





Preview text:
MIDTERM 2
11. True. Market order is an order to buy/sell a security at the best price currently available
13. False. Matching price in June 8, 20XY is 31.8
=> The floor price of HOSE in June 9th equals: 31.8 x (1 – 7%) = 29.57
However, tick size= 50 => Floor price = 29.55 not 32.582c
Exercise 1: Suppose that you sell short 100 shares of IBX, now selling at $70 per share
a. What is your maximum possible loss?
b. What happens to the maximum loss if you simultaneously place a stop-buy order at $78?
a, The price increasing → → the loss is increasing →
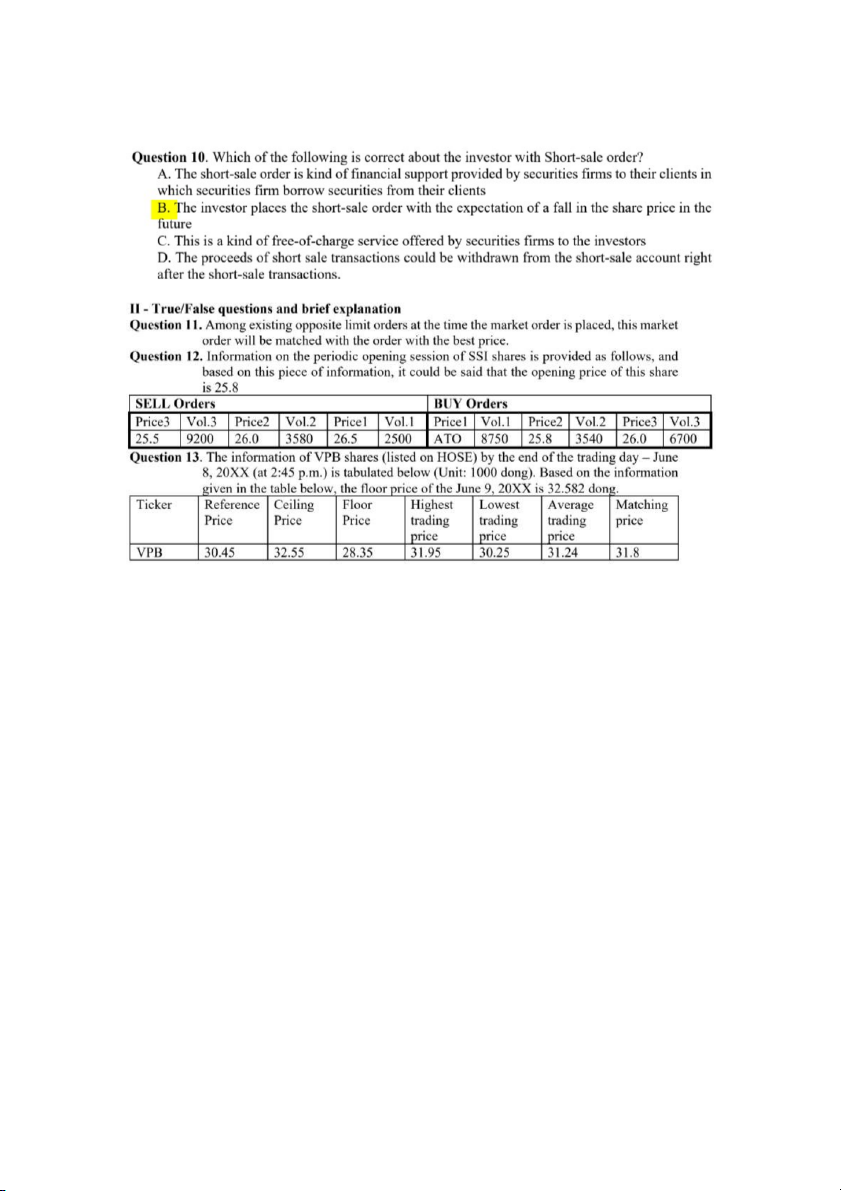
b) The maximum loss: (70-78) x100 = -800
Exercise 2: Dee Trader opens a brokerage account and purchases 300 shares of Internet Dreams at
$40 per share. She borrows $4,000 from her broker to help pay for the purchase. The interest rate on the loan is 8%.
a. What is the margin in Dee’s account when she first purchases the stock?
b. If the price falls to $30 per share by the end of the year, what is the remaining margin in her
account? If the maintenance margin requirement is 30%, will she receive a margin call?
c. What is the rate of return on her investment?
a) Investment value: 40 x 300 = 12,000 Loan = 4,000
→ Initial margin = Investment value – Loan = 12,000 – 4,000 = 8,000
b) At the end of the year, price fall to 30 per share
Current investment value = 30 x 300 = 9,000 Loan = 4,000
Current margin = Current investment value – Loan = 9,000 – 4,000 = 5,000
Current margin rate = x 100% = 55.56% > maintainance margin = 30%
→ She will not receive a margin call b) ROR = x 100% = -37.5% Cách tính khác: ROR = =
Bản chất ROR là lấy giá trị final value – initial value rồi chia cho initial valur
Exercise 3: Old Economy Traders opened an account to short sell 1,000 shares of Internet Dreams
from the previous problem. The initial margin requirement was 50%. (The margin account pay no
interest). A year later, the price of Internet Dreams has risen from $40 to $50, and the stock has
paid a dividend of $2 per share.
a. What is the remaining margin in the account?
b. If the maintenance margin requirement is 30%, will Old Economy receive a margin call?
c. What is the rate of return on her investment?
a. Initial short sale value = 40 x 1,000 = 40,000
Initial margin = 40,000 x 50% = 20,000
Total deposit = Initial short sale value + Initial margin = 20,000 + 40,000 = 60,000
Current value of borrowed share = 50 x 1,000 = 50,000
Current margin = Total deposit - Current value of borrowed share = 60,000 – 50,000 = 10,000
b. Current margin rate = x 100% = 20% < maintenance rate = 30%
→ Trader will receive a margin call c. Rate of return: ROR =
Exercise 5: You have borrowed $20,000 on margin to buy shares in Disney, which is now selling at
$40 per share. Your account starts at the initial margin requirement of 50%. The maintenance
margin is 35%. Two days later, the stock price falls to $35 per share.
a. Will you receive a margin call?
b. How low can the price of Disney shares fall before you receive a margin call? a) Loan = 20,000
Giải thích: Initial margin + Loan = Investment value. Mà Initial margin requirement là 50% => Loan cx
chiếm 50% => Có Loan tính được Investment value
Investment value = 20,000 : 0.5 = 40,000. Meanwhile, cost of share = 40 => Number of share = 1,000 shares Initial margin = 20,000
When stock price falls to $35, Current investment value = 1,000 x 35 = 35,000
Current margin rate = x 100% = 42.8% > maintenance rate = 35%
(Remaining margin = Current investment value – Loan ) → No margin call
b) Receive margin call when: Current margin rate < Maintenance margin rate
= x 100% < 35% ↔ P < 30.77
Exercise 7: FBN, Inc.., has just sold 100,000 shares in an initial public offering. The underwriter’s
explicit fees were $70,000. The offering price for the shares was $50, but immediately upon issue
the share price jumped to $53.
a. What is your best guess as to the total cost to FBN of the equity issue?
b. Is the entire cost of the underwriting a source of profit to the underwriters? Explicit cost = 70,000
Loss from undervaluing = 53 – 50 = 3 per share
Implicit cost = 3 x 100,000 = 300,000
→ Total cost = 300,000 + 70,000 = 370,000
b) This is a classical example of the Principle Agent problem Moral Hazard, can not verify effort
undertaken by the agent, the underwriter’s research effort
Exercise 8: You are looking to investment securities by involving with the purchase of shares listed
on the market. You go to the securities company and open a trading account and deposit $7,000.
You plan to buy shares VNM.
a. On 12/12/2010, the stock price of VNM is $8.5 per share, if you want to buy 1000 shares VNM, what do you do?
b. Suppose that ten days later the share price of VNM decrease to $6 per share. Will you receive a
margin call? What happen if you don’t meet the margin call? Assuming that:
- Maintenance margin is 80%
- Brokerage fees are 0.3% of transaction value
- Interest rate is 0.1% / day
a) Investment value = 1,000 x 8.5 = 8,500
Initial margin = Investment value – deposit = 8,500 – 7,000 = 1,500
→ Because You want to buy shares → Deposit 7,000 into the Buy-on-margin account and make a loan of 1,500
b) After 10 days, share price pf VNM decrease to 6
Current investment = 6 x 1,000 = 6,000
Current margin = Current investment – Initial margin = 6,000 – 1,500 = 4,500
Current margin rate = x 100% = 75% < Maintenance margin = 80% → Receive the margin call
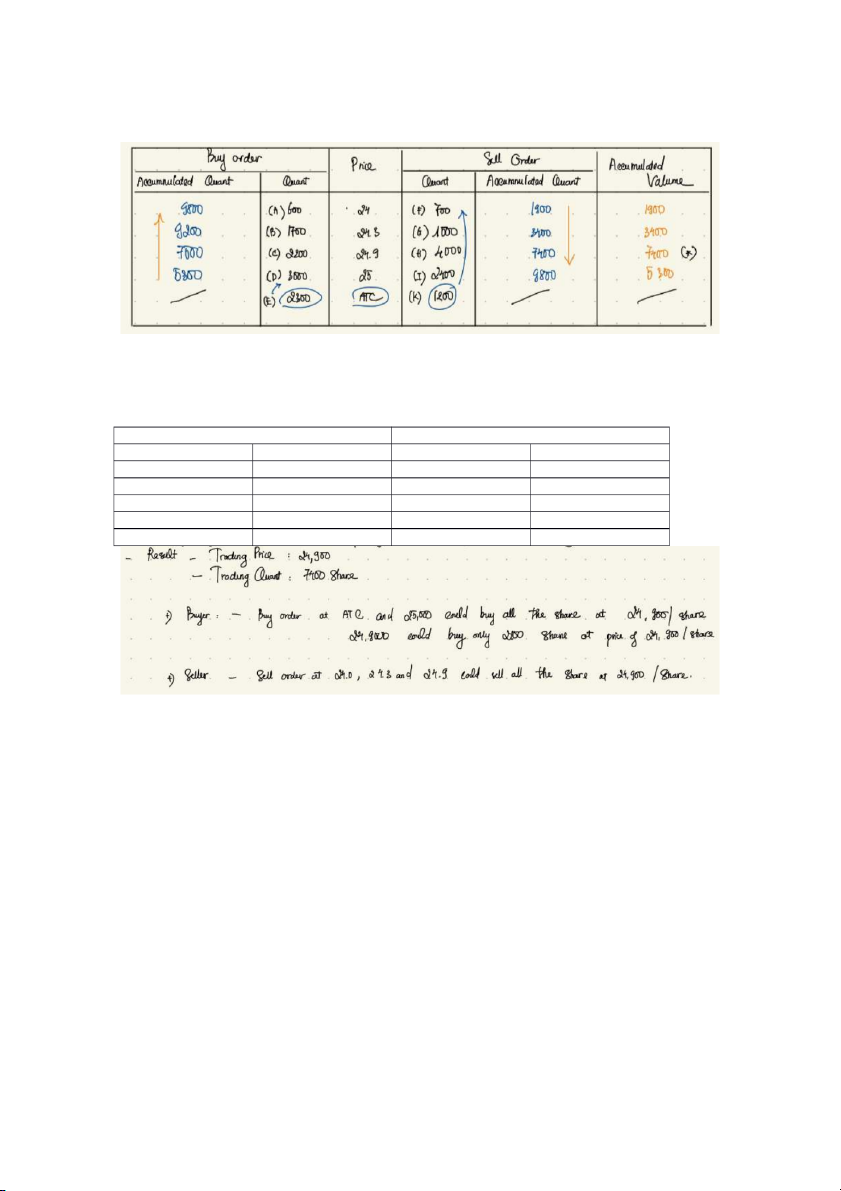
Exercise 9: Assume that the last execution price before the call market period of that day was
24.000 VND, the trading system selected period of 14:30 – 14:45 as the closing session, and at that
time, there were orders of stock XYZ as below. Determine the closed price of XYZ company stock?
a. Determine the trading result? Accumulated Quantity Quantity Accumulated Tradable Price quantity (buy) (sell) quantity quantity - 2,300 (E) ATC 1,200 (K) - - 2,300 + 3,000 7,400 + 2,400 3,000 (D) 25,000 2,400 (I) 5,300 = 5,300 = 9,800 5,300 + 2,200 3,400 + 4,000 2,200 (C) 24,900 4,000 (H) 7,400 = 7,500 = 7,400 7,500 + 1,700 1,900 + 1,500 1,700 (B) 24,300 1,500 (G) 3,400 = 9,200 = 3,400 9,200 + 600 = 1,200 + 700 = 600 (A) 24,000 700 (F) 1,900 9,800 1,900
Price: lớn bé; ATC lớn nhất
Buy: cao thấp
Sell: thấp cao
- At the price of 24,900, the volume of tradable quantity is highest with 7,400 closing price = 24,900 - The trading results: Buying Selling Investor Amount Investor Amount E 2,300 K 1,200 D 3,000 F 700 C 2,100 G 1,500 H 4,000 total 7,400 total 7,400
b. Calculate the brokerage fee of investor K and investor E. The brokerage fee rate is 0,35%.
Fee of K = (1,200 x 24,900) x 0.35% =
Fee of E = (2,300 x 24,900) x 0.35% =
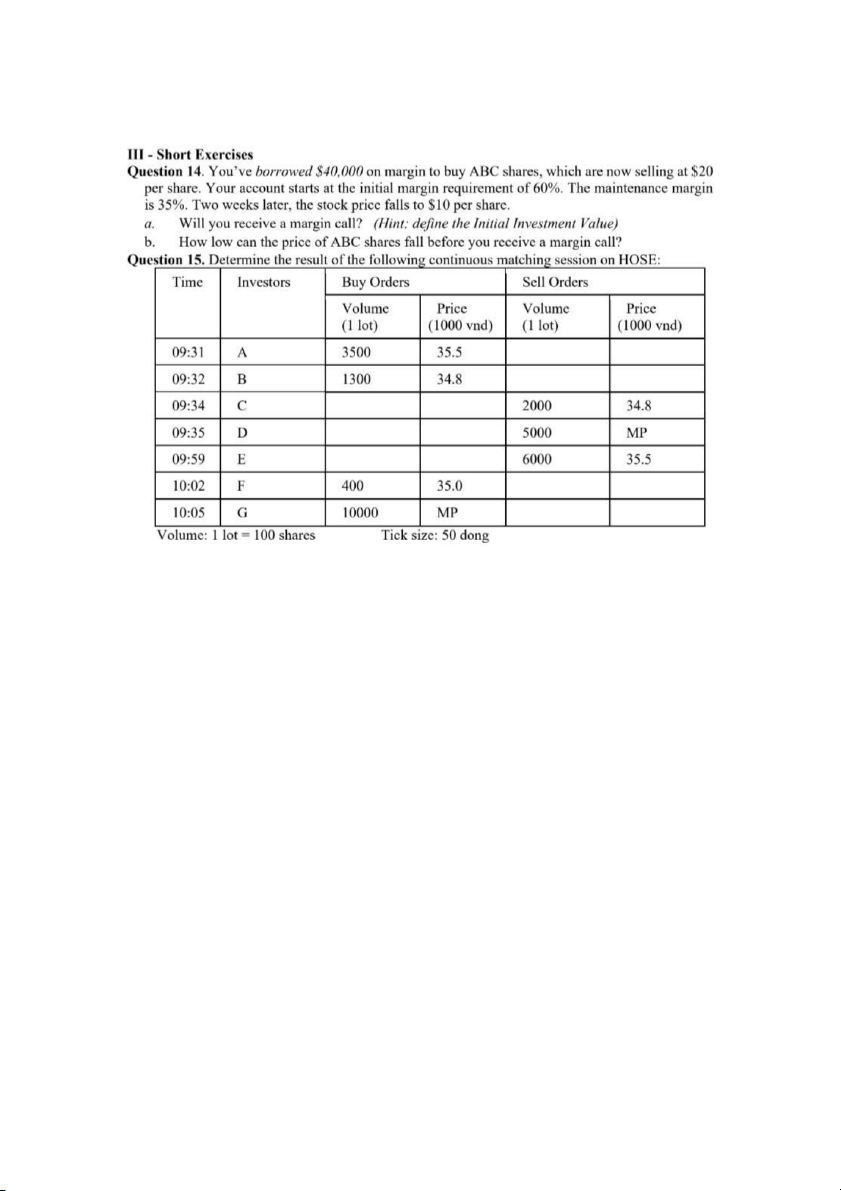
Exercise 10: Assume that during the morning trading section, the trading system receive orders of
stock ABC as below. Based on continuous orders matching, determine the results of this stock Time Investor Buying Price Selling Price quantitative quantitative 09:16 A 3,000 35.5 09:17 B 1,000 35 09:18 C 2,500 35.4 09:19 D 3,000 35.6 09:20 E 3,200 MP → Answer Matching Remaining BUY order Remaining SELL order (09:16) No transaction A (3,000 – 35.5)
(09:17) B – A ( 1,000 – 35.5) A (2,000 – 35.5)
(09:18) C – A (2,000 – 35.5) C (500 – 35.4)
(09:19) C – D (500 – 35.6) D (2,500 – 35.6)
(09:20) E – D (2,500 – 35.6) E (700 – [35.6 – 0.05]) → E (700 – 35.65)
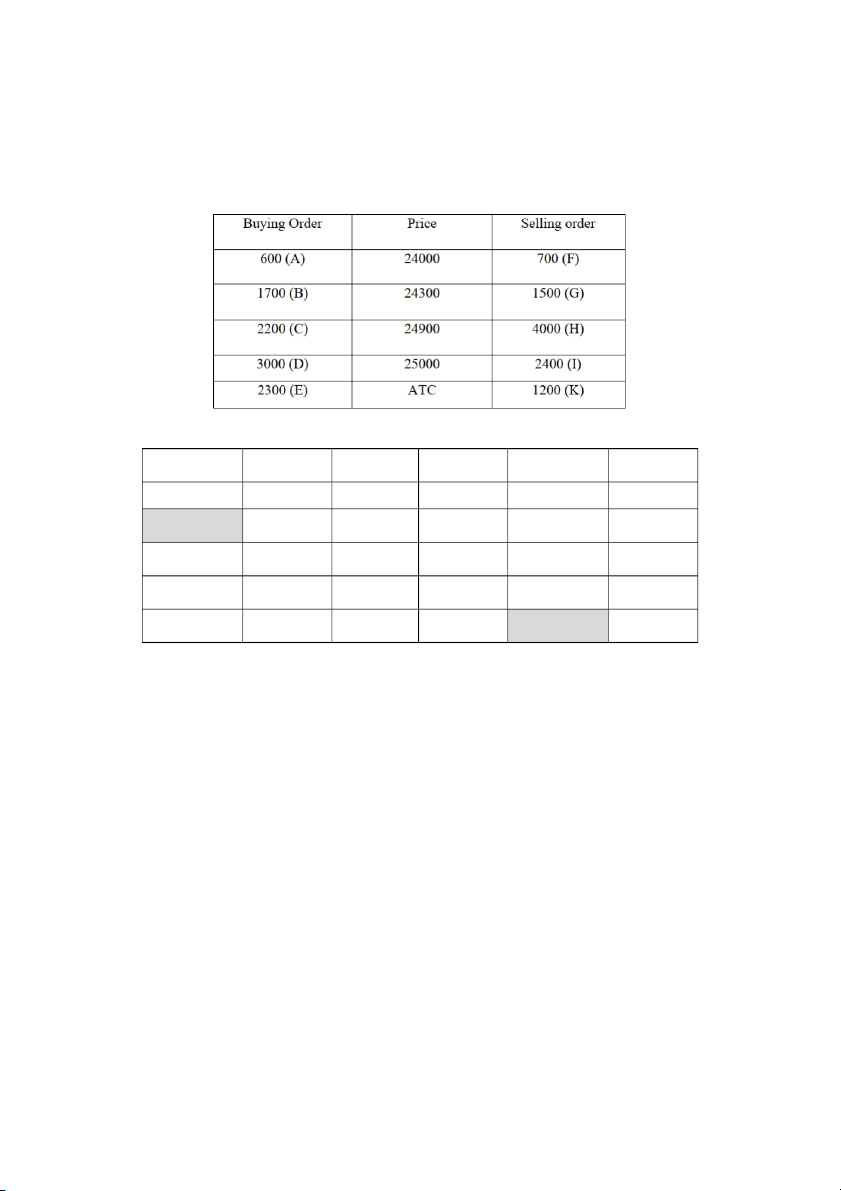
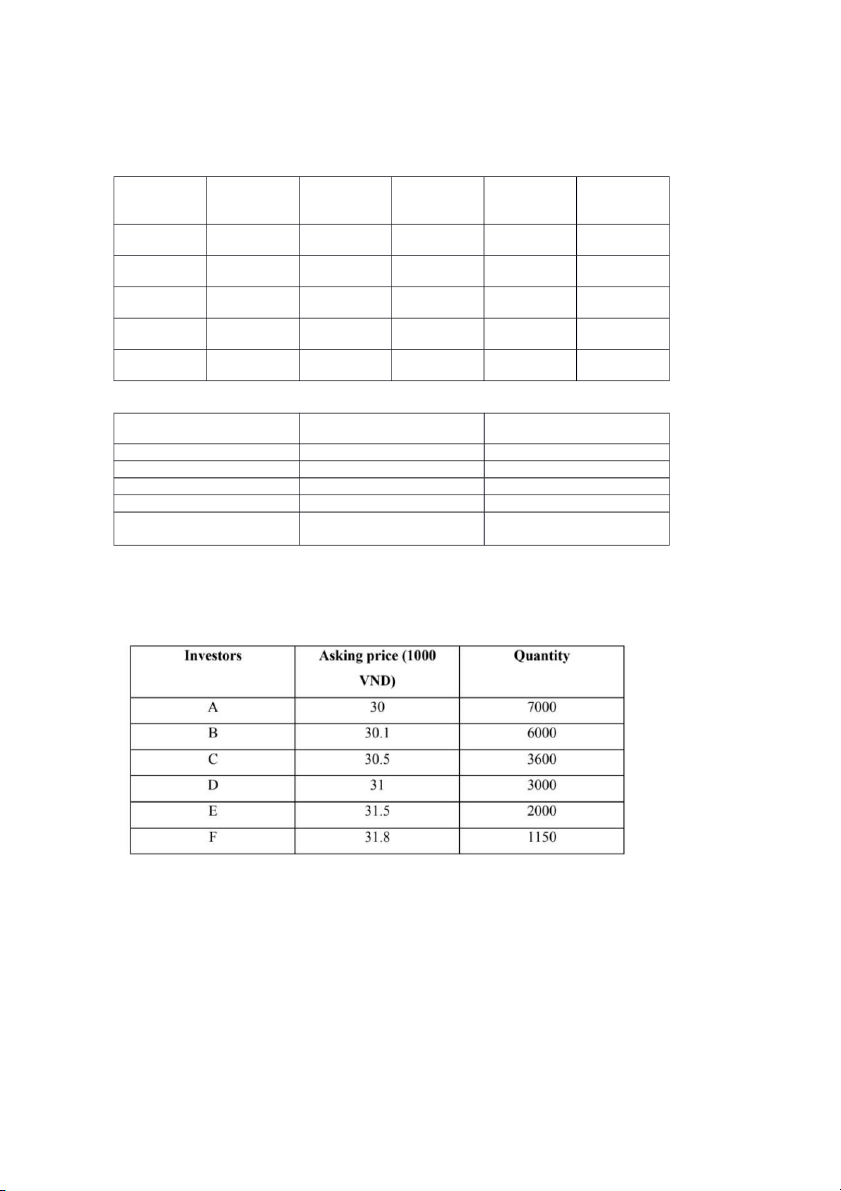
Exercise 11. Joint- stock company A announces they will issue 18000 new shares by multi-price
share auction. Starting price is 30000/share.
All information about price and quantity of each investor is as follow
a. Determine investors who success in this share auction and the price and quantity they could buy
b. Determine the average price Investor Asking price Quantity Accumulated Quantity F 31.8 1,150 1,150 E 31.5 2,000 3,150 D 31 3,000 6,150 C 30.5 3,600 9,750 B 30.1 6,000 15,750 A 30 7,000 22,750
At the price of 30, company could issue all 18,000 shares Result of the auction Winning investor F E D C B A Winning quantity 1,150 2,000 3,000 3,600 6,000 2,250 Winning price 31.8 31.5 31 30.5 30.1 30 b) Average price = x100% = 30,581
Exercise 12: An Dutch Bond Auction for raising 500 Billion Dong for Forever A Loan Corporation
is shown in the following table:
Name of Investors (Bidders) Interest rate(%) Auction volume A 0 100 B 7.35 250 C 7.4 150 D 7.5 70 E 7.55 300 F 7.85 80
a. Determine auction results (realized interest rates and volume for that auction and each bidder)
b. Does the 0% rate affect the result of the auction, try to explain why the investor bid 0% → Answer Investor Interest rate Auction volume Accumulated Quantity A 0 100 100 B 7.35 250 350 C 7.4 150 500 D 7.5 70 570 E 7.55 300 870 F 7.85 80 950
At the interest rate of 7.4, company could raise 500 billion dong Winning investor A B C Winning quality 100 250 150 Winning interest rate 0 7.35 7.4
b) The results will change. F offers the lowest interest rate of 0%, So that A will give the priority to buy
bonds. A will sell for F first, next is EDCBA and will stop when the value reaches the size of 500b dong
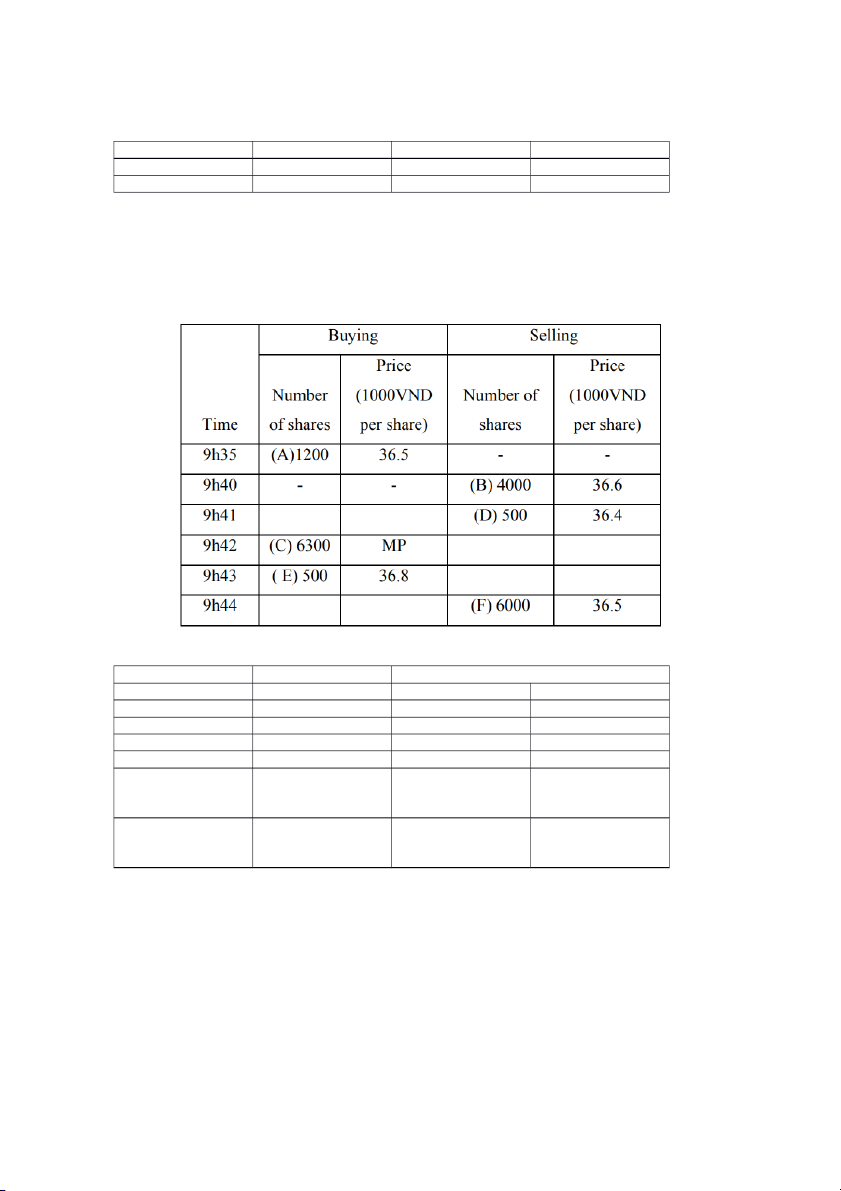
13. On Oct 16, 20X7, no-right trading day (the day that stock purchasers will has no rights related
to stocks bought on) of Cash-Dividend Payment with 20% paying rate, continuous trading data of
XYZ shares (HNX) is shown in the following table:
a) Determine the matching prices and trading volume for each time Time Results Remaining orders Buy Sell 9:35 No transaction A (1,200 – 36.5) 9:40 No transaction A (1,200 – 36.5) B (4,000 – 36.6) 9:41 D-A (500 – 36.5) A (700 – 36.5) B (4,000 – 36.6) 9:42 B-C (4,000 – 36.6) C (2,300 – 36.65) A (700 – 36.5) 9:43 No transaction C (2,300 – 36.65) E (500 – 36.8) F_E (500 – 36.8) 9:44 F_C (2,300 – 36.65) F (2,500 – 36.5) F_A (700 – 36.5)
Với lệnh MP: giá còn lại = buy +, sell -
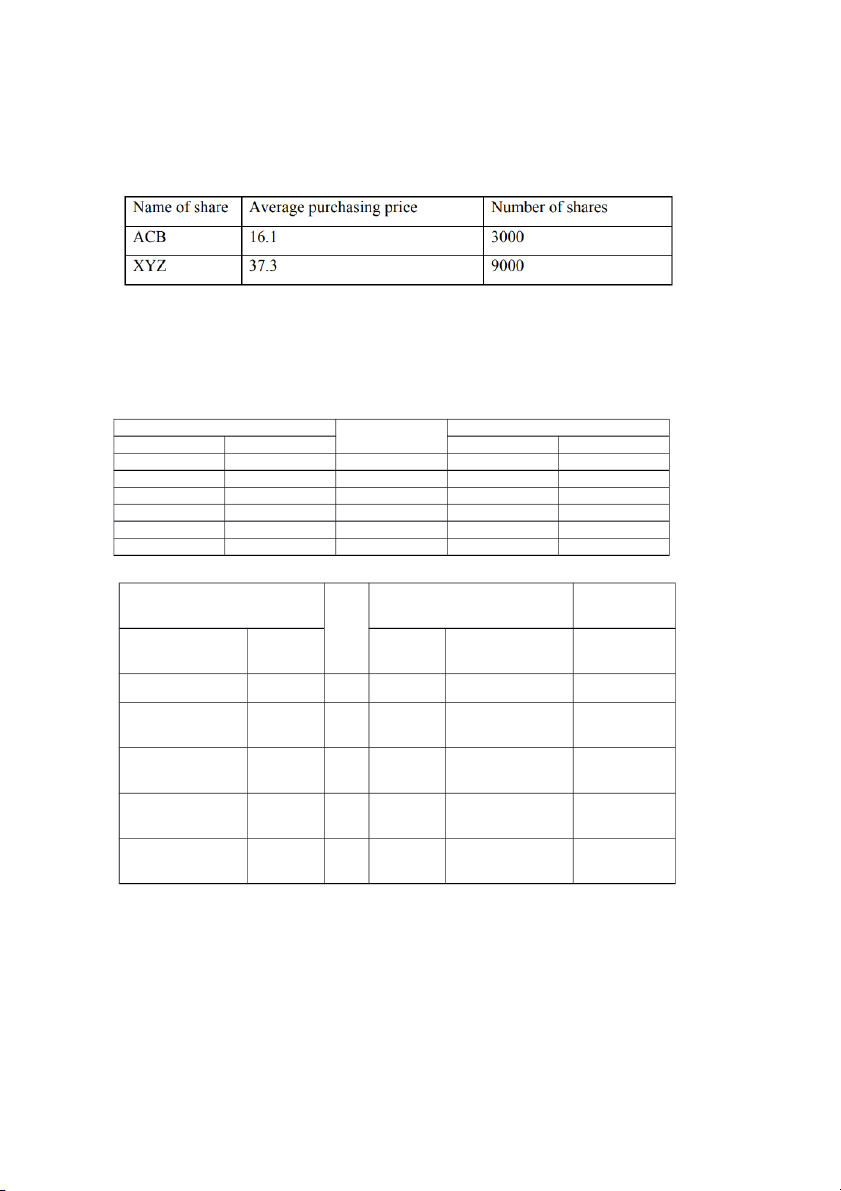
b) Providing that an investor’s trading account on Oct 15, 20X7 is detailed as follows,
determine cash dividends that investor would receive.
Dividend per share = 20% x 10,000 = 2,000 This investor holds: 9,000 XYZ
→ Total dividend = 2,000 x 9,000 = 18,000,000 dong
→ X would receive 18,000,000 VND
Exercise 15: A call auction database of XYZ shares is as following: Buying order Price Selling order Investors No. of shares No. of shares Investors A 3,500 ATO B 2,700 25.6 5,000 G C 1,300 25.8 2,800 H D 4,600 26 200 I E 4,000 26.2 0 F 800 26.5 1,200 K → Answer Buy Order Price Sell order Accumulaed value Accumulated Quantity Quantity Accumulated quantity quantity - A. 3,500 ATO - - - 14,200 + 1,300 = B. 2,700 25.6 G. 5,000 5,000 5,000 16,900 12,900 + 1,300 = C. 1,300 25.8 H. 2,800 5,000 + 2,800 = 7,800 14,200 7,800 8,300 + 4,600 = D. 4,600 26 I. 200 7,800 + 200 = 8,000 12,900 8,000 4,300 + 4,000 = E. 4,000 26.2 0 8,000 8,000 8,300 3,500 + 800 = 4,300 F. 800 26.5 K. 1,200 8,000 + 1,200 = 4,300 9,200
Ưu tiên giá ATO hoặc ATC , sau
Ưu tiên giá ATO hoặc ATC, sau Điền giá trị nào
đó đi từ giá cao đến giá thấp
đó đi từ giá thấp đến giá cao thấp hơn
At the price of 26 and 26.2, the tradable quantity reaches the highest of 8,000 shares
Since the closing price of previous trading day is 26.1 => Trading price of this opening session is 26.2
Principal: Lựa chọn giá nào gần với giá closing price nhất. Nếu chênh như nhau thì chọn giá cao hơn
=> Result: trading price = 26.2; trading quantity = 8,000
Buyer: Ưu tiên khớp các giá từ cao đến thấp đến khi hết mức trading quantity = 8,000
Buy order at the price of 26.5 could buy all the shares with price of 26.2 (khớp 4,300)
Buy order at the price of 26.2 could buy 3,700 shares with price of 26.2 (khớp 8,000 - 4,300 = 3,700)
Seller: Ưu tiên khớp các giá từ thấp đến cao đến khi hết mức trading quantity = 8,000
Sell order at 25.6, 25.8, 26 could sell all the shares at the price of 26,2/share.
( Giá 25.6 khớp 5,000 shares; 25.8 khớp 2,800 shares; 26 khớp nốt 200 shares là đủ 8,000)
Insert bảng The trading results
Exercise 16: Mekong Fisheries Joint Stock Company (AAM, listed on HOSE) announces its
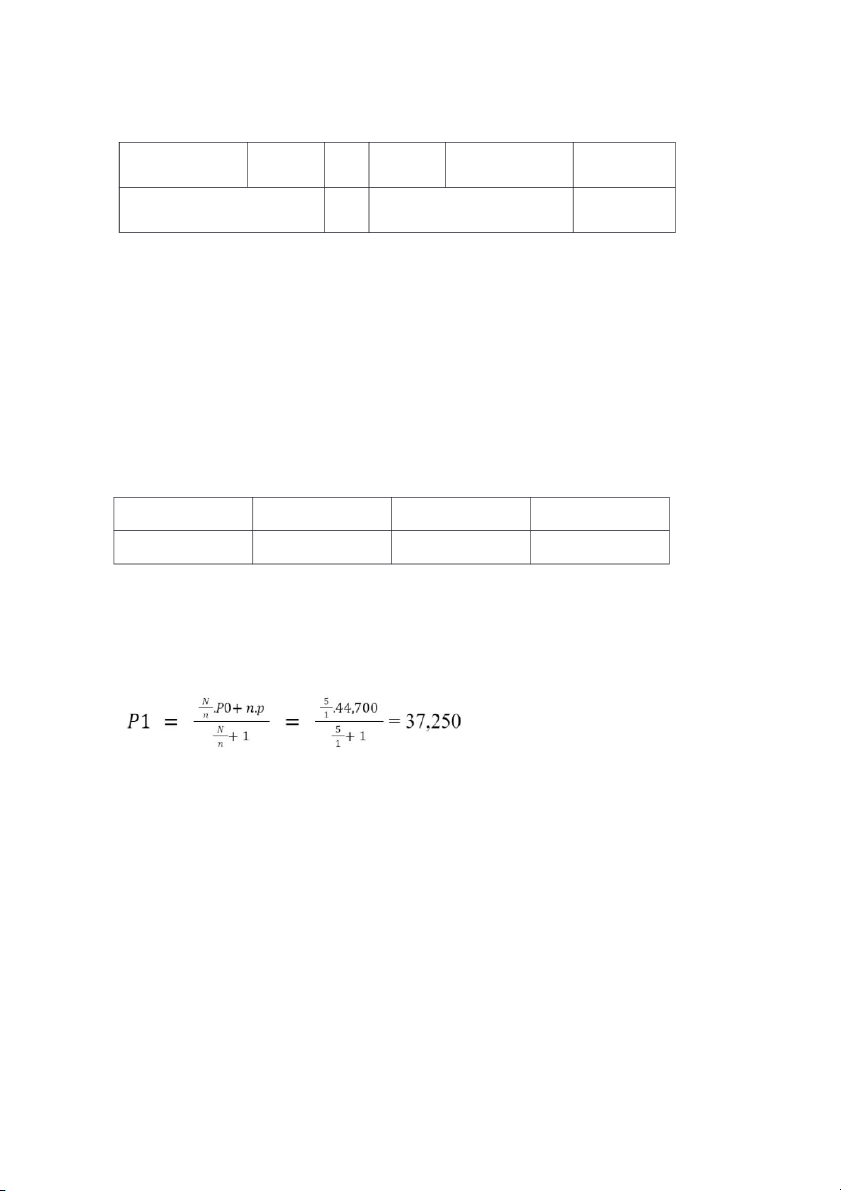
dividend payment policy for the year 2012 as following: Share Code Face Value Record Date Dividend payment ratio AAM VND 10,000 June 7, 2013 In cash: 30% In shares: 20%
Determine AAM’s market price on ex-date. Suppose that AAM’s closing-price on June 4, 2013 is
VND 44700, and the payment process of Vietnam’s stock market is T+3 Payment process is T+3
Dividend ratio: 20% => N/n = 5/1 Record date: June 7, 2013
Closing price on June 4, 2013 is 44,700 => P0 = 44,700
Policy of AAM is payment dividend of shares => Issuing price = P = 0
N = number of outstanding shares in dividend payment ratio
n = new share in dividend payment ratio
P0 = opening market price of share p = issuing price
Value of share purchase right: Qm = P0 - P1 = 44,700 - 37,250 = 7,450
Exercise 17: Thang Long Invest Group (TIG, listed on HNX) discloses information related to its
share dividend payment policy as following:
- Ex-date: August 01, 2017 (Tuesday)
- Record-date: August 02, 2017 (Wednesday)
- Content: Paying dividend in shares for outstanding investors
- Dividend payment ratio: 20:1 (An investor with 20 outstanding shares receives 01 new share)
- Rounding rule: The number of new shares that investors can receive under
TIG’s share dividend payment policy are rounded down to units before the decimal sign (for
example: if the investor A, based on TIG’s policy, can receive 111.1 shares, after rounding, he/she receive 111 shares only)
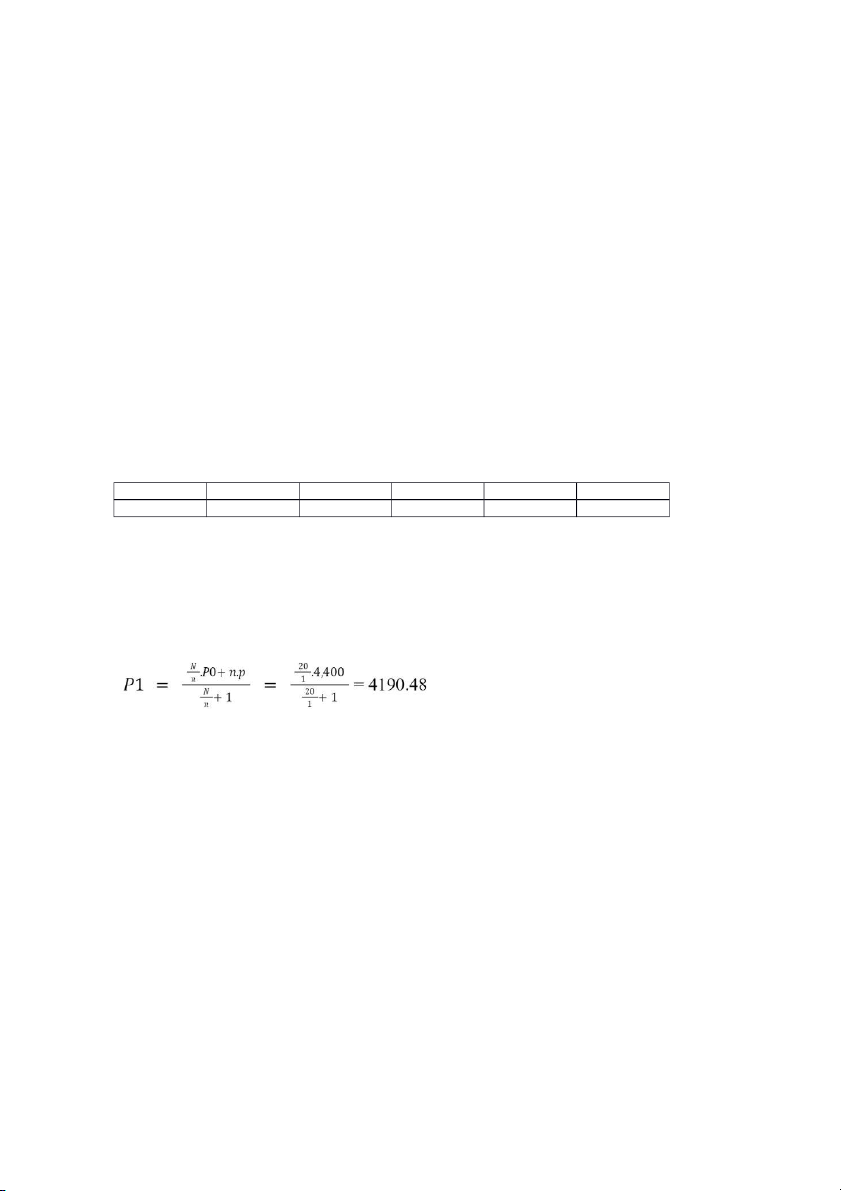
Determine TIG’s market price on the ex-date, given TIG’s closing prices on following days: Share code Jul. 31 Jul. 28 Jul. 27 Jul. 26 Jul. 25 TIG VND 4,400 VND 4,600 VND 4,600 VND 4,600 VND 4,500
The payment process of Vietnam’s stock market is T+2
TIG’s market price before Ex-date is P0 = 4,400 in 31/7
TIG’s policy is share dividend payment => Issuing price = P = 0
TIG’s market price on Ex-date:
N = number of outstanding shares in dividend payment ratio
n = new share in dividend payment ratio
P0 = opening market price of share p = issuing price
Exercise 18: Van Phat Hung Corporation (VPH, listed on HOSE) releases information on their coming
issuance of share purchase rights to outstanding investors. Summary of the company’s announcement is as below:
- Type of shares: Common shares
- Face Value: VND 10,000
- Ex-date: Oct 31, 2017 (Tuesday)
- Record-date: Nov 01, 2017 (Wednesday)
- Issuing price: VND 10,000
- Issuing ratio: 5:1 (01 outstanding share is equivalent to 01 share purchase right, and
05 share purchase right could be used to buy 01 new share under the coming issue)
- Rounding rule: the number of new shares that investors could buy based on their outstanding
shares and rights are rounded down to units before the decimal sign (for example: if the
investor A has share purchase rights to buy up to 24.2 share, after rounding, he/she could buy 24 shares only)
- Registration and payment for executing rights: Nov 07, 2017 – Dec 04, 2017
a/ Determine VPH’s market price on the ex-date, and the value of share purchase right. Given that:
Payment process of Vietnam’s stock market is T+2
Closing price of VPH shares on Oct 30, 2017 is VND 12900
Closing price on Oct 30, 2017 is the opening price on Nov 1, 2017
VPH’s market price on ex-date:
N = number of outstanding shares in dividend payment ratio
n = new share in dividend payment ratio
P0 = opening market price of share p = issuing price
The value of share purchase price = Qm = P0 - P1 = 12,900 - 12,416.67 = 483.33
b/ Suppose that an investor A is holding 5000 VPH shares on Oct 26, 2017. Determine
(1)-the number of new shares that A could buy
Number of shares A could buy = 5,000 x 1/5
(2) value of all the rights A has
(3) -the amount of money that A has to pay VPH to execute all rights that A owns, for each of
following cases (from b.1 to b.9):
b.1. A continues to hold 5000 VPH shares until Dec 31, 2017
b.2. A sells 5000 VPH shares on Nov 08, 2017 (Wed.)
b.3. A sells 5000 VPH shares on Oct 27, 2017 (Friday)
b.4. A sells 5000 VPH shares on Oct 31, 2017 (Tue., ex-date)
b.5. A sells 5000 VPH shares on Nov 01, 2017 (Wed., Record date)
b.6. A buys 2000 VPH shares on Oct 30, 2017 (Mon.)
b.7. A buys 3000 VPH shares on Oct 31, 2017 (Tue, ex-date)
b.8. A sells 3000 VPH shares on Oct 30, 2017 (Mon.)
b.9. A sells 5000 VPH shares on Nov 08, 2017 (Wed.)
c/ Determine A’s investment profit by Dec 29, 2017 for each of cases listed above (b.1. – b.9.). Given that:
VPH shares’ closing price on Dec 29, 2017 is VND 11250;
A sells all his VPH shares on Dec 29, 2017 with closing price;
A did not place any other buy/sell orders between Oct 26 and Dec 28, except for orders specified
in above cases (b.1 to b.9)