









Preview text:
CHAP 8
Planning: the process of setting objectives & determining how best to accomplish them.
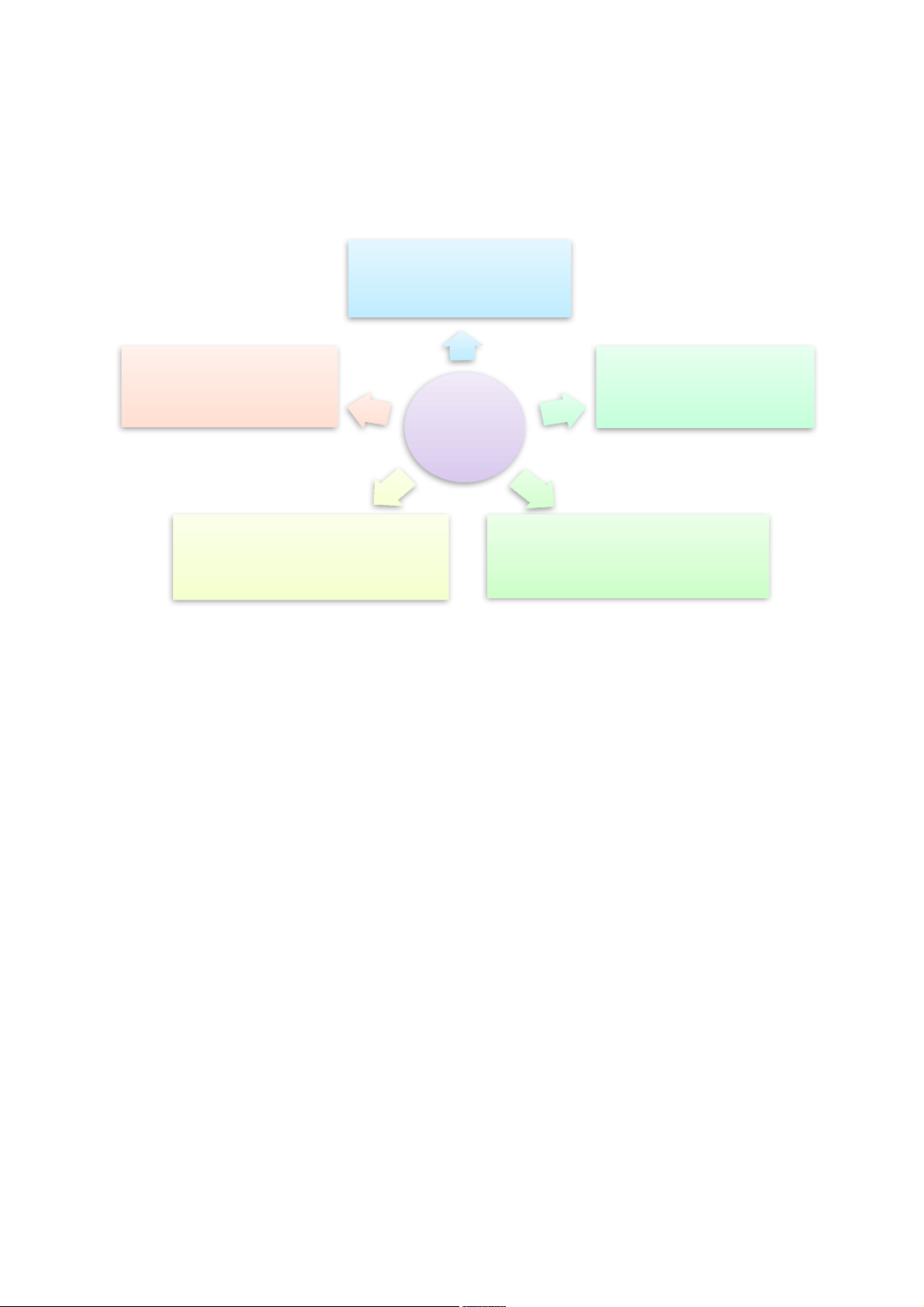
Why and how managers plan 1. Importance of planning
Planning – to set the direction •Decide where you want to go
•Decide how best to go about it
Organizing – to create structures
Leading – to inspire effort
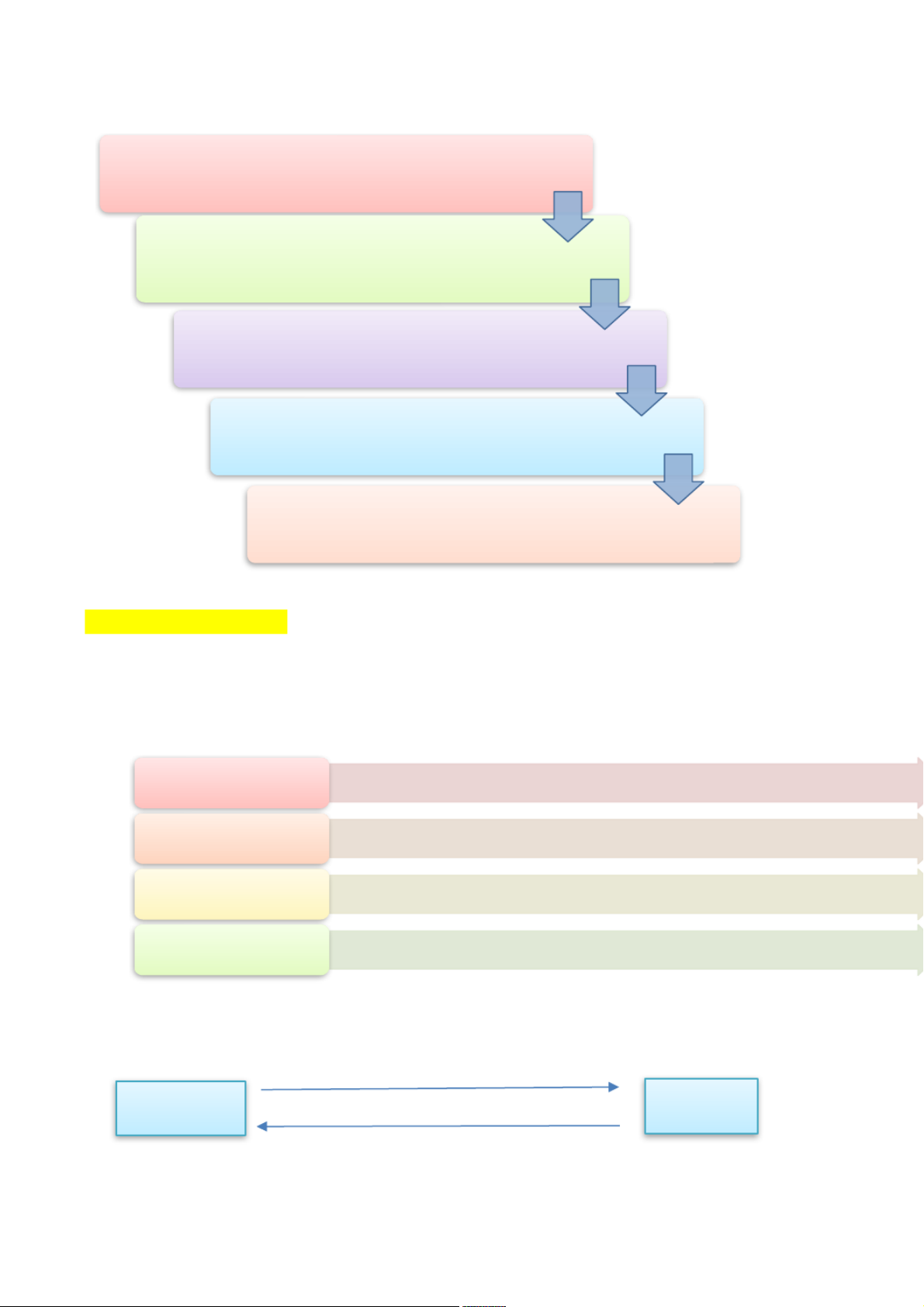
Controlling – to ensure results •Measure performance •Take corrective action 2. Planning process -
Objectives & goals are specific results or desired outcomes that one intends to achieve.
-A plan is a statement of intended means (Phuong tien du dinh) for accomplishing objectives.
-Planning is an ongoing process, done continuously while dealing with an otherwise busy & demanding work setting
Define your objectives – identify desired outcomes or results in very specific ways
Determine where you stand vis-à-vis objectives –
evaluate current accomplishments relative to the desired results
Develop premises regarding future conditions – anticipate future events
Analyze alternatives & make a plans – list & evaluate possible actions
Implement the plan & evaluate results – take action &
carefully measure your progress toward objectives 3. Benefits of planning
-Planning improves focus and flexibility: An organization with flexibility is willing to &
able to change & adapt to shifting circumstances without losing focus, & it operates
toward the future rather than the past.
-Planning improves action orientation: Action oriented
keeping a results-driven sense of direction
Priority oriented making sure the most important things get first attention Advantage
ensuring that all resources are used to best advantage oriented
anticipating problems & opportunities so they can be best
Change oriented dealt with.
-Planning improves coordination and control: Objectives & standards for measuring how
things are going & identifying what could be done to make them go better Planning Control
The follow-through to ensure that things work out as planned
=> It’s a lot easier to spot when things aren’t going well and make the necessary adjustment
4. Planning and time management: in daily living and in management, it is important to distinguish between: Top priority High priority (must do) (should do) Low priority No priority (would be nice to (really do not need do) to do)
Types of plans used by managers
1. Long-range and short-range plans
2. Strategic and tactical plans: a vision classifies the purpose of the organization and
expresses what it hopes to be in the future
Strategic plans identify long-term direction for the organization
-Set board action directions
-Create a frame reference for allocating resources for maximum performance impact
Tactical plans are developed and used to implement all or parts of strategic plans
Nhiều tactical -> strategy Top managers Middle managers
Tactical plans: in business often take the
form of functional plans that indicate
how difference components of the First-line managers
enterprise will contribute to the overall strategy Non-managerial workers
•Production plans – dealing with work methods & technologies.
•Financial plans – dealing with money & capital investments.
•Facilities plans – dealing with facilities & work layouts.
•Logistics plans – dealing with suppliers & acquiring resource inputs.
•Marketing plans – dealing with selling & distributing goods or services.
•Human resource plans – dealing with building a talented workforce.
3. Operational plans: guide behavior & describe what needs to be done in the short term to
support strategic & tactical plans. -
Standing plans like policies & procedures that are used over & over again. -
Single-use plans like budgets that apply to one specific tasks or time period 4.
Takeaway 4 (quan trọng) 1. Goal setting Specific Desired outcomes clear to anyone Attainable Timely Realistic, possible to Linked to due date & accomplish Great timetable goals Challenging Measurable
Include “stretch,” focused on No doubt when doing better accomplished, or missed 2. Goal alignment
-Goal set everywhere in the organization should ideally help advance its overall mission
of purpose (những người chức vụ nhỏ vẫn nên biết về mục tiêu của công ty) -
Goal alignment: the process by which you keep your workforce working towards your company’s overall goals
-The conversations between team leaders (supervisors) & team members (subordinates)
should result in agreements on:
(1) Performance objectives for a given time period
(2) Plans through which they will be accomplished
(3) Standards for measuring whether they have been accomplished
(4) Procedures for reviewing performance results
=> Management by objective (MBO) (Peter Drucker)
Goal alignment between team leader & member Jointly plan Individually set Jointly control Set objectives Perform tasks Review results Set standards (member) Discuss implications Choose actions Provide support Renew cycle (leader)
3. Participation and involvement D e fi n p la ig o b jctfi v e sD trm in w h g a d -à o b jc lp fu Iy & k




