







Preview text:
DNA & Genome Tran Thi Thuy Linh, PhD. Nội dung
• 5.1. Học thuyết trung tâm của Sinh học phân tử
• 5.2. Cấu trúc và sự tổ chức của DNA trong bộ gen
• 5.3. Sao chép và sửa sai của DNA
• 5.4. Bộ gen người và Dược học hệ gen
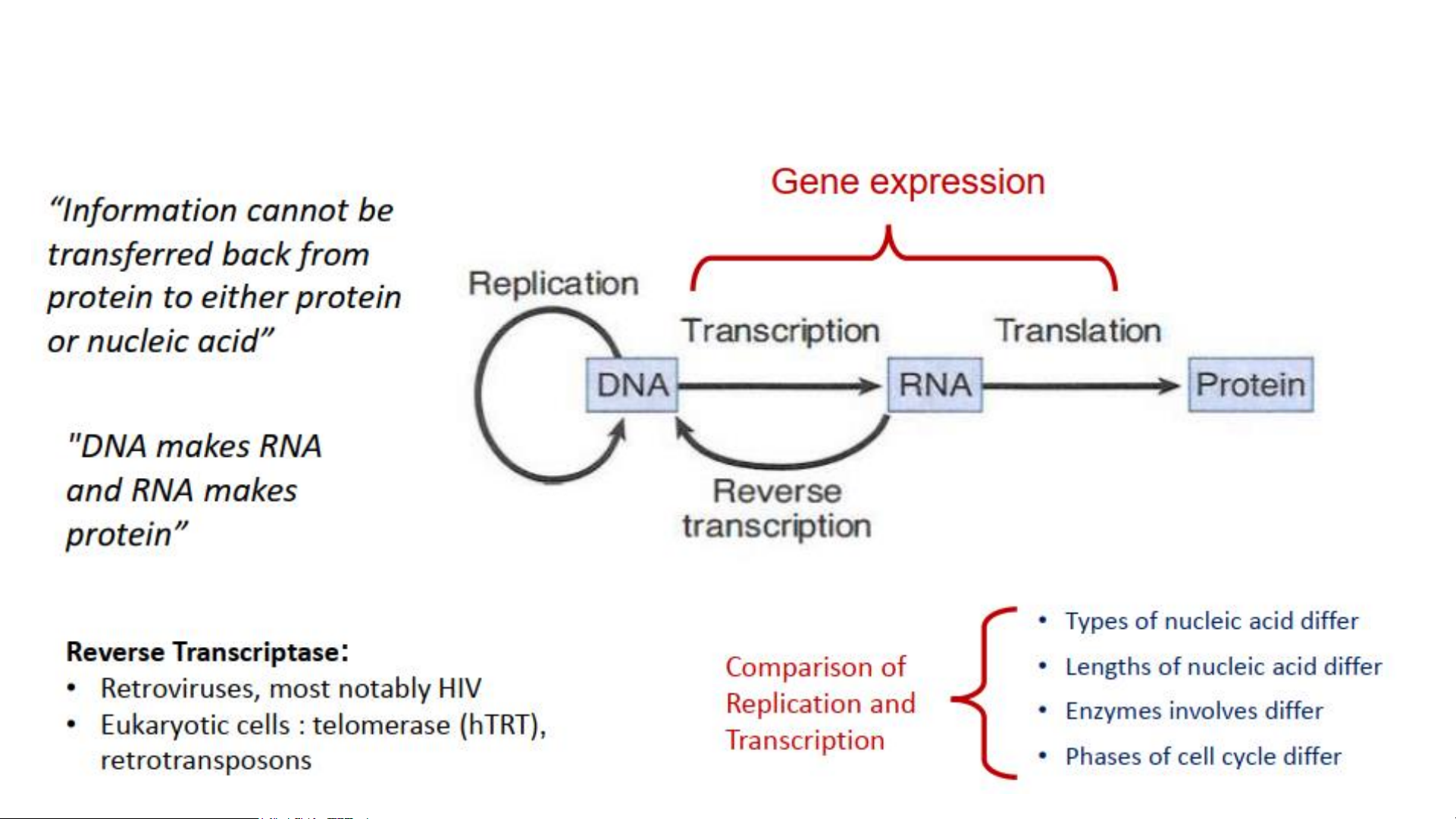
1/ CENTRAL DOGMA OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The cell cycle in Eukaryote
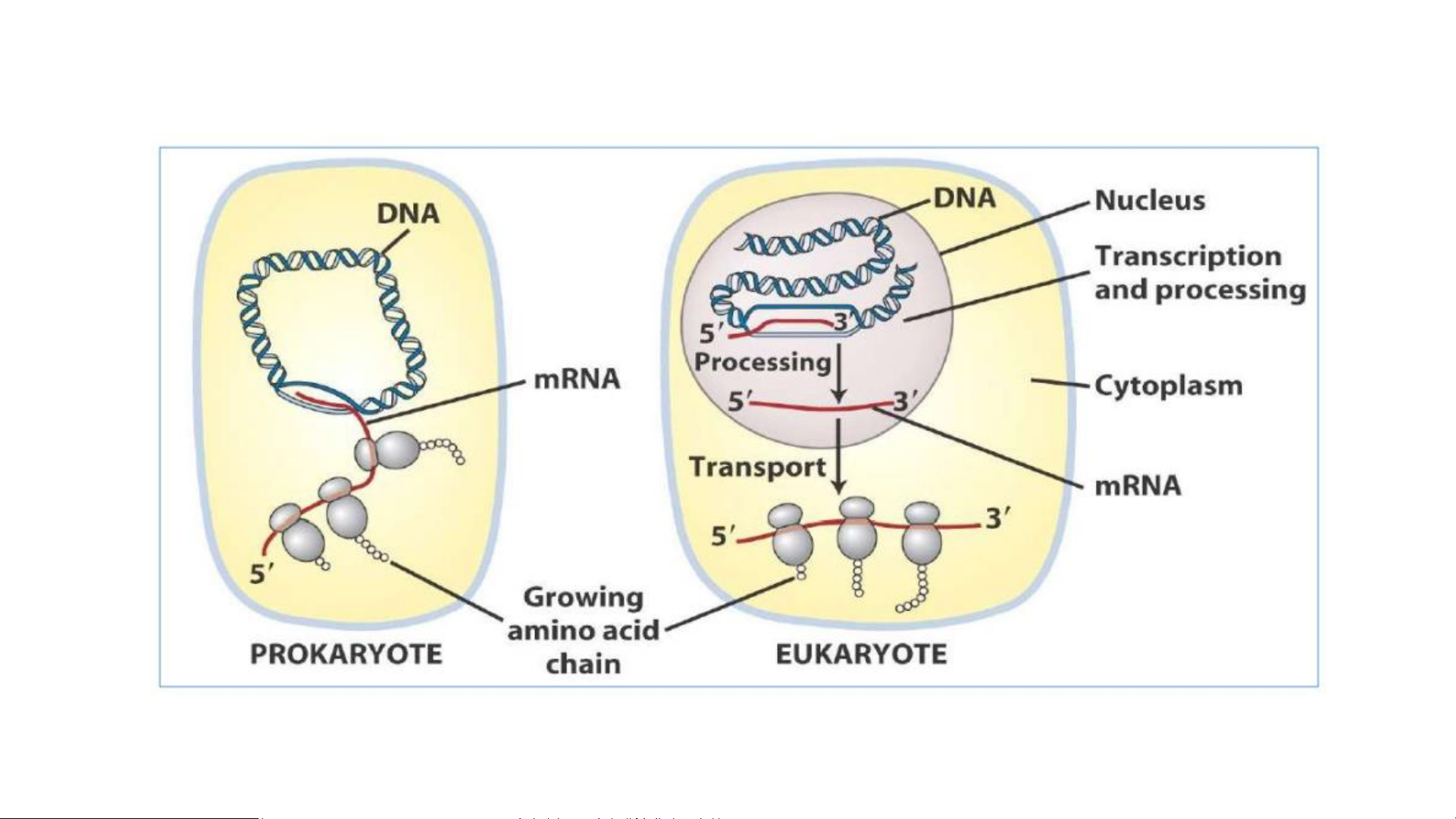
The genetic information flow in prokaryote and eukaryote (Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th Edition)
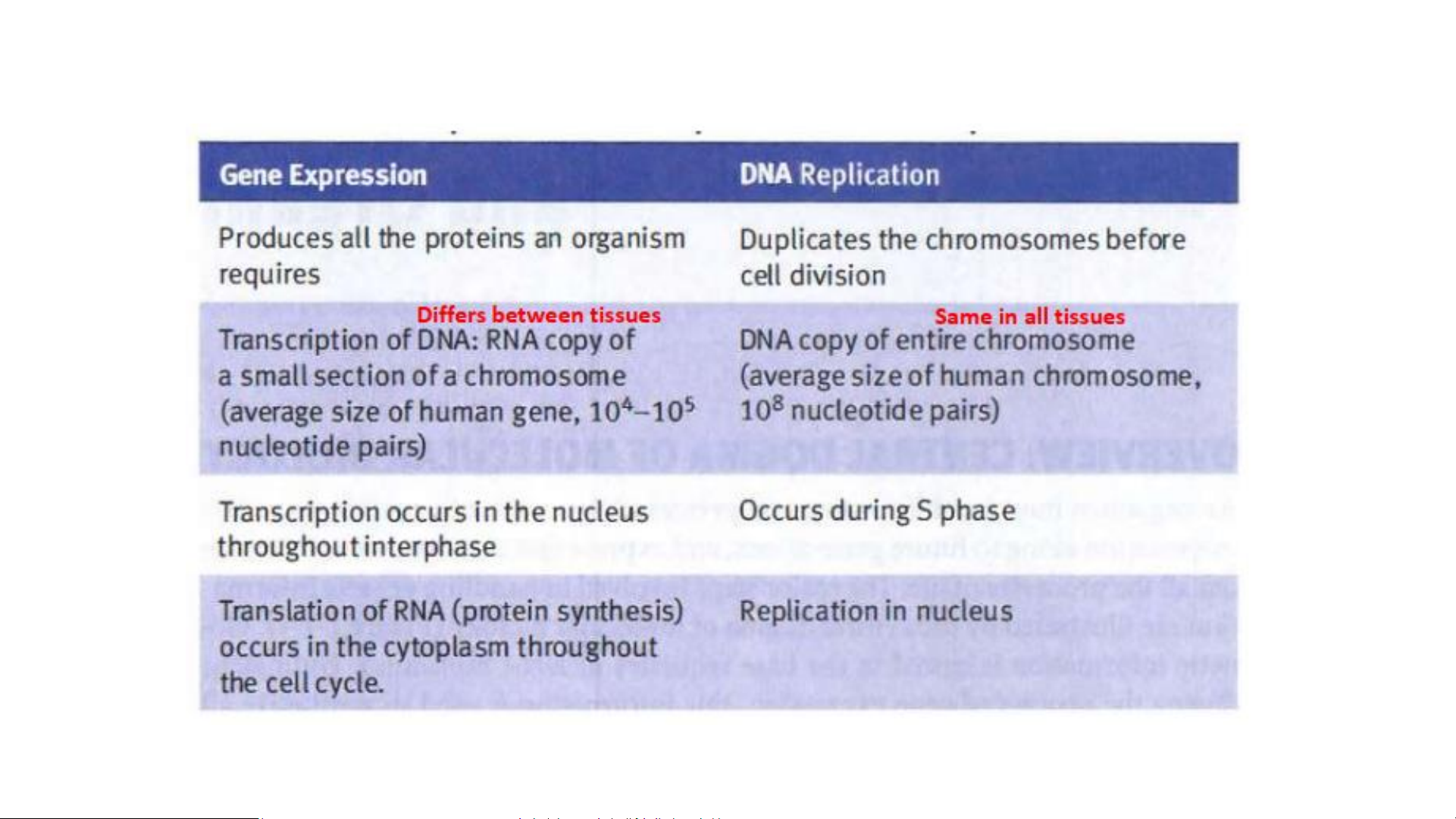
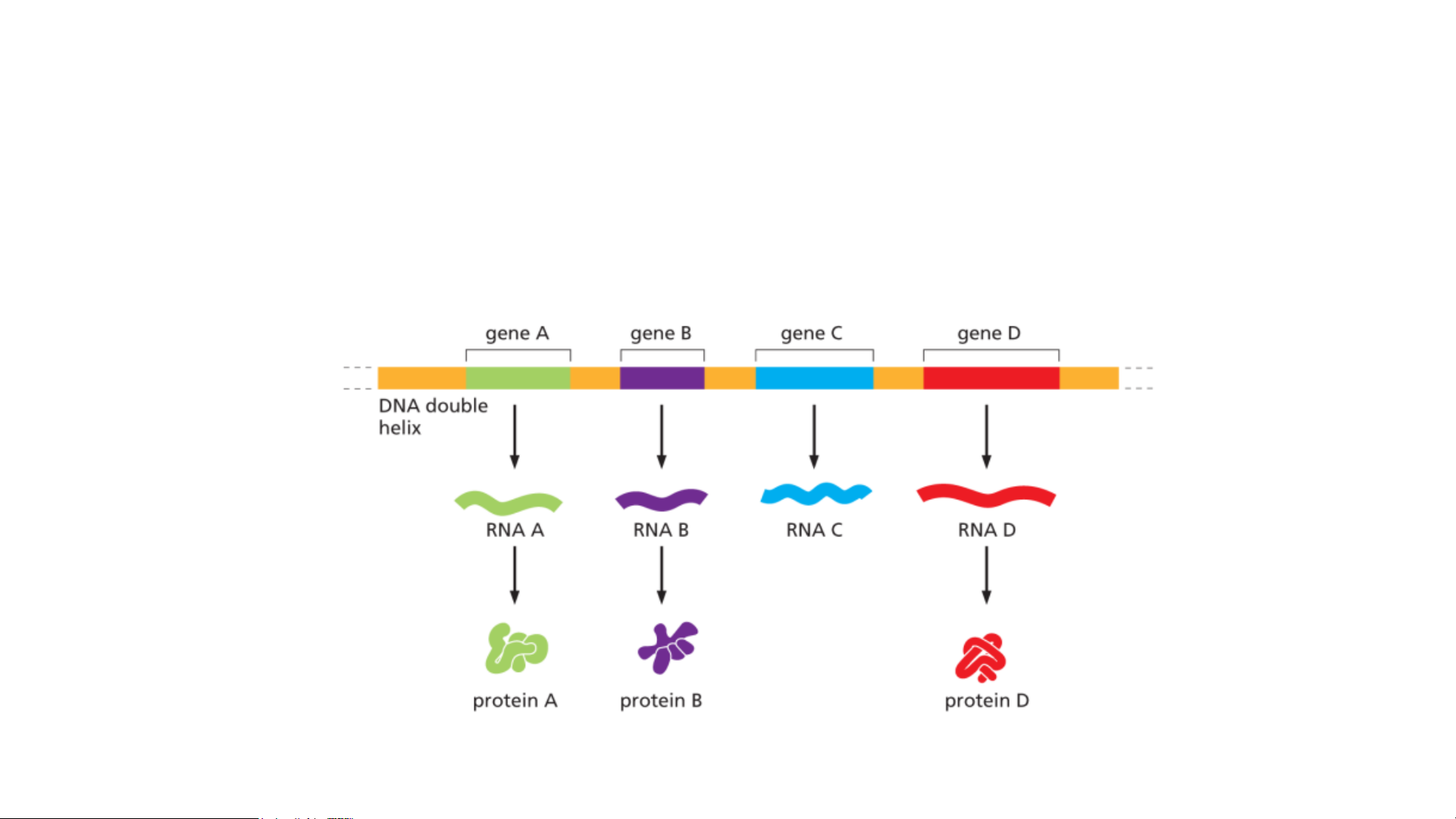
Comparison of Gene Expression and DNA replication Gene expression
Gene expression—the process by which the nucleotide sequence of a
gene is transcribed into the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule
and then, in most cases, translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein.
Most genes contain information to make proteins. DNA replication STRUCTURE OF NUCLEIC ACID
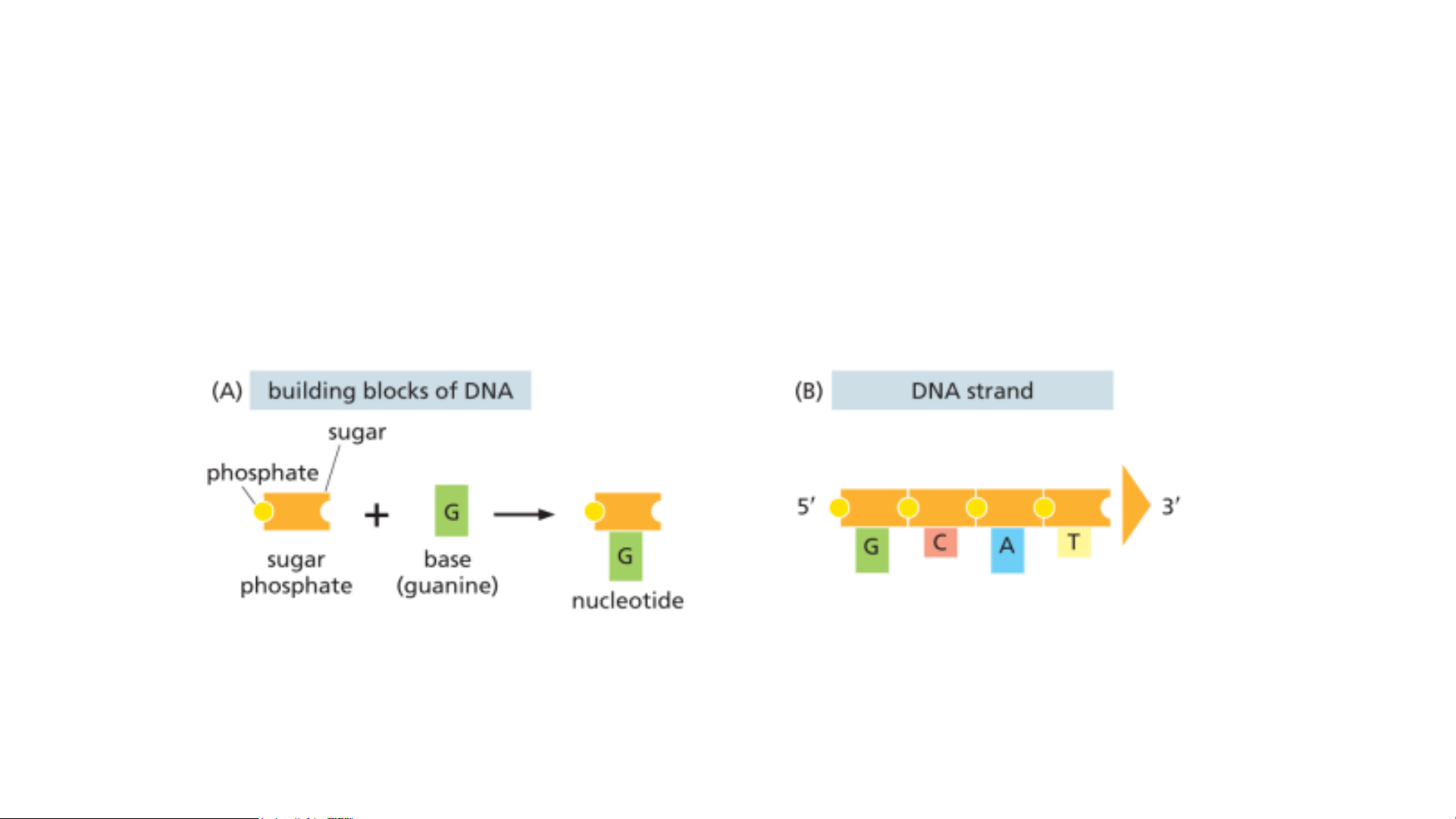
• A molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) consists of two long
polynucleotide chains. Each chain, or strand, is composed of four
types of nucleotide subunits, and the two strands are held together
by hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides
(A) Each nucleotide is composed of a sugar phosphate covalently linked to a base—guanine (G) in this figure.
(B) The nucleotides are covalently linked together into polynucleotide chains, with a sugar–phosphate
backbone from which extend the bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine (A, C, G, and T). STRUCTURE OF NUCLEIC ACID
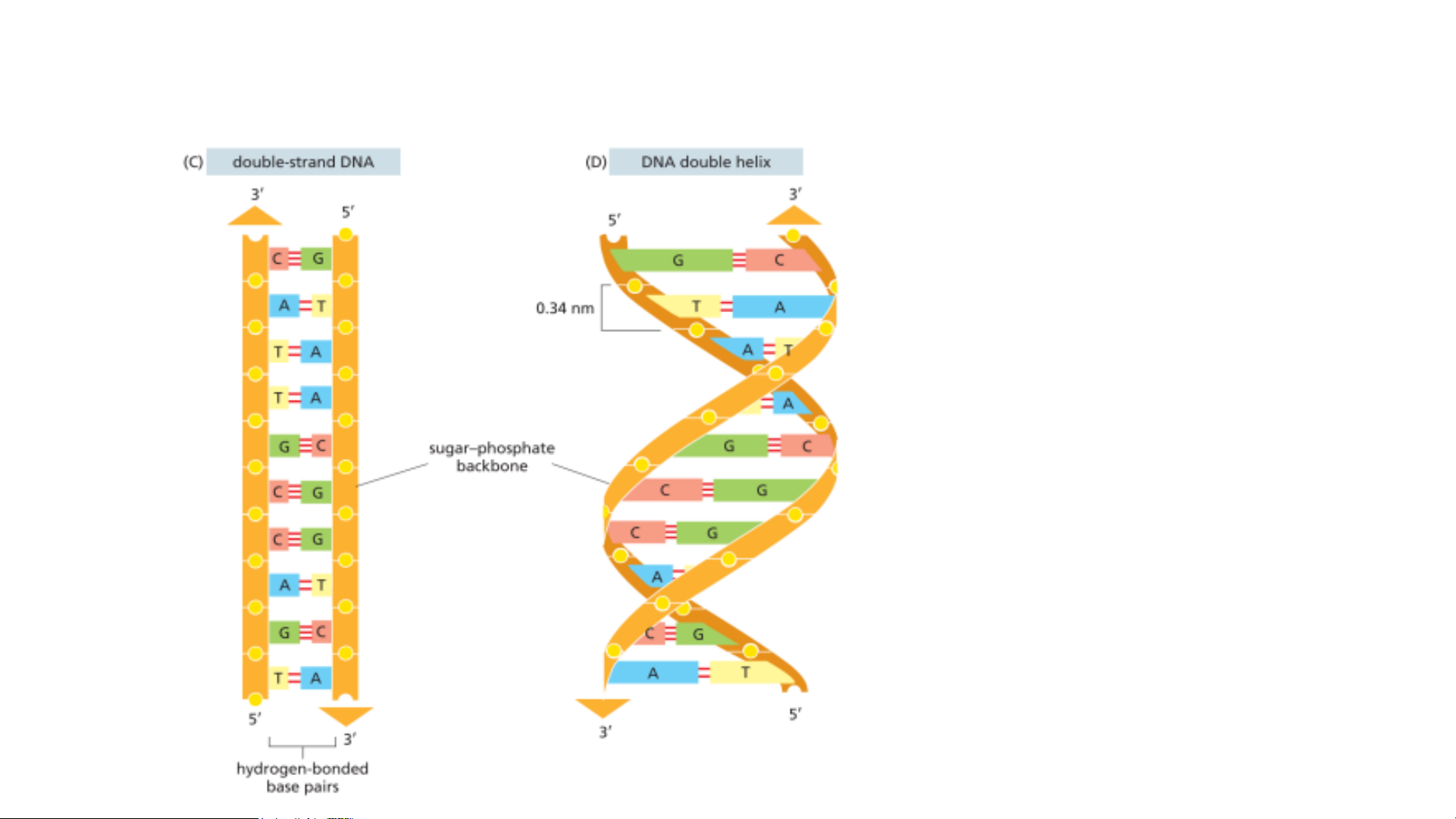
(C) A DNA molecule is composed of two
polynucleotide chains (DNA strands) held
together by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases.
(D) Although the DNA is shown straightened
out in (C), in reality, it is wound into a double helix, as shown here. Nucleotides
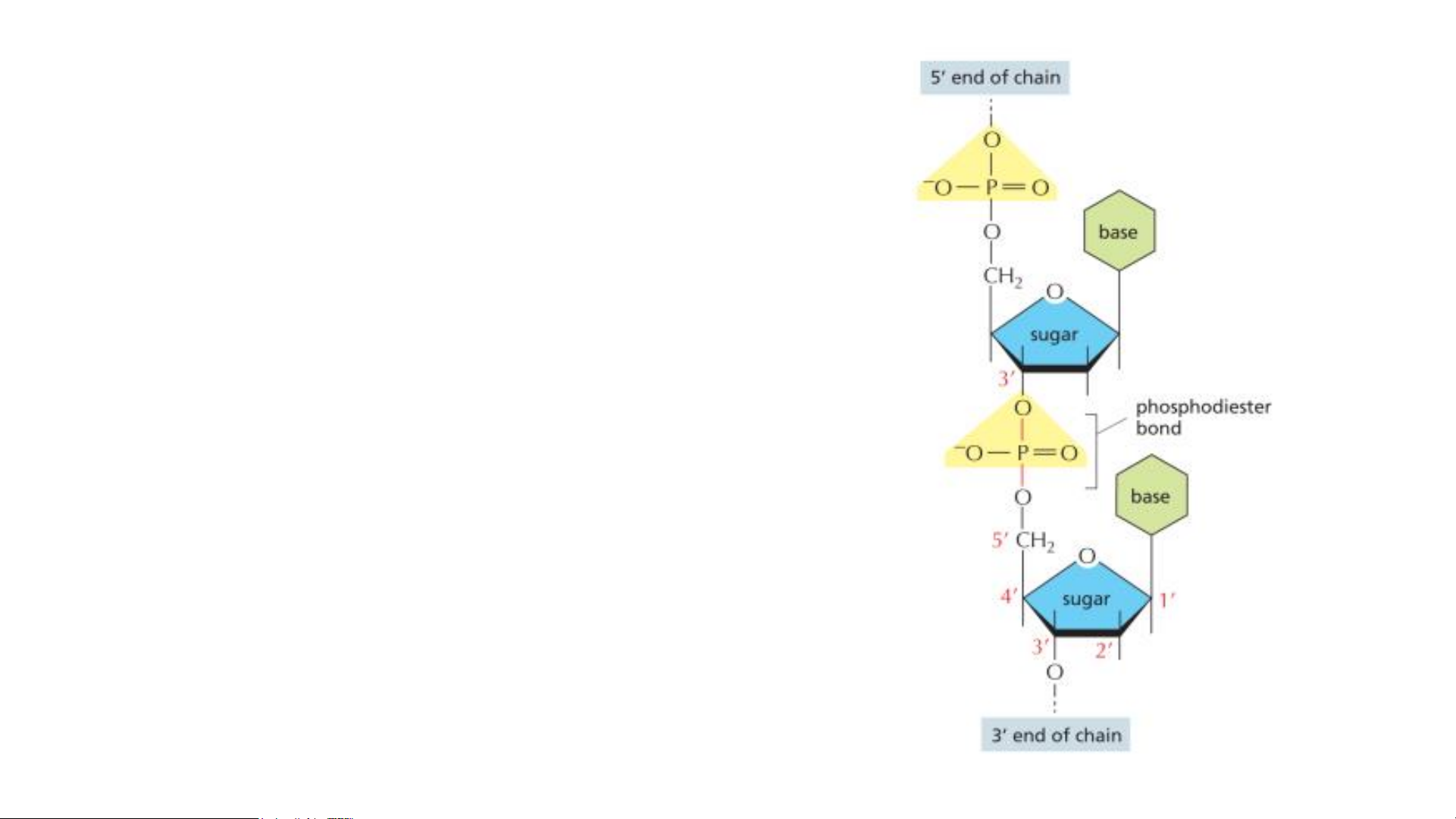
The nucleotide subunits within a DNA strand
are held together by phosphodiester bonds.
These bonds connect one sugar to the next. The
chemical differences in the ester linkages—
between the 5′ carbon of one sugar and the 3′
carbon of the other—give rise to the polarity of the resulting DNA strand.
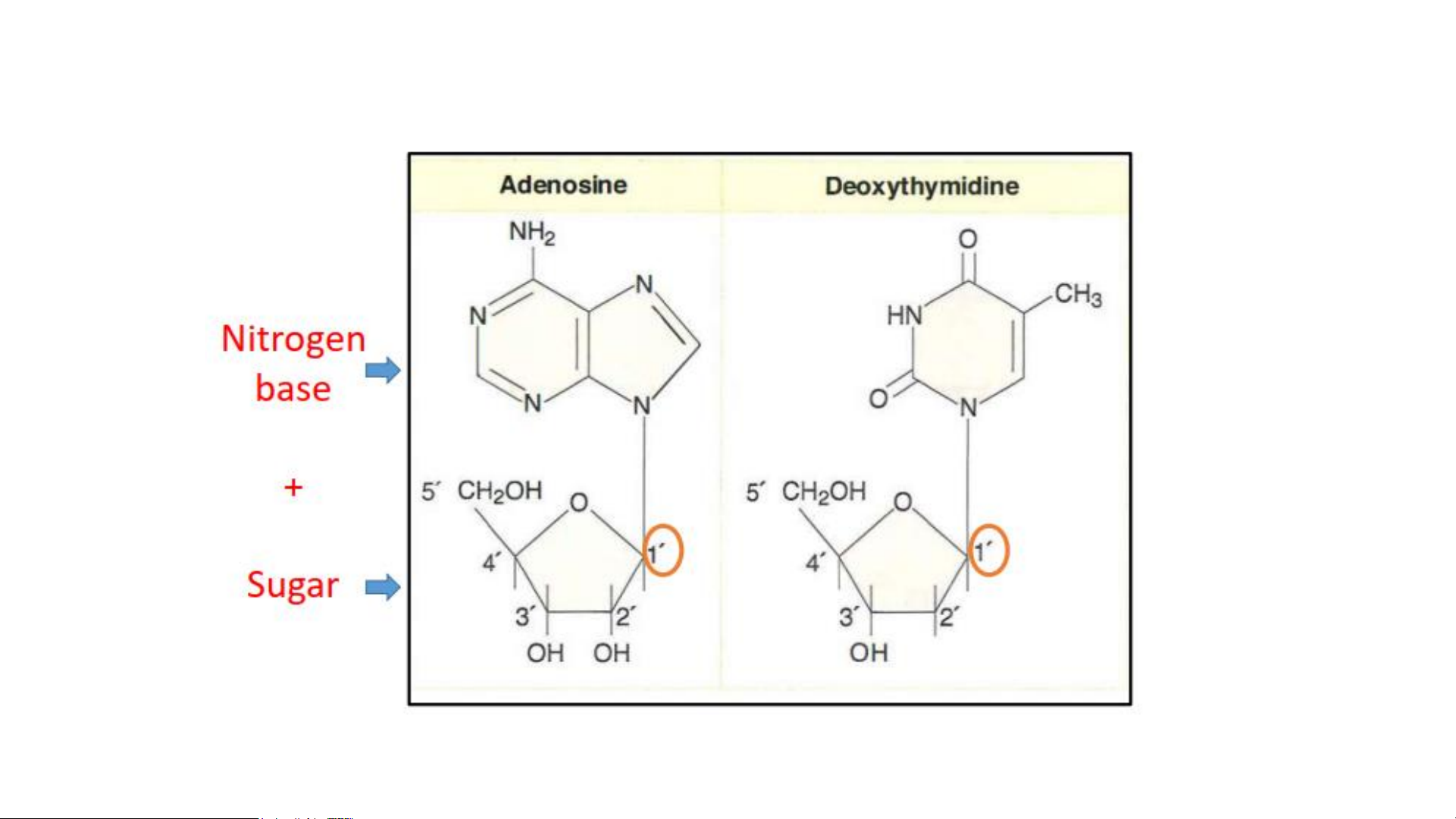
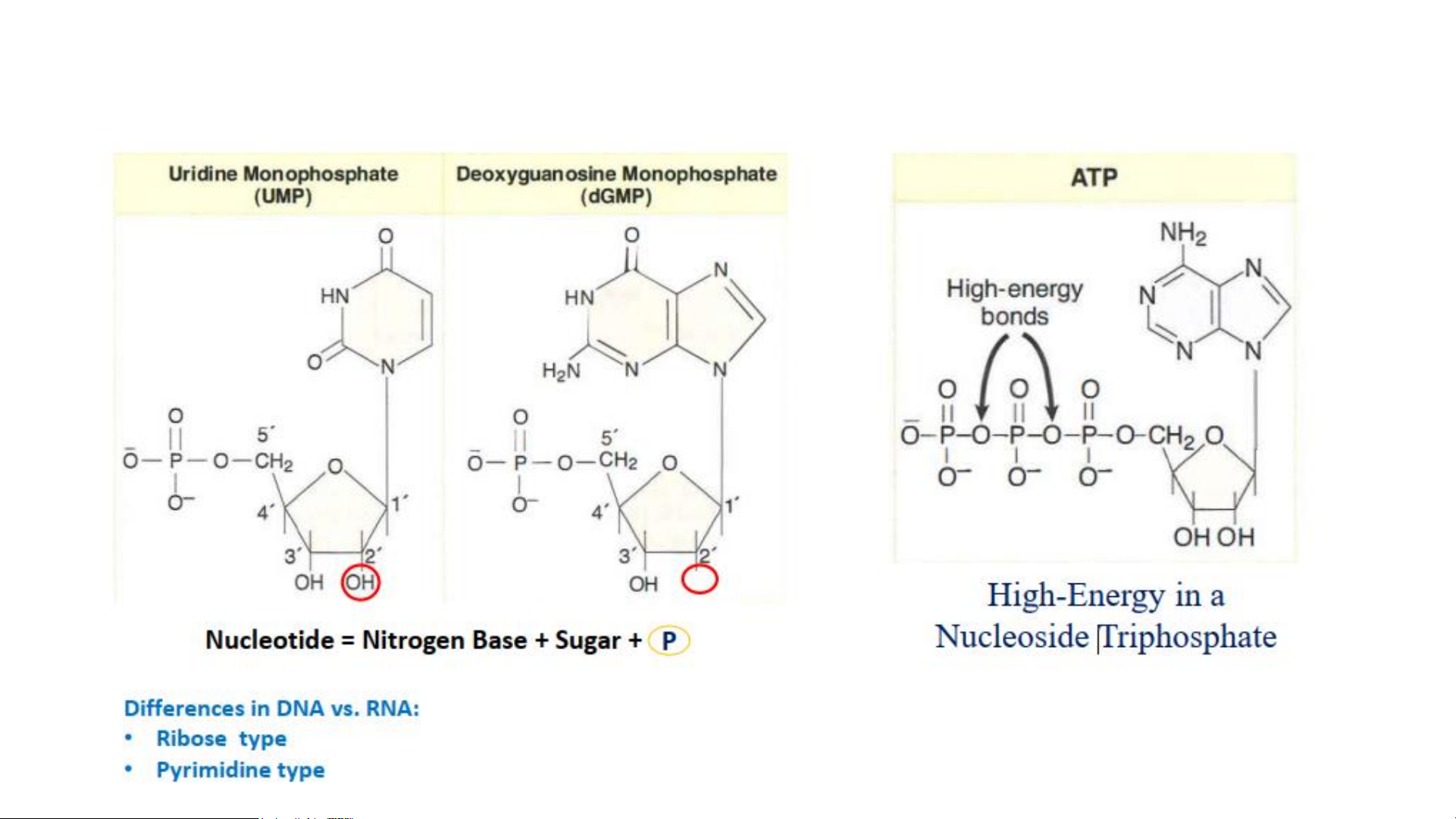
Structure of Bases in Nucleic Acids Nucleosides Nucleotides
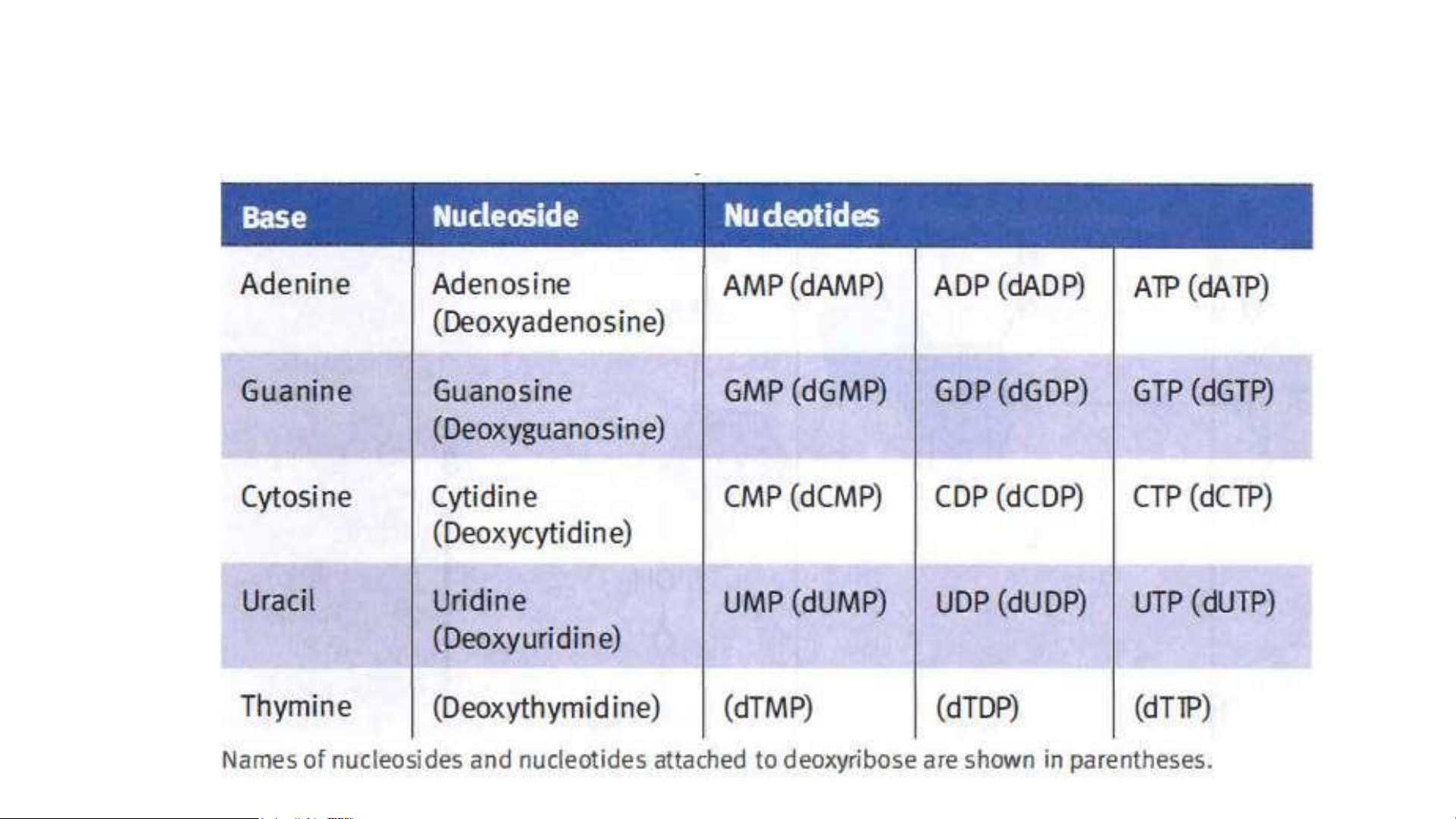
Nomenclature of Important Bases, Nucleosides, and Nucleotides
Structure of double stranded DNA
The two strands of the DNA double helix are held together
by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
Which of the following statements are correct? Explain your answers.
1. A DNA strand has polarity because its two ends contain different bases.
2. G-C base pairs are more stable than A-T base pairs.
The Structure of DNA Provides a Mechanism for Heredity



