






Preview text:
CHAPTER 10: BE10.3 (LO2)
Zhang Ltd. (see BE10.2) borrowed HK$1,000,000 on March 1 on a 5-year, 12% note to help
finance construction of the building. In addition, the company had outstanding all year a 10%, 5-
year, HK$2,000,000 note payable and an 11%, 4-year, HK$3,500,000 note payable. Compute the
capitalization rate used for interest capitalization purposes. Principal Interest Rate Interest 5-year note $2,000,000 10% $200,000 4-year note $3,500,000 11% $385,000 Total $5,500,000 $585,000
Capitalization rate used for interest capitalization purposes = $585,000 = 10.64% $5,500,000 BE10.10 (LO3)
Mehta SE traded a used welding machine (cost €9,000, accumulated depreciation €3,000) for
office equipment with an estimated fair value of €5,000. Mehta also paid €3,000 cash in the
transaction. Prepare the journal entry to record the exchange. (The exchange has commercial substance.) Office Equipment $5000 Accumulated Depreciation $3000 Loss on Disposal $4000 Machine $9000 Cash $3000
E10.3 (LO1) (Acquisition Costs of Trucks)
Haddad Corporation operates a retail computer store. To improve delivery services to customers,
the company purchases four new trucks on April 1, 2019. The terms of acquisition for each truck are described below.
1. Truck #1 has a list price of $15,000 and is acquired for a cash payment of $13,900.
2. Truck #2 has a list price of $20,000 and is acquired for a down payment of $2,000 cash
and a zero- interest-bearing note with a face amount of $18,000. The note is due April 1,
2020. Haddad would normally have to pay interest at a rate of 10% for such a borrowing, and
the dealership has an incremental borrowing rate of 8%.
3. Truck #3 has a list price of $16,000. It is acquired in exchange for a computer system that
Haddad carries in inventory. The computer system cost $12,000 and is normally sold by
Haddad for $15,200. Haddad uses a perpetual inventory system.
4. Truck #4 has a list price of $14,000. It is acquired in exchange for 1,000 ordinary shares in
Haddad Corporation. The shares have a par value per share of $10 and a market price of $13 per share. Instructions
Prepare the appropriate journal entries for the foregoing transactions for Haddad Corporation.
(Round computations to the nearest dollar.) 1. Truck No.1 $13,900 Cash $13,900 2. Truck No.2 $18,364 Cash $2,000 Notes Payable $16,364 $18,000
Present Value of Truck No.2 = $2,000 + 1+10% = $18,364 3. Truck No.3 $15,200 Cost of Goods Sold $12,000 Inventory $12,000 Sales $15,200 4. Truck No.4 $13,000 Share Capital – Ordinary $10,000 Share Premium – Ordinary $3,000 E10.7
a. Capitalisation rate computed Principal Interest Rate Interest Short – term loan €1,600,000 10% €160,000 Long – term loan €1,000,000 11% €110,000 €2,600,000 €270,000 €270,000
Capitalisation rate =
€2,600,000 = 10.38% Avoidable interest Weighted – Average Accumulated Expenditures Interest Rate Avoidable Interest €2,000,000 12% €240,000 €1,800,000 10.38% €186,840 €3,800,000 €426,840 b. Actual Interest Construction loan €2,000,000 x 12% €240,000 Short – term loan €1,600,000 x 10% €160,000 Long – term loan €1,000,000 x 11% €110,000 Total €510,000
Because avoidable interest < actual interest, use avoidable interest
Total cost = €5,200,000 + €426,840 = €5,626,840 5,626,840−300,000
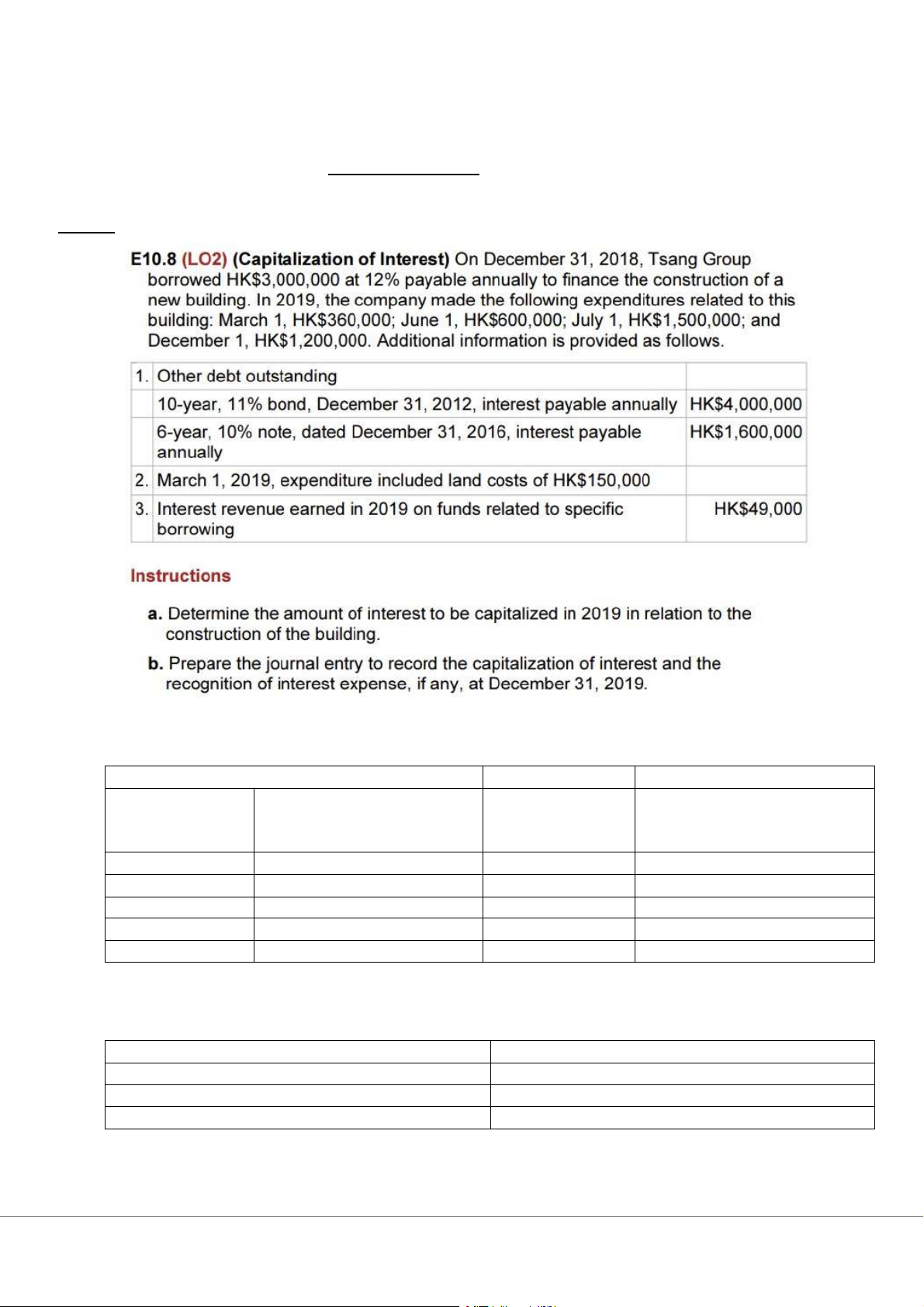
Depreciation Expense = 30 = 177,561 E10.8
a. Weighted – Average Accumulated Expenditures Computation Expenditures Weighted Date Amount Capitalisation – Average Accumulated Period Expenditures Mar 1 $360,000 10/12 $300,000 Jun 1 600,000 7/12 350,000 Jul 1 1,500,000 6/12 750,000 Dec 1 1,200,000 1/12 100,000 $3,660,000 $1,500,000
Actual Interest Computation $3,000,000 x 12% $360,000 4,000,000 x 11% 440,000 1,600,000 x 10% 160,000 $960,000
Avoidable Interest = $1,500,000 x 12% = $180,000
Use Avoidable Interest for Capitalisation purposes because it is lower than Actual Interest
b. Interest Expense = $960,000 – 180,000 + 49,000 = $829,000 Building 131,000 Interest Expense 829,000 Cash 960,000
E10.18 (LO3) (Non – Monetary Exchange)
Montgomery Ltd. purchased an electric wax melter on April 30, 2020, by trading in its old gas
model and paying the balance in cash. The following data relate to the purchase. Instructions
Prepare the journal entry(ies) necessary to record this exchange, assuming that the exchange (a)
has commercial substance, and (b) lacks commercial substance. Montgomery's year ends on
December 31, and depreciation has been recorded through December 31, 2019.
a. Exchange has commercial substance 12,700− 5x7 400 Depreciation Expense = = 12 800
Gain/Loss on Disposal of Old meter
= Fair Value – Carrying Amount = 5,200 – (12,700 – 7,200) = 500 Gain 500
Cost of New meter = 10,000 + 5,200 = 15,200 Journal Entry Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation – Melter 800 800 Melter 15,200
Accumulated Depreciation – Melter 8,000 Gain on Disposal of PPE 500 Melter 12,700 Cash 10,000
b. Exchange lacks commercial substance Cost of New meter
= Cash paid + Fair value of Old meter + Gain deferred
= 10,000 + 5,200 - (5,200 – 4,700) = 14,700 Journal Entry Depreciation Expense 800 Accumulated Depreciation – 800 Melter Melter 14,700
Accumulated Depreciation – Melter 8,000 Melter 12,700 Cash 10,000 E10.24 Jan. 30
Accumulated Depreciation – Buildings = 112,000 x 5% x 17 = 95,200
Gain/Loss on Disposal of PPE = - 5,100 – (112,000 – 95,200) = - 21,900 Journal Entry Acc Depreciation – Buildings 95,200 Loss on Disposal of PPE 21,900 Buildings 112,000 Cash 5,100 Mar. 10
Accumulated Depreciation – Buildings = 70% x 16,000 = 11,200
Gain/Loss on Disposal of PPE = 2,900 – 300 – (16,000 – 11,200) = - 2,200 Journal Entry Cash 2,600 Acc Depreciation – Machinery 11,200 Loss on Disposal of PPE 2,200 Machinery 16,000 Mar. 20 Machinery 3,000 Cash 3,000 May 18
Accumulated Depreciation – Buildings = 4,000 x 60% = 2,400
Gain/Loss on Disposal of PPE = 2,400 – 4,000 = - 1,600 Journal Entry Machinery 5,500 Acc Depreciation – Machinery 2,400 Loss on Disposal of PPE 1,600 Machinery 4,000 Cash 5,500 Jun. 23
Building Maintenance and Repairs Expense 6,900 Cash 6,900