






Preview text:
Human Computer Interaction Chapter 01 - Introduction Trinh Thanh Trun g Sch o o lof ICT,
Upon completion of this lesson, students will be able to: HUS
• Recall the concepts of interactive system and human- T computer interaction
• Identify the different components of an interactive system
• Explain the HCI roles and benefits
• Show necessary usability criteria of interactive systems Hu m an Co m p uter Interact Objectives oi n 2 Sch o o lof ICT, 1. Definitions HUS
2. Key principles in Human Computer Interaction T 3. Usability Hu m an Co m p uter Interact Content oi n 3 Definitions • Interactive system • Human computer interaction
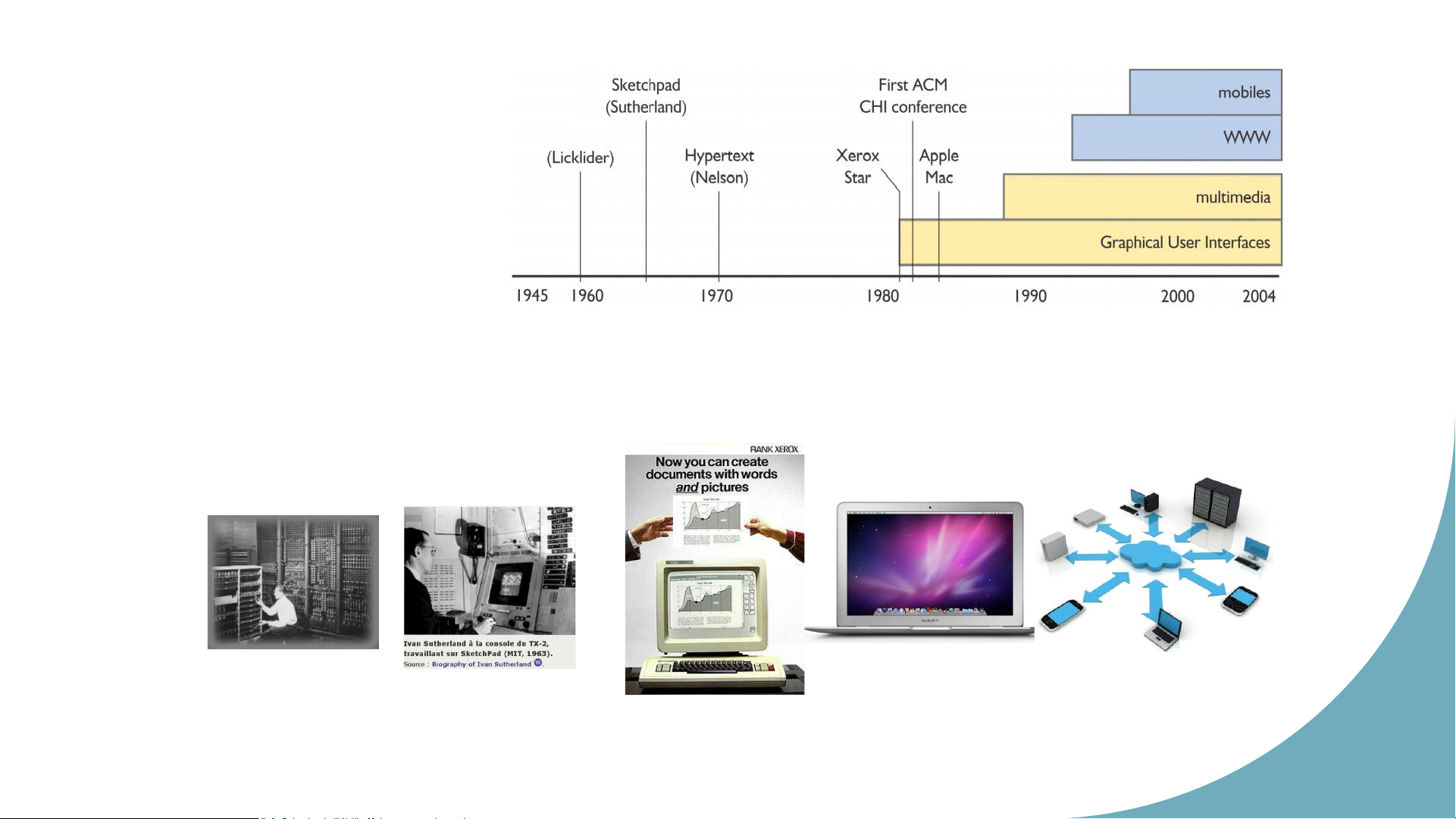
Baecker & Buxton’s definition ACM SIGCHI’s definition 4 Sch o o lo History f ICT, HUS T Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 5 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T Interactive System
• Interactive system: any system that accepts input from the user and provides information as output to the user Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 6 Sch o o lof ICT,
• Which ones are interactive systems? Why ? HUS T A. Lamp B. Digital microwave oven C. Mechanical microwave oven D. Mobile phone E. Pocket calculator Hu m an Co m p uter Interact Quiz oi n 7 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T
Human Computer Interaction • Definitions: •
Baecker & Buxton’s definition • ACM SIGCHI’s definition
• Baecker & Buxton, 1987:
“HCI involves a set of processes, dialogues and actions employed by a user to interact with a computer Hu
to perform a specific task” m an Co m p uter Interactoin 8 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T Example • What is it ? • When does it appear ?
• Through it, could user interact with the
application by means of giving a decision or asking something ? Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 9 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T
Human Computer Interaction ACMSIGCHI 1992:
“HCI is a discipline concerned with the design, evaluation and implementation of interactive computing
systems for human use and with the study of major phenomena surrounding them”
• HCI: Human - Computer Interaction Hu
• CHI: Computer - Human Interaction m an Co
• IHO: Interaction Humains Ordinateur m p uter In
• IHM: Interaction Homme Machine teractoin 10 Sch o o l Example o f ICT, HUS T Hu m an Source: Co
Source: http://www.apple.com/ipod/
http://www.samsung.com/vn/consumer/mobile-devices/smartphones/ m p uter Interactoin 11 HCI Principles • Interactive components
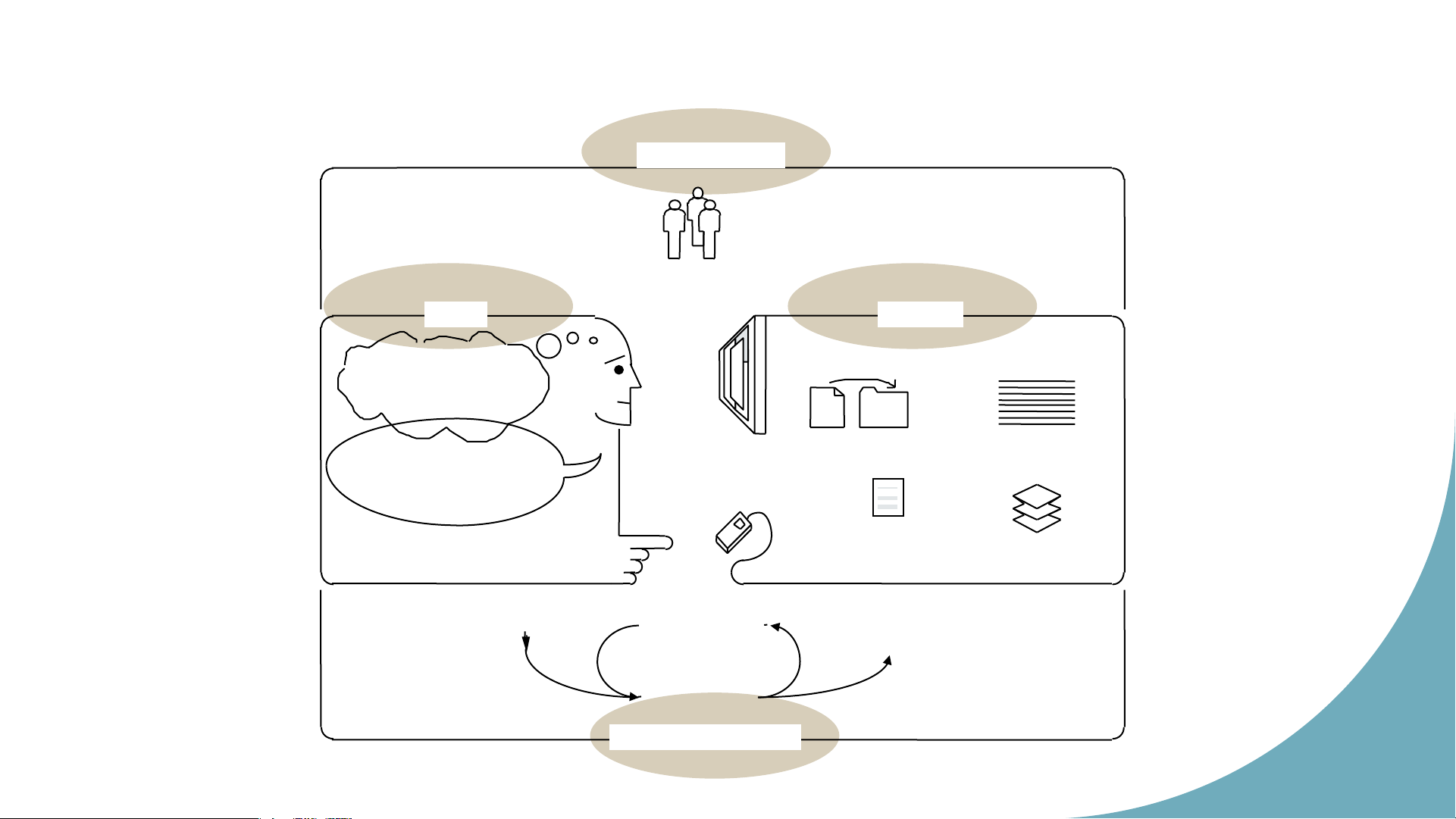
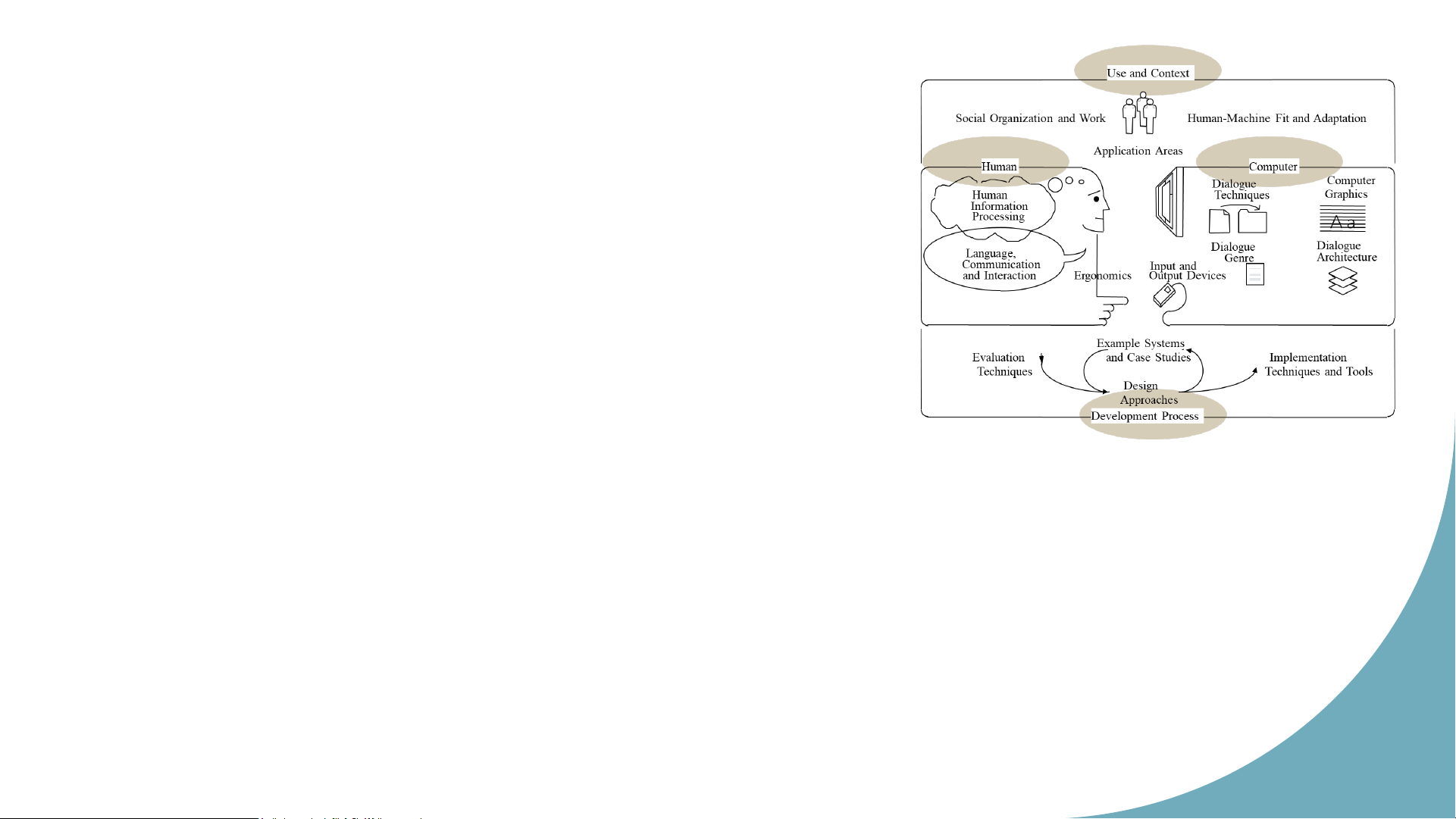
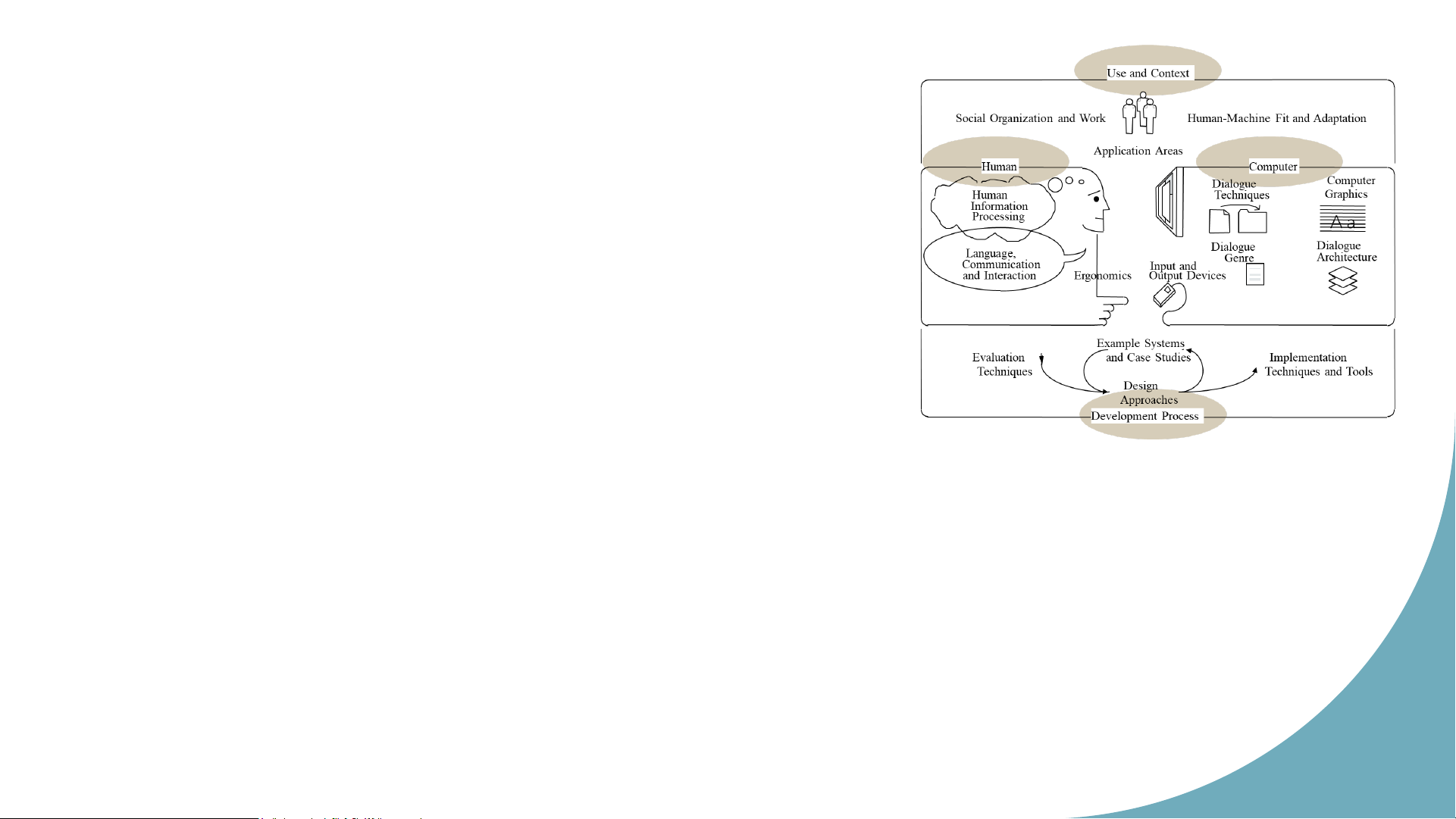
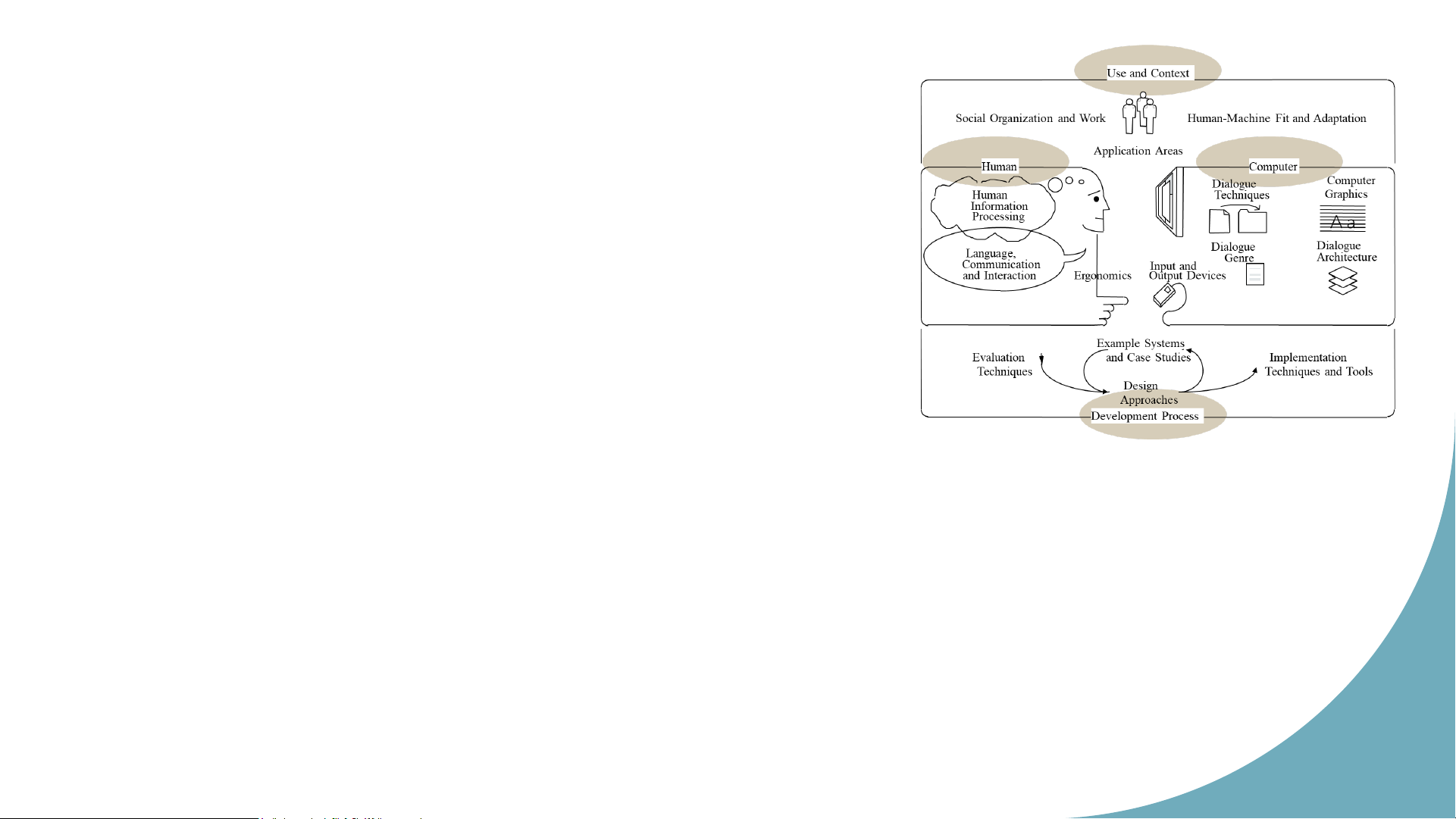
• Interaction means and tools • Interaction quality 12 Sch o o l Interaction components o f ICT, HUS HCI’s map T Use and Context Social Organization and Work
Human-Machine Fit and Adaptation Application Areas Human Computer Dialogue Computer Human Techniques Graphics Information Processing A a Dialogue Dialogue Language, Genre Architecture Communication Input and and Interaction Ergonomics Output Devices Hu m an Example Systems Co m Evaluation and Case Studies Implementation p u Techniques Techniques and Tools ter In Design tera Approaches ct oi Development Process n 13 Source: ACM SIGCHI Sch o o lo Interaction components f ICT, HUS a) Use and context T
Applications use computer resources
Organizations (social, commercial,...) interact with
these applications to accomplish given task. Interaction scope: Individual / group Text oriented communication Message oriented communication
Online help, continuous system control Hu m Computer aided design an Co .... m p uter In . teractoin 14 Sch o o lo Interaction components f ICT, HUS b) Human T
Objective: define human as an information processor Perception Storage Processing
Language, communication and interaction
Syntax and semantic of language Formal model of language Conventional interaction Hu m Ergonomics an Co Layout and control m p ute
Relationships between human and environments r In tera Cognitive and sensory limits ct oi n ... 15 Sch o o lo Interaction components f ICT, HUS
c) Computer and interactive architecture T I/O devices Dialogue techniques Dialogue genre Computer graphics
Dialogue architecture: software architectures and standards for interfaces Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 16 Sch o o lo Interaction components f ICT, HUS d) Development process T Design and techniques Design approaches
Implementation techniques and tools Evaluation techniques Patterns and case studies Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 17 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T
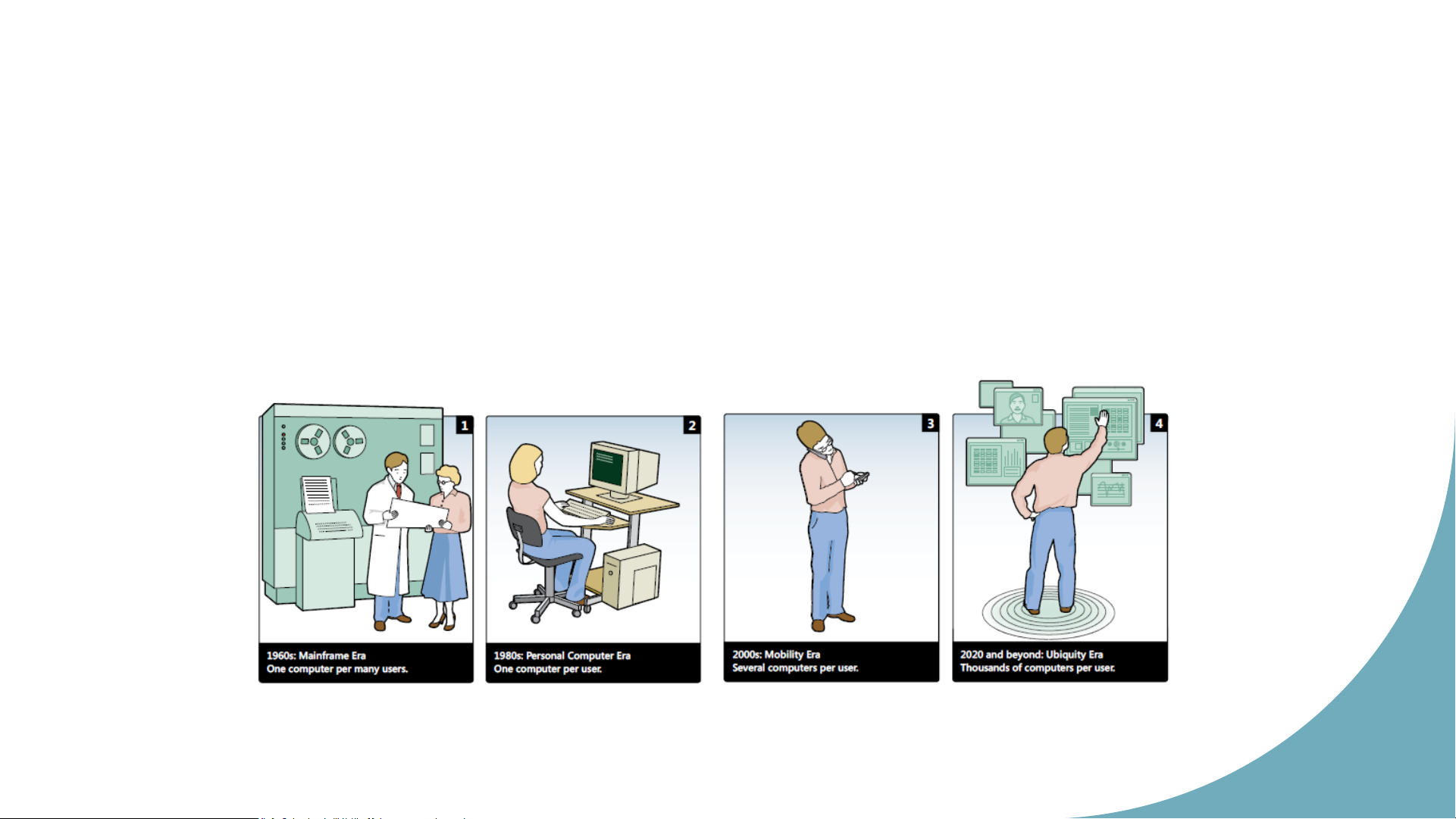
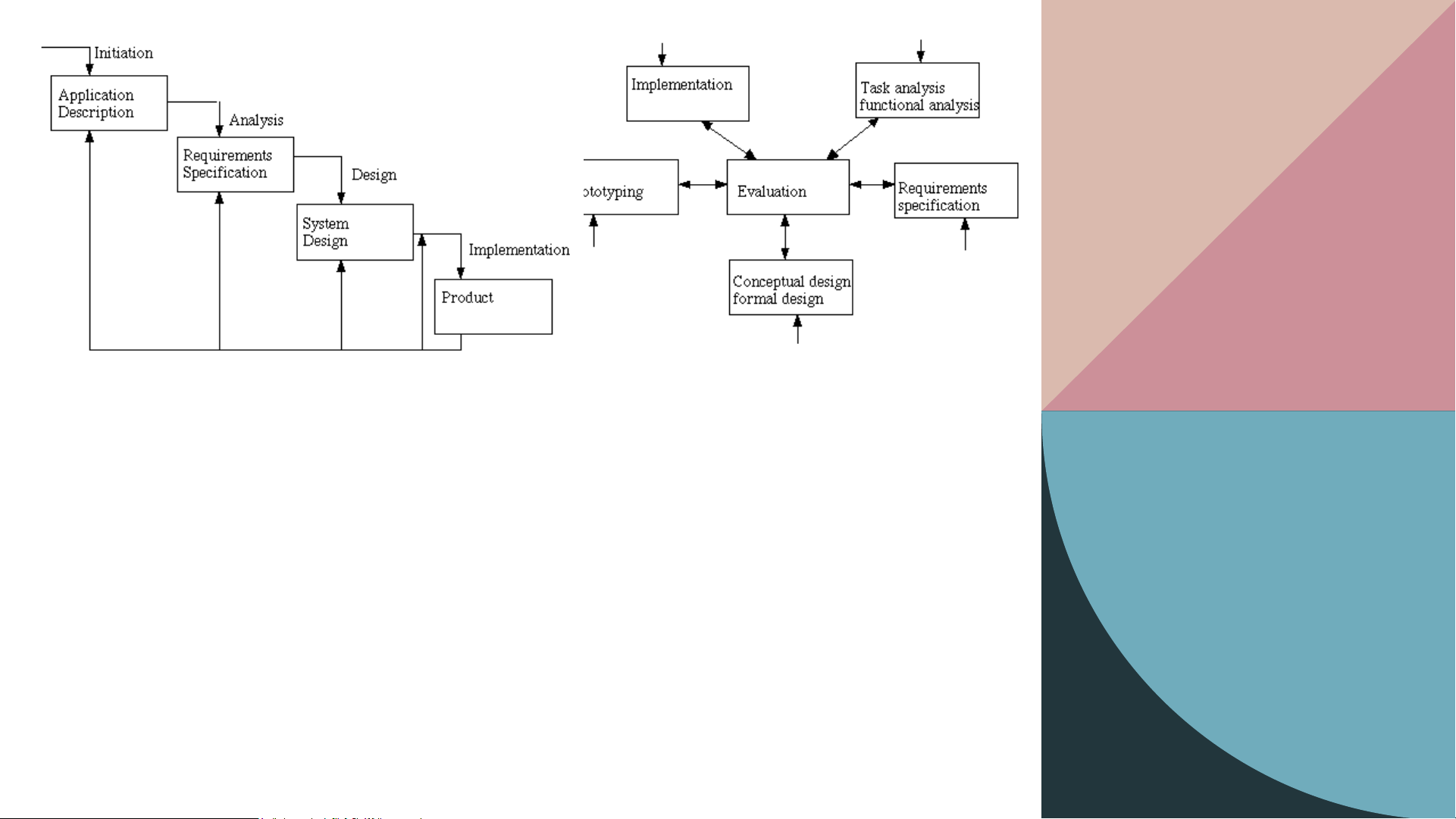
Model assumes that the design is
The design of interactive systems
fixed before entering to the next
typically does not follow a specific phase of design. order of steps. [HCI Hix Hartson 1993] Hu m an Co m p uter Interact Development process oi n 18 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T Means and tools
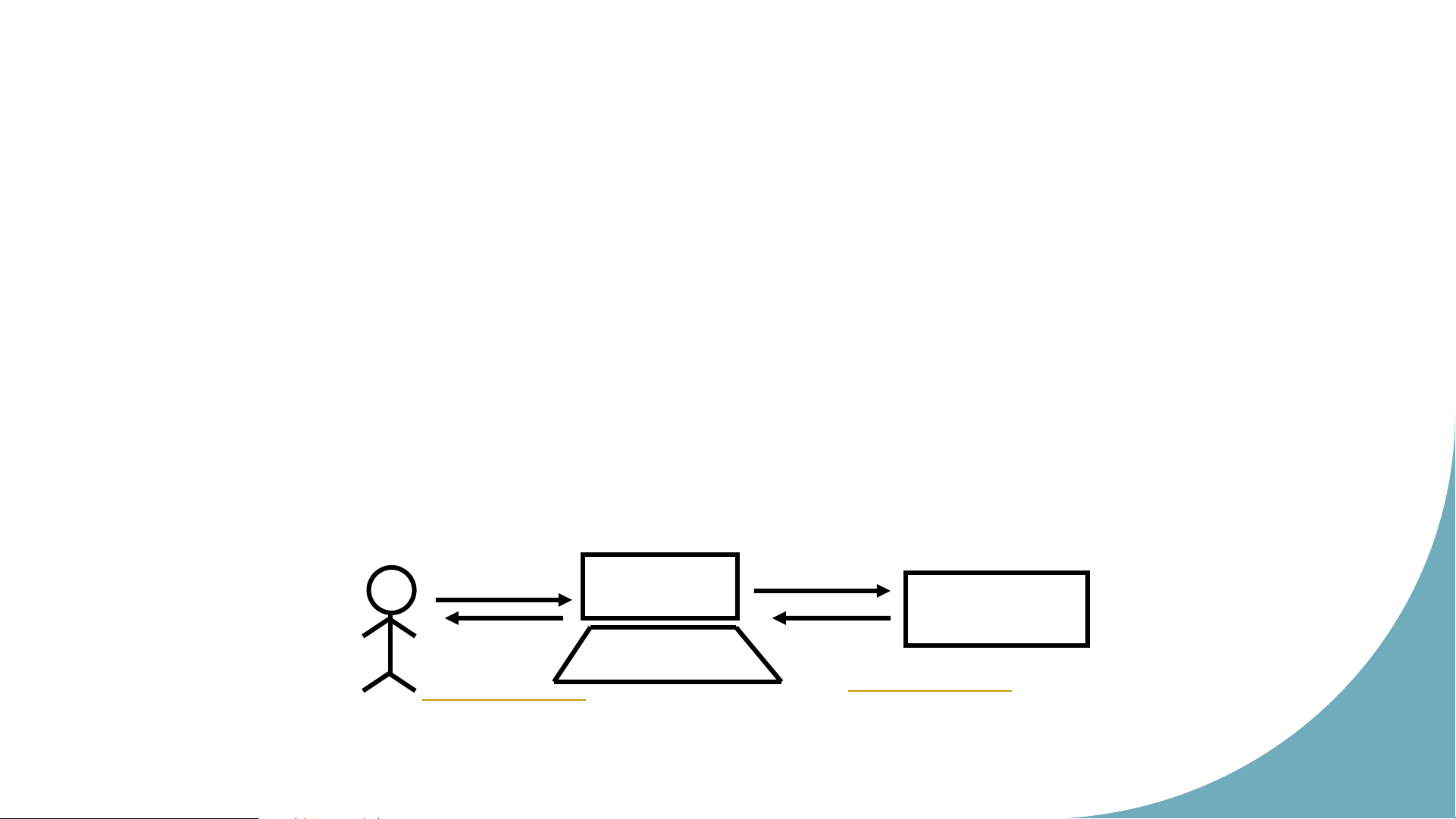
• Main interaction components: Human and Computer • Communication:
Means: Through environment (software)
Communication tools: Programming language, devices Requirement Hu m an Tasks Co m p Response uter Interactoi Dialog Exchange between n modules 19 Sch o o lof ICT, HUS T Quality
• First: correct input, correct output
• Next: incorrect input, correct output
• Today: user-friendly, easy to use Hu m an Co m p uter Interactoin 20




