







Preview text:
Software Analysis and Design
Module 6.2: Unify Analysis Classes 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 1 Content
❖ Responsibility of analysis class
❖ Attributes and Associations of analysis class ❖ Unify Analysis Classes ❖ Checkpoints 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 2 Describe Responsibilities
• What are responsibilities? • How do I find them? 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 3
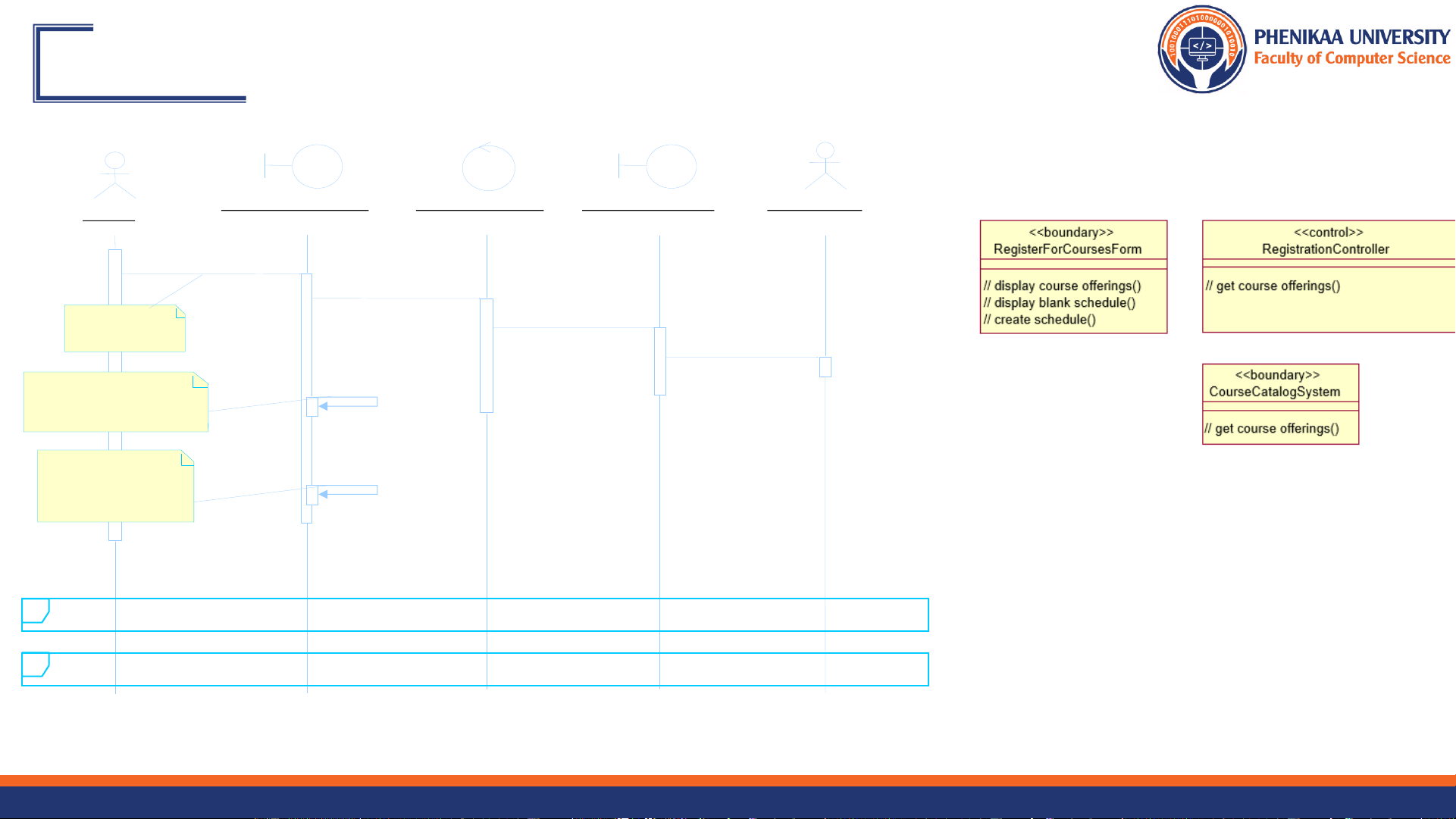
Example: Sequence Diagrams : RegisterForCoursesForm : RegistrationController : CourseCatalogSystem : Course Catalog : Student 1: // create schedule( ) 2: // get course offerings( ) Create a new
3: // get course offerings(forSemester) schedule 4: // get course offerings( ) A list of the available
5: // display course offerings( ) course offerings for this semester are displayed A blank schedule
6: // display blank schedule( ) is displayed for the students to select offerings ref Select Offerings ref Submit Schedule 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 4
Maintaining Consistency: What to Look For ❖ In order of criticality
❖ Redundant responsibilities across classes
❖ Disjoint responsibilities within classes
❖ Class with one responsibility
❖ Class with no responsibilities
❖ Better distribution of behavior
❖ Class that interacts with many other classes 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 5 Content
❖ Responsibility of analysis class
❖ Attributes and Associations of analysis class ❖ Unify Analysis Classes ❖ Checkpoints 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 6 Finding Attributes
❖ Attributes are used to store information. They are atomic things with no responsibilities. <> ClassName ❖ Finding Attributes Attribute : Type = InitValue Attribute : Type = InitValue ❖ Attribute : Type = InitValue
Properties/characteristics of identified classes
❖ Information retained by identified classes <> CourseOffering
❖ “Nouns” that did not become classes number : String = "100" startTime : Time
❖ Information whose value is the important thing attribute endTime : Time days : Enum
❖ Information that is uniquely "owned” by an object numStudents : Int
❖ Information that has no behavior 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 7
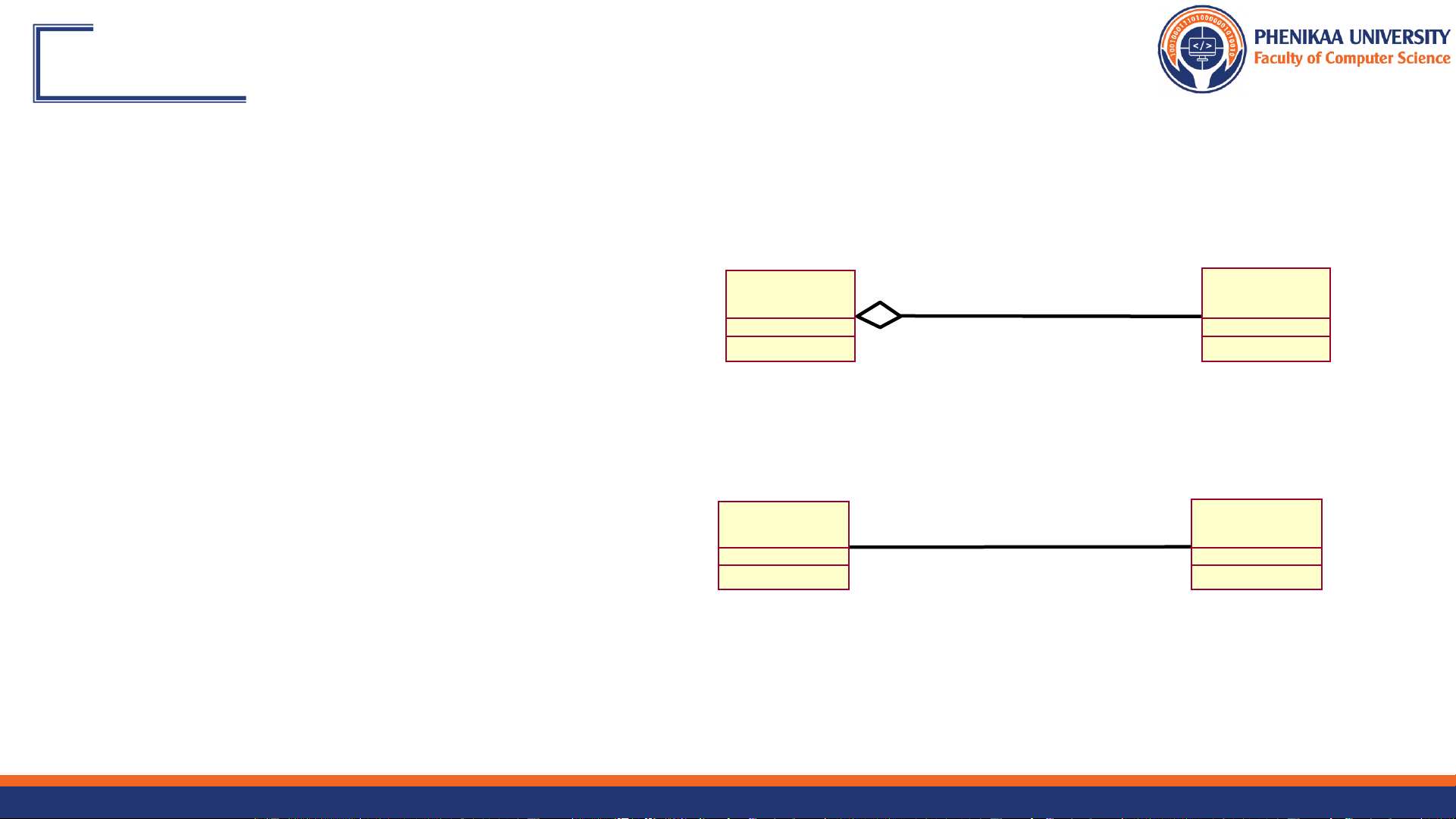
Review: What Is an Association?
❖ The semantic relationship between two or more classifiers that
specifies connections among their instances
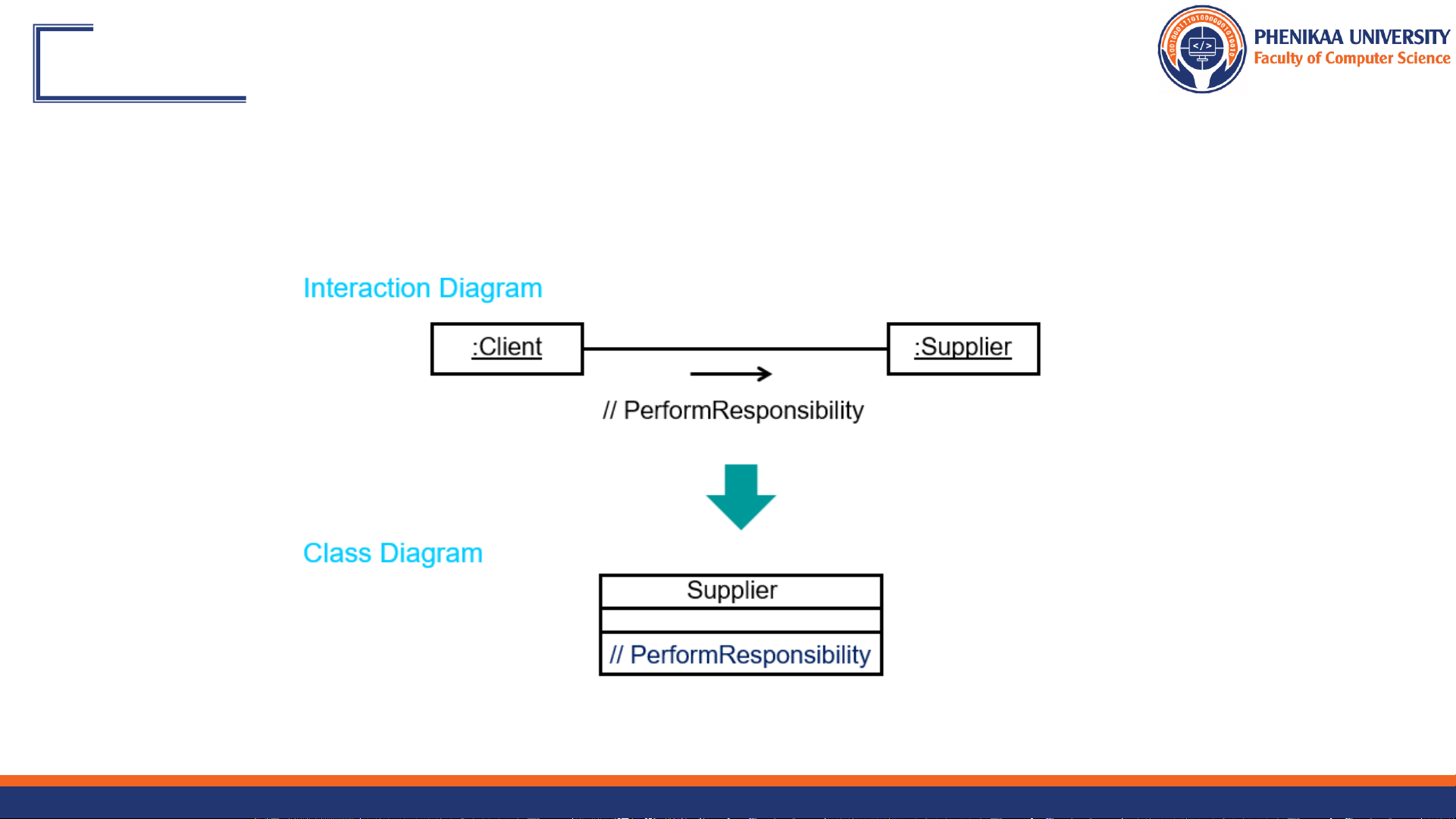
❖ A structural relationship, specifying that objects of one thing are connected to objects of another <> <> <> Student Schedule Course 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 8 Finding Relationships Communication Diagram PerformResponsibility :Client :Supplier Link Client Supplier Class Diagram Client 0..* 0..* Supplier PerformResponsibility() Association Relationship for every link! 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 9
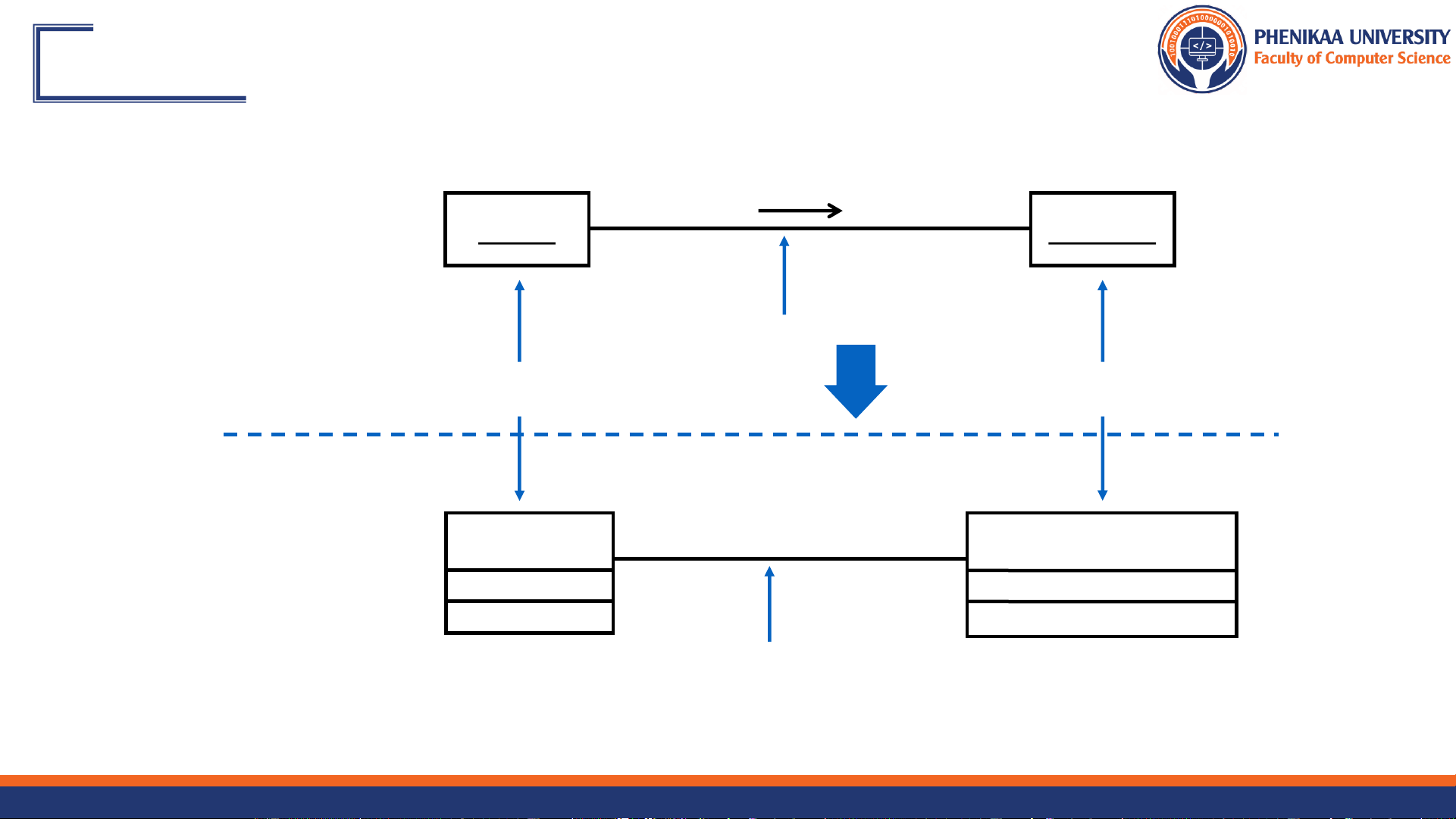
Review: What Is Aggregation?
❖ A special form of association that models a whole-part relationship
between an aggregate (the whole) and its parts Whole/aggregate Part <> <> <> 0..* 0..2 Student Schedule CourseOffering 1 0..* 1 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 10
Association or Aggregation?
❖ If two objects are tightly bound by a whole-part relationship
❖ The relationship is an aggregation. Car Door 1 0..2,4
❖ If two objects are usually considered as independent, although they are often linked Car Door
❖ The relationship is an association. 1 0..2,4
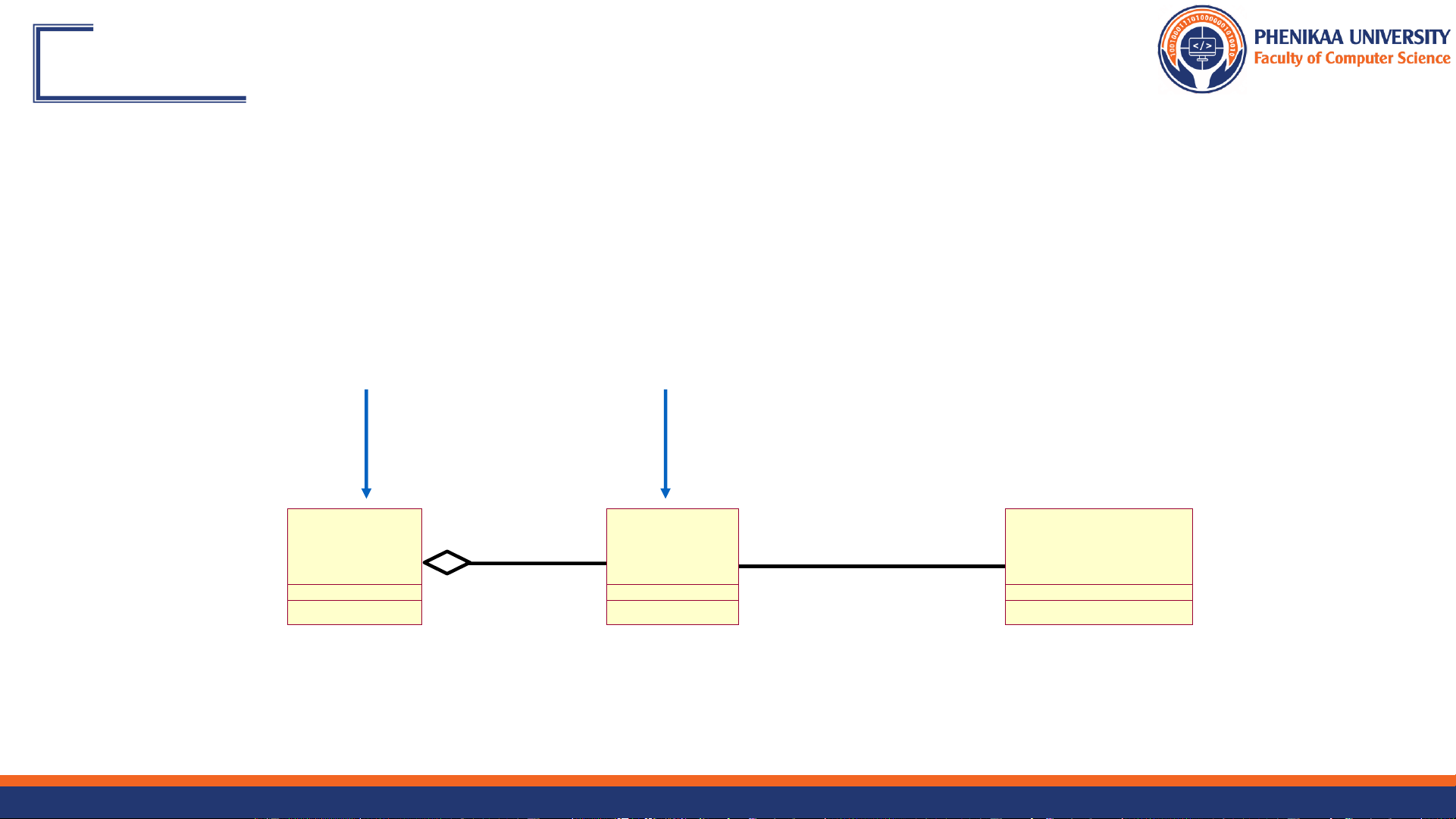
When in doubt, use association. 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 11 What Are Roles?
❖ The “face” that a class plays in the association <> <> <> CourseOffering Instructor Professor Department Department Head Role Name <> Course Prerequisites 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 12
What Does Multiplicity Mean?
❖ Multiplicity answers two questions:
❖ Is the association mandatory or optional?
❖ What is the minimum and maximum number of instances that can be linked to one instance? <> <> 0..* 1 CourseOffering Course 0..* Prerequisites 0..3 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 13
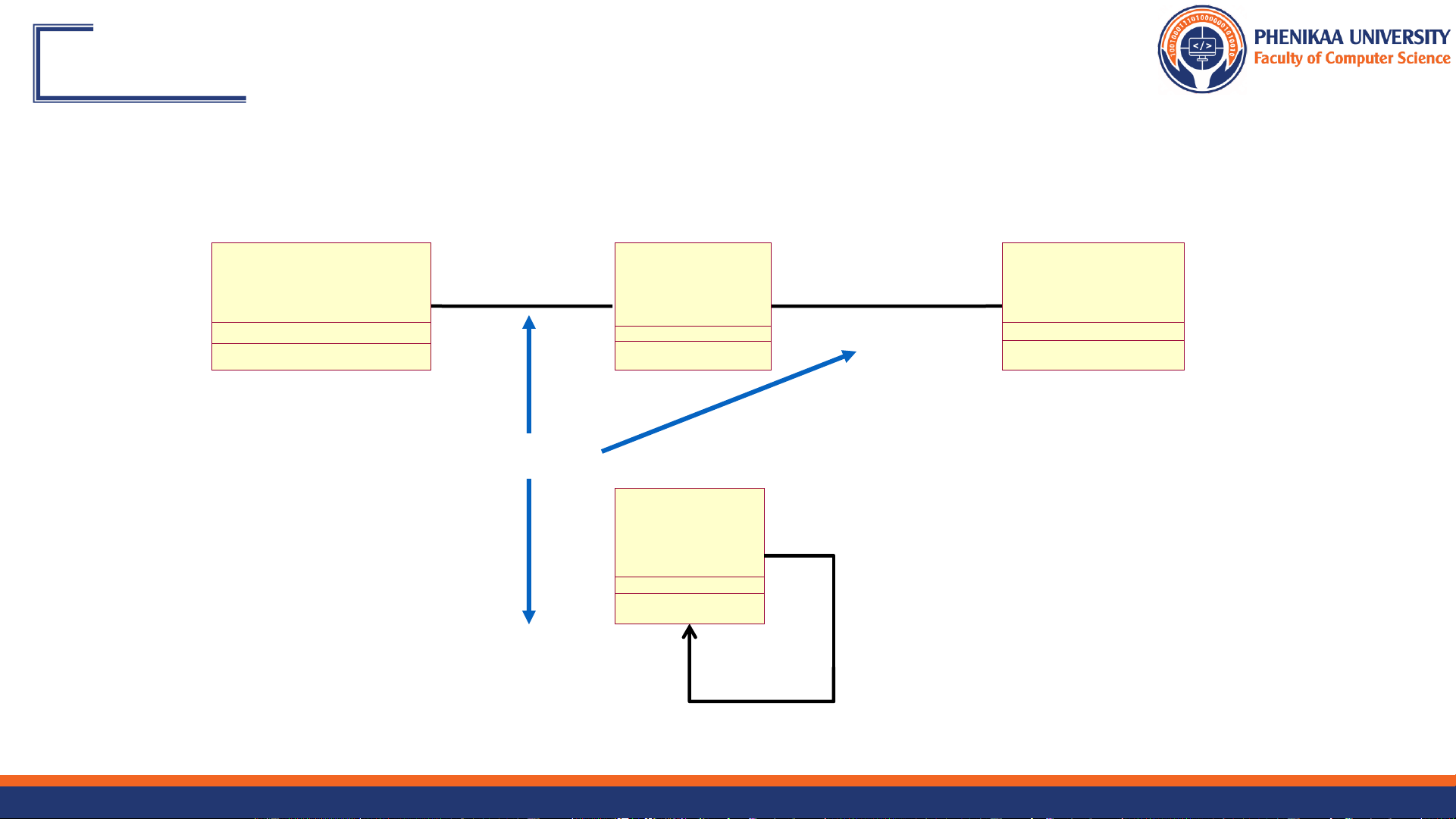
Example: Finding Relationships <> <> RegisterForCoursesForm RegistrationController 1 1 0..1 currentSchedule 0..1 <> <> <> primaryCourses Student Schedule CourseOffering 1 0..* 0..* 0..4 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 14 Content
❖ Responsibility of analysis class
❖ Attributes and Associations of analysis class ❖ Unify Analysis Classes ❖ Checkpoints 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 15
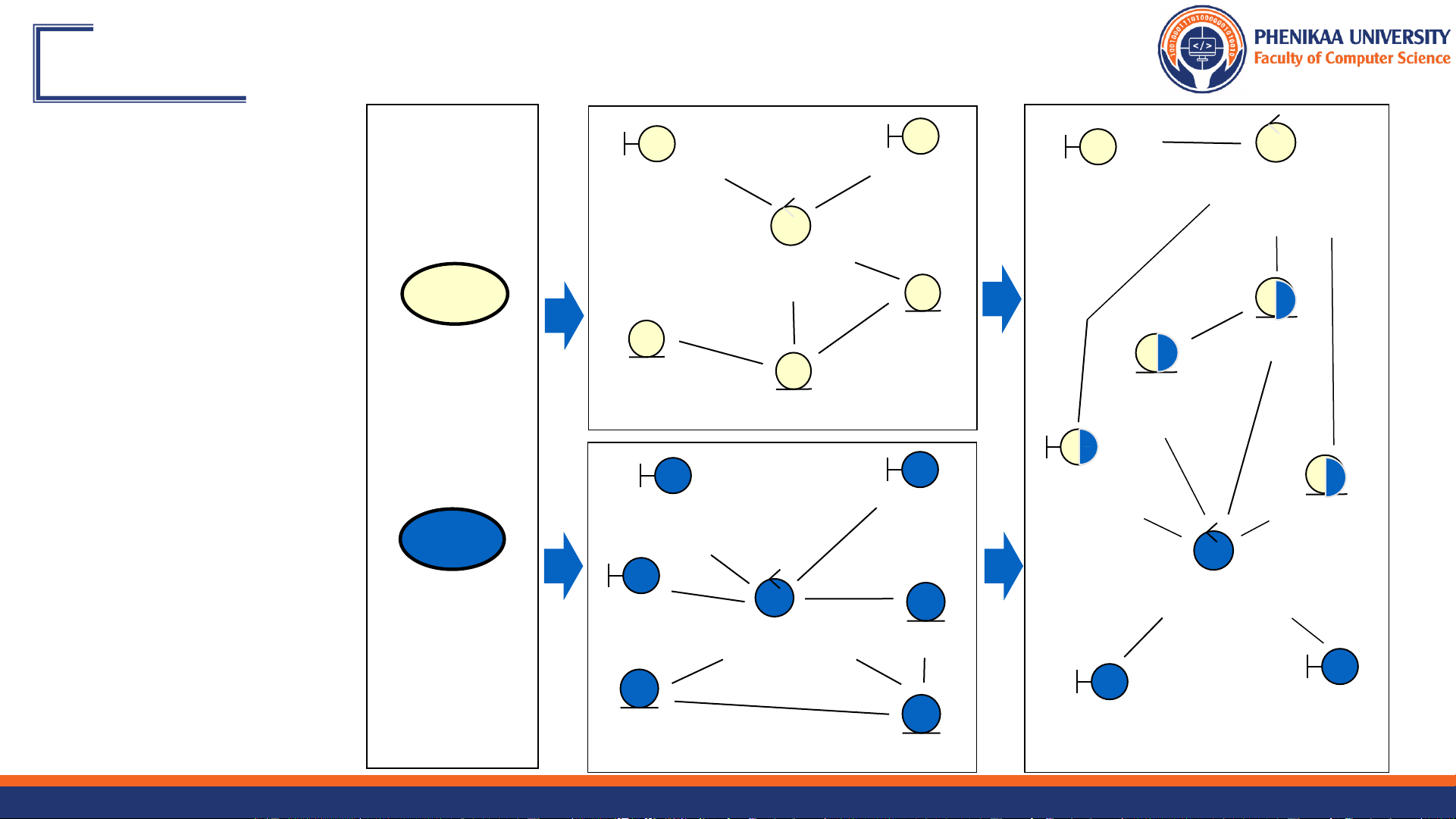
Unify Analysis Classes (Hợp nhất lớp phân tích) Course RegisterFor RegisterFor Registration Catalog CoursesForm CoursesForm Controller System Registration Controller Student Student Register for Courses Course Offering Course Schedule Offering Course CloseRegistration Course Catalog Schedule Form Catalog System System Close Registration CloseRegistration Billing Controller System CloseRegistration Student Controller Course CloseRegistration Offering Form Schedule 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 16 Evaluate Your Results Glossary Design Model Supplementary Specification Use-Case Model Analysis Classes 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 17 Content
❖ Responsibility of analysis class
❖ Attributes and Associations of analysis class ❖ Unify Analysis Classes ❖ Checkpoints 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 18
Checkpoints: Analysis Classes
❖ Are the classes reasonable?
❖ Does the name of each class clearly reflect the role it plays?
❖ Does the class represent a single well-defined abstraction?
❖ Are all attributes and responsibilities functionally coupled?
❖ Does the class offer the required behavior?
❖ Are all specific requirements on the class addressed? 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 19
Checkpoints: Use-Case Realizations
❖ Have all the main and/or sub-flows been handled, including exceptional cases?
❖ Have all the required objects been found?
❖ Has all behavior been unambiguously distributed to the participating objects?
❖ Has behavior been distributed to the right objects?
❖ Where there are several Interaction diagrams, are their relationships clear and consistent? 9/27/2024 Faculty of Computer Science 20



