













Preview text:
Comp Net MID REVIEW
1, Wi-Fi uses networks to connect devices to the Radio wave Electric signal Optic fiber Infrared
2, What is the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) of the Application layer? Data Segments Packets Frames Bits
3, Consider a network link between two hosts, which delay is not fixed? Processing Transmission Propagation Queuing
4. In encapsulation, which layers do not add "Header" to the data pass from the upper layer Application Physical Link (Data Link) Transport Network
5. A list of protocols used by a communication system is called a protocol architecture protocol suite protocol stack reference model OSI model 6. ADSL stands for
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line Access Digital Secure Line
Asymmetric Digital Secure Line
7.______and_____ are the two primary ways to enable LAN connections Infrared, Bluetooth Ethernet, Wi-Fi Internet, Wifi Cable, Infrared
8. What type of signals are transmitted across fibre optic cables? Electric Light Sound Radio
9. A group of devices connected together located in the same building or location is aSmall Area Network Metropolitan Area Network Wide Area Network Local Area Network 10.
A gamer in Saigon says: "I play World of Warcraft online game, US server and my ping
is always less than 100msec". What will you say? He's bluffing Wow, It's great Meh... What a noob I will play Vo Lam Truyen Ky
11. Computer networks can be used to share Printer Internet access Files Time Appliances
12. Does propagation delay depend on transmission rate? Not at all Yes but not much
Yes, a higher transmission rate hence a higher propagation delay
Yes, a higher transmission rate hence a lower propagation delay
13. What are the wireless technologies to accessthe Internet? 802.11 Cellular Sattelite GPS
14. Which ones are network delays? Propagation Transport Bandwidth Processing
15. What is the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) of theNetwork layer? Data Segments Packets Frames Bits 16. What is bandwidth?
The amount of data that can be transferred in a given time
The diameter of ethernet and fiber optic cables used in a network
The type of cables used in the network
The maximum network speed of a computer
17. Disadvantages of circuit-switched networks
May take a long time to establish connection
Cannot transmit any other data even if the channel is free
Cannot guarantee minimum bandwidth at all Number
of "slots" is limited and fixed
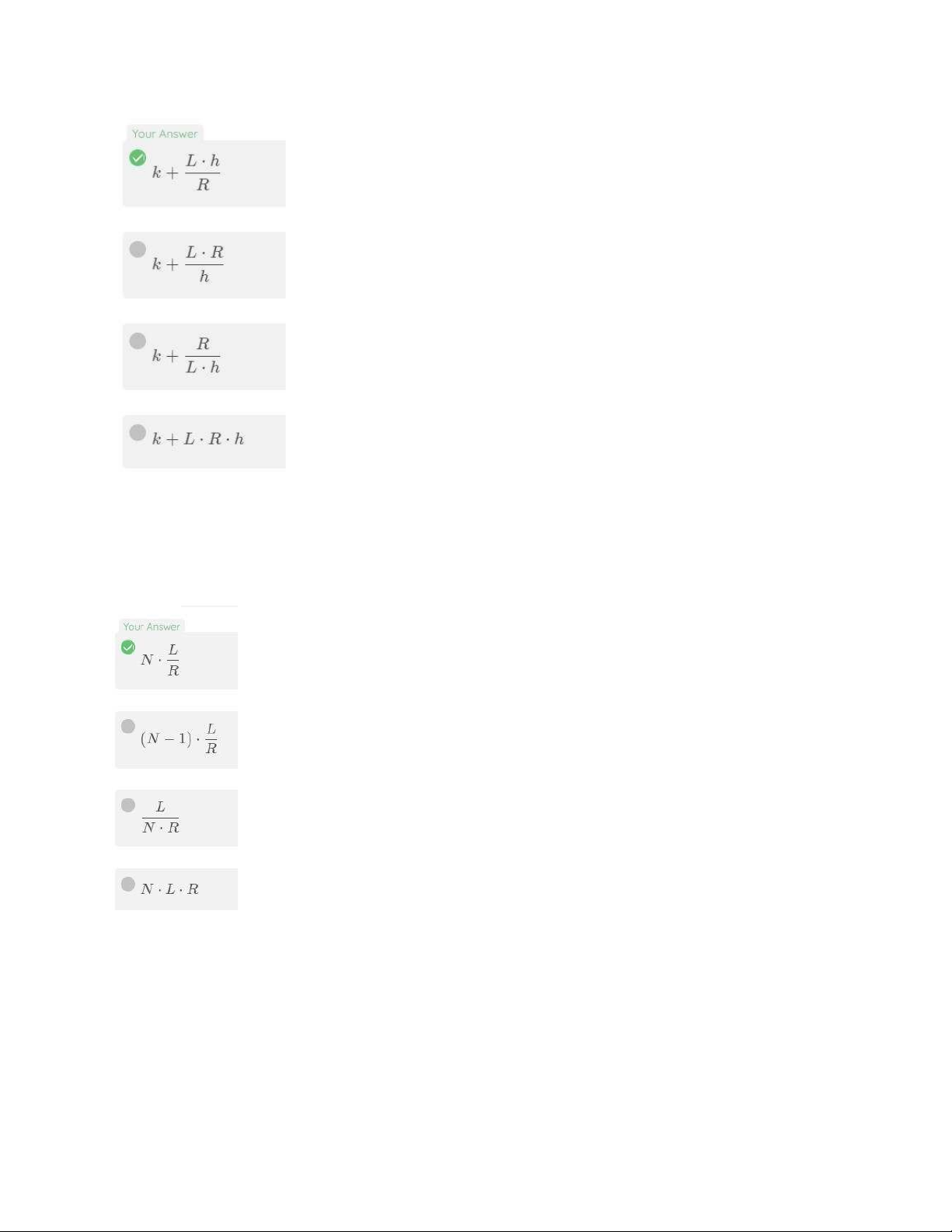
18. How long does it take to send a packet of size L from Host A to Host B over a
circuitswitched network that uses TDM with h slots and has transmission rate of R,
connection setup time is k secs?
19. Suppose one packet of size L transmits over N dedicated links with transmission rate R.
How much time will it take? Given that all the links distance are short and the processing time is negligible 20. Internet is A network of networks
The global system of interconnected computer networks Interconnected Network
A global network of billions of computer and electronic devices
21. The most common cables used in the Ethernet nowadays are Twisted-pair copper wire Fiber cable Coaxial cable Ribbon cable Jelly-filled telecom cable
22. In networks, which is correct about hosts and end systems? They are the same
Systems are more complicated than hosts
Hosts are PC, Laptop... Systems are servers, mainframe Both are network links
23. To link different ISPS of the same level together, we need a (an) ISP IXP IAP IP 24. MAN stands for Mobile Access Network Mesh Area Network Metropolitan Area Network Modern Access Network
25. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a router process? Application Transport Network Data Link Physical
26.____are all the layers of the Internet protocol stack.
Application, Transport,Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Presentation, Secure, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Transporter, Network, Data Link, Physical
27. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a host process? Application Transport Network Data Link Physical 28. What is Starlink?
Satellite constellation that provides Internet access by SpaceX
A communicator to deep space to find extraterrestrial intelligence
A new space telescope to replace Hubble
A global fiber Internet access proposed by Elon Musk
29. Fiber Optic Cables are faster than Ethernet cables True False
30. What is the current most common Internet subscription for households in Vietnam?Dial-up ADSL FTTH ISDN
31. What is the full meaning of Wi-Fi? Wireless Frequency Wireless Fiber Wired Fidelity Wireless Fidelity
32. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a hub process? Application Transport Network Data Link Physical
33. What is the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) of the Data Link layer? Data Segments Packets Frames Bits
34. In local wired networks nowadays, the mostcommon form of connector is RJ 11 RJ 48 RJ 45 RJ21
35. Host A transfers a 4MB file to Host B over a network link with a throughput of 1Mbps. At
least how much time is needed to complete? Response 32 36. Internet is a WAN? True False
37. What is the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) of the Transport layer?Data Segments Packets Frames Bits
38. Suppose we are sending P Packets of size L over N dedicated links with transmissionrate
R. How much time will it take? Given that all the links distance are short and the processing time is negligible
39. Which of the following can affect the performance of a network?
Whether the connection is wired or wireless
The number of users sharing the network Bandwidth
Computer OS: Windows, Mac OSX, Linux...
40. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a switch process? Application Transport Network Data Link Physical 41. LAN stands for Local Area Network Legal Access Network Legendary Access Node Local Admin Network
42. A network _____ is a set of rules governing the format and meaning of the messages
that are exchanged by the peer entities within a layer. primitive service interface protocol
43. What are the advantages of circuit-switched networks?
Can guarantee end-to-end bandwidth
After connection setup, communication link is dedicated
Data need to be split into smaller pieces
Do not require connection setup
44. Does propagation delay depend on packet size? Not at all Yes but not much
Yes, a bigger packet hence a higher propagation delay
Yes, a bigger packet hence a lower propagation delay
45. What is the PDU (Protocol Data Unit) of thePhysical layer? Data Segments Packets Frames Bits
46. Host A wants o send a large file to Host B. The path from Host A to Host B has 3 links: R1
= 500 kbps, R2 = 2 Mbps and R3 = 1 Mbps. What is the throughput? Assume there is no traffic in the network Response 500 47. WAN stands for Weak Access Node Working Area Network Wide Area Network World Access Network Web Access Network
48. ________are all the layers of the OSI reference model.
Application, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Presentation, Secure, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
Application, Transporter, Network, Data Link, Physical
49. Example of circuit-switched networks
Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) IP telephone Voice over IP Ethernet
50. What is the specification that enables computers to communicate with each other on a wired connection? Ethernet Wi-Fi Bluetooth Radio waves
51. In order to access the Internet at home, we need to subscribe to a (an). ISP IXP Wifi Access Point LAN
52. Satellite Internet access should use which of the following types to achieve a better user
experience? Geostationary Satellites GPS Satellites GLONASS Satellites Low-Earth Orbit Satellites
53. Internet Standards are mostly developed by which organizations?W3C (World Wide Web Consortium)
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
ICANN (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)
IAB (Internet Architecture Board)
IESG (Internet Engineering Steering Group)
54. What are the common network attacks?
Denial of Service (DoS) or Distributed DOS IP spoofing Physical offense Fraud Packet ID Scam
55. What type of signals are transmitted across Ethernet cables? Electric Light CMSA/CD Radio
56. Bob and Alice both transfer the same 10KB packet from Saigon to New York during night time (GMT +7)
Bob uses 10Mbps VNPT ADSLAlice uses 100Mbps VNPT FTTH (Fiber To The Home)
Alice can transfer 10 times faster than Bob
The two packets will arrive in New York almost the same time
Alice packet will arrive much sooner than Bob's
Bob packet will arrive much sooner than Alice's I have no idea
57. Computers on a network may be linkedtogether through: Internet Websites Radio signal Sound
58. In network, a (an) ______ is a specification that defines how data is delivered and
interpreted between two adjacent layers on the same host /end system. primitive service interface protocol
59. What are the main types of satellites used in communications? Geostationary Satellites GPS Satellites GLONASS Satellites Low-Earth Orbiting Satellites
60. What are the transmission rates of Ethernet LAN? 10MBps 100Mbps 1Gbps 10Gbps




