

Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 A) • Total Revenue (TR) Equation:
TR=Price per unit×QTR = \text {Price per unit} \times QTR=Price per unit×Q
Given that the Maxistand sells for $120 per unit, we get: TR=120QTR = 120QTR=120Q •
Total Cost (TC) for each process type:
TC=Fixed Cost+(Variable Cost per Unit×Q)TC = \text{Fixed Cost} + (\ text{Variable Cost per Unit} \times Q)TC=Fixed Cost+
(Variable Cost per Unit×Q) where:
Variable Cost per Unit=Labor+Material+Energy\text{Variable Cost per
Unit} = \text{Labor} + \text{Material} + \ text{Energy}Variable Cost per
Unit=Labor+Material+Energy Let's compute the total variable costs for each process type: Fixed Process Type Variable Cost per Unit Cost Mass
$1,260,0 30+18+12=6030 + 18 + 12 = Customization 00 6030+18+12=60
$1,000,0 24+26+20=7024 + 26 + 20 = Intermittent 00 7024+26+20=70
$1,625,0 28+15+12=5528 + 15 + 12 = Repetitive 00 5528+15+12=55 Continuous
$1,960,0 25+15+10=5025 + 15 + 10 = 00 5025+15+10=50
Thus, the Total Cost (TC) equations are:
o Mass Customization: TC=1,260,000+60QTC = 1,260,000 +
60QTC=1,260,000+60Q o Intermittent: TC=1,000,000+70QTC = 1,000,000 +
70QTC=1,000,000+70Q o Repetitive: TC=1,625,000+55QTC = 1,625,000 +
55QTC=1,625,000+55Q o Continuous: TC=1,960,000+50QTC = 1,960,000 + 50QTC=1,960,000+50Q
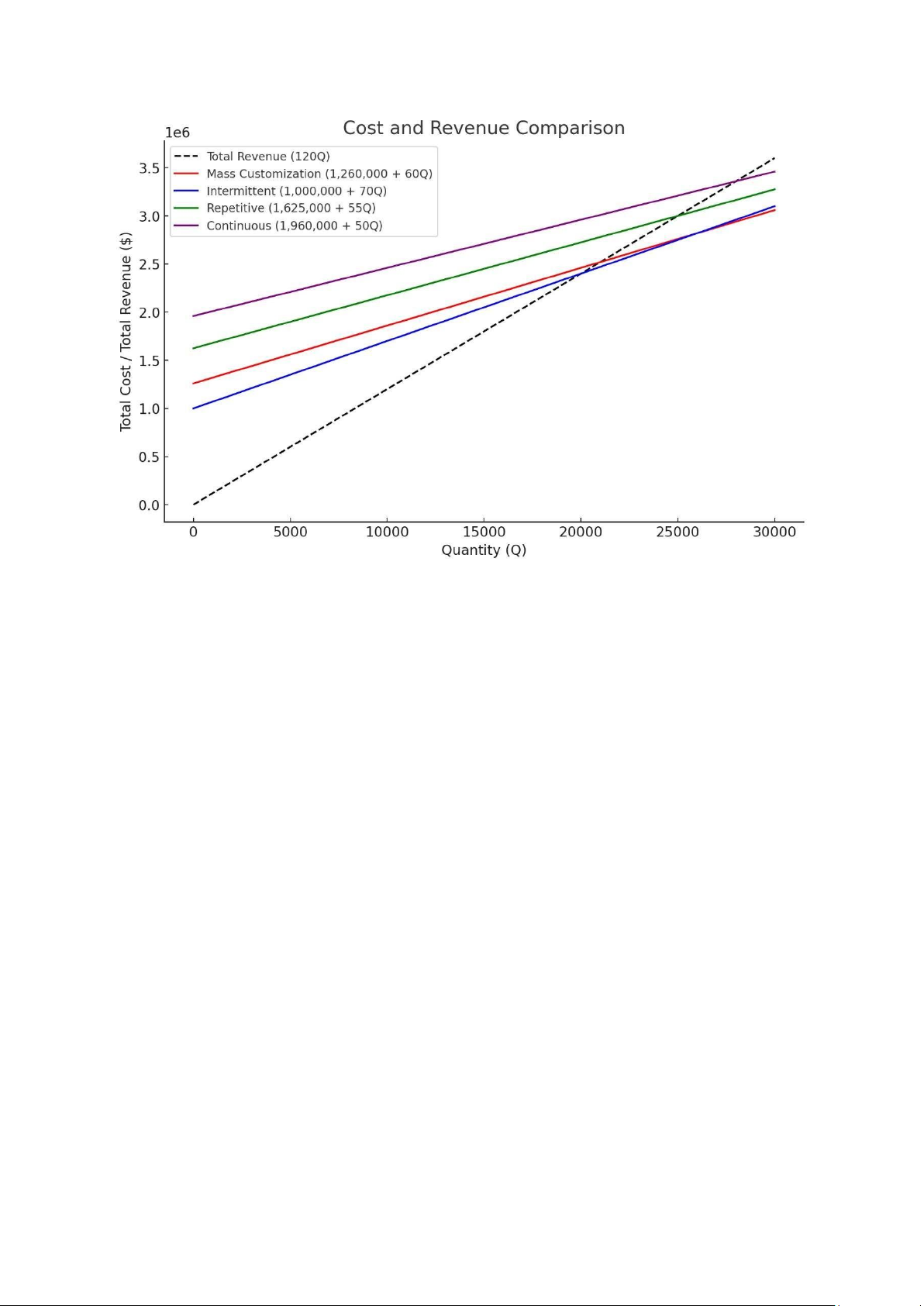
We will plot Total Revenue (TR) along with the Total Cost (TC) for all four process types. I'll generate the graph now. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 B)
A cross-over point is where two cost functions are equal:
Fixed Cost1+(Variable Cost1×Q) =Fixed Cost2+(Variable Cost2×Q)\ text{Fixed Cost}_1 +
(\text{Variable Cost}_1 \times Q) = \text{Fixed Cost}_2 + (\text{Variable Cost}_2 \times
Q)Fixed Cost1+(Variable Cost1 ×Q)=Fixed Cost2+(Variable Cost2×Q)
Let's compute the cross-over points between different process types.
Step 4: Interpretation of Cross-Over Points
The cross-over points indicate where one process becomes more costeffective than another. Key findings: •
Mass Customization vs. Intermittent: Q=26,000Q = 26,000Q=26,000 •
Intermittent vs. Repetitive: Q=41,667Q = 41,667Q=41,667 •
Intermittent vs. Continuous : Q=48,000Q = 48,000Q=48,000 •
Repetitive vs. Continuous : Q=67,000Q = 67,000Q=67,000
Since the projected demand is 24,000 units, we choose the Intermittent Process because it
has the lowest cost at this quantity. C) lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 Profit is given by:
Profit=Total Revenue−Total Cost\text {Profit} = \text{Total Revenue} - \ text{Total
Cost}Profit=Total Revenue−Total Cost For 24,000 units, we calculate the profit for each process:
\text{Profit} = 120(24,000) - \text{Total Cost} \]
The calculated profits at 24,000 units are: • Mass Customization: $180,000 •
Intermittent: $200,000 (Highest Profit) • Repetitive: -$65,000 (Loss) • Continuous: -$280,000 (Loss)
Thus, Intermittent Process is the best choice for maximizing profit at the given demand



