Microeconomics
Danh sách Tài liệu
-
Trade - True/False, Discussion, and MC Questions | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
5 3 lượt tải 14 trangIf Ha can produce more math problems per hour and more book reports per hour than Hieu can, then Ha cannot gain from trading math problems and book reports with . => false 2. It is possible for the U.S. to gain from trade with Germany even if it takes U.S workers fewer hours to produce every good than it takes German workers. => true 3. Trade allows a country to consume outside its production possibilities frontier. 4. => true. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Elasticity Concepts and Questions | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
4 2 lượt tải 9 trangNecessities tend to have inelastic demands, whereas luxuries have elastic demands. 2. Goods with close substitutes tend to have more elastic demands than do goods without close substitutes. 3. The demand for gasoline will respond more to a change in price over a period of five weeks than over a period of five years. 4. Price elasticity of demand along a linear, downward-sloping demand curve increases as price falls. 5. If demand is perfectly inelastic, the demand curve is vertical, and the price elasticity of demand equals 0. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Lecture Notes on Wants, Demands, Supply & Quantity | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
4 2 lượt tải 4 trangWants are directed by our surroundings towards reaching certain needs. Therefore human’s wants can be varied depending on each individual’s perception, environment, culture, and society. o For example, an American needs food but he may want a hamburger, fried potato, and beer; a Chinese needs food but he may want a bowl of noodles and a cup of hot tea. Cloths are required for a person to cover himself but we can see people wearing jeans, suit just because of cultural influence. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Exercise Questions on Economics Concepts | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
2 1 lượt tải 6 trangThe economising problem is essentially one of deciding how to make the best use of: A: virtually unlimited resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants. B: limited resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants. C: unlimited resources, to satisfy limited wants. D: limited resources, to satisfy limited wants. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Bài tập, Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Perfect Competition Insights and Analysis | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
2 1 lượt tải 3 trangWhy is a firm in perfect competition a price taker? 2. In perfect competition, what is the relationship between the demand for the firm’s output and the market demand? 3. In perfect competition, why is a firm’s marginal revenue curve also the demand curve for the firm’s output? 4. China’s Phone Makers Look to India for Growth China produces smartphones, and hundreds of millions of Chinese have bought one. With intense competition among more than 150 brands, China’s smartphone producers are looking to capture the Indian market. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Government Policy Analysis & Surplus Calculations | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
2 1 lượt tải 15 trangRefer to Figure 1-2. The benefit to the government is measured by a. tax revenue and is represented by area A+B. b. tax revenue and is represented by area B+D. c. the net gain in total surplus and is represented by area B+D. d. the net gain in total surplus and is represented by area C+H. 12. Refer to Figure 1-2. The total surplus with the tax is represented by area a. C+H. b. A+B+C. c. D+H+F. d. A+B+D+F. 13. Refer to Figure 1-2. The loss in total welfare that results from the tax is represented by area a. A+B+D+F. b. A+B+C. c. D+H+F. d. C+H. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Solutions - Microeconomic Theory | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
1 1 lượt tải 6 trangThe demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is A) infinitely elastic. B) perfectly inelastic. C) downward sloping. D) none of the above. Answer: A 2.In general, economists assume that firms A) maximize accounting profit. C) maximize sales. B) maximize economic profit. D) none of the above. Answer: B Use the following to answer questions 3-6: A F C A V C M C P r i c e Q u a n t i t y P * Q * 3.In the graph above at a price of P*, in the above graph, the profit maximizing level of output is A) Q*. B) above Q*. C) below Q* but above zero. D) zero. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Practice Exercises for Economics Concepts and Applications | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
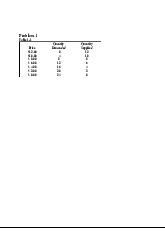
2 1 lượt tải 6 trangThe economising problem is essentially one of deciding how to make the best use of: A: virtually unlimited resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants. B: limited resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants. C: unlimited resources, to satisfy limited wants. D: limited resources, to satisfy limited wants. QUESTION 2 Production possibilities (options) Capital goods Consumer goods Refer to the above data, if the economy is producing at production option C, the opportunity cost of the tenth unit of consumer goods will be: A: 4 units of capital goods. B: 2 units of capital goods. C: 3 units of capital goods. D: of a unit of capital.Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệu, Bài tậpTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
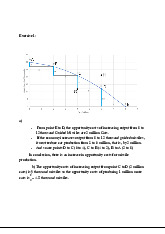
Group Assignment 1: Analyzing Opportunity Costs | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
3 2 lượt tải 5 trangIn conclusion, there is an increase in opportunity costs for missile production. b) The opportunity costs of increasing output from point C to D (2 million cars) is 9 thousand missiles so the opportunity costs of producing 1 million more cars is 9 2 = 4.5 thousand missiles. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệuTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước -
Assignment 3: Effects of Demand and Supply Shifts | Microeconomics | Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh
3 2 lượt tải 8 trangHurricane Katrina led to the migration of citizens from New Orleans to Baton Rouge. As a result, the increase in the city’s population shifted the demand curve to the right. - While before the hurricane, there were 3,600 homes listed for sale in the city, but a week after the storm, there were only 500. Tài liệu được sưu tầm và soạn thảo dưới dạng file PDF để gửi tới các bạn cùng tham khảo, ôn tập đầy đủ kiến thức, chuẩn bị cho các buổi học thật tốt. Mời bạn đọc đón xem!
Danh mục: Trường Đại học Quốc tế, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhMôn: MicroeconomicsDạng: Tài liệu, Bài tậpTác giả: Mai Nguyệt4 ngày trước