:
Để hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế thành công, các doanh nghiệp cần
hiểu rõ về thị trường tiềm năng và khách hàng quốc tế. Nghiên cứu về
xu hướng tiêu dùng, phân tích thị trường và đối thủ cạnh tranh là cách
để tìm ra những cơ hội và xác định chiến lược marketing phù hợp.
2.2. Xây dựng chiến lược marketing toàn cầu:
Các doanh nghiệp cần phát triển chiến lược marketing toàn cầu,
đồng thời điều chỉnh và tùy chỉnh theo từng thị trường cụ thể. Điều
này bao gồm việc tạo ra thông điệp và tài liệu quảng cáo phù hợp với
văn hóa và ngôn ngữ địa phương, sử dụng các kênh quảng cáo và tiếp
thị phù hợp với thị trường đó.
2.3. Xây dựng và quản lý thương hiệu:
Xây dựng một thương hiệu mạnh là yếu tố quan trọng để thành
công trong hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế. Các doanh nghiệp cần tạo dựng 17
một hình ảnh và giá trị thương hiệu độc đáo, chất lượng và đáng tin
cậy. Việc sử dụng các công cụ quảng cáo, quan hệ công chúng và xây
dựng mạng lưới liên kết giúp tăng cường nhận diện thương hiệu và
xây dựng lòng tin với khách hàng quốc tế.
2.4. Sử dụng công nghệ và kỹ thuật số:
Công nghệ và kỹ thuật số đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc tiếp
cận và tương tác với khách hàng quốc tế. Các doanh nghiệp cần sử
dụng các nền tảng trực tuyến, mạng xã hội, email marketing và công
cụ phân tích dữ liệu để đưa ra chiến lược tiếp thị hiệu quả và tối ưu hóa kết quả.
2.5. Hợp tác và liên kết quốc tế:
Hợp tác và liên kết với các đối tác quốc tế là cách tốt nhất để mở
rộng mạng lưới kinh doanh và tiếp cận thị trường quốc tế. Tham gia
vào các sự kiện, triển lãm quốc tế hoặc kết nối thông qua các tổ chức
và liên minh kinh doanh là cách tốt để tìm kiếm cơ hội hợp tác và xúc tiến giao dịch.
Qua việc hiểu và áp dụng các chiến lược marketing quốc tế, các
doanh nghiệp trong ngành marketing ở Việt Nam có thể tận dụng cơ
hội từ hội nhập kinh tếquốc tế. Điều này giúp tăng cường sức cạnh
tranh, mở rộng thị trường và thúc đẩy sự phát triển của ngành
marketing trong quá trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế của Việt Nam..
3. Quản trị kinh doanh
Liên hệ với ngành quản trị kinh doanh, nhóm chúng em cũng thấy được sự
quan trọng trong quá trình hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế của Việt Nam. Việc phát triển
và nâng cao hiệu quả trong lĩnh vực quản trị kinh doanh sẽ tạo điều kiện thuận lợi
cho các doanh nghiệp tham gia vào môi trường kinh doanh quốc tế, tăng cường khả
năng cạnh tranh và thúc đẩy sự phát triển kinh tế của quốc gia.
Để liên hệ với việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế trong ngành quản trị kinh doanh ở
Việt Nam, có một số khía cạnh quan trọng cần được xem xét: 3.1.
Đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực: 18
Để đáp ứng yêu cầu của môi trường kinh doanh quốc tế, cần đầu
tư vào đào tạo và phát triển nhân lực chất lượng cao trong lĩnh vực
quản trị kinh doanh. Điều này bao gồm việc nâng cao trình độ chuyên
môn, kỹ năng quản lý, hiểu biết về quy định và thực tiễn quản trị kinh doanh quốc tế. 3.2.
Nắm vững quy định và quy chuẩn quốc tế:
Các doanh nghiệp cần có kiến thức về các quy định và quy chuẩn
quốc tế liên quan đến lĩnh vực kinh doanh của mình. Điều này đảm
bảo tuân thủ các quy tắc và tiêu chuẩn quốc tế, giúp tăng cường tính
cạnh tranh và xây dựng lòng tin với đối tác quốc tế. 3.3.
Mở rộng mạng lưới kết nối:
Quan hệ và kết nối với các đối tác quốc tế là yếu tố quan trọng
trong việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế. Các doanh nghiệp có thể tham gia
vào các sự kiện, hội thảo và triển lãm quốc tế, tìm kiếm cơ hội hợp tác và xúc tiến giao dịch. 3.4.
Áp dụng công nghệ và quản lý thông tin:
Công nghệ thông tin đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc nâng cao
hiệu quả quản trị kinh doanh và tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho hội nhập
kinh tế quốc tế. Các công nghệ như hệ thống quản lý tài chính, hệ
thống quản lý quan hệ khách hàng (CRM) và hệ thống quản lý chuỗi
cung ứng (SCM) có thể giúp nâng cao năng suất và khả năng tương tác với đối tác quốc tế. 3.5.
Nghiên cứu thị trường và chiến lược tiếp cận:
Hiểu rõ thị trường quốc tế và chiến lược tiếp cận sẽ giúp các
doanh nghiệp quản trị kinh doanh tìm kiếm cơ hội và đối tác phù hợp.
Nghiên cứu thị trường, phân tích xu hướng và tiềm năng cạnh tranh là
những yếu tố quan trọng để xây dựng chiến lược kinh doanh hiệu quả.
Tóm lại, liên hệ với việc hội nhập kinh tế quốc tế trong ngành quản trị kinh
doanh ở Việt Nam đòi hỏi sự nâng cao năng lực quản lý, đào tạo nhân lực chất
lượng cao, tuân thủ quy định và quy chuẩn quốc tế, mở rộng mạng lưới kết nối với 19




