


















Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|59372584
GIAO DỊCH THƯƠNG MẠI QUỐC TẾ K60 - cô Nga
Giao dich thuong mai quoc te (Trường Đại học Ngoại thương) Scan to open on Studeersnel
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
CHAP 1. OVERVIEW (self-study) A/OVERVIEW * Mode Of Supply
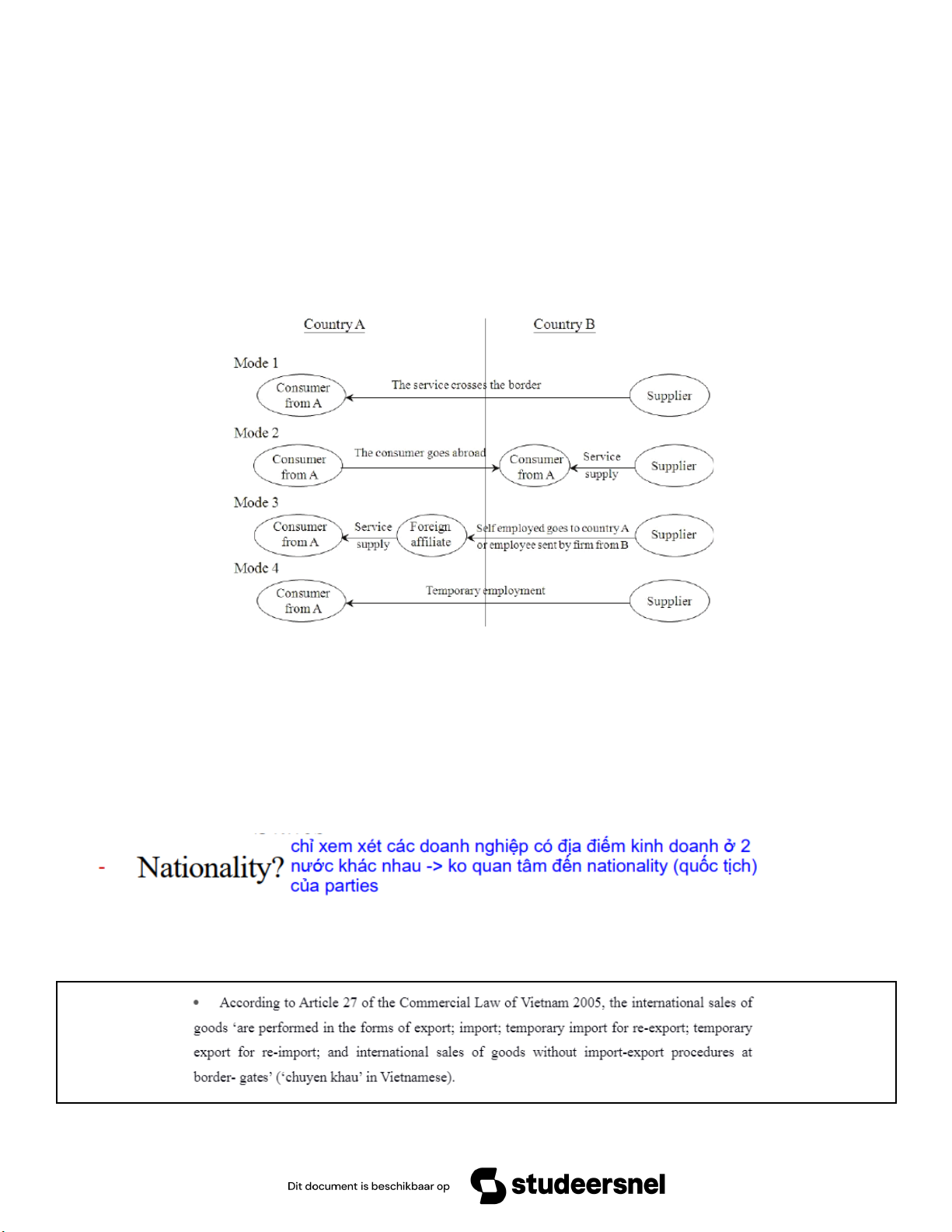
1 - cross-border: sản xuất ở nước supply r xuất sang nước consume
2 - consumption abroad: consumer nước consum qua nước supply để tiêu thụ
3 - commercial presence: supply mở chi nhánh ở nước consume để cho consumer nước đó tiêu thụ
4 - presence of natural pesons: thuê employee từ nước consum (xuất khẩu lao động) * Mode Of Transaction:
- Def: the method through which a transaction is conducted
- no unified classification: ko có sự phân loại thống nhất
* International Sales Of Goods: >> CISG:
- “parties whose places off bussiness arre in different states” >> VCL 2005:
- Không có def về Int Sales of Goods nhưng có quy định về forms
- What element determines “international sales”?
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
B/ FORMS OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE I/ Direct import/export
● Def: seller & buyers in different territories/customs area DIRECTLY negotiation and conclude
contracts (trực tiếp conduct transactions to sign hợp đồng on FREE AND VOLUNTARY BASIS) ● Features: ○ most widely used
○ legally allowed & without the assisstance of third parties
○ a complete/part of a commercial activity
○ proactively deal with market value II/ Re-exportation 1. Def:
the transaction in which PROFIT is gained by exported in the same state as previously imported
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- XK hàng hóa đã nhập trước đây mà chưa qua khâu chế biến nào tại nước tái xuất nhằm mục đích thu
về ngoại tệ lớn hơn chi phí nhập khẩu 2. Features:
>> re-exportation vs. transit of goods? - Seller chính là buyer
- Mục đích là chênh lệch giá
- Thường có 3 bên tham gia vào transaction (triangular)
- Hàng hóa có nhu cầu lớn, hay biến động => thì reE mới chênh lệch đc giá 3. Classification
a/ Temporary I for reE (Tái xuất thực nghĩa)
b/ Transfer of goods through border-gates (chuyển khẩu)
>> Example of re-exportation
>> Differences and similarities between transfer border gate and re-exportation?
- Similarities: kind of international transaction - Differences:
+ Tạm nhập tái xuất vẫn phải thủ tục và trả tiền thuế như bình thường
+ Chuyển khẩu: về ownership thì ko cần qua
- custom control: vẫn phải kiểm soát hải quan nhưng k cần làm custom procedures
- custom procedures: thủ tục hải quan sẽ phải kê khai, nộp thuế cho việt nam
- bond warehouse: kho ngoại quan
- trans-shipment: khu trung chuyển
Có 3 hình thức chuyển khẩu:
(1) Hàng hóa đc vận chuyển thẳng từ exporter sang importer mà không qua nước tái xuất => open và
2 bên có thể ko cần qua bên thứ 3
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
(2) Hàng hóa được vận chuyển từ nước xuất khẩu đến nước nhập khẩu có qua cửa khẩu của nước tái
xuất nhưng không làm thủ tục nhập khẩu vào và ko làm thủ tục xuất khẩu ra khỏi nước tái xuất
(3) Hàng hóa được vận chuyển từ nước xuất khẩu đến nước nhập khẩu có qua cửa khẩu và được đưa
vào kho ngoại quan/khu vực trung chuyển hàng hóa tại cảng nước tái xuất, ko làm thủ tục nhập khẩu và xuất khẩu 4. ReE transaction
- L/C: commitment of issuing bank
- Không có LC trả trước tại trả rồi thì đòi làm clg =)))))))
- B2B L/C còn có thể gọi là baby LC, còn có master L/C
III/ Countertrade (mua bán đối lưu - hàng đổi hàng) 1. Def:
Countertrade is a reciprocal form of international trade in which goods or services are exchanged for
other goods or services rather than for hard currency. 2. Features
>> Có giống reE không?
Không, tuy nhiên nó là 2 parties nhưng chỉ dùng 1 hợp đồng duy nhất
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- Là dạng trao đổi hàng hóa đặc biệt, exporter cũng chính là importer, seller chính là buyer
- exchange value khác với use value 3. Reasons for development
- The company run out of currency -> sell comodity of goods
- If company/country want to maintain balance of payment otherwise will result in deficit/surplus =>
countertrade in order to make bought goods = sold goods >> why?
- if the low quality product => they can use countertrade to penetrate these low quality product =>
maintain competiveness for the same product
- trao doi mat hang ma nuoc khac competitive in
if u want to create new partnership with new countries/capitability to set up a 4. Classification [1] Barter:
+ buyẻr and seller just exchange the goods (hàng đổi hàng)
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 + Not focus on value
+ Vd. China exchange bananas for buses
[2] offset: thằng xuất nguyên liệu để mua lại 1 thành phẩm
VD. VN nghèo có nhiều tài nguyên, xuất khẩu sắt-thép cho TQ để mua lại 1 final product => use value
ở đây có lợi cho VN sau này
+ difference between the 2 terms? [3] counter-purchase:
>> Khác gì với barter? - Có currency xuất hiện - Acts as future purchase
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 [4] buyback:
+ quite similar with offset
+ differences between offset and buyback? the suppliers of capital, plants & equipment, buyback acts as an investment
+ difference between buyback and counter-purchase; counter-perchase chir laf mua laij chuws mac du
goods nos ko lien quan toiws nhau, trong khi buyback thi goods lien quan den nhau (vd thi co the
cung cap ca tech hoac trainning lam xe)
[5] switch trading: cấn nợ,
- we have 3 parties: brazil, uk and poland
>> explain the relationship between surplus country and deficit country and third parties that export to
surplus country in switch trading?
có 3 giao dịch độc lập: A giao cho B, C giao cho A
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- thì qhe chính là A và B, trong buôn bán là trade surplus do A mua nhiều hơn (mua cả C và B) - Export = trade surplus
- Import = trade defcit (đang có obligation phải trả tiền)
B và C có thể ở trong cung 1 quốc gia => thì B trả cho C sẽ đỡ tốn currency hơn khi trả cho A
switch trading này vẫn là countertrade nhưng k còn giữa 2 nước mà còn 3 nước
=> brazil chuối sang poland, nhưng brazil mún pens mà uk có pens thì brazil mua từ uk rồi poland trả cho uk
Ứng dụng hiện nay: quan chức sang các nước ký hiệp định cam kết VN mua máy bay từ US thì US có
thể cam kết mua agricultural từ VN => điều kiện ràng buộc để bán đc goods
IV/ Import or Export through intermediary 1. Def
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 - đại diện thương nhân - môi giới thương mại - đại diện ủy thác
=> các hoạt động về trung gian thương mại 2. Features
- if we use direct I/E => 2 parties sẽ directly negotiate với nhau còn trong case này 2 parties k thể
legally allowed to make contract - entrust: ủy thác >> WHEN?
- Khi lần đầu tiên tham gia thị trường nước ngoài hoặc penetrate new market without much knowledge about that market
- Ít vốn, hàng hóa không có nhiều hoặc nhu cầu không thường xuyên
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- Các hàng hóa cần có mặt tại thị trường, hoặc do quy định của luật pháp 3. Classification a/ Broker: môi giới Def Feature
=> perate under short-term authorization (làm theo ủy thác từng lần)
- broker just connect buyer and seller, be4 they connect they have to
examine the legality of 2 parties but they do not involve in responsible
for the results/risks after transaction
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- they also have no rights to sign or conclude contract
=> ít khi thấy tên broker ở trong các hợp đồng, tụi nó behind the contract chứ k được stated b/ Agency: đại lý Def
Agency có quyền được sign and conclude contract
● Thương nhân trung gian đứng ra cung cấp dịch vụ thương mại cho khách hàng
nhằm thu tiền thù lao (remuneration)
● Remuneration có thể là fixed amount hoặc % theo sales hoặc chênh lệch giữa giá mua & giá bán
có giống switch trader ko?
- Không vì switch trader là dàng trao đổi hàng hóa, không có currency xuất hiện Feature
Xét theo phạm vi quyền hạn:
(1)universal agent: đại lý toàn quyền - làm all mọi việc cho principals
(2)general agent: tổng đại lý - chỉ làm 1 vài phần công việc cho principals
(3)special agent: đại lý đặc biệt - chỉ làm 1 việc duy nhất Types of
Name khác basically just depend on the name of authority they are represent agent s
Xét theo mức độ ủy quyền:
- Mandatory agent: đại lý thụ ủy (làm hoàn toàn theo ủy thác của người khác,
dùng danh nghĩa và trả chi phí đều của principal)
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- Commission agent: đại lý hoa hồng (làm theo sự ủy thác với danh nghĩa
agency nhưng cost do principals chịu và thù lao là tiền hoa hồng là % sales or fixed amount)
- Merchant agency: đại lý kinh tiệu - hoạt động trên chính danh nghĩa và cost
của agent. Thù lao sẽ là chênh lệch giữa giá mua/bán giữa principals và customers
Ngoài ra còn một số đại lý khác
- Consignee/agent carrying stock: đại lý ký gửi - một dạng của commission
agent nhận bán hàng từ kho của agent ra thị trường
- Del credere agent: đảm bảo khả năng thanh toán của KH
- Sole agent: đại lý duy nhất của market nào đó
- Factor: principals giao quyền chiếm hữu hàng hóa/chứng từ sở hửu hàng hóa
được phép cầm cố/đứng tên agent nếu có lợi cho principals
V/ Import or Export through commodity exchange 1. Def
- Commodity Exchange: sở giao dịch hàng hóa, special market, different from traditional market (where
buyer and seller knoew each other) còn ở CX thì 2 parties ko biết nhau
=> Đây là hình thức thông qua môi giới của sở giao dịch, ngta bán các hàng hóa có khối lượng lớn + chất
lượng ổn định với price at thời điểm giao kết hợp đồng và thời điểm giao hàng để ăn chênh lệch giá
- seller & buyers chỉ interact với CX chứ ko biết về partner mua bán của mình
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
>> Does the definition cover all the transactions? Không, chỉ làm transaction cho các loại hàng mà CX list out ra thui
- Sàn gd hóa thì nếu hiểu theo Luật Enterprise thì có thể coi như là 1 công ty, nhưng in general là thì nó
giống special market, thì người bán và người mua phải tuân theo rule/obl của CX 2. Features
- short-sale: mua bán khống - Bán khống là việc người bán (trong TH này là comodity exchange) nghĩ
rằng giá của goods đó sẽ giảm trong tương lai. 3. Classification
- Thường trên sàn chỉ có future/forward với option thui
https://mxv.com.vn/hang-hoa/nong-san/ngo.html Spot
- Có nghĩa là sign contract hôm nay thì giao hàng within hôm nay lun/ or transact within 2 days ion
- Giá được xác đình hôm nay và giao hàng hôm nay (Giao dịch giao ngay)
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 Forward
- Giá xác định vào hôm nay cho future delivery (> 2 days) transact
- Duration sẽ là bội số của 30 ngày (90, 60, 120 ~~~) ion Hedging transact ion Option transact ion (Hợp đồng quyền mua)
- Put option: quyền chọn bán => được quyền bán hoặc ko bán
- call option: quyền chọn mua => được quyền mua hoặc ko mua
+ Nếu em bán quyền chọn mua thì ko có quyền nữa phải theo bên kia =>
có lợi cho người người mua quyền chọn hơn là người bán quyền chọn
+ Lợi nhuận của người bán option chỉ là premium thui còn lỗ có thể vô biên
=> Mình mua 1 cái quyền để, the trader actually buys the right to affect the transaction
- Writer: người bán quyền chọn, đươc quyền bán hoặc ko bán => Có
quyền bán hoặc k bán nhưng nếu
- Holder: người mua quyền chọn chính là người mua hàng hóa => buyer.
Thì nếu holder mua thì writer phải bán
-> in any case, he always loses the option fee
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
- Option Châu Âu: phải chờ tới ngày đáo hạn để bán, tức là giá sẽ được quyết định vào maturity
- Option Mỹ: có thể bán ngang, linh hoạt trả giá at any time
Option position: có 2 loại option
VD. 500k/unit mà size là 10k units
=> Mua option này thì trả thêm 2$ cho mỗi unit => lỗ maximum là 20k$
>> Ổng exercise khi nào? - Call option:
+ Đằng nào cũng lỗ 20k$ rồi thì có thể exercise tại >500k$
+ Khoản cắt lỗ: 500k$ - 502k$ - Put option: Bán <500k$
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 CHAP 2. INCOTERMS I/ Overview
1. The Incoterms rules are derived from 'International Contract Terms
=> FALSE. Không derived từ Int’ contract terms
2. The Incoterms rules are a set of International Commercial Law
=> FALSE. k có tính bắt buộc, dựa trên agreement của hai bên
3. The Incoterms rules are not applicable to domestic trade transactions
=> FALSE. có thể apply cho domestic, từ 2010 trở đi đã áp dụng được cho domestic roài
4. The Incoterms rules address the transfer of property/title/ownership of the goods sold
=> FALSE. nó ko điều chỉnh những nội dung trên. Incoterms điều chỉnh trách nhiệm của người bán và người mua đến giao
hàng và nhận hàng chứ không nói về chuyển giao về quyền trên hàng hoá.
5. The Incoterms rules are applicable to contract of carriage
=> FALSE. Incoterms điều chỉnh giao hàng trong sales contract. contract of carriage độc lập với sale contract, contract of
carriage là giữa người bán/người mua với carriers
6. The Incoterms" rules are automatically applicable to sale of goods contract
=> FALSE. are not automatically vì nó không bắt buộc phải apply, nhưng nó chỉ bắt buộc khi có đề cập Incoterms trong
contract nhưng một khi đã chọn Incoterms rồi thì bắt buộc phải tuân theo
7. Variations of Incoterms rules (FOB Stowed and trimmed; CIF landed;...) are stipulated in Incoterms
=> FALSE. Variation là seller và buyer agree, thay đổi, change các cái standard, modify lại cái incoterm. Tuy nhiên những
cái variation này sẽ không quy định trong incoterms. Nên là khi dùng là phải redefine lại nó là gì
8. Use of trademark symbol (the circled R trademark indicator) is required when referring to Incoterms => FALSE.
9. The Incoterms rules cater for materials transported by pipeline, such as oil and gas
=> FALSE. The Incoterms rules do not specifically cater to materials transported by pipeline. They are more focused on
various modes of transport and the obligations between buyer and seller in international trade. Quiz 1. F
Incoterms = “International Commercial Terms” 2. F
Incoterms are trade practices/customs (tập quán) NOT law (not promulgated by the State but
naturally established; not binding to everyone)
3. F (since Incoterms 2010: applicable for both domestic and international trade transactions) 4. F
refer to Art. 7 (Incoterms DO NOT ADDRESS the transfer of property/title/ownership of the
goods sold – chuyển quyền sở hữu hàng hoá – among many other issues) to address this issue,
refer to the contract or the specific related law 5. F
not applicable DIRECTLY to contract of carriage 6. F
NOT automatically applicable, only binding to parties involved if mentioned in the contract
7. F (related to statement No. 2)
parties can make revisions/amendment in the contract for
Incoterms are mere trade practices, they do not recognize those variations 8. F
refer to Art. 15 (validity remains unchanged w/ or w/o the ®) 9. T
Incoterms are freq EXCLUDED in GAFTA (Hiệp hội thương mại về thức ăn chăn nuôi và ngũ cốc) contracts
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 T/F statements
1. Incoterms rules can be referred to “delivery terms”, “shipping terms” and “payment terms” interchangeably F
2. The use of incoterms leaving the year out implies that the latest ver will prevail F refer to Art. 11
3. Incoterms can be applied to domestic trade only F
4. Incoterms could be used as applicable law for the sales contracts F refer to Art. 8
1/ History & development
- What: a set of the most commonly-used three-letter trade terms, reflecting business-to-business
practice in sale of goods contract
- Who: International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) - When: 1936 (1st ver)
- Why: harmonize & standardize the meanings of trade terms at an international level global
standard rule of interpretation; avoid misunderstandings “It is better for two parties to a contract to
mean the same thing by the term they use than to quarrel afterwards as to which of the two meanings is the best”. Discussion
Case: seller (VN) export rice to Japan buyer (Kobe) - carriage contract
- custom clearance/ custom formalities (thông quan): export & import clearance - insurance
- transfer of risks (e.g. who will be in charge of the damaged goods during transportation)
⇨ Incoterms deal with: obligations, costs, risks ⇨ ANS: - Incoterms = Trade terms T
- Incoterms = Shipping terms to a certain degree, however shipping terms cover << incoterms
- Incoterms = Delivery terms (same as above) - Incoterms = Payment terms
F; however, Incoterms do have an impact on the calculations of the price
- (?) Incoterms are revised every 10 years F 2/ Fundamentals
- DO: as mentioned in the Discussion table above
- DO NOT: Incoterms are not the comprehensive rule:
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|59372584 3/ Remarks
- Not of mandatory use in a sale contract
- NOT price clauses but do have an impact on the pricing
- Sales contracts based on a former version remain valid according to the terms of that version o Incoterms is not the law
o Seller & buyer can go with any version if they so agree
o If the version is not specified
whether they conducted previous trade practices w/ e/o then that ver
prevails for the current contract, otherwise, disputes may occur
- Buyers and sellers should refer to the appropriate version
- It is possible to add clauses or change the wording of Incoterms Discussion Case:
1. The contract b/w VIET COTTON YARN INVESTMENT TRADING JSC & FETA TEKSTIL SAN.TIC.LTD.STI:
“ALL OTHER CONDITIONS, WHICH NOT STATED IN THIS CONTRACT, WILL REFER TO INCOTERMS 2000”
⇨ Risk: Incoterms are not comprehensive, they do not cover all the important issues that may arise
2. The contract No. BVQA400 b/w FORMOSA INDUSTRIES CORPORATION & NANYA PLASTICS CORPORATION:
“The INCOTERMS 2000 will be used for this contract”
⇨ Risk: Incoterms can be used for the delivery terms only, otherwise Incoterms is not the rule 4/ Classifications
Downloaded by T? Uyên (nkiki4448@gmail.com)



