

Preview text:
CHAP 9:
Takeaway 1 Managerial control
1. Importance of controlling
•Controlling: the process of measuring performance & taking action to ensure desired results.
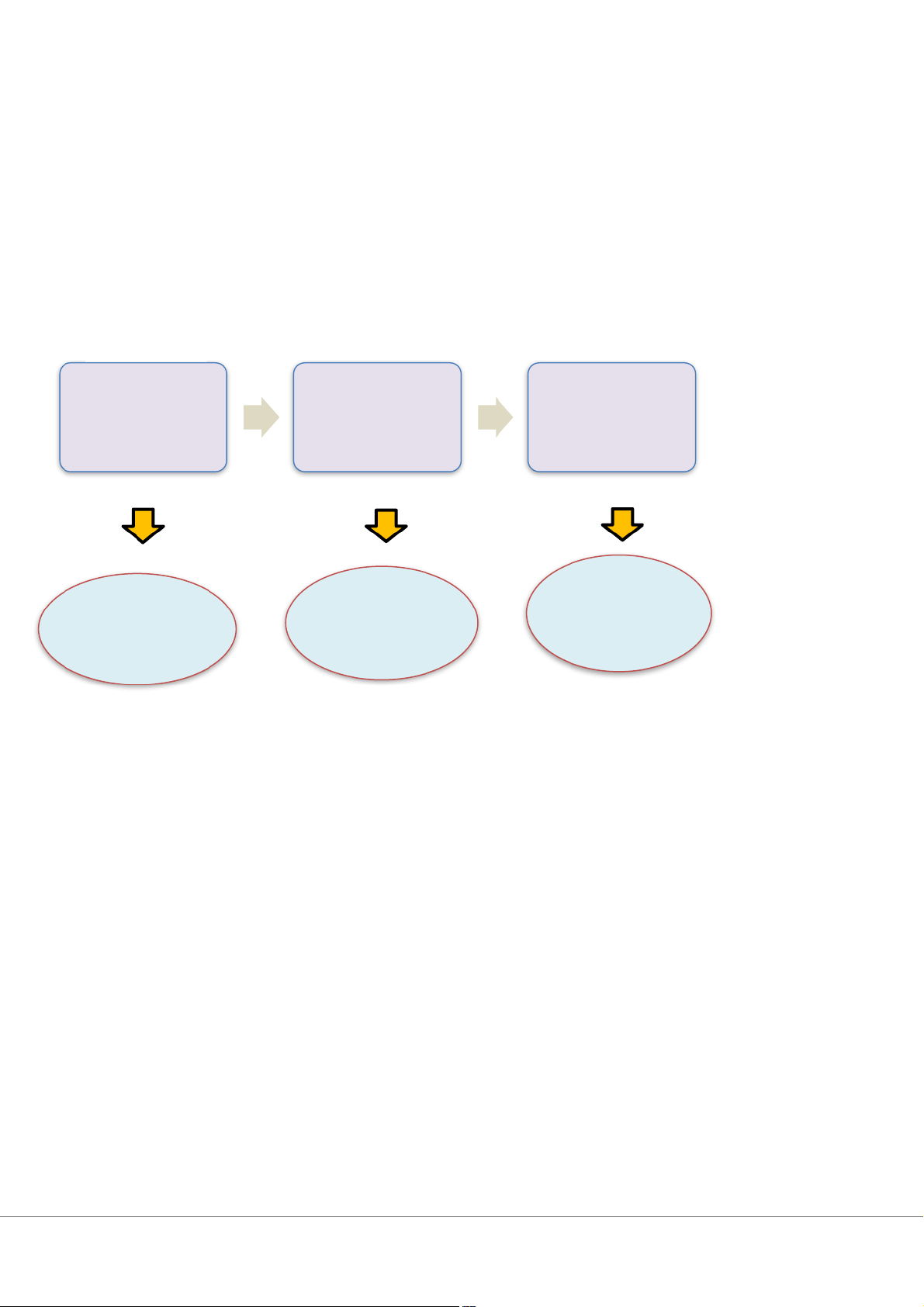
•An after-action review is a systematic assessment of lessons learned and results accomplished in a completed project. 2. Types of control Work inputs Work throughouts Work outputs Feedforward controls Concurrent controls Feedback controls Ensure the right Ensure the right Ensure that final directions are set & things are being done results are up to the right resource as part of workflow desired standards inputs are available operations Solve problems Solve problems Solve problems after they while they are before they occur occurring occur
Feedforward controls (preliminary controls) ensures that: ( thông báo trước …) - Objectives are clear -
Proper directions are established -
The right resources are available to accomplish the objectives
Concurrent controls (steering controls) make sure things are being done according to plan
Feedback controls (post-action controls) focus on the quality of end results prevent future problems
3. Internal and external control
(1) Allow & expect people to control their own behavior Internal control Self-control
Bureaucratic/administrative control External control Clan/normative control Market/regulatory control
(2) Structure situations to make sure things happen as planned Internal control Self-control
Self-control is internal control that occurs through self-discipline in fulfilling work & personal responsibilities Managers can do:
unlocking: help people to be good at self-management.
allowing: give them freedom.
supporting: encourage them to exercise self-discipline in performing their jobs.
The organizational culture should be like:
emphasize participation, empowerment & involvement.
everyone treats each other with respect & consideration
Bureaucratic/administrative control External control Top
Bureaucratic/administrative control managers
Bureaucratic control flows through the organization’s hierarchy Middle managers of authority. First-line managers Non-managerial workers External control Clan/normative control
•Clan control influences behavior through norms and expectations set by the organizational culture.
•Clan control happens as persons who share values and identify strongly with one another behave in consistent ways.
Takeaway 2 The Control Process St T ep a kea4 ne cti c oe y nssar Establ o peirS s bj t e S foep h r c t M t r i & ea pe mv s ep m 1 r t s fo anc ea 2 a s ur e e nc al nda e r a d ctu Com o S part bj ep e pei a rt ec c t 3 t foi ua rm ve t l s a anc & e h s nda r w ds




