















Preview text:
HOA SEN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF
LOGISTIC – INTERNATIONAL TRADE FINAL REPORT
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT ------&------ TOPIC: WAREHOUSING OF NIKE Course ID : BA401DE01
Instructor : NGÔ HỮU KHÁNH LINH Group:
1. Nguyễn Thị Tuyết Ngân - 22004931
2. Nguyễn Quỳnh Nhã Phương - 22012492 3. Phan Thuý Ngân - 22012494
Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, ngày 01 tháng 07 năm 2023. HOA SEN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF
LOGISTIC – INTERNATIONAL TRADE FINAL REPORT
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT ------&------ TOPIC: WAREHOUSING OF NIKE Course ID : BA401DE01
Instructor : NGÔ HỮU KHÁNH LINH Group:
1. Nguyễn Thị Tuyết Ngân - 22004931
2. Nguyễn Quỳnh Nhã Phương - 22012492 3. Phan Thuý Ngân - 22012494
Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, ngày 01 tháng 07 năm 2023. TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS ............................................................................................... i
LIST OF FIGURES ..................................................................................................... iii
LIST OF TABBLES ..................................................................................................... iv
INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................... 1
1. THE OVERVIEW OF NIKE .................................................................................... 2 1.1
Introduction of Nike ................................................................................................. 2
1.1.1 Historical development of Nike ............................................................................................... 2
1.1.2 Logo and slogan of Nike ........................................................................................................... 2
1.1.3 Nike timeline .............................................................................................................................. 4 1.2
Organizational structure of Nike ............................................................................. 6 1.3
Main products of Nike .............................................................................................. 8 1.4
Market of Nike ........................................................................................................ 10 1.5
Industry Competitors of Nike ................................................................................ 11
2. LITERATURE REVIEW ABOUT WAREHOUSING .......................................... 14 2.1
Warehousing Strategies .......................................................................................... 14 2.2
Stock Controls ......................................................................................................... 15 2.4
Material Handling ................................................................................................... 16 2.5
Technology Adoption .............................................................................................. 16 2.6
Supply Chain Collaboration .................................................................................. 17 2.7
Sustainability Initiatives ......................................................................................... 17
3. CURRENT SITUATION OF IMPLEMENTING WAREHOUSE OF NIKE ..... 18 3.1
Warehouse Infrastructure ...................................................................................... 18 3.2
Inventory management ........................................................................................... 20
3.2.1 The effectiveness of the strategy ............................................................................................ 21
3.2.2 Limitations and vulnerabilities .............................................................................................. 21 i
3.2.3 Alternative Inventory Strategy .............................................................................................. 21 3.3
Automation and Technology Integration .............................................................. 22 3.4
Supply Chain Resilience ......................................................................................... 25
4. DRAWBACKS ......................................................................................................... 27
5. PROPOSED SOLUTION ....................................................................................... 29
CONCLUSION .............................................................................................................. v
REFERENCES ............................................................................................................ vi ii LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Nike logo evolution (Source: Footy Headlines) ............................................. 3
Figure 2: Organizational leadership structure of Nike (Source: Organimi) ................. 6
Figure 3: Nike Air Max was released in 1987 ............................................................... 8
Figure 4: Some of the major Nike product lines (Source: Business Apac) .................... 9
Figure 5 Some models of Nike training and casual clothes (Source: Pinterest) ........... 9
Figure 6: The percentages of workers and total sales in each country of Nike ........... 10
Figure 7: Top 10 countries with the most Nike factories in the world ........................ 11
Figure 8: Warehousing Strategies ............................................................................... 14
Figure 9: Stock Controls .............................................................................................. 15
Figure 10: Operations Management Warehouse ......................................................... 15
Figure 11. Robots support Nike’s supply chain logistics ............................................. 16
Figure 12 Move to zero the journey of nike ................................................................. 17
Figure 13: Sustainability Initiatives of Nike ................................................................ 18
Figure 14. Nike Warehouse Indianapolis .................................................................... 19
Figure 15. Nike Warehouse Bethlehem Pa Address .................................................... 20
Figure 16. Robotics of Nike ......................................................................................... 22
Figure 17. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning of Nike ........................ 23
Figure 18. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) of Nike ...................................... 24
Figure 19. Mobile Technology of Nike ........................................................................ 24 i ii LIST OF TABBLES
Table 1: Comparation the success factors of Nike and Adidas 12 i v INTRODUCTION
Nike is a renowned name in the world of athletic excellence and global
innovation, recognized for its cutting-edge designs and unwavering commitment
towards pushing boundaries. The brand has become a symbol of distinction in the realm
of sports. At the core of this extensive empire lies a concealed powerhouse - the Nike
Warehouse. This report aims to provide an intriguing insight into the internal operations
of this remarkable facility, scrutinizing its significance within Nike's supply chain and
the impact it has on the brand's global operations.
The Nike Warehouse enables the smooth movement of products that empower
athletes and enthusiasts across the globe, and serves as a dynamic space where raw
materials undergo a transformation to emerge as cutting-edge footwear, apparel, and
equipment that redefine performance and inspire excellence. The Nike Warehouse use
wherein cutting-edge technology is in perfect harmony with the expertise of skilled
professionals. Each stage of the journey, from conception to final delivery, is
meticulously planned and executed to ensure optimal efficiency and customer
satisfaction. Moreover, the Nike Warehouse embodies the brand's commitment to
sustainability and responsible manufacturing beyond its role in the global supply chain.
Nike has implemented innovative practices within the warehouse to reduce its
environmental footprint, such as energy-efficient systems, waste reduction initiatives,
and responsible sourcing of materials. By combining efficiency with environmental
stewardship, Nike serves as a profound example for the industry, demonstrating that
excellence and sustainability can indeed go hand in hand.
In this report, we will conduct a comprehensive exploration of the core of the
Nike Warehouse, where we will uncover its state-of-the-art technologies, innovative
procedures, and the individuals responsible for facilitating it all. We will delve into the
inventory management systems and quality control protocols that enable Nike to
distribute its renowned products to customers worldwide. 1
1. THE OVERVIEW OF NIKE
1.1 Introduction of Nike 1.1.1
Historical development of Nike
The antecedent of Nike was the Blue Ribbon Sports Company, which was
founded by Phil Knight in 1964 with the aim of importing reasonably priced Japanese
athletic footwear, specifically those bearing the Onizuka brand, into the United States.
Phil Knight's collaboration with Bill Bowerman, who subsequently became Nike's most
ingenious sports footwear designer, was significant in contributing to the global success
of Nike shoes within the sports footwear manufacturing industry.
Nike, a supplier of athletic clothing and equipment, is headquartered in the
United States, specifically in Beaverton, situated in the Portland metropolitan area of
Oregon. Nike's name is derived from the winged deity associated with triumph in Greek mythology.
Several subsidiaries of Nike are presently dispersed across the globe. In addition
to the highly recognized Nike brand, Nike also possesses many other renowned brands
such as Cole Haan, Converse Inc., Hurley, LLC, and Nike Gold. Having a workforce
that can number in the thousands, the organization employs staff members in various
Asian countries including China, Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan and Korea. 1.1.2
Logo and slogan of Nike
In 1971, Blue Ribbon Sports (BRS), which is now known as Nike, enlisted the
services of Carolyn Davidson, a college student, to construct the brand logo. Davidson
not only created the logo and christened it "Swoosh," but also recommended that the
brand name be changed from Dimension 6, which was originally proposed by founder Phil Knight, to Nike.
Recognizing that the Nike font in the Nike logo was too juvenile and unathletic,
Nike opted to modify the font to Futura Bold, a sans-serif font that was overhauled and 2
replaced in 1978. The new Nike logo font is remarkable, appealing, and commanding,
with all parameters being meticulously calculated and the distances between the letters
being precisely proportioned. If one scrutinizes the Nike logo closely, they will observe
that the letter "E" in the Nike logo concludes with a connection to the swoosh logo.
The 1985 Nike logo underwent a transformation that involved the addition of a
black square to the logo, but this alteration was brief.
Nike's current logo has undergone a transformation by removing the brand name,
resulting in a minimalist design featuring only a comma. The iconic Swoosh has become
the embodiment of athleticism, speed, excellence, and resilience, and is recognized as
one of the most recognizable symbols globally. Due to its simple nature, the Nike logo
has become a reliable indicator of progress and prosperity.
Figure 1: Nike logo evolution (Source: Footy Headlines)
The motivational slogan 'Just do it' by Nike, which dates back to 1970, was
created with an aim to encourage people to persevere. The inception of this catchphrase
has been speculated upon, but what remains noteworthy is the slogan's widespread
acceptance and endorsement by Americans, which has solidified its status as one of the
most impactful and memorable catchphrases in history. 3 1.1.3 Nike timeline
In 1964, Blue Ribbon Sports was established by Phil Knight and Bill Bowerman.
In 1971, Nike Inc. was formed after severing ties with Onitsuka Tiger (now Asics), with
a swoosh logo designed by a student from Portland State University, Carolyn Davis, for
a fee of $35. During the same year, Bowerman devised the iconic sole pattern for Waffle
Trainers by incorporating rubber into a waffle iron.
In 1972, Ilie Nastase, a Romanian tennis player, became the first athlete to sign an endorsement deal with Nike.
In 1979, Nike introduced a patented technology called "Air" with the new Tailwind shoe.
In 1980, Nike completed its IPO with a price of 18 cents per share.
In 1984, Nike signed Michael Jordan, which resulted in the launch of the Air Jordan series.
In 1987, Nike released an advertisement for the new Air Max shoes, utilizing The
Beatles' "Revolution," which marked the first time that the band's music was used in an advertisement.
In 1988, Nike launched its first "Just Do It" campaign, which featured Walter Stack, an
iconic 80-year-old runner, dashing across the Golden Gate Bridge.
In 1989, Nike launched another ad campaign called "Bo Knows," which showcased the
talent of baseball and football star Bo Jackson.
In 1990, Nike opened its first Niketown store in Portland, Oregon, marking a significant
milestone in the company's history.
1991 was a year of controversy for Nike, as Jeff Ballinger, an activist, published a report
that exposed the low wages and poor working conditions faced by workers in 4
Indonesian Nike factories. The company responded to this by implementing its first factory codes of conduct.
In 1996, Nike signed the legendary Tiger Woods.
In 1998, Nike faced widespread protests and criticism, which prompted the company to
raise the minimum age of its workers, increase monitoring, and adopt U.S. OSHA clean-
air standards in its overseas factories.
In 1999, saw the unfortunate passing of Nike co-founder Bill Bowerman at the age of 88.
In 2002, Nike acquired Hurley, a surf-apparel company, further expanding its portfolio.
In 2003, Nike continued to strengthen its roster of athletes by signing Lebron James and Kobe Bryant.
In 2004, Nike acquired Converse for a whopping $309 million. As the same year, Phil
Knight steps down as CEO and president of Nike, but retains chairman role as William
D. Perez becomes the company's new CEO.
In 2008, Nike signs Derek Jeter.
In 2012, Nike becomes official supplier for NFL apparel.
In 2015, Nike becomes official supplier for NBA apparel.
In 2018, Nike unveils ad campaign featuring athlete and political activist Colin
Kaepernick, garnering a mix of public approval and backlash. 5
1.2 Organizational structure of Nike
Figure 2: Organizational leadership structure of Nike (Source: Organimi)
Nike's operational activities are under the purview of the global corporate
leadership team, comprising 16 individuals holding C-level, presidential, and vice
presidential roles. The Chairman Emeritus and Executive Chairman are part of this
team, but the primary responsibility for ensuring the company's goals and vision are
realized rests with the President & CEO. 6
Nike's corporate framework comprises two discernible components, aside from
the all-encompassing global corporate leadership, which oversees the organization's
diverse brands and divisions worldwide. Firstly, the global enterprise is segregated into
semi-autonomous geographic regions, namely North America, Western Europe,
Eastern/Central Europe, Greater China, Japan, and Emerging Markets.
Each regional division endeavors to optimize its operations in the regional
markets for sports shoes, apparel, and equipment in order to accommodate cultural and
regional diversities. Prior to the year 2022, Nike's regional markets were comparatively
less segmented and were constituted of four geographical areas, namely North America,
Greater China, Asia Pacific and Latin America (APLA), and Europe, Middle East, and
Africa (EMEA). The decision by Nike to further segment its geographic divisions into
seven regions has been impelled by various factors, including the Beijing Olympics
which stimulated sales beyond 50 percent.
Moreover, Nike adopts a matrix organizational structure that comprises a blend
of horizontal and vertical structures. As we have previously discussed on our blog, a
matrix structure involves several lines of authority, wherein employees report to
multiple supervisors and managers based on their roles and the projects they are working on.
The intricate nature of this particular organizational structure may seem intricate
and perplexing, however, it is in fact quite suitable for a company like Nike, which
concurrently manages hundreds of distinct product lines, campaigns, projects, and
various other operations. Despite the matrix structure resulting in multiple reporting
relationships, Nike's operational and communications procedures are standardized,
thereby ensuring that employees are cognizant of their responsibilities and to whom
they are accountable. These characteristics of Nike's organizational structure are
instrumental in facilitating growth and stability. The corporate leadership team at a
global level is able to maintain control over the organization's operations, while the
semi-autonomous regional divisions provide flexibility in addressing market-specific consumer requirements. 7
1.3 Main products of Nike
Nike, a prominent sports equipment producer, has generated a substantial
inventory of sporting goods. Their initial offering consisted of a running shoe, and at
present, they are involved in the production of shoes, jerseys, shorts, flats, basketball
shoes, and an assortment of other items for numerous sports such as track and field,
baseball, ice hockey, tennis, football, lacrosse, basketball, and cricket. Nike, Inc.'s
development of Nike Air Max, a line of shoes, dates back to its initial release in 1987.
Figure 3: Nike Air Max was released in 1987
Nike manufactures a diverse range of footwear products tailored to various
athletic disciplines, complemented by sport-specific accessories including but not
limited to garments, headwear, bands, balls, and eyeglasses. Nike's principal
merchandise categories are commonly linked to physical activities, such as:
Nike running: incorporates lightweight materials in the sole to enhance durability
during training and running activities, similarly to Nike shox products.
Nike women: offers sportswear with a feminine touch.
Nike soccer and football: both feature shoe soles designed for deep and soft grip,
ensuring players' comfort during the game.
Nike basketball: suitable for playing basketball. 8
Nike 6.0+: ideal for action sports such as windsurfing and skiing.
Nike ID: a combination product between Nike and iPod, catering to individuals who
value modernity and technology. Nike ID allows users to measure their running pace.
In 2006, Nike collaborated with Apple to launch Nike+ technology, enabling
runners to track their distance, pace, and time. Initially, using the shoe sensor, Nike+
has now evolved to a GPS app on the iPhone.
Figure 4: Some of the major Nike product lines (Source: Business Apac)
In addition to its offering of sportswear, Nike additionally produces a range of
casual wear products. These Nike products are tailored to appeal to a diverse array of
audiences spanning various age groups, including men, women, and children.
Figure 5 Some models of Nike training and casual clothes (Source: Pinterest) 9 1.4 Market of Nike
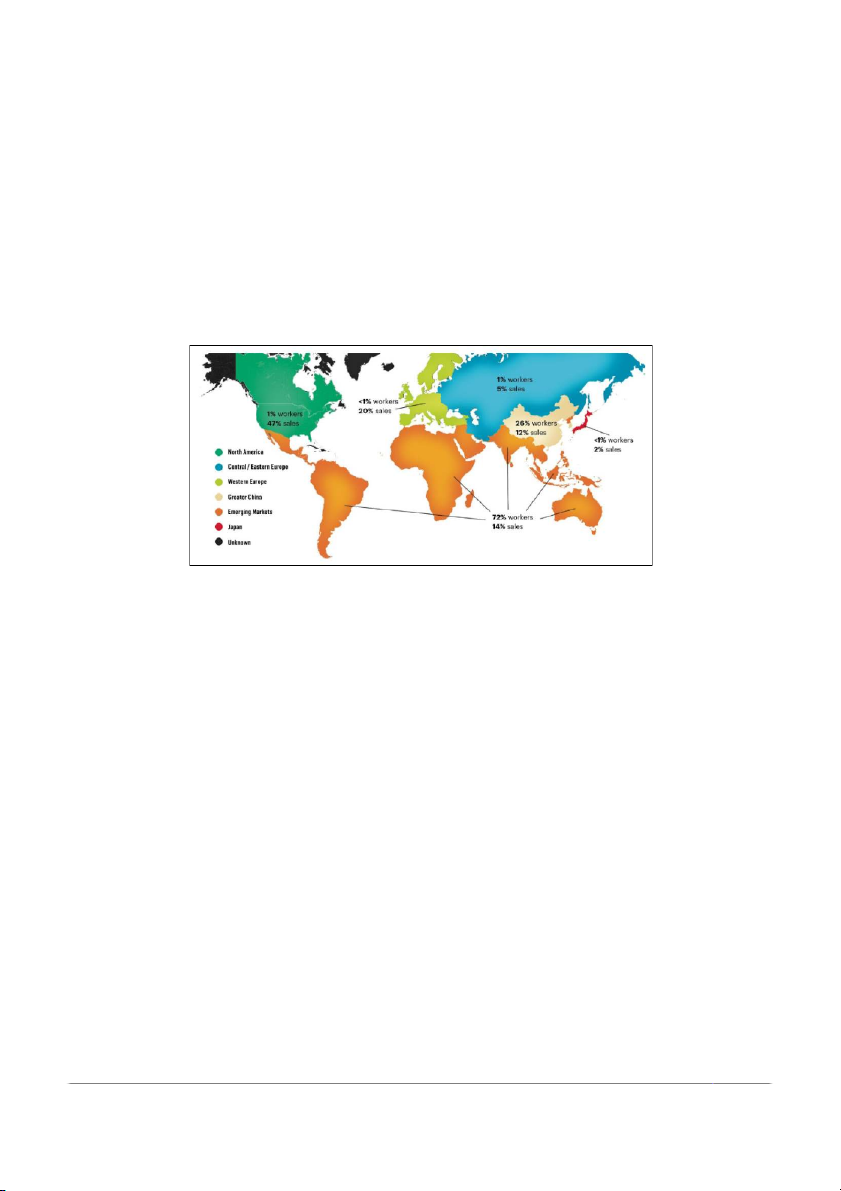
The global market is dominated by Nike, which holds a significant share of 62%.
As of May 2021, NIKE boasts an extensive network of over 1000 retail stores, a
workforce exceeding 30,000 employees, and more than 600 partner factories operating
in over 170 countries worldwide. Notably, in the United States, Nike has established more than 300 stores.
Figure 6: The percentages of workers and total sales in each country of Nike
(Source: Adobe Express)
Nike has the option of pursuing two distinct courses of action, with regards to
the production of branded items and capturing a larger market share in the premium
segment. The first option involves the ownership and operation of factories, while the
second option entails outsourcing. Capable outsourcing facilities can be located both
domestically and internationally.
Outsourcing domestically provides certain advantages such as easy tracking,
access to skilled workers, and well-understood labor standards. However, this option
tends to be more expensive when compared to outsourcing in emerging countries.
Outsourcing to third-world countries is typically motivated by low wages, but
this approach poses challenges in terms of regulating product quality and ensuring
satisfactory working conditions over which the company may have little control. 10
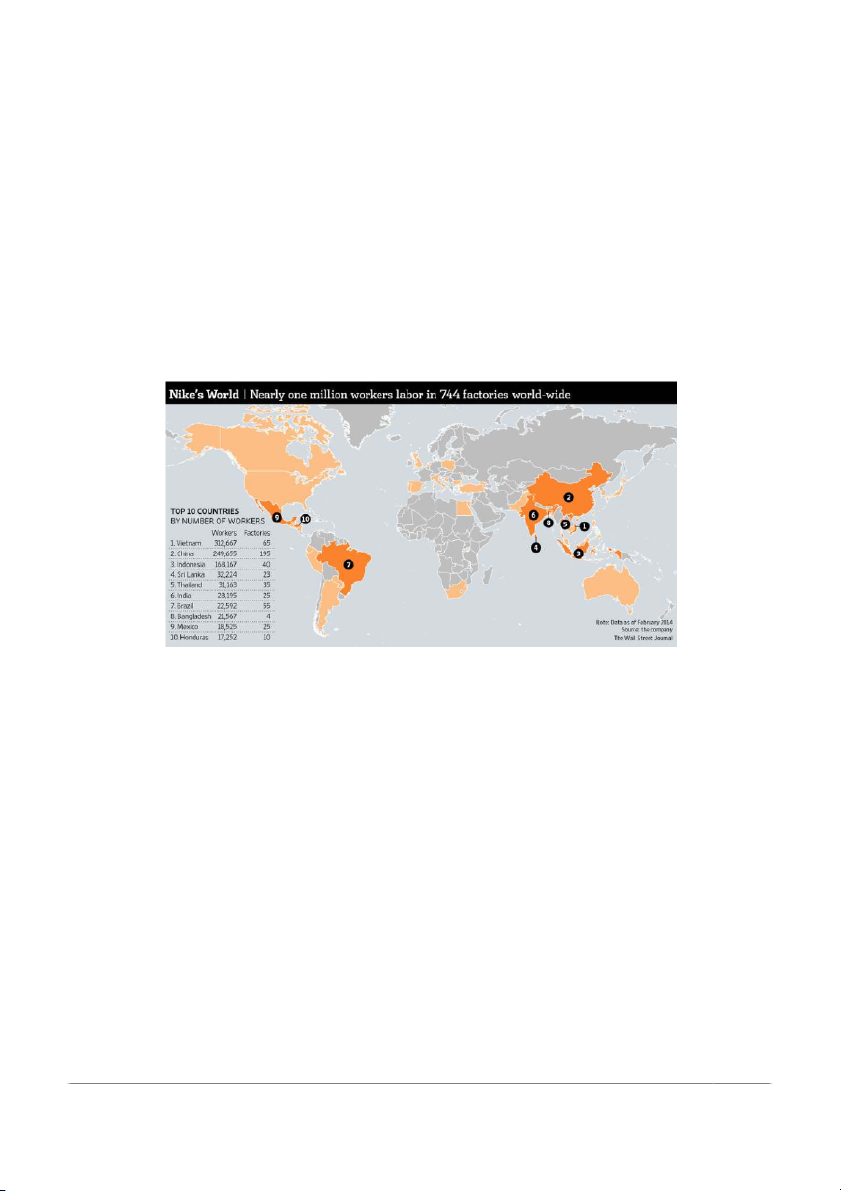
In this instance, Nike has implemented an outsourcing methodology by
leveraging outsourcing facilities situated across a diverse global network, which
includes production factories located in Vietnam. The complete range of product
production activities is dispersed among these manufacturing facilities and is supervised
by a team of Nike personnel who oversee the production progress and maintain strict
surveillance on the quality of the product output. Nike's involvement in this process is
restricted to the domains of research, prototyping, promotion, and distribution of the products to end consumers.
Figure 7: Top 10 countries with the most Nike factories in the world
(Source: The Wall Street Journal)
1.5 Industry Competitors of Nike
Although established at a later time, Nike has emerged as a formidable contender
in the sports and footwear industry, rivaling established companies such as Adidas
(1949), Converse (1908), Puma (1948), New Balance (1906), and Reebok (1958).
Despite the acquisition of Converse by Nike and Reebok's ownership by Adidas, the
competition remains between these two companies. Currently, Adidas remains Nike's
primary competitor, with both brands consistently vying for top rankings in the
competitive Shoes Game. This analysis will delve into the key elements that constitute the Nike and Adidas brands. 11
Table 1: Comparation the success factors of Nike and Adidas Nike Adidas
Market share Nike commands an impressive
80% market share in the North Adidas strategically leverages
American market, with basketball, the Russian and Asian
running, and skate shoes being the markets, thereby elevating the
most dominant product categories. brand's prominence beyond
Notably, the revenue generated that of Nike in these regions.
from the United States and Canada This approach is aimed at
accounts for up to 40% of Nike's narrowing the gap with the global revenue,
underscoring industry leader, Nike, as was
North America's status as the the case a decade and a half company's unparalleled ago. stronghold. Representative Cristiano Ronaldo Lionel Messi celebtity Message - Powerful, fierce, relaxed,
dynamic, innovative, high-tech, -Professional, winning, exciting, american style. always ready, high-tech.
- Accompany athletes to their -Classic European style. peak. - Maximum support for
- Bring creative inspiration to all athletes when competing. athletes encouragement in the world. 12 Product Offers products geared
Wide range of products, including primarily towards traditional athletics, basketball,
running sports such as football, tennis
shoes, competition and training and general sports.
equipment. Brands under the Subsidiaries on the Adidas support of Nike:
Umbro, list: Reebok, Taylor Made, Converse, Cole Haan. Rockport. Advertising -Advertising through famous and athletes. sponsoring - Sponsoring races, sports
-Sponsoring races, World Cup, event. Euro sports. -Advertising through -Outdoor advertising. outstanding athletes with
-Promoting image through Slogan: slogan “Nothing is “Bringing inspiration and impossible”.
creativity to all athletes all over the world”. Manufacturing Adidas is also gradually strategy
Nearly all products are outsourced adopting a similar approach to
in Asia, and the Beaverton Nike, with almost all of the
headquarters is where all Nike design and development work
products are designed, developed, being done in Germany and and marketed. manufacturing outsourced in Asia.
Comparation the success factors of Nike and Adidas (Source: Studocu) 13
2. LITERATURE REVIEW ABOUT WAREHOUSING
In today's competitive business environment, efficient warehousing, stock
control, and material handling are crucial. As a global brand with a vast product range
and extensive distribution network, Nike encounters particular difficulties in managing
its inventory and optimizing its warehousing operations. This literature review delves
into the strategies and practices that Nike employs to tackle these challenges.
2.1 Warehousing Strategies
Figure 8: Warehousing Strategies
Nike employs a combination of company-owned facilities and third-party logistics
providers (3PLs) for their warehousing strategies. Their warehouses are strategically
located near major markets, enabling efficient order fulfillment and reducing
transportation costs. By utilizing advanced technologies like warehouse management
systems (WMS), automation, and robotics, Nike streamlines their operations, improves
inventory accuracy, and enhances order processing efficiency. 14




