


Preview text:
CÂU HỎI ÔN TẬP CUỐI KỲ
1. What are the reasons of the port management reform? (Trình bày nguyên nhân cải
cách hệ thống cảng biển?) Containerization. Multimodal transport.
Mechanization and automation of loading and unloading in ports.
Reduce the workforce in the port.
The tendency of movement to the estuary to ensure the draft of the ship.
The number types of ship is increasing.
2. Describe different type of port cost. Provide the example of each (Mô tả các chi phí cảng biển. Cho ví dụ)
Service costs of a seaport are the expenses that the port has to spend when operating the
port to provide services to customers.
Port service activities are divided into 3 main groups as follows:
Group 1: Services related to port waters. These are services related to the port
access such as buoy and mooring services, berthing, pilotage, push-pull service and ship offloading;
Group 2: Services related to port land. Including cargo handling services, port crane
rental as well as other port facilities and equipment, warehousing services;
Group 3: Delivery services. Including activities of loading goods onto shippers'
vehicles, transferring goods to the CFS (container freight station) for
packing/unloading of containers, moving goods in/out of the warehouse and other port transportation services. Short term cost: •
It is not advisable to change many resources at once in the short term. •
In the short term, wharfs and factory offices, for example, can be permanent
resources. Port operators have enough time in the long run to change resources,
such as considering berth expansion or building more offices and factories. •
Port costs associated with fixed port resources are the port operator's fixed costs
when operating the port (FC) (These costs do not change as the throughput changes. ). •
The opposite is known as port variable cost (VC). Now, the port operator's total
short-run cost, STC, for throughput is Q. Long term cost:
Long-term costs for all port operators are volatile. The figure below depicts the total long-
term cost (LTC) of the port operator as the volume of cargo passing through the port
changes. LTC divided by Q yields the port operator's long-run average total cost (LATC).
The operator's long-run marginal cost is the additional cost of the total long-run cost as
throughput increases by one unit.
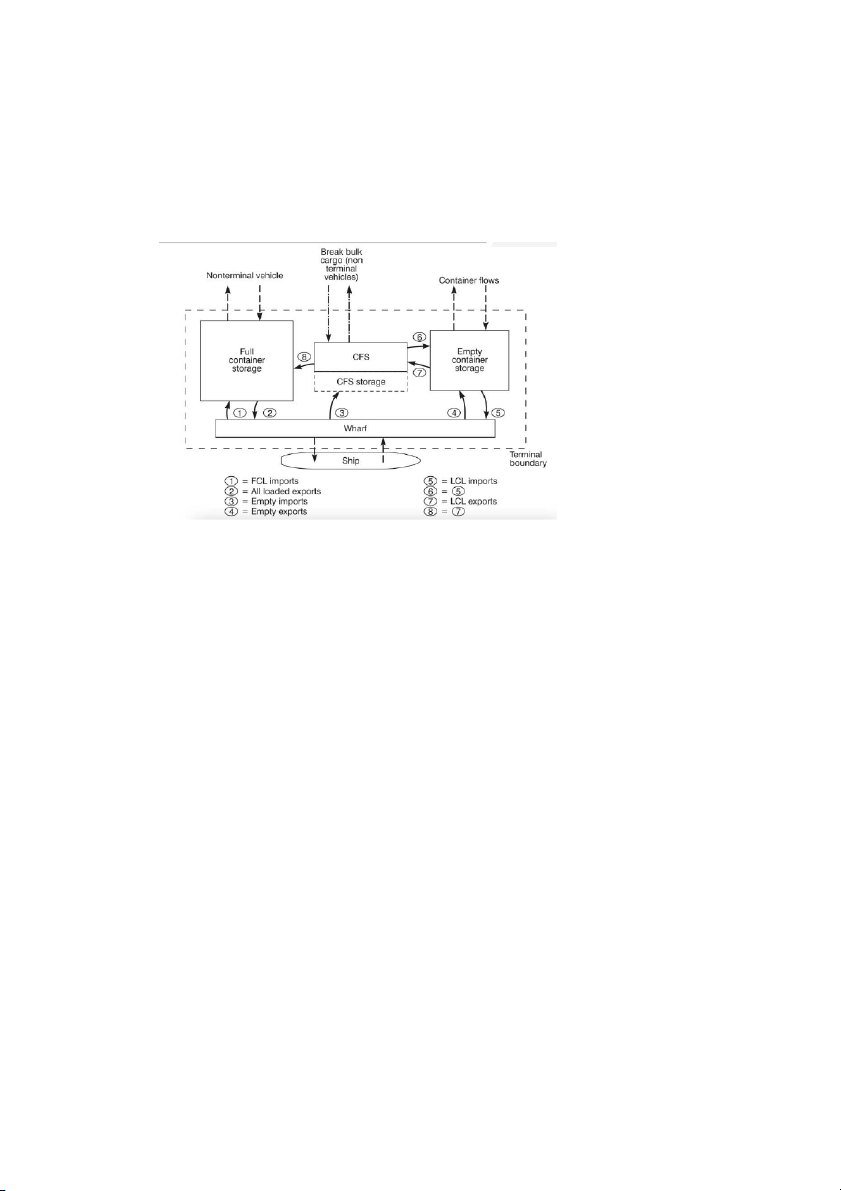
3. Draw the container port layout (Vẽ sơ đồ cảng container)
4. Explain how the government intervenes on the management and operations of
Vietnam seaports in terms of fire safety and environmental protection (Nêu vai trò
của chính phủ trong phòng chống an toàn cháy nổ và bảo vệ môi trường)
- The Director of the Maritime Port Authority is responsible for coordinating with the
competent fire prevention and fighting agency in the area under his/her management.
Develop the necessary fire prevention plan for the ship's operation.
- The Director of the Port Authority is responsible for directing rescue operations for ships
caught fire or explosion in the seaport waters until the competent commander of the full
time fire and explosion prevention and fighting force has the authority to do so. present at the scene.
- The director of the port enterprise is the person responsible for directing the response to
fire and explosion incidents occurring in the port area until the competent commander of
the fulltime fire and explosion prevention and fighting force is present.
5. The responsibilities of the captain when loading and unloading goods, repairing,
and cleaning ships in seaport waters (Trách nhiệm của thuyền trưởng trong quy trình
chấp xếp, xếp dỡ hàng hóa, sửa chữa tàu biển)
- Before carrying out activities of loading and unloading cargo, and repairing and cleaning
ships, the captain is responsible for preparing necessary conditions for maritime safety,
and labour safety protection and must comply with the regulations. Strictly comply with
the relevant provisions of the law.
- The captain is only allowed to close the hatch cover or let people into the hold after
checking and making sure that no unforeseen situation occurs.
- During the course of the ship’s loading and unloading, if detecting signs of unsafety, the
master or operator of cargo loading and unloading activities must immediately suspend work for handling.
- When an occupational accident occurs on board the ship, the master must quickly
organize first aid for the victim, take necessary measures to limit subsequent
consequences and immediately notify the Port Authority; at the same time, perform the
declaration, investigation, record-making, statistics and report on occupational accidents
according to the provisions of the labour law.
6. Design standard and objectives of container port (Tiêu chuXn thiết kế và mục đích của cảng container) Design standard:
- The capacity of a container terminal is usually measured in terms of the number of
containers that can be handled by the terminal per year. Since containers come in two
standard sizes – 20 feet and 40 feet respectively-the capacity is usually expressed in terms
of 20-ft, container equivalents called TEU.
- Container Terminals May Serve:
Mainline transocean vessels 230 to 250 m. long (11,0 to 12,8 m, Draft), with a
carrying capacity of 1.800 to 4.200 TEUs.
Mainline secondary service with 200 to 230 m. long and 10,0 to 11,2 draft vessels
with a carrying capacity of 750 to 1.800 TEUs.
Container feeder vessels or barges, used in coastal intraportal feeder service 120 m.
to 150 m. long, 7-8 draft, with a carrying capacity of 150 to 500 TEUs. Function container port: Transportation
Commercial and industrial functions
Loading and unloading container cargo from marine transport means to other means of transport.
Storing, packing and preserving container cargo.
Stevedoring cargo between means of transport.
Provided ship with food, water, and fuel. Rescue and refuge for ships.
Provided technical inspection and ship repair services.
7. Government regulations on seaport (Nai dung quản l礃Ā nhà nưcc về cảng biển)
The relevant Ministries, branches and People's Committees of the provinces and
centrally-run cities are responsible for directing and guiding the operation of
specialized state management agencies to perform well the coordination. State
management activities at seaports.
Examine, inspect and strictly handle violations in accordance with the law.
Implement the application of information technology to management activities to
ensure favourable and effective conditions for maritime activities at seaports and navigational channels.
8. Numbering on container ships (Hệ thống đánh số vi trí chất xếp trên tàu container)
This system identifies the position of each container on board by a 6-digit code in the order: Bay - Row – Tier
Bay: denoted by the first 2 numbers of the code, indicating the position of the
container lined up vertically of the ship, numbering increasing from the bow to the
stern. Containers of 20' type: numbered 01; 03; 05... Containers of 40' type:
numbered 02; 04; 06... The "Fly" code of the 40' container is the even number
between the two odd numbers identifying the two 20' containers that it occupies.
Row: is indicated by the middle 2 numbers of the code, indicating the position of
the container lined up horizontally of the ship, numbered increasing from the
middle of the ship to the 2 sides. Containers on starboard side, numbered: 01; 03,
05... Containers on port side, numbered 02; 04; 06...Container in the middle, numbered 00.
Tier: indicated by the last 2 digits of the code, indicating the container position
according to the stacking height on the ship. In the basement: number 02; 04; 06...
from the bottom layer upwards. On deck: numbered 82; 84; 86...from the first layer on deck and above.




