



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Chap 9: Layout Decisions
I/ Lý Thuyết về types of layouts:
1. Office layout: Positions workers, their equipment, and spaces/offices to
provide for movement of information.
2. Retail layout: An approach that addresses flow, allocates space, and
responds to customer behavior.
+The main objective of retail layout is to maximize profitability per square foot of floor space.
3. Warehouse and Storage layout: Addresses trade-offs between space and material handling.
=>Maximize the total “cube” of the warehouse – utilize its full
volume while maintaining low material handling costs.
4. Fixed-position layout: Addresses the layout requirements of large, bulky
projects such as ships and buildings.
5. Process-oriented layout: Deals with low-volume, high-variety production.
6. Work cell layout: Arranges machinery and equipment to focus on
production of a single product or group of related products.
7. Product-oriented layout: Seeks the best personnel and machine utilizations
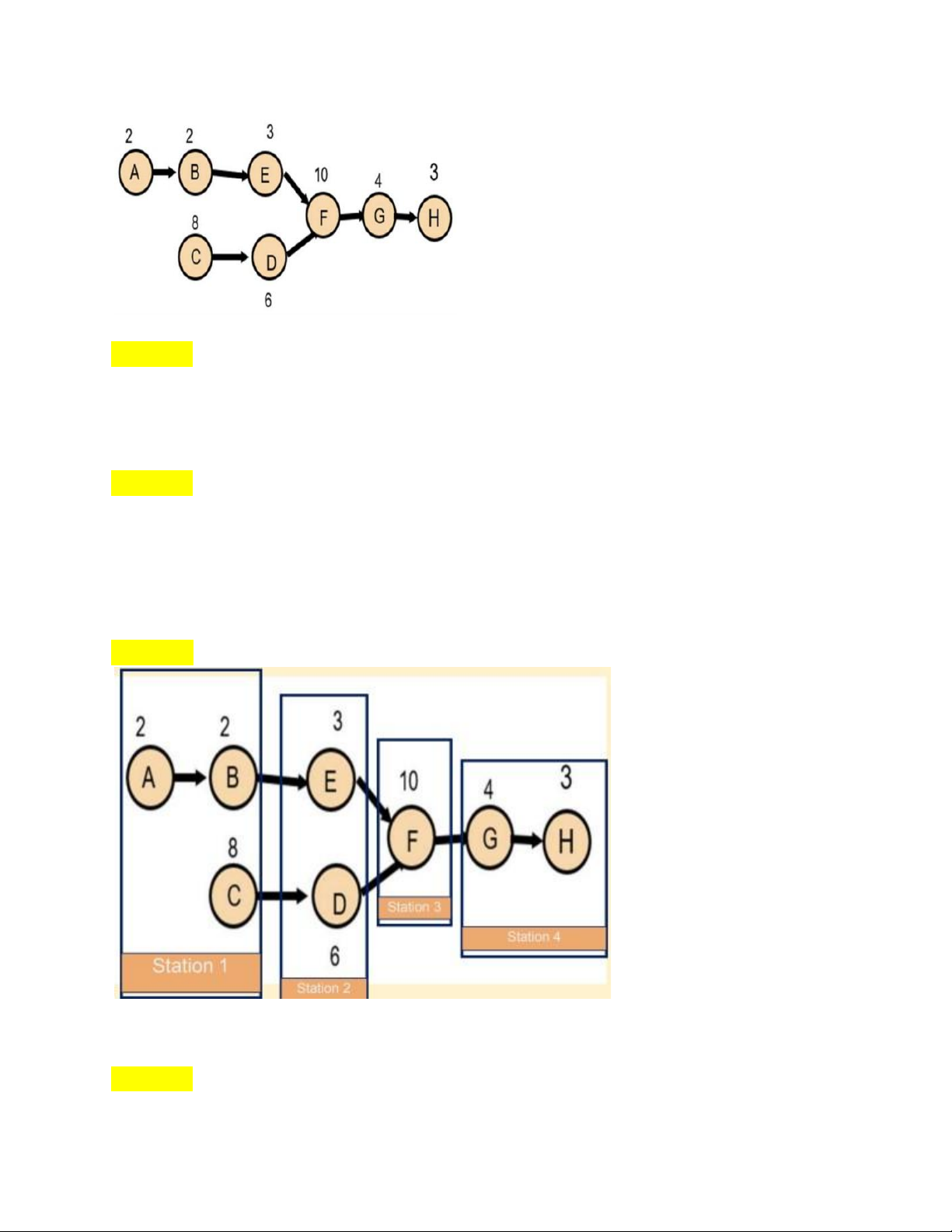
in repetitive or continuous production. II/ PRECEDENCE DIAGRAM Chia làm 2 dạng:
+Dạng 1: Most following tasks
-Bước 1: vẽ cái diagram lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
-Bước 2: Tính cycle time
Cycle time = (Production time available per day) / (units required per day)
-Bước 3: Tính Theoretical minimum of workstations
Theoretical minimum of workstations = (Total performance time) / (Cycle time)
*Lưu ý: làm tròn số lên
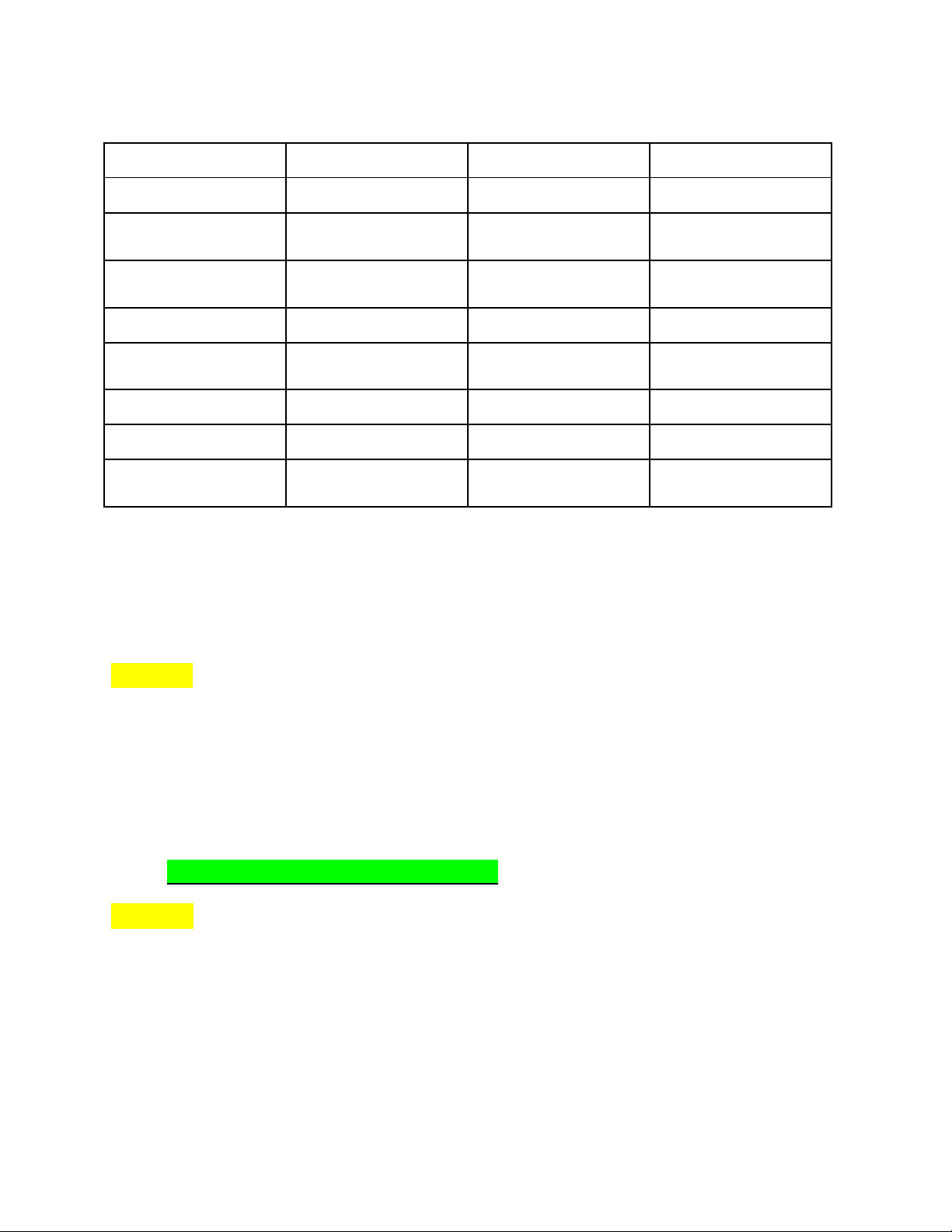
-Bước 4: Chia tasks into each station => Actual station = 4
-Bước 5: Tính idle time per cycle and efficiency: lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 Với Cycle time = 12 Station Tasks Time Time Left 1 A 2 12-2=10 B 2 10-2=8 C 8 0 2 D 3 9 E 6 3 3 F 10 2 4 G 4 8 H 3 5
=>Total idle time per cycle = 0 + 3+ 2+ 5 = 10 (mins)
=>Efficiency = (total performance time) / (actual station * largest assigned cycle time)
-Bước 6: Tính total idle time is present in an 8-hour shift? 8 hours = 480 minutes
=>Cycle = 480 / largest assigned cycle time = 480 / 12 = 40 cycles
=>Total idle time in 8-hour shift =The idle time per cycle * Cycle = 10 * 40 = 400 minutes.
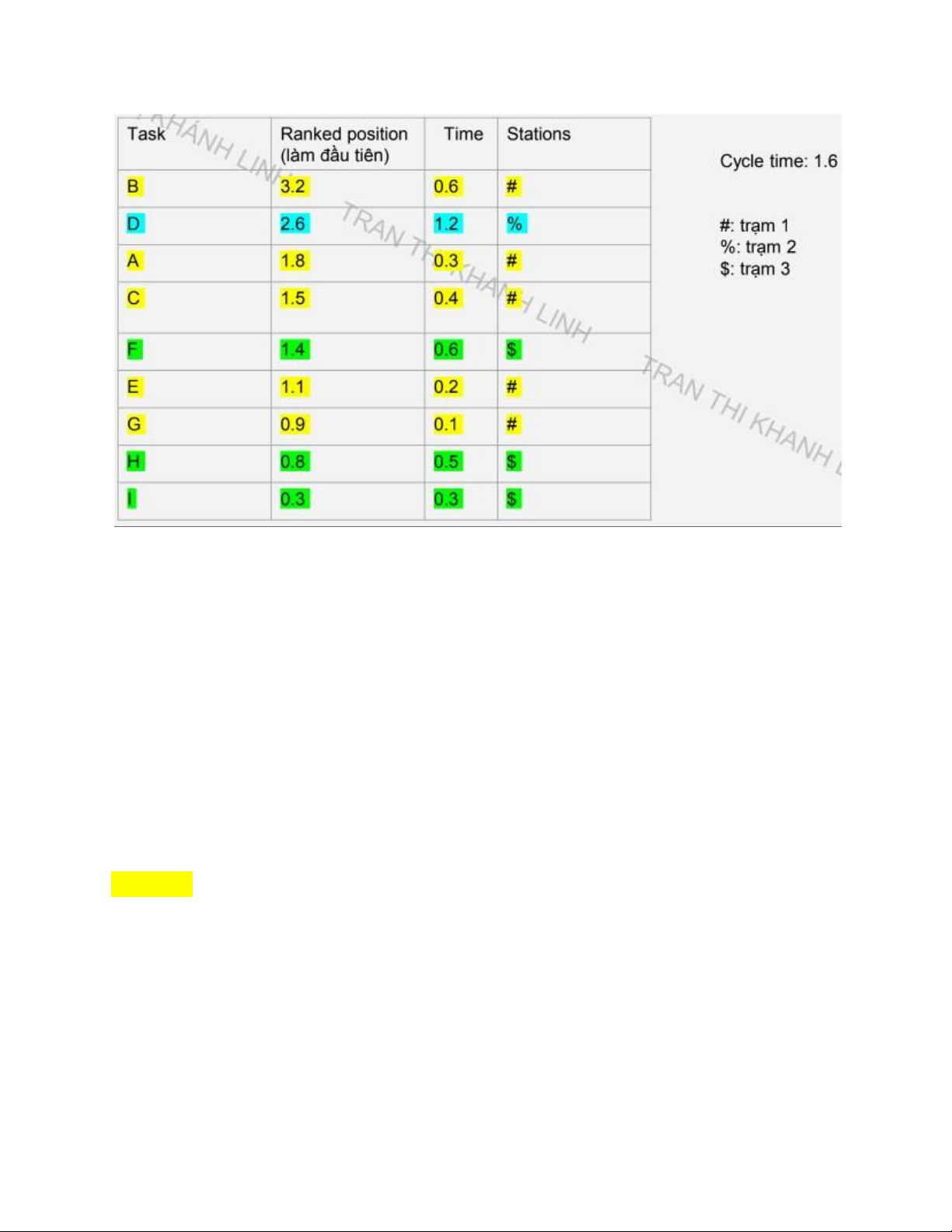
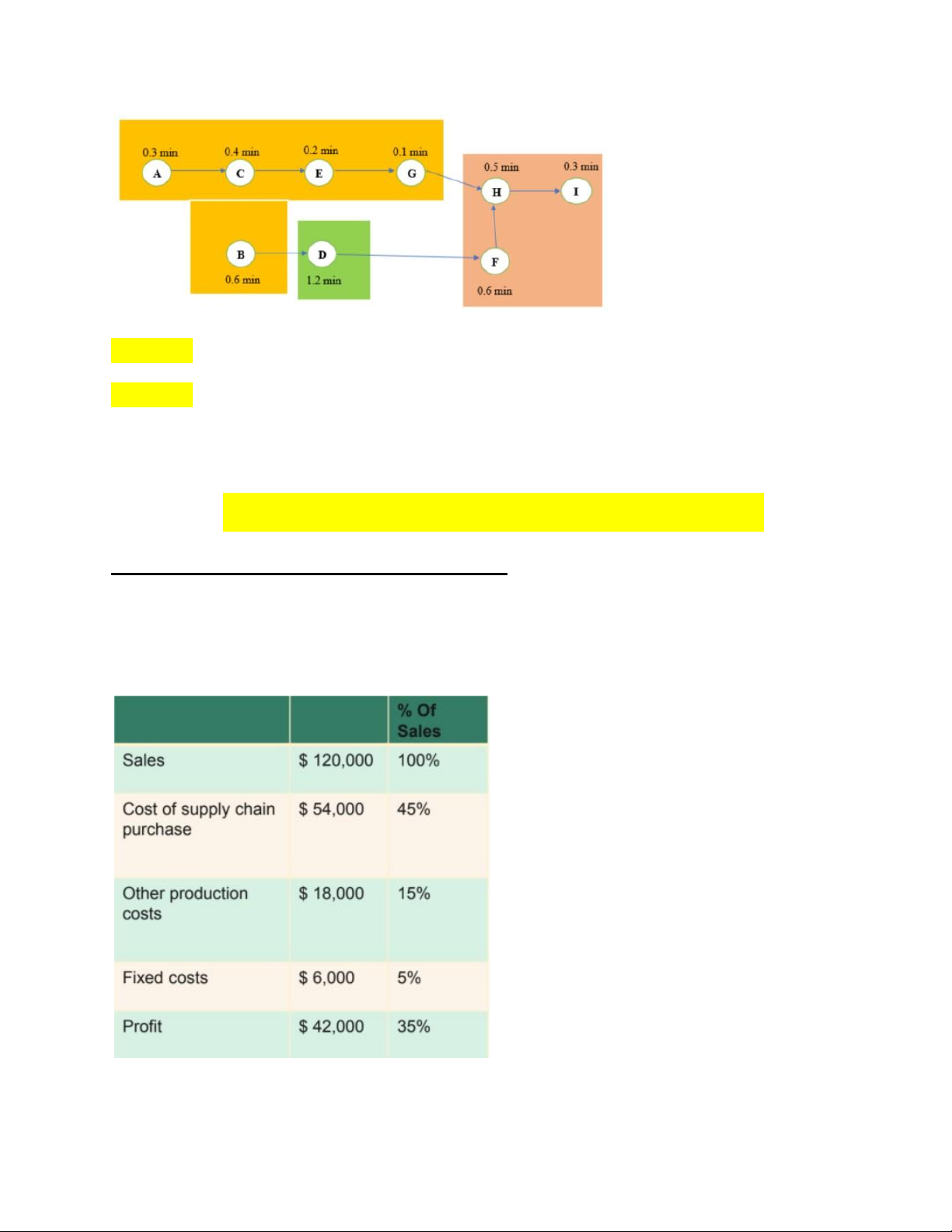
+Dạng 2: Ranked positioned weight
-Bước 1: Vẽ cái diagram và Tính Ranked position của từng task lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
(*Lưu ý: làm từ phải sang trái)
-Bước 2: Tính cycle time (Giống ở Dạng 1)
Cycle time = (Production time available per day) / (units required per day)
-Bước 3: Tính Theoretical minimum of workstations (Giống ở Dạng 1)
Theoretical minimum of workstations = (Total performance time) / (Cycle time)
-Bước 4: Chia tasks vào station theo “Ranked Positional Weight” rule. lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
+Đầu tiên làm là sắp xếp theo thứ tự giảm dần của ranked position.
+Từ ranked position mới điền task và time tương ứng.
+Assign stations sao cho tổng time phải < or = cycle time
(*Lưu ý: khi mà assign vào từng station thì cần phải nhìn lại chart ở bước 4. Ví dụ,
sau khi làm trạm 1 xong tới trạm 2 thì tại sao ko gộp D với I lại vì nếu cộng lại sẽ
là 1.5 < cycle time = 1.6 vì theo chart ở bước 4 thì D với I, 1 đứa ở Tây và 1 đứa ở
Đông nên ko thể gộp lại đc dù có tổng time nhỏ hơn)
-Bước 5: Vẽ lại chart sau khi gộp: lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
-Bước 7: Tính idle time per cycle and efficiency (Giống ở Dạng 1)
-Bước 8: Tính total idle time is present in an 8-hour shift? (Giống ở Dạng 1)
Chap 11: Supply Chain Management
I/ Tăng profit dựa trên 2 strategy
+Supply chain strategy = giảm cost of capital +Sale strategy = tăng sale VD: lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
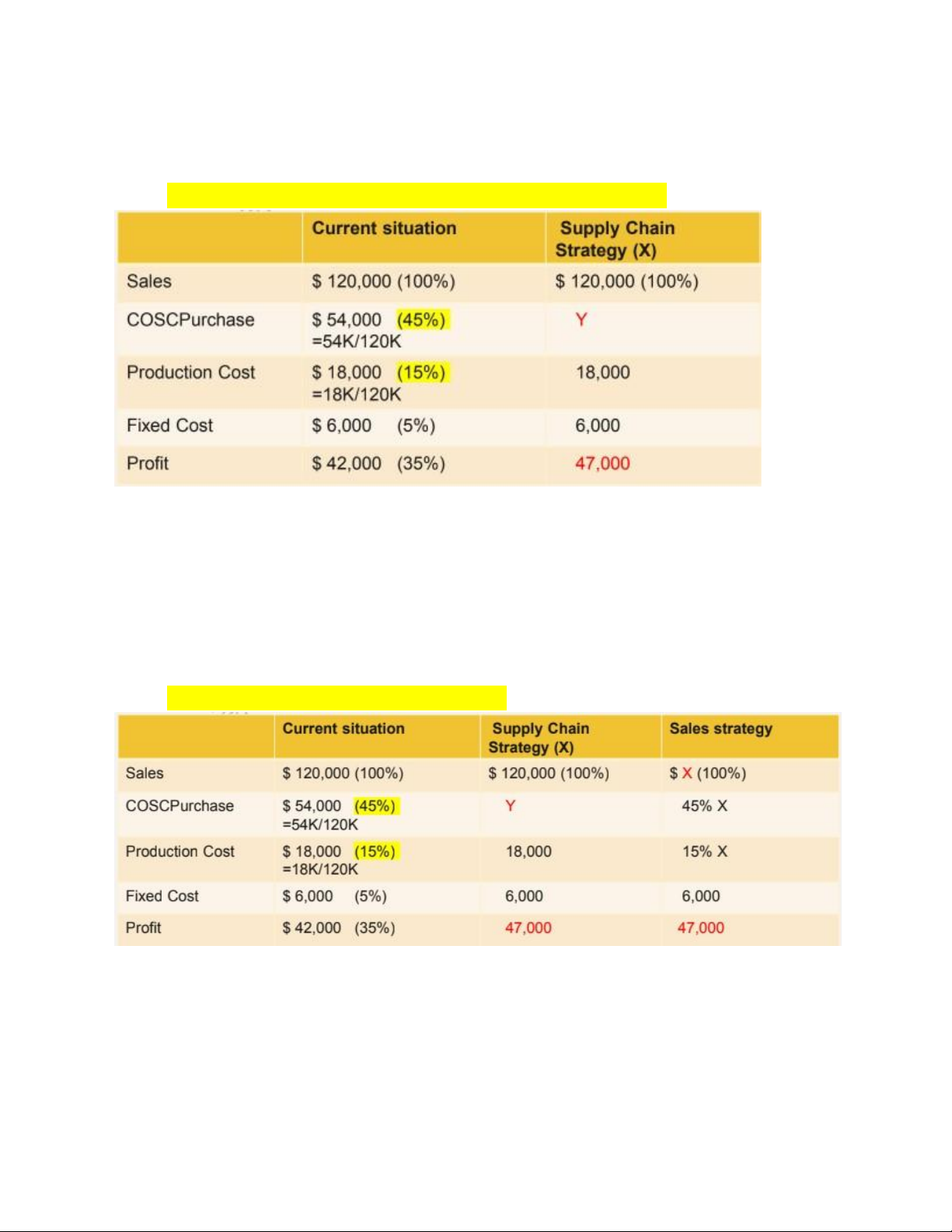
Đề hỏi: h muốn tăng profit lên 47000 thì cần giảm cost of material với tăng sale ntn?
+Áp dụng Supply chain strategy (giảm cost of capital)
⇨ 47000 = 120000 – (Y + 18000 + 6000)
⇨ Y = 49000 = cost of capital
Change in cost of capital = [(49000 – 54000) / 54000] *100= -9.29%
⇨ If we use supply chain strategy, COSCP will decrease 9.3%
+Áp dụng Sales Strategy (tăng sales)
⇨ 47000 = X – (45%X + 15%X + 6000) ⇨ X = 132500
Change in sales = [(132500 – 120000) / 120000] *100= 10.42% lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
⇨ If we use sales strategy, Sales will increase 10.42%
II/ Một số công thức Inventory:
1. Percentage invested in inventory = (total inventory investment / total assets) * 100
2. Inventory turnover = cost of goods sold / total inventory investment
3. Weeks of supply = inventory investment / (Annual cost of goods sold/52 weeks)
Chap 12: Manage inventory I/ EOQ model:
Q = Number of pieces/units per order
Q* = Optimal number of pieces per order (EOQ)
D = Annual demand in units for the inventory item
S = Setup or ordering cost for each order
H = Holding or carrying cost per unit per year
a/ 1 số công thức:
+Annual setup cost = Number of orders placed per year * Setup or order cost per order = (D/Q)*S
+Annual holding cost= Average inventory level * Holding cost per unit per year= (Q/2)*H
+Optimal order quantity when annual setup cost = annual holding cost lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 ⇨ Q*= EOQ= 2𝐻𝐷𝑆
+Expected number of orders = Demand/optimal order quantity = D/Q*
+Expected time between orders = Number of working days per
year/Expected number of orders = t/N.
+Total annual cost = Setup cost + Holding cost = (D/Q)*S + (Q/2)*H
b/ Reorder point của EOQ
+ROP = Demand per day * Lead time for a new order in days= d*L
+d= D/number of working days in a year =…..
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- II/ POQ model:
Q = Number of pieces/units per order
Q* = Optimal number of pieces per order (EOQ)
D = Annual demand in units for the inventory item
S = Setup or ordering cost for each order H =
Holding or carrying cost per unit per year p =
Daily production rate t = Length of the
production run in days a/ 1 số công thức:
+Annual setup cost = Number of orders placed per year * Setup or order cost per order = (D/Q)*S
+Annual holding cost= Average inventory level * Holding cost per unit per year= ½ H*Q(1-d/p)
+Optimal order quantity when annual setup cost = annual holding cost lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 ⇨ Q*=POQ= 𝐻(2𝐷𝑆− ) 1 𝑑𝑝 b/ ROP của POQ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
III/ Quantity discount:
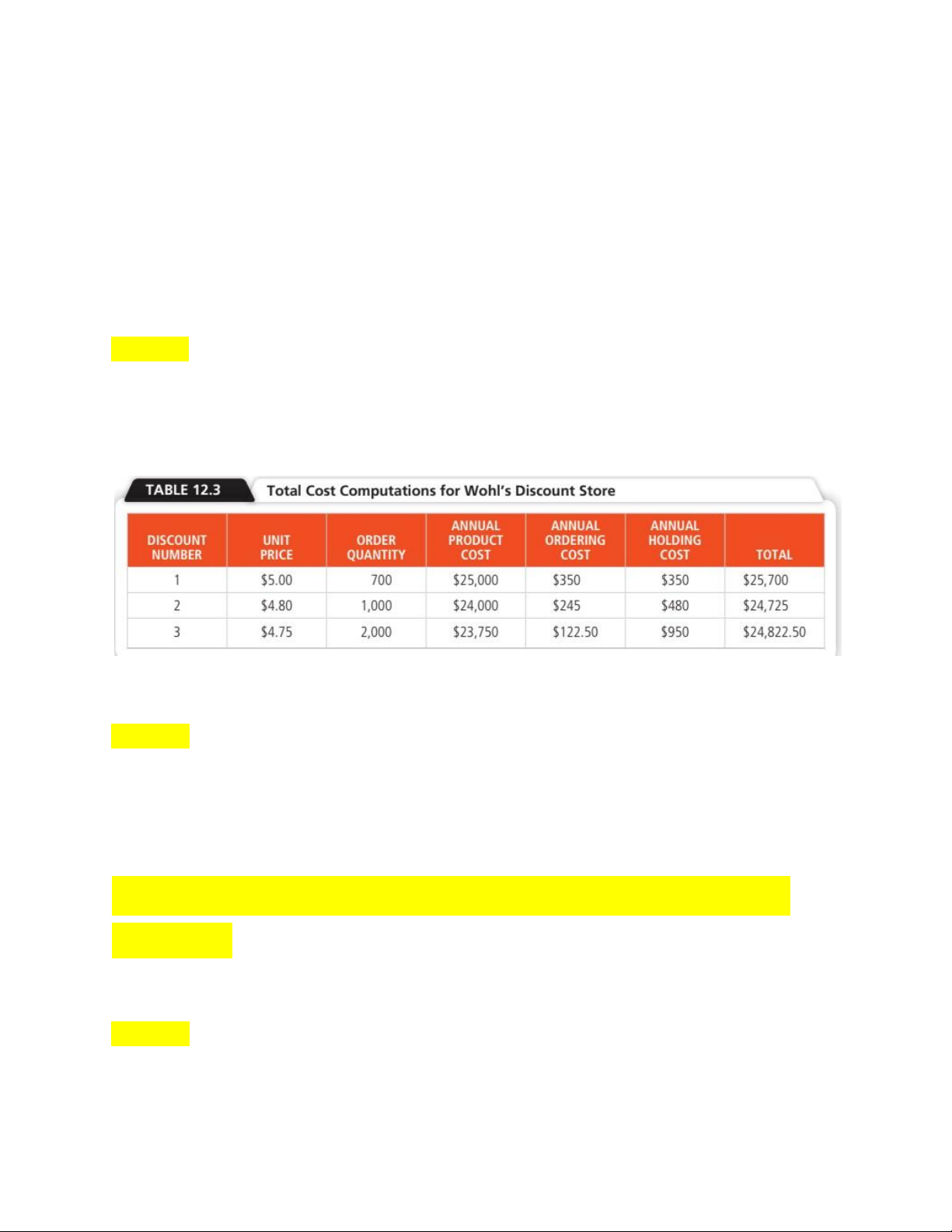
Bước 1: Tính Q* của theo từng giá
+ Q*= 2𝐼𝑃𝐷𝑆 =…… Ví dụ: =>Q*(1) = 700 =>Q*(2) = 714 => Q*(3) = 718
Bước 2: Điều chỉnh Q* theo đúng số lượng được giảm lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
+Với mức giá $5 thì cần mua 0-999 units mà Q*(1) = 700 (thỏa)
+Với mức giá $4.8 thì cần mua 1000-1999 units mà Q*(2) = 714 – điều chỉnh lên Q*(2) = 1000
+Với mức giá $4.75 thì cần mua 2000 and more mà Q*(3) = 718 – điều chỉnh lên Q*(3) = 2000
Bước 3: Tính total cost theo từng thằng Q*
Total annual cost = Setup cost + Holding cost + Product cost = (D/Q)*S + (Q/2)*IP + PD
Bước 4: chọn Q* có total cost nhỏ nhất
=>Choose 1000 units per order because of its lowest total cost.
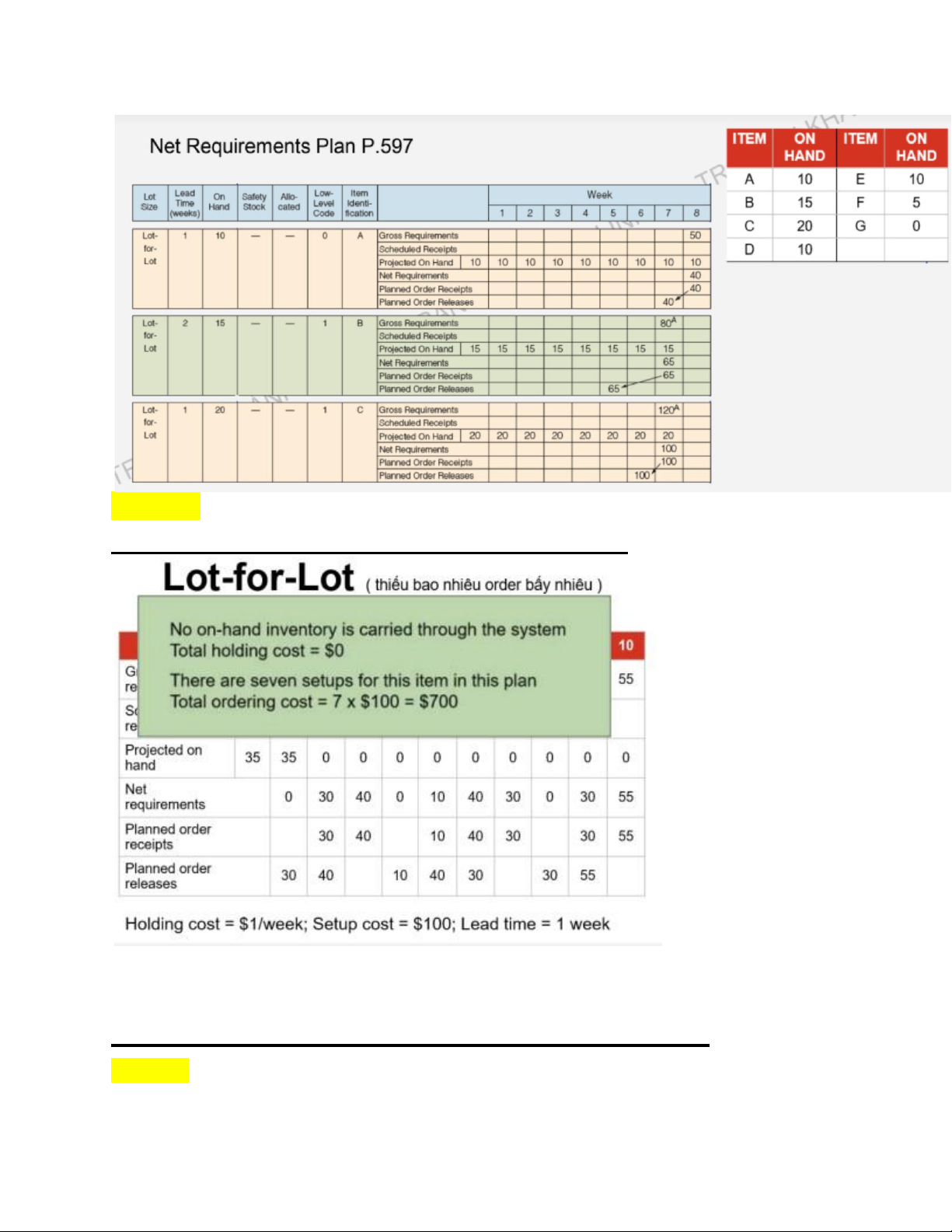
Chap 14: Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP
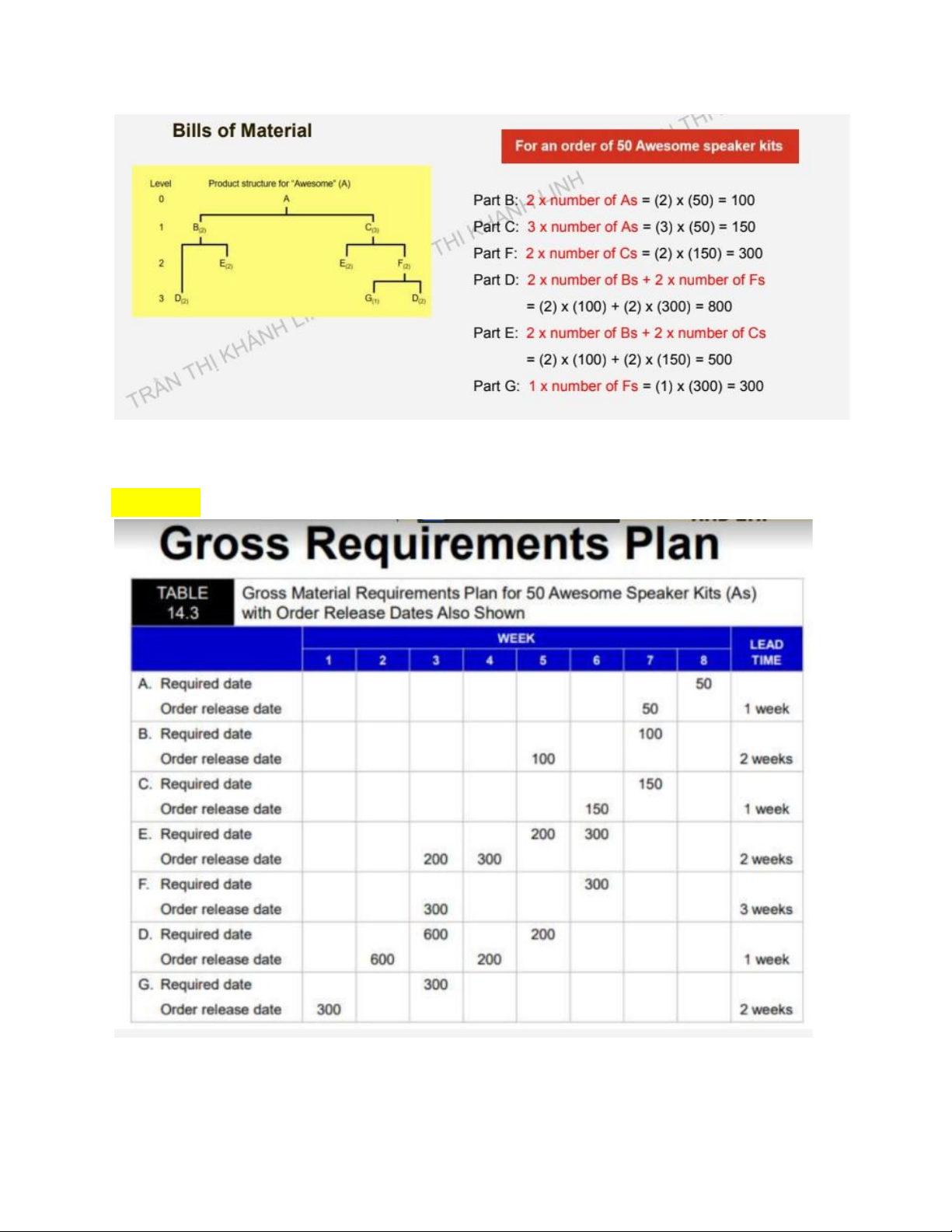
Bước 1: Bills of Material (Product structure) lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Bước 2: Gross Requirements Plan lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Bước 3: Net Requirement Plan
I/ Lot-for-lot (Thiếu bao nhiu đặt bao nhiu)
II/ EOQ lot size (oder theo cùng 1 số lượng cụ thể)
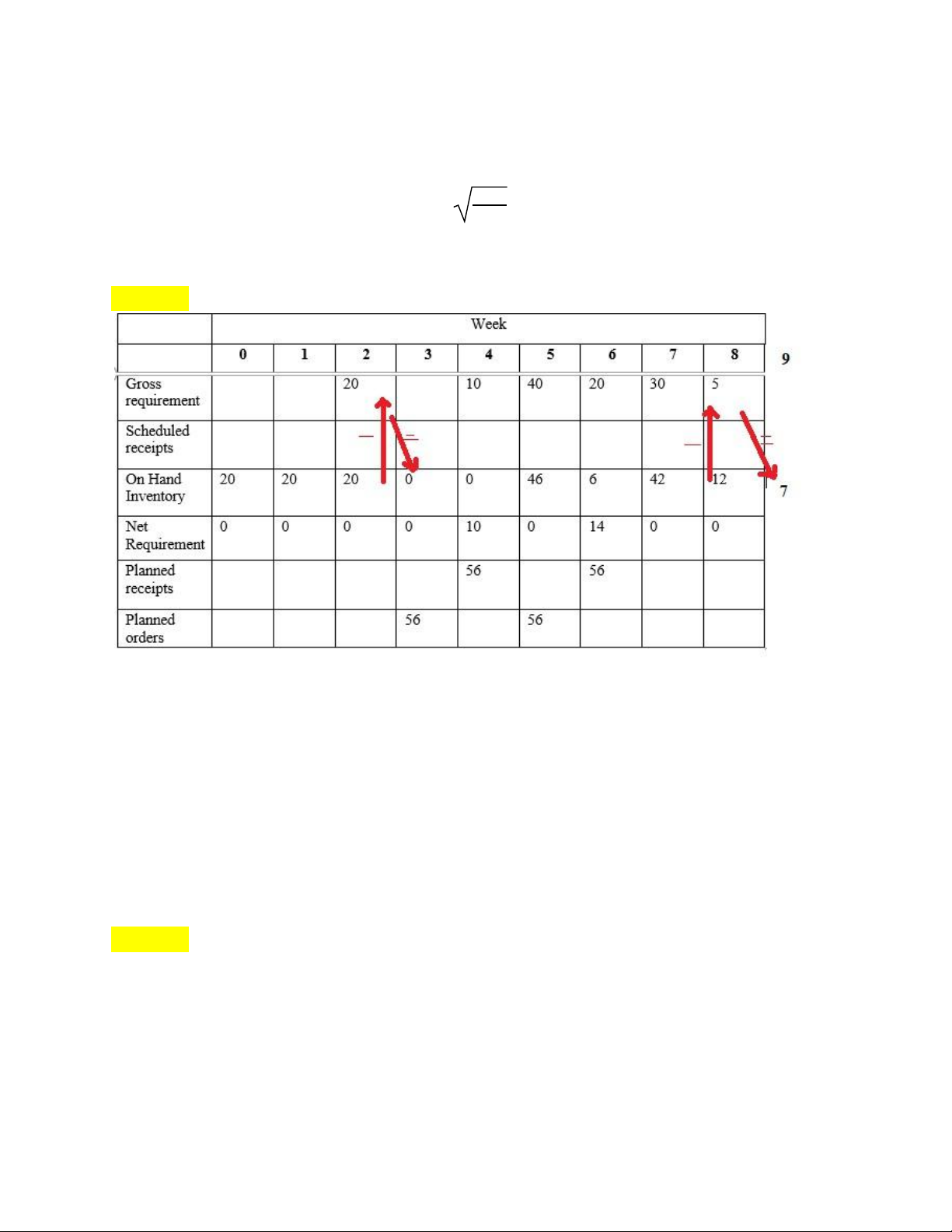
Bước 1: Tính EOQ = Q* lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
+Average Demand in each week = (20+10+40+20+30+5) / 8 = 15.625 (units)
+Annual demand = 15.625 * 52 weeks = 813 (units)
+Economic order quantity: EOQ = 2𝐻𝐷𝑆 = 56 (units)
Bước 2: Vẽ bảng EOQ MRP table *Lưu ý:
+Số 20 ở tuần 1 dòng “On hand Inventory” là số hàng tồn kho của tuần 0
+Số 20 ở tuần 2 dòng “On hand Inventory” là số hàng tồn kho của tuần 1 +……
+ Số 7 ở tuần 9 dòng “On hand Inventory” là số hàng tồn kho của tuần 8
Bước 3: Tính total cost for 8 weeks
“Đề cho Holding cost = $1 per unit per week và Setup cost = $100 per order”
+Holding cost for 8 weeks = $1*inventory of week 1 + $1*inventory of week 2 +…+$1*inventory of week 8 lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
=$1*20 + $1*0 +….+$1*7= $133 for 8 weeks
+Setup cost for 8 weeks= Setup cost per order in 8 weeks * Số orders = 2*100 =$200
=>Total cost for 8 weeks = Holding cost + Setup cost = 133+200 = $333.
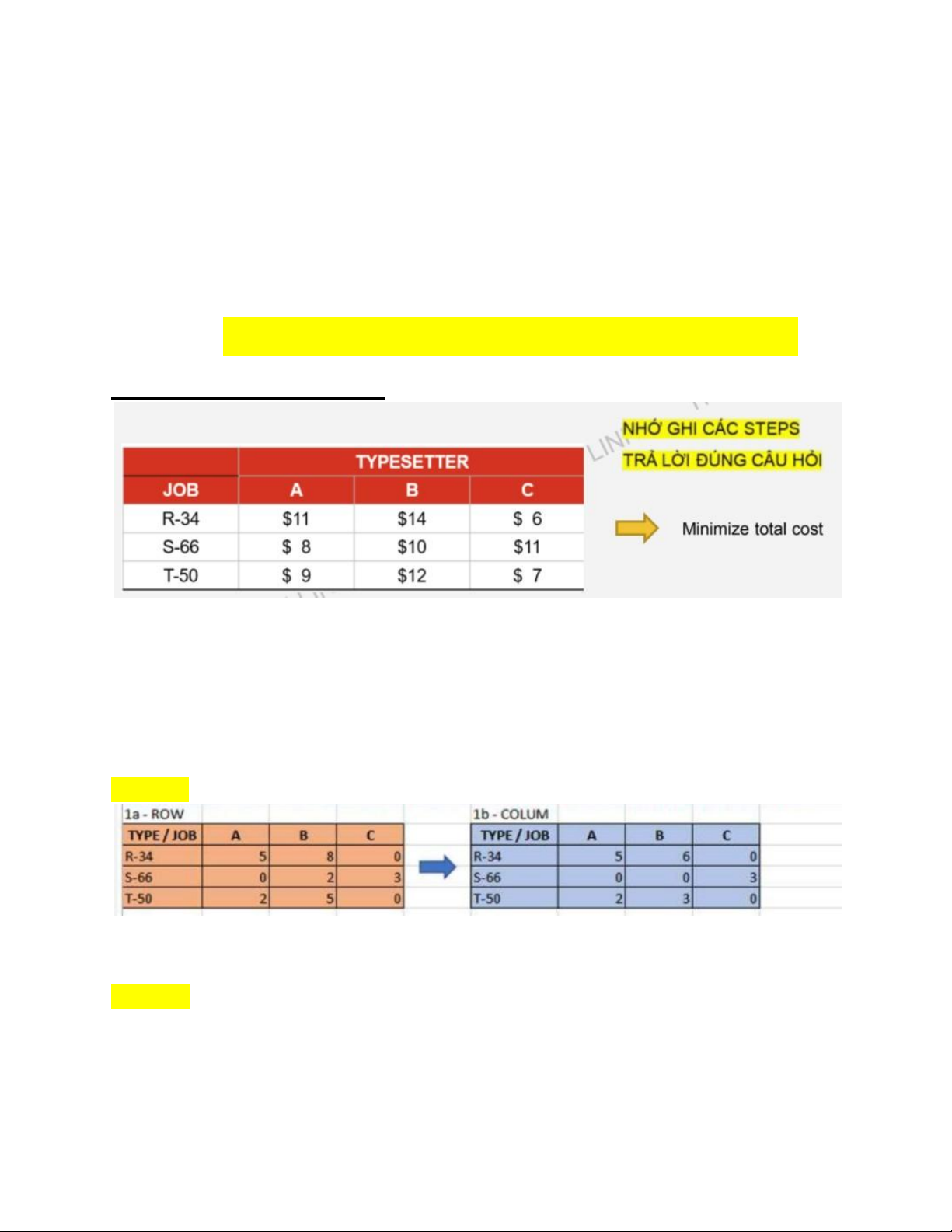
Chap 15: Scheduling in the Short-Term I/ Assignment Method:
*Lưu ý to đùng: Khi tính Maximum production or Maximum….
=> Thì phải chọn ra số lớn nhất trong table và lấy số đó trừ từng ô để tạo ra 1 bảng
mới rồi mới dô bước 1
Bước 1: Trừ số nhỏ nhất theo hàng ngang và hàng dọc
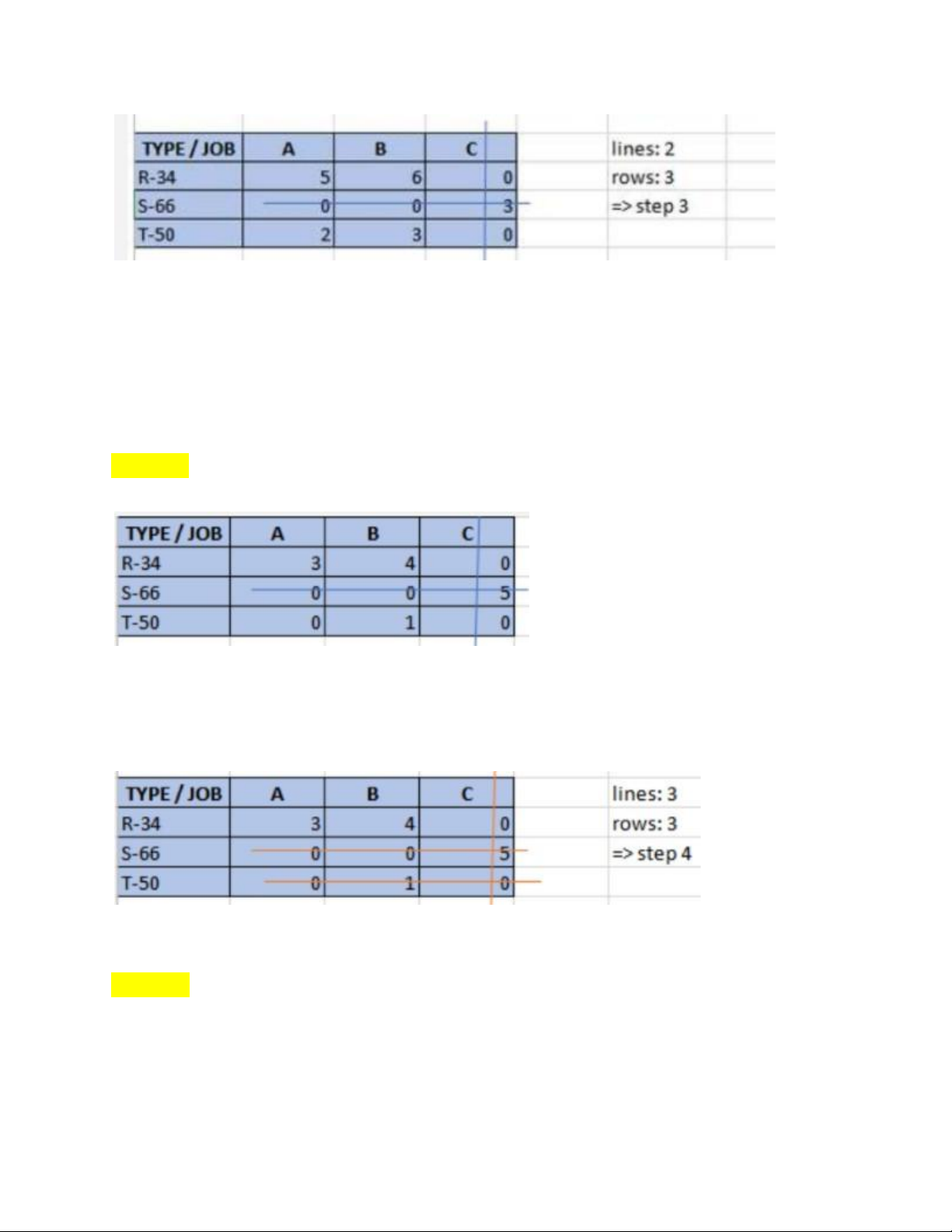
Bước 2: kẻ đường gạch tối thiểu sao cho cover hết số 0 trong table lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008 *Lưu ý:
+Nếu Số gạch < số cột or số dòng => Tiếp bước 3
+Nếu số gạch = số cột or số dòng = > Tiếp bước 4
Bước 3: Trong những số ko có đường gạch đi qua, lấy từng số trừ cho số nhỏ
nhất và cộng số nhỏ nhất ấy cho giao điểm của những đường gạch. *Lưu ý:
+Sau khi xong bước 3 thì quay về bước 2 để kẻ tiếp đường gạch sao cho
cover hết số 0. Ta được như sau:
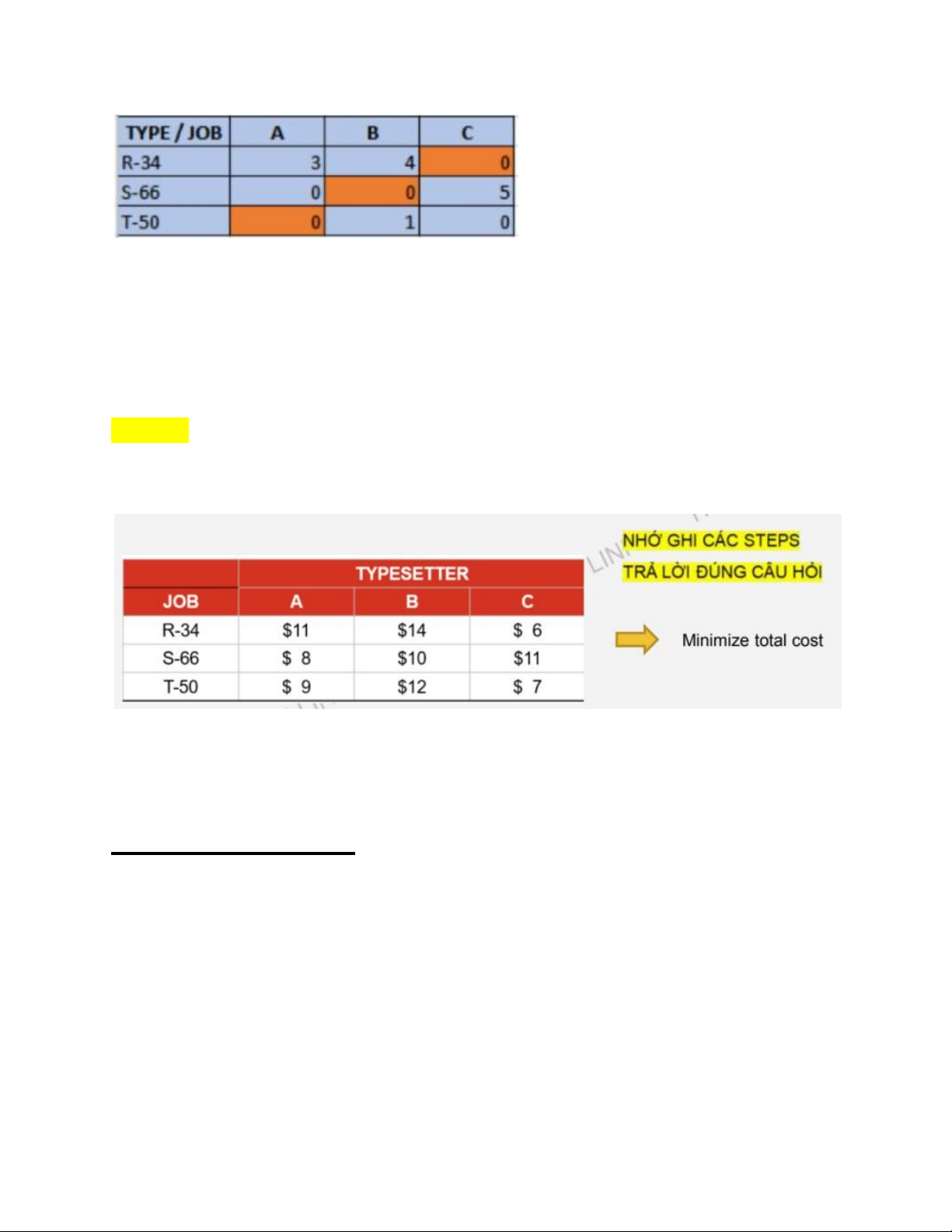
Bước 4: Phân chia task cho từng người để được minimum cost lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
*Lưu ý: ưu tiên số 0 đứng một mình theo hàng dọc hoặc hàng ngang. Ví dụ, theo
hàng ngang thì chỉ có hàng R-34 có 1 số 0 ở C vì vậy gán R-34 cho C.
=> Gán R-34 cho C; Gán S-66 cho B; Gán T-50 cho A
Bước 5: Tính total cost
Sau khi quyết định được task nào gắn cho người nào được minimum cost thì ta quay dề bảng original.
=>Từ đây chúng ta tính total cost = 6 + 10 + 9 = $25 II/ Sequencing Jobs:
1. FCFS: First come, first served
2. SPT: Shortest processing time
3. EDD: Earliest due date 4. LPT: Longest processing time *Ví dụ về SPT: lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
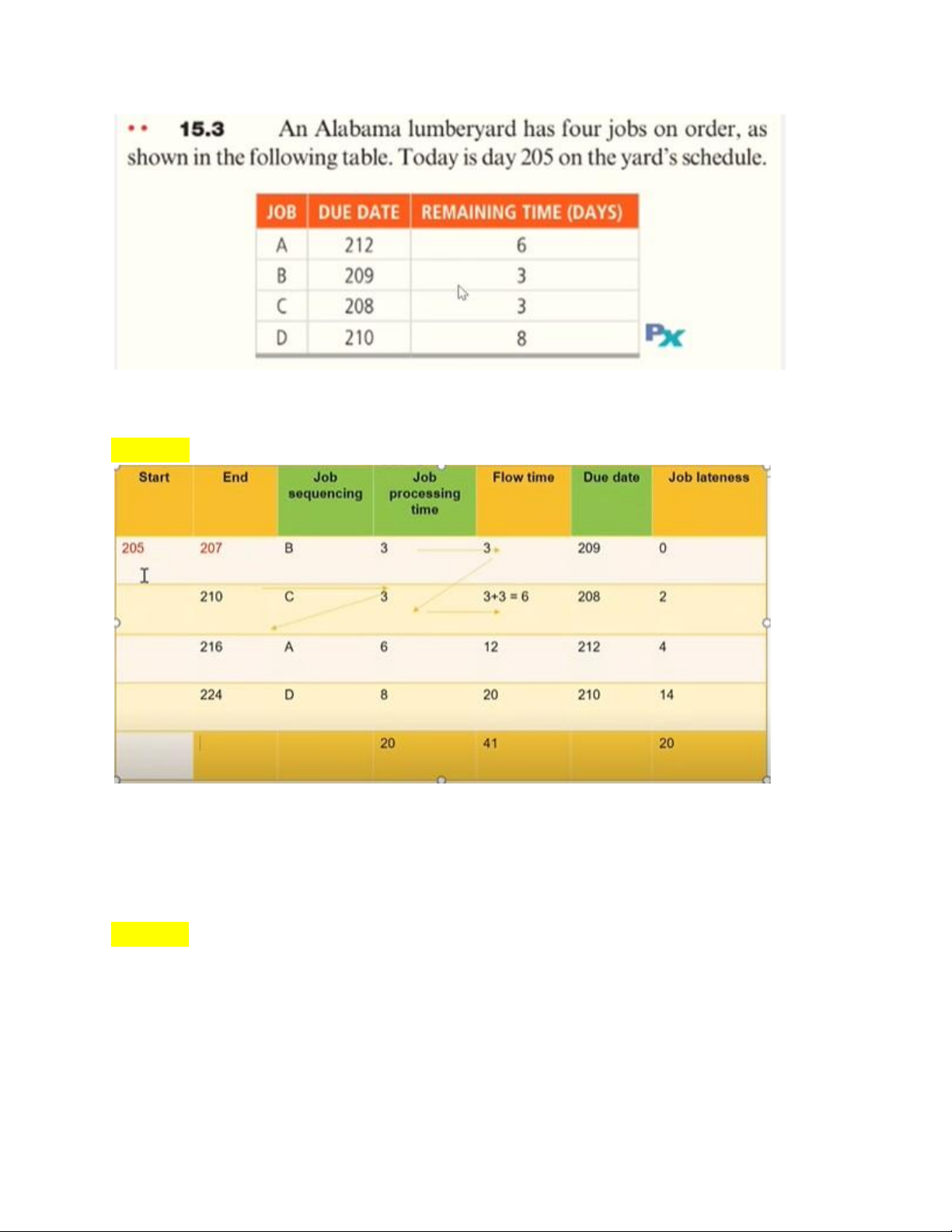
Bước 1: kẻ bảng và tính toán số liệu
*Lưu ý: ngày hiện tại là 205 cách 3 ngày sẽ là ngày 207, nhưng từ những ngày sau thì cộng bình thường
Bước 2: Tính toán 1 số công thức từ số liệu bảng trên
+Average completion time = (Sum of total flow time) / (number of jobs) = 77/5 =15.4 days
+Utilization metric = (total job work time) / (Sum of total flow time) =28/77 = 36.4% lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
+Average number of jobs in the system = (sum of total flow time) / (total
job work time) = 77/28 = 2.75 jobs
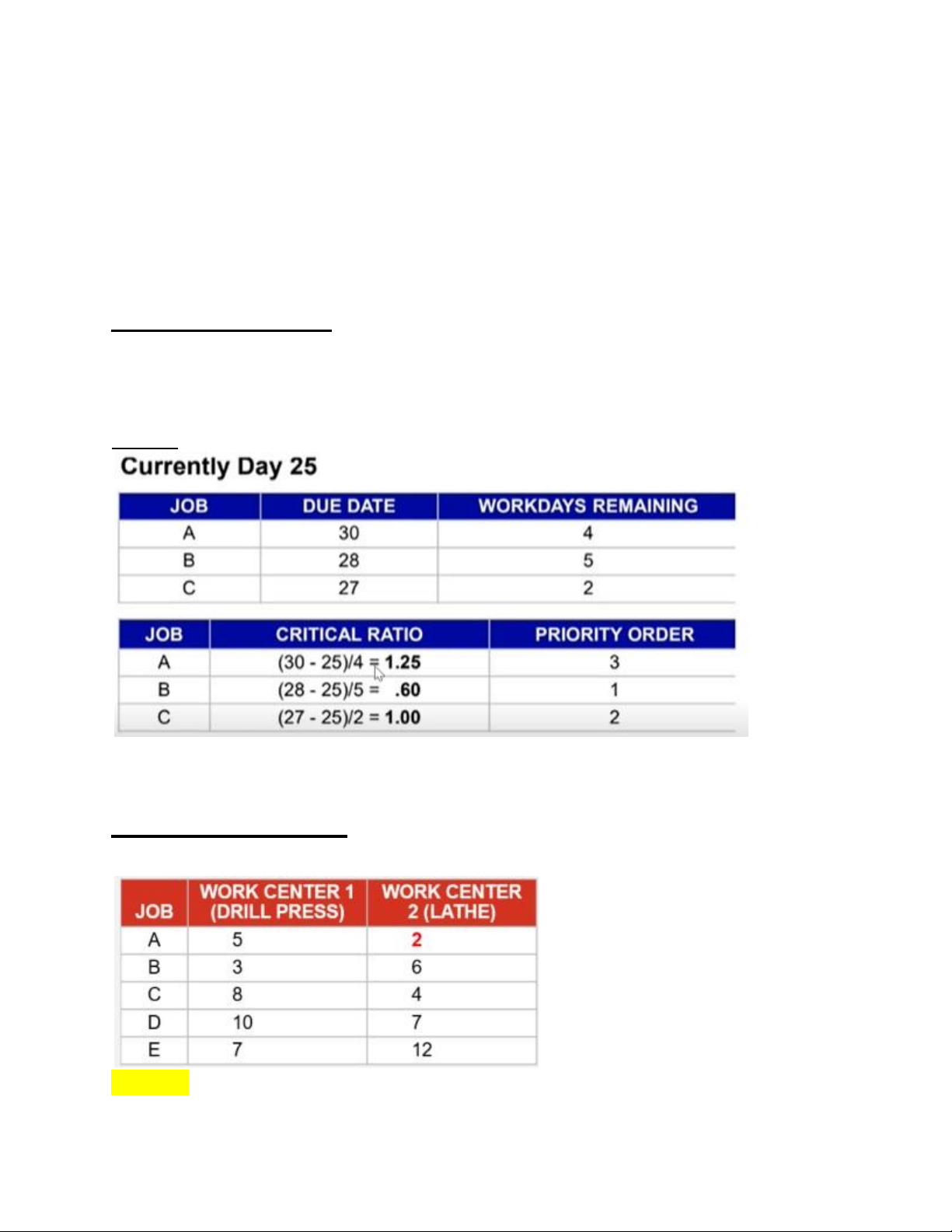
+Average job lateness = (total late days) / (number of jobs) = 11/5 = 2.2 days III/ Critical Ratio: Công thức:
+Critical Ratio = (Due date – Today’s date) / (Total shop time remaining) *Ví dụ: IV/ Johnson’s Rule: Đề cho:
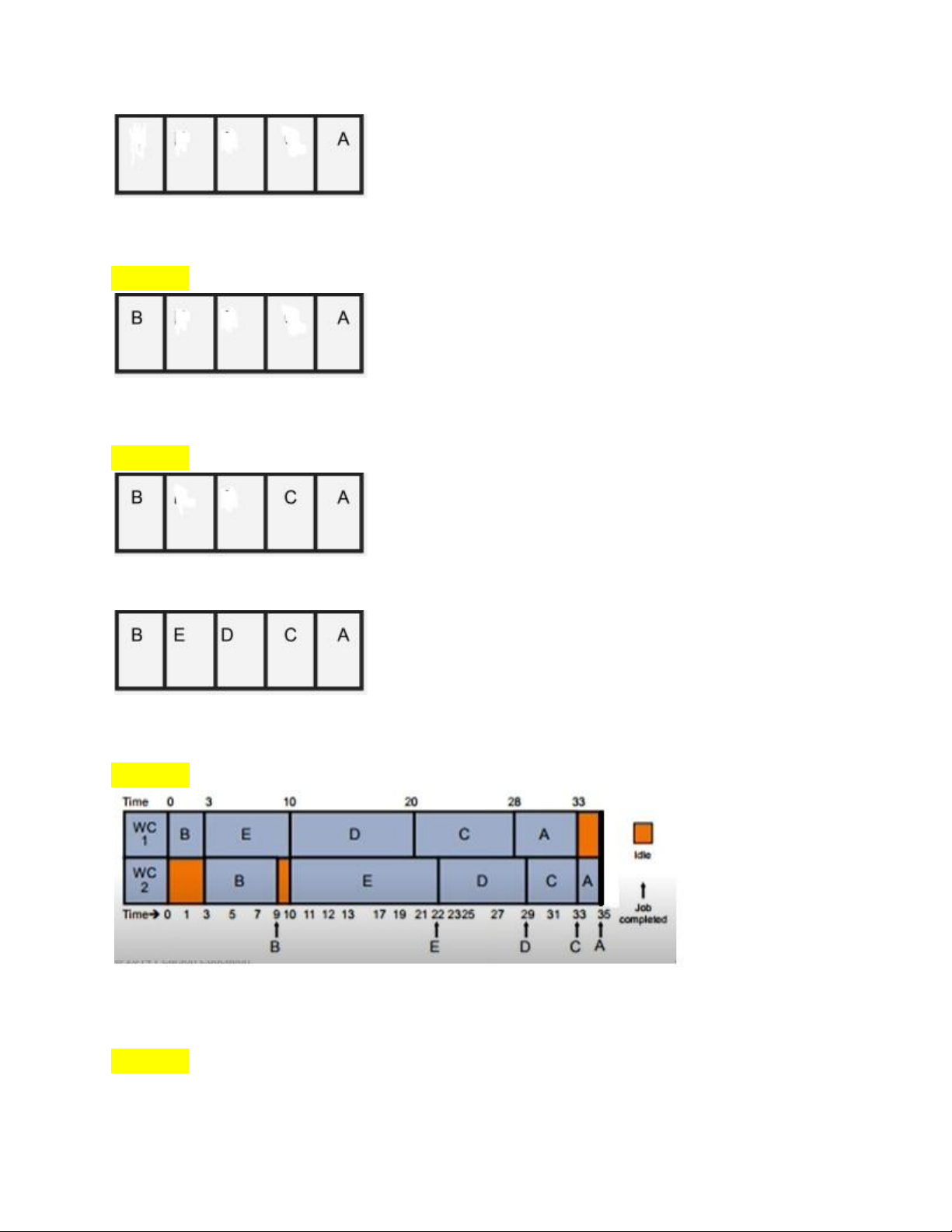
Bước 1: Trong cột bên phải chọn job có time nhỏ nhất bỏ vào bên phải khung lOMoAR cPSD| 58097008
Bước 2: Trong cột bên trái chọn job có time nhỏ nhất bỏ vào bên trái khung
Bước 3: Trong cột bên phải chọn job có time nhỏ kế bỏ vào bên phải khung
Và tiếp tục như vậy cho đến khi fill bảng ta được như sau:
Bước 4: Kẻ bảng thòi gian
*Lưu ý: khi 1 job đang làm ở WC1 thì không thể làm đồng thời ở WC2
Bước 5: Tính total production time and total idle time



