
































































































































































































Preview text:
Introduction to
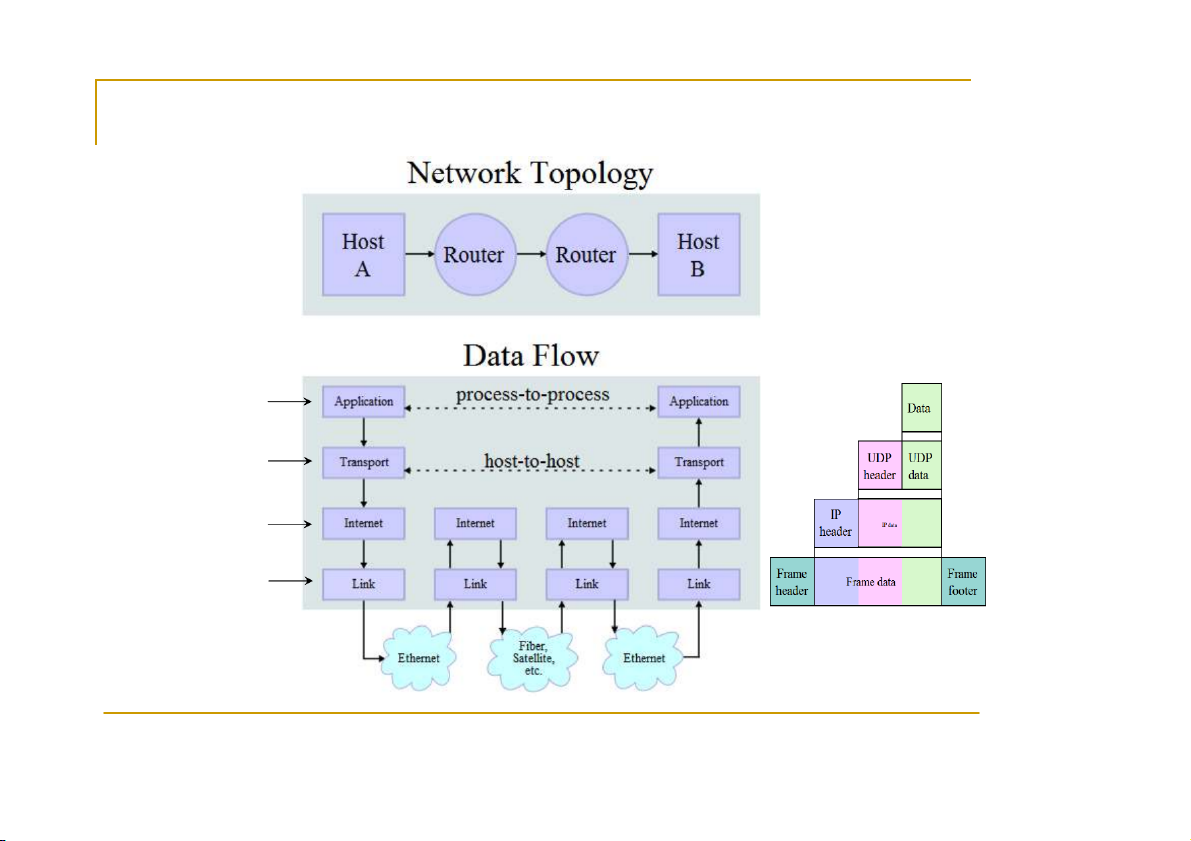
Sockets Programming in C using TCP/IP Professor: Panagiota Fatourou TA: Eleftherios Kosmas CSD - May 2012 Introduction Computer Network Host hosts, routers, communication channels Router Ho H s o t s s t s run applications Ro R ut o e ut r e s r s forward information Communication Pac Pa k c e k t e s t : sequence of bytes channel contain control information e.g. destination host Pro Pr t o o t c o o c l o l is an agreement meaning of packets structure and size of packets
e.g. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 2 Protocol Families - TCP/IP
Several protocols for different problems ) Pro Pr t o o t c o o c l o l S u S it i e t s e s or Pro Pr t o o t c o o c l o l F a F mi m li i e li s e : s :TCP/IP TCP/IP provides en e d n - d t - o t - o e - n e d n
d connectivity specifying how data should be formatted, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received at the destination
can be used in the internet and in stand-alone private networks it is organized into layer ye s r CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 3 TCP/IP * FTP, SMTP, … Tr T a r n a s n p s o p r o t r L a L ye y r e r TCP T CP o r r U DP Ne N t e wo t r wo k r k L a L y a e y r e r IP I Co C m o m m u m n u i n c i a c t a i t o i n o n Cha Ch n a n n e n l e s l
* image is taken from “http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TCP/IP_model” CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 4 Internet Protocol (IP) provides a da d t a a t gr a a gr m a m service
packets are handled and delivered independently bes be t s - t e - f e f f o f r o t r t protocol
may loose, reorder or duplicate packets
each packet must contain an IP I ad a d d r d e r s e s s s of its destination CS556 - Distributed Systems
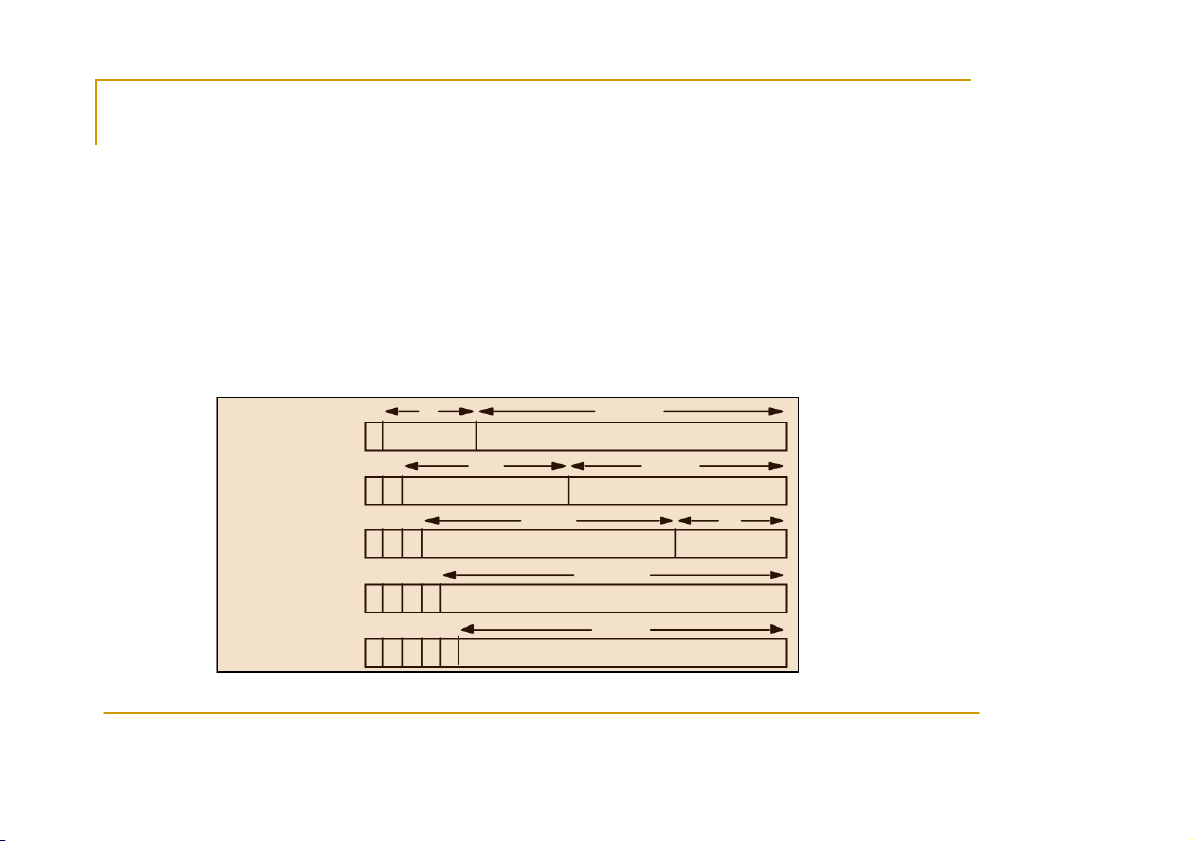
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 5 Addresses - IPv4 The 32 3
2 bits of an IPv4 address are broken into 4 4 o c o t c e t t e s t , or 8 bit fields
(0-255 value in decimal notation).
For networks of different size,
the first one (for large networks) to three (for small networks) octets can be used to identify the ne n t e w t o w r o k r , while
the rest of the octets can be used to identify the nod no e d e on the network. Range of addresses 7 24 1.0.0.0 to Class A: 0 Network ID Host ID 127.255.255.255 14 16 128.0.0.0 to Class B: 1 0 Network ID Host ID 191.255.255.255 21 8 192.0.0.0 to Class C: 1 1 0 Network ID Host ID 223.255.255.255 28 224.0.0.0 to Class D (multicast): 1 1 1 0 Multicast address 239.255.255.255 27 240.0.0.0 to Class E (reserved): 1 1 1 1 0 unused 255.255.255.255 CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 6
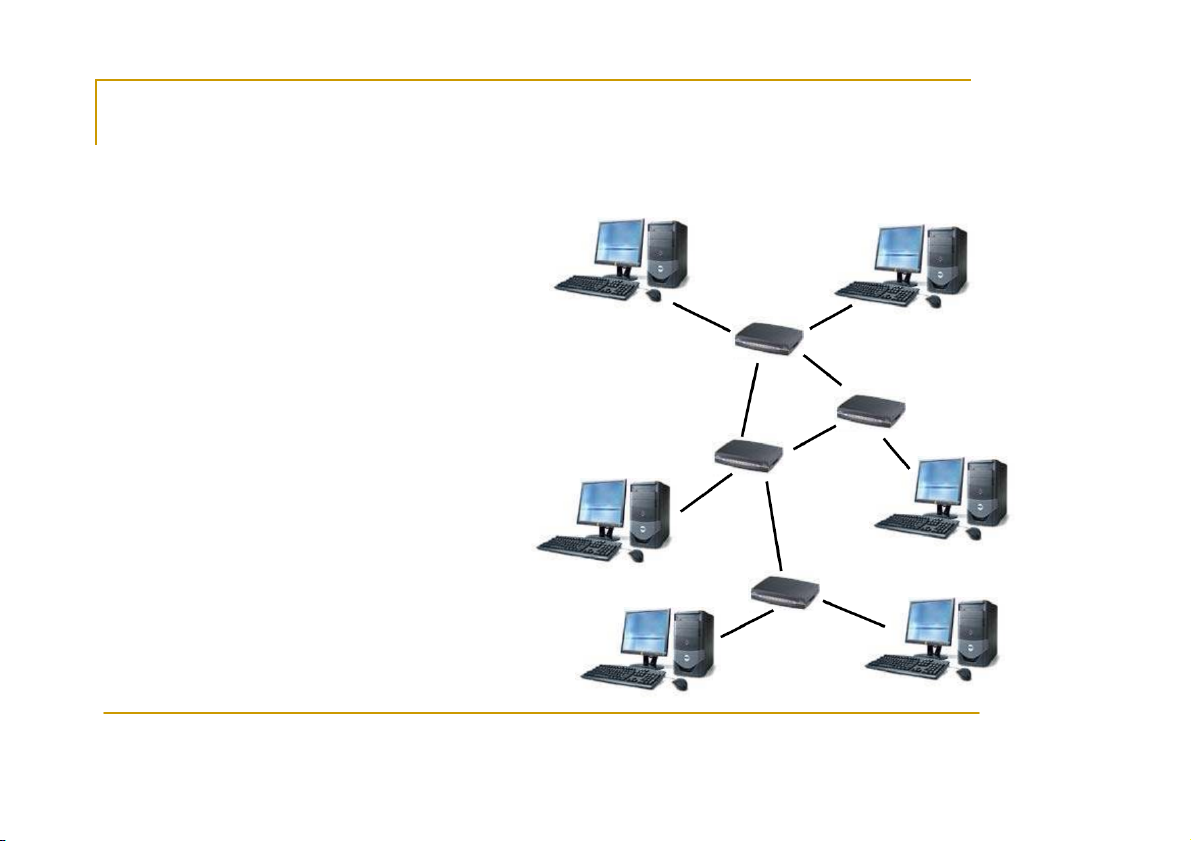
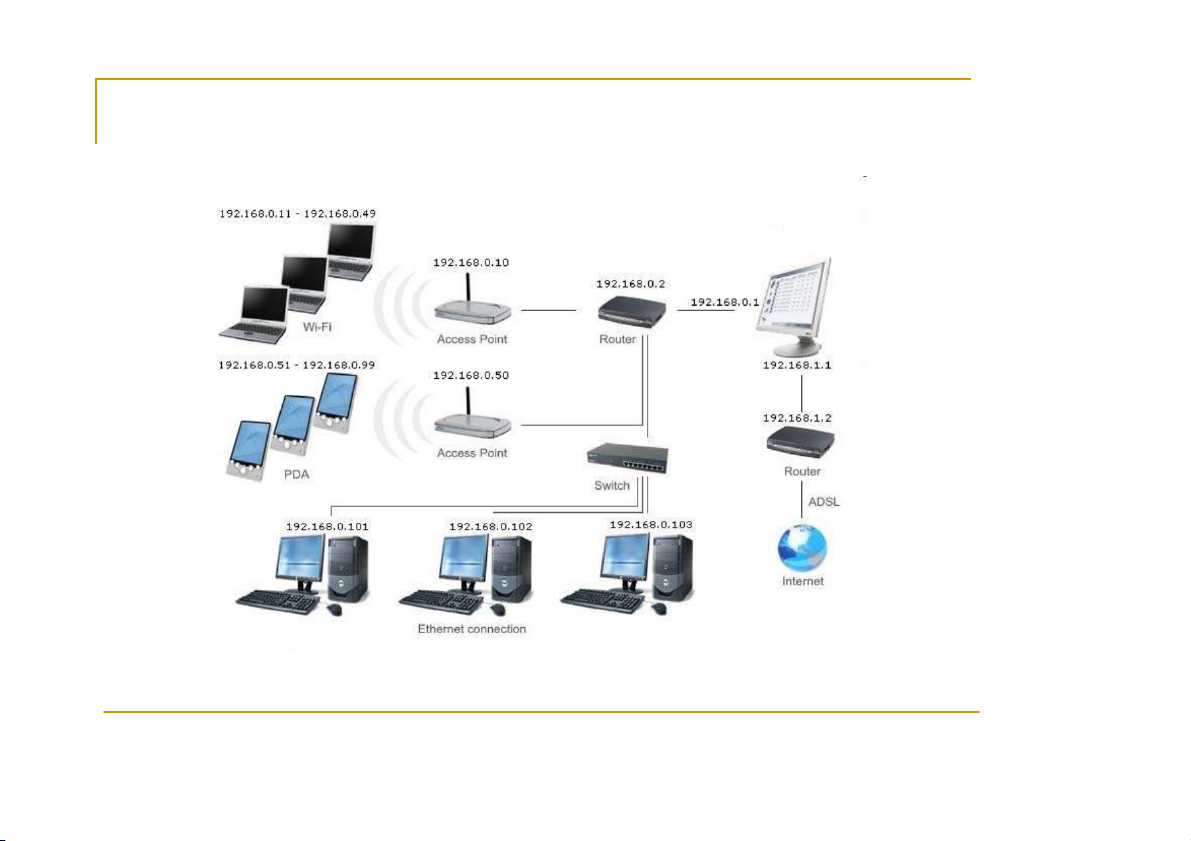
Local Area Network Addresses - IPv4 CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 7 TCP vs UDP Both use por po t r n um n be um r be s r
application-specific construct serving as a communication endpoint
16-bit unsigned integer, thus ranging from 0 to 65535 ) to provide end e - nd t - o t - o end e nd transport UDP: User Datagram Protocol no acknowledgements no retransmissions
out of order, duplicates possible
connectionless, i.e., app indicates destination for each packet
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol reliable by b t y e t - e s - t s r t e r a e m a m c h c a h n a n n e n l e
l (in order, all arrive, no duplicates) similar to file I/O flow control connection-oriented bidirectional CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 8 TCP vs UDP
TCP is used for services with a large data capacity, and a persistent connection
UDP is more commonly used for quick lookups, and single use query-reply actions.
Some common examples of TCP and UDP with their default ports: DNS lookup UDP 53 FTP TCP 21 HTTP TCP 80 POP3 TCP 110 Telnet TCP 23 CS556 - Distributed Systems
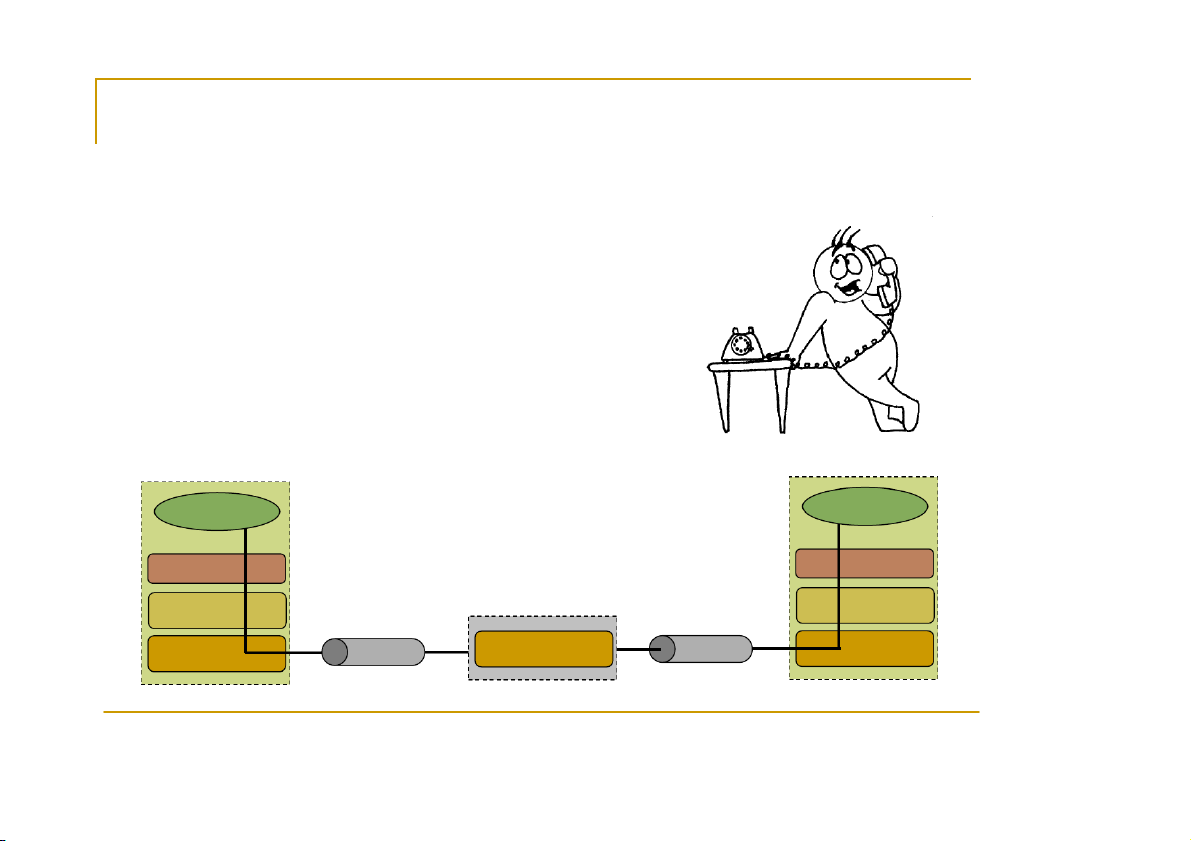
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 9 Berkley Sockets Universally known as So S c o k c e k t e s t
It is an abstraction through which an
application may send and receive data Provide generic a generic c a c c e c s e s s s to interprocess communication services
e.g. IPX/SPX, Appletalk, TCP/IP Standard API for networking App Ap l p i l c i at a i t o i n o App Ap l p i l c i at a i t o i n o So S c o k c e k t e So S c o k c e k t e TC T P C TC T P C IP I Ch C a h n a n n e n l I el l P I Ch C a h n a n n e n l e IP I Ho H s o t s Ro R u o t u e t r e Ho H s o t s CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 10 Sockets Uniquely identified by an internet address
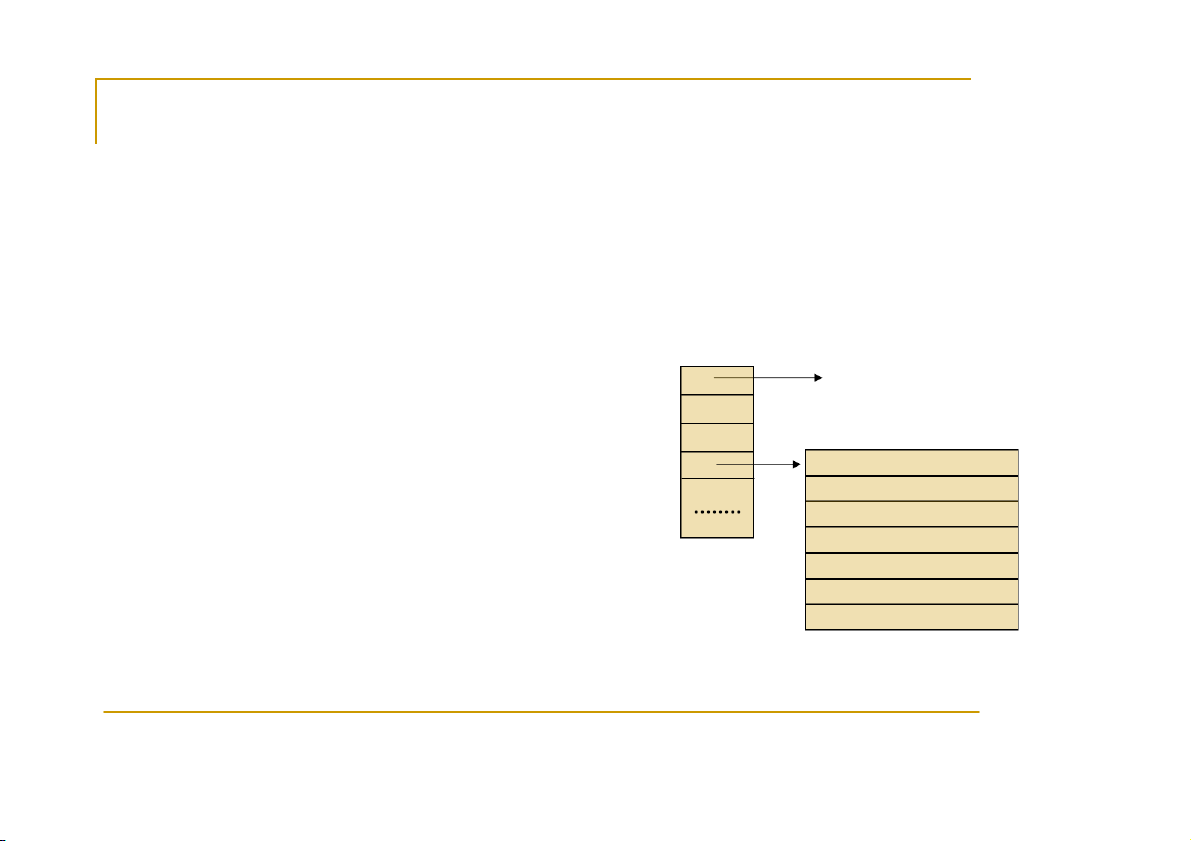
an end-to-end protocol (e.g. TCP or UDP) a port number Two types of (TCP/IP) sockets Descriptor Table internal data St S r t e r a e m a m sockets (e.g. uses TCP) 0 structure for file 1 1
provide reliable byte-stream service 2 Da D t a a t g a r g a r m a m sockets (e.g. uses UDP) Family: PF_INET Service: SOCK_STREAM
provide best-effort datagram service Local_IP: messages up to 65.500 bytes Remote_IP: Local_Port:
Socket extend the convectional UNIX I/O facilities Remote_Port: …
file descriptors for network communication
extended the read and write system calls CS556 - Distributed Systems
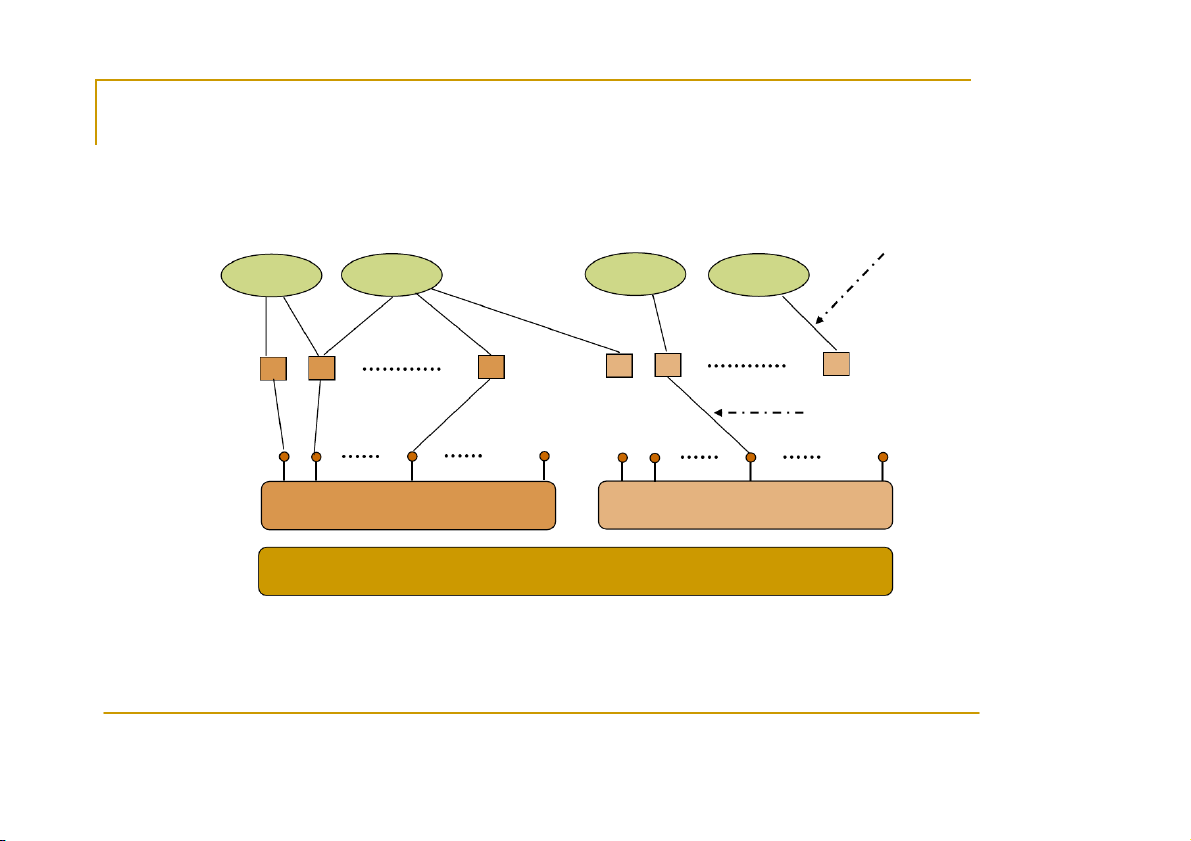
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 11 Sockets Descriptor references Applications TCP sockets UDP sockets Sockets bound to ports TCP ports 1 2 65535 1 2 65535 UDP ports TCP UDP IP CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 12 Socket Programming CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 13 Client-Server communication Se S r e v r e v r e r
passively waits for and responds to clients pa p s a s s i s v i e v e socket Cli C e li n e t n initiates the communication
must know the address and the port of the server ac a t c i t v i e v e socket CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 14 Sockets - Procedures CS556 - Distributed Systems
Tutorial by Eleftherios Kosmas 15




