
Preview text:
FUNDAMENTALS OF ECONOMICS
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Session Objective
✓By the end of this session students should be able to Explain the basic
economic problem of scarcity and choice
✓ By the end of this session students should be able to Differentiate
between microeconomics and macroeconomics
✓ By the end of this session students should be able to Apply the concept
of opportunity cost to real-life economic decisions
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
“Why can’t we have everything we want in life?”
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Definition
Economics is the study of how people, businesses, and
governments make choices to use limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants.
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Core Concepts ✓ Wants are unlimited ✓ Resources are limited ✓ Choices are necessary
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Scope of Economics: Economics studies
✓ How consumers choose
✓ How firms/organizations produce
✓ How governments manage the economy
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING • Scope of Economics:
1. How consumers choose: Economics studies how people decide ✓What to buy ✓How much to buy ✓When to buy ✓What to give up
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Example
A student has THB 1,000 . The following are the needs a. Food = THB 400 b. Clothes = THB 700 c. Mobile Data = THB 300 Total : THB 1,400
The student has to choose and give up , what the student gives up is called Opportunity cost.
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Based on the example the following questions are answered through the study of economics
1. Why people prefer some goods over others 2. How price affects buying 3. How income changes choices
4. How taste, fashion, culture affect decisions
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
2. How firms/organizations produce : Economics studies how businesses decide a. What to produce b. How much to produce c. How to produce d. For whom to produce
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Firms also face scarcity: a. Limited money b. Limited workers c. Limited machines d. Limited raw materials
So, firms/organizations must choose wisely
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Example : A bakery can Produce a) 100 Cakes b) 200 Breads
But it cannot make both in large quantity due to ✓ Limited oven ✓ Limited workers ✓ Limited time
So, the bakery has to choose
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Based on the example the following questions are answered through the study of economics
1. How firms use land, labor, capital 2. How cost affects production 3. How profit guides decisions
4. How competition affects prices
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
3. How Governments Manage the Economy : Economics studies how governments ✓ Collect money (taxes)
✓ Spend money (education, health, roads) ✓ Control prices ✓ Create jobs ✓ Control inflation
✓ Support under privilege people
Government also faces scarcity, like limited money and unlimited needs of the people
So, government must choose.
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Example : Government has THB 430,000,000
✓ Hospitals need THB 258,000,000 ✓ Roads need THB 215,000,000
✓ Schools need THB 172,000,000
Total need ≈ THB 645,000,000, Money available = THB 430,000,000
So, government must decide what to fund more and what to delay
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Based on the example the following questions are answered through the study of economics 1. Why governments tax 2. How budgets are made 3. How policies affect people 4. How prices are controlled 5. How jobs are created
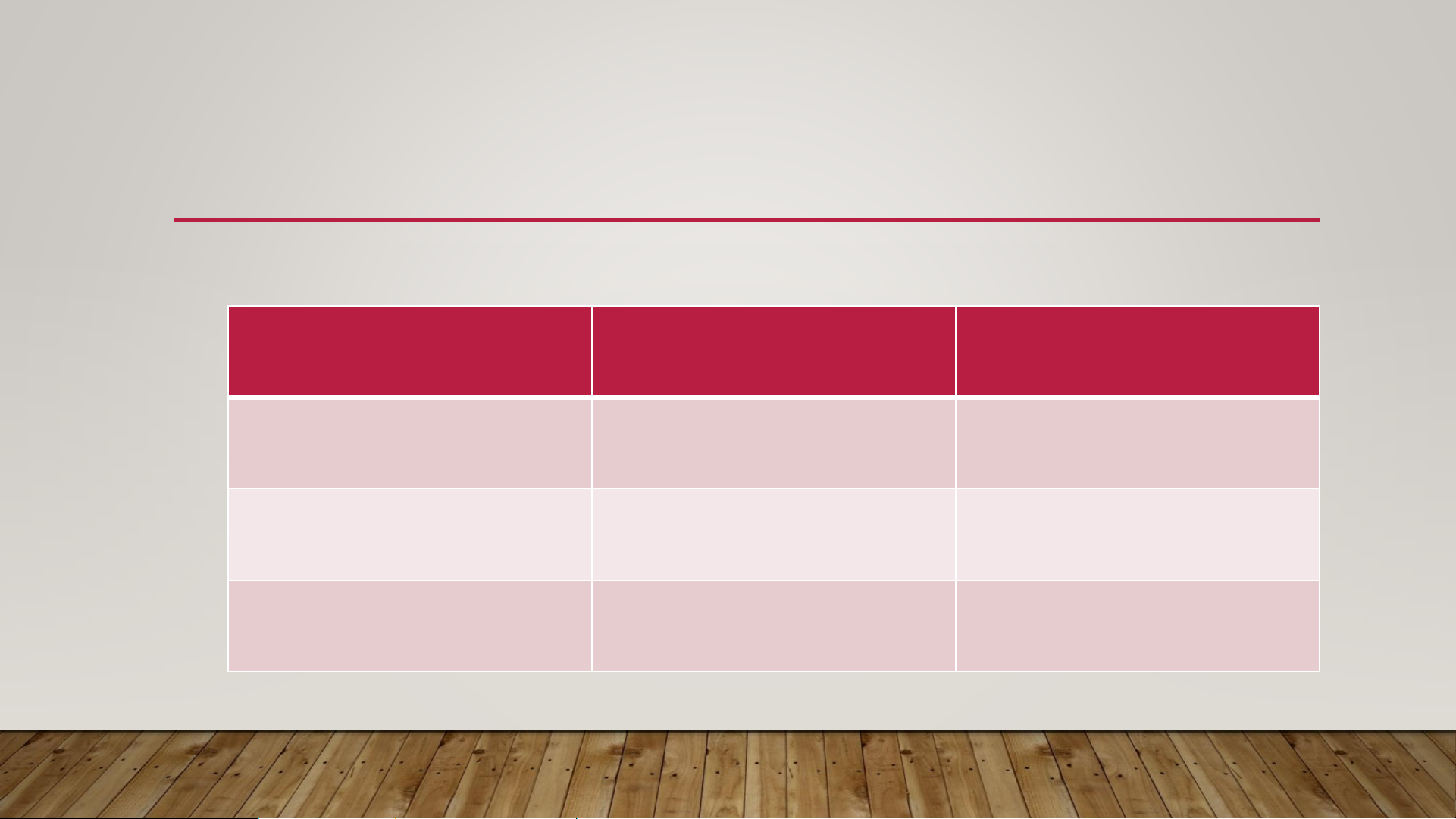
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING Scope of Economics Area Who is involved Main Question Consumers People What should I buy? Firms Businesses What should we produce? Government State How to manage the economy?
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Microeconomics vs Macroeconomics
Economics is divided into two big branches so that we can study problems at different levels:
✓ Microeconomics → small units
✓ Macroeconomics → the whole economy
Microeconomics is looking at individual trees and Macroeconomics is looking at the entire forest
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS & ECONOMIC THINKING
Microeconomics: Microeconomics studies the behavior of individual units, such as:
✓ Consumers (you, your family)
✓ Firms (shops, factories, companies) ✓ Workers ✓ Buyers and sellers ✓ Individual markets



