Preview text:
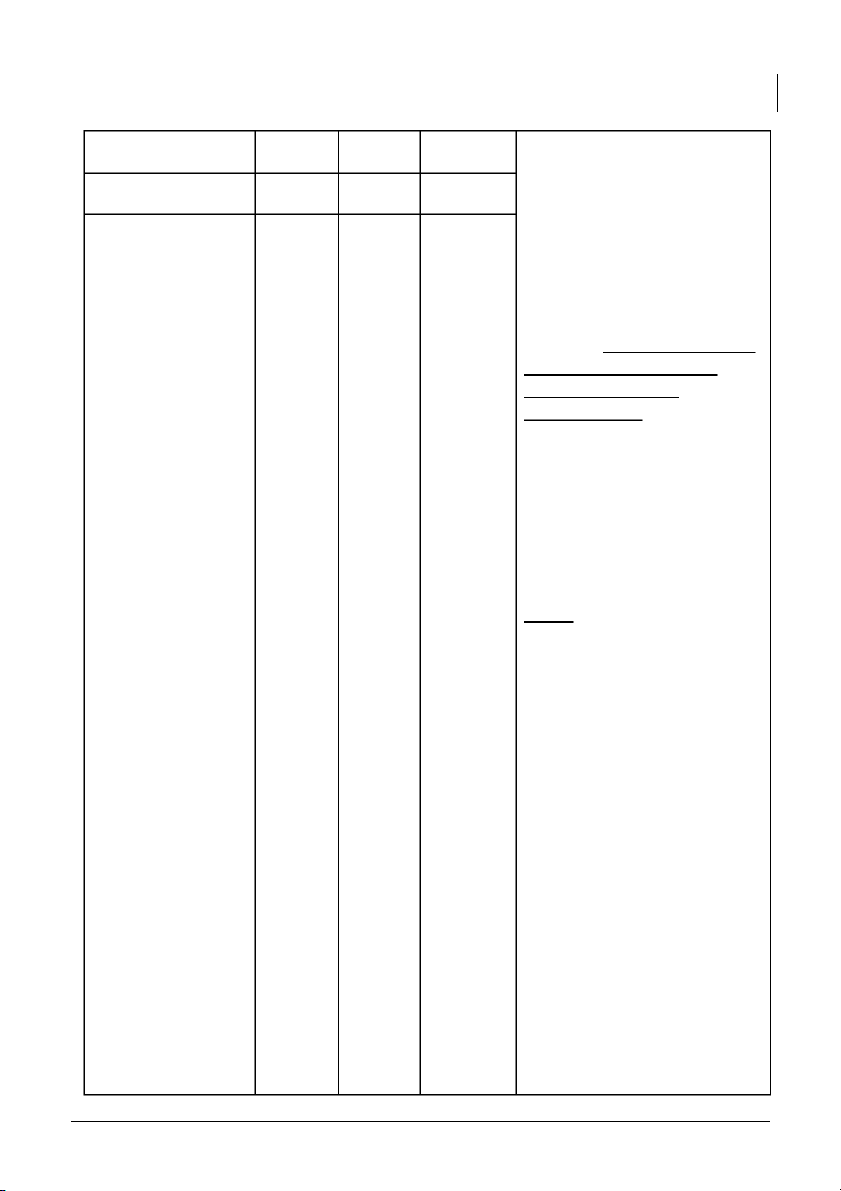
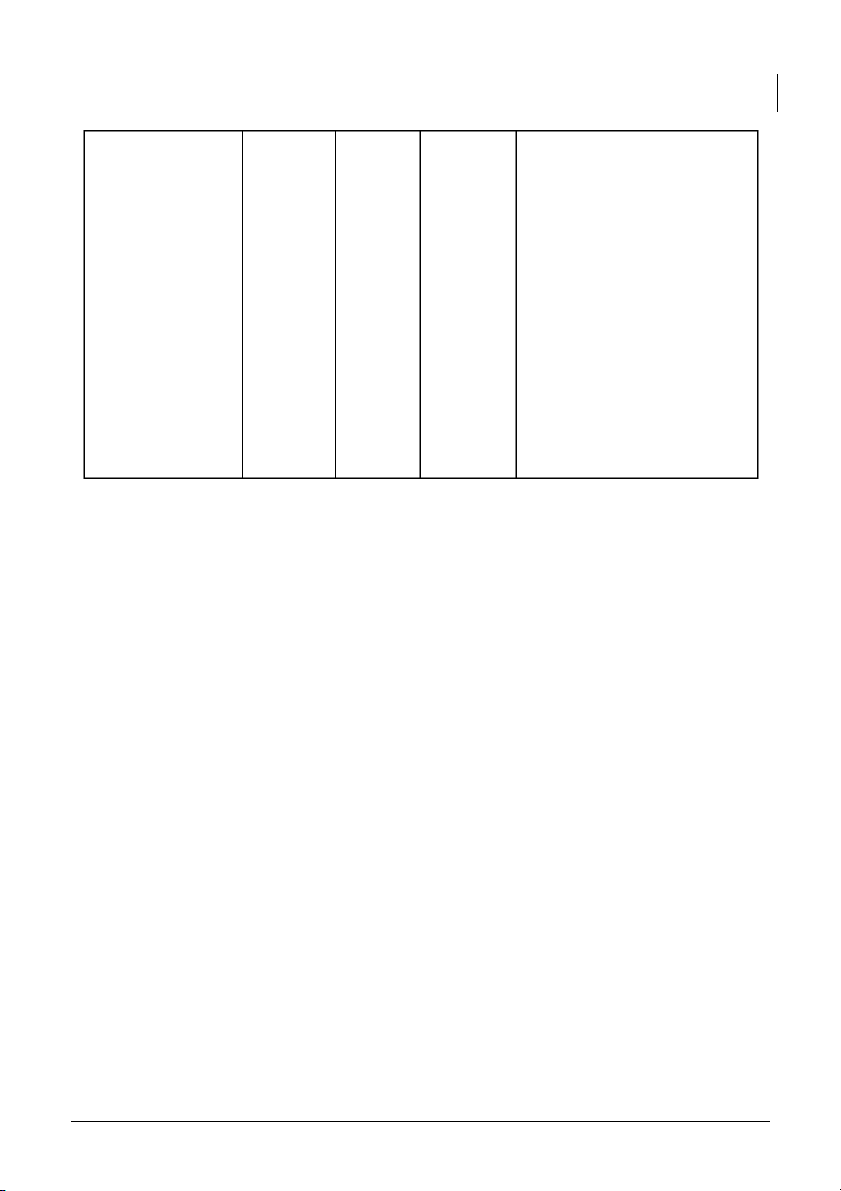
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 6 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY Steps of calculating the pH 0.1M acetic acid 2.83 2.71 2.51x10^-4 value of Acetic Acid: 0.01M acetic acid 3.28 3.28 2.5x10^-5 1. Calculate the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) from the measured pH by using the formula: [H3O+] = 10^-pH
2. Use the initial concentration
of the week acid ([HA]^0) and the concentration of
hydronium ions to set up the equilibrium expression for the dissociation of acetic acid:
Ka = [(H30+)x(A-)] / [HA]^0 3. Subtitutes the values
obtained into the equilibrium expression and solve for Ka. Detail: 0.001M acetic acid 3.97 3.97 1x10^-5 - 0.1M Acetic Acid: Measured pH = 2.83 [H30+] = 10^-2.83 = 5.01X10^-3 M
Initial concentration = 0.1M KA = [5.01X10^-3]^2/0.1 = 2.51X10^-4 - 0.01M Acetic Acid: Measured pH = 3.28 [H30+] = 10^-3.28 = 5.01X10^-4 M
Initial concentration = 0.01M
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 7 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
KA = [5.01X10^-4]^2/0.01 = 2.5X10^-5 - 0.001M Acetic Acid: Measured pH = 3.97 [H30+] = 10^-3.97 = 1.12X10^-4 M
Initial concentration = 0.001M
KA = [1.12X10^-4]^2/0.001 = 1.25X10^-5 Comments: -
The provided experiment investigates the pH values of acetic acid solutions at different concentrations.
Acetic acid is a week acid, and its concentration in water results in the formation of hydronium ions
(H3O+) and acetate ions (A-). The pH of the solution is determined by the concentration of hydronium
ions, which can be calculated using the formula [H3O+] = 10^-pH. -
The equilibrium expression for the dissociation of acetic acid (CH3COOH <-> CH3COO- + H+) is
represented by the acid dissociation constant (Ka), defined as the ratio of the concentrations of
products to reactants at equilibrium. This can be expressed as Ka = [(H3O+)x(A-)] / [HA]^0, where
[HA]^0 is the initial concentration of the weak acid. -
By substituting the calculated concentration of hydronium ions ([H3O+]) and the initial concentration of
acetic acid [HA]^0 into the equilibrium expression, we can solve for the acid dissociation constant (Ka). -
For the provided experiment, the measured pH values and initial concentrations of acetic acid were
used to calculate the KA values for each solution. The results indicate that as the concentration of
acetic acid decreases, the KA values also decrease, indicating weeker acidity. -
Overall, these calculations demonstrate the relationship between pH, acid concentration, and the acid
dissociation constant for acetic acid solutions, providing valuable insights into its acid-base properties. 4. pH OF SALTS (10 pts) Measured pH Explanation Predicted Solution 1st 2nd pH (Group_1__) (Group__2_)
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline
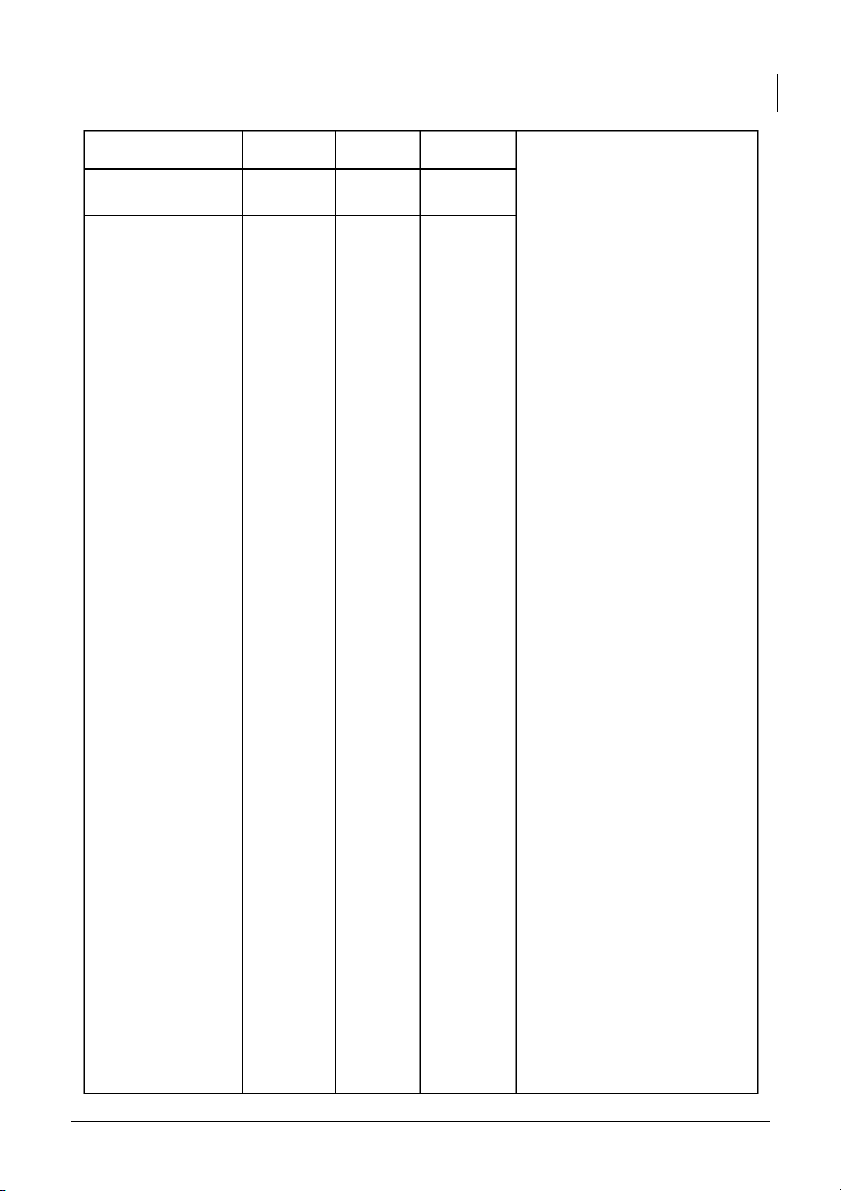
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 8 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 7 7.71 7.95 To calculate the pH value of 0.1M NaCl salt solutions, we need to >7 7.76 7.92 consider the hydrolysis of the 0.1M CH3COONa
salt in water and the resulting <7 5.66 6.61 effect on the solution’s pH. 1. 0.1M NaCl
- Predicted pH: 7 (since NaCl is a neutral salt)
- Measured pH: 7.71 (Group 1) and 7.95 (Group 2)
- Explanation: The predicted pH of 7 for NaCl solution matches the measured pH values quite closely, although
there are slight discrepancies. The measured pH value may deviate due to factors such as impurities in the salt, experimental error, or 0.1M NH4Cl variations in pH measurement techniques. 2. 0.1M CH3COONa
- Predicted pH: > 7 (since
CH3COONa is a salt or a weak acid)
- Measured pH: 7.76 (Group 1) and 7.92 (Group 2)
- Explanation: The predicted pH being greater than 7 aligns with the measured pH values, suggesting that the acetate ion from CH3COONa hydrolyzes to produce a slightly basic solution.
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline
International University, Vietnam National University - HCMC 9 CHEMISTRY LABORATORY 3. 0.1M NH4Cl
- Predicted pH: < 7 (since
NH4Cl is a salt or a weak base)
- Measured pH: 5.66 (Group 1) and 6.61 (Group 2)
- Explanation: The predicted pH being less than 7 also matches the measured pH values. NH4Cl hydrolyzes to produce NH4OH and HCl, leading to the solution’s slightly acidic pH due to the presence of NH4OH. Comments: -
The experiment aimed to investigate the pH values of different salt solutions, comparing the predicted
pH values with the measured ones to access the accuracy of the predictions. -
The comparison between predicted and measured pH values provides valuable insights into the
behavior of salt solutions and the hydrolysis reactions involved. While there are minor discrepancies
between predicted and measured values, the general trends align with expectations based on hydrolysis. -
For the 0.1M NaCl solution, the predicted pH of 7 closely matches the measured pH values of 7.71 and
7.95, indicating that NaCl, being a neutral salt, does not significantly alter the pH of the solution. Any
discrepancies between the predicted and measured pH values could be attributed to experimental
errors or variations in the purity of the NaCl used. -
Similarly, for the 0.1M CH3COONa solution, the predicted pH values being greater than 7 align with the
measured pH values of 7.76 and 7.92, indicating a slightly basic solution. This concurrence supports
the understanding that CH3COONa undergoes hydrolysis to produce acetate ions, resulting in a pH higher than neutral. -
For the 0.1M NH4Cl solution, the predicted pH values being less than 7 match well with the measured
pH values of 5.66 and 6.61, indicating a slightly acidic solution. This agreement supports the
expectation that NH4Cl, as a salt of a weak base, hydrolyzes to produce an acidic solution due to the formation of ammonium ions. -
While there are some discrepancies between predicted and measured pH values, the trends align with
expectations based on salt hydrolysis. These minor differences could be attributed to experimental
errors, variations in concentration measurements, or impurities in the salt used. Nevertheless, the
experiment provides valuable insights into the behavior of salt solutions and their impact on pH.
The report must be typed and handed in together with the signed data sheet by the deadline