







Preview text:
Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 CHAPTER 11:
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURES AND DESIGNS
- Organizing is the process of arranging people and other resources to work
together to accomplish a goal. → create a division of labor and then coordinate
results to achieve a common purpose.
I. What is organizational structure?
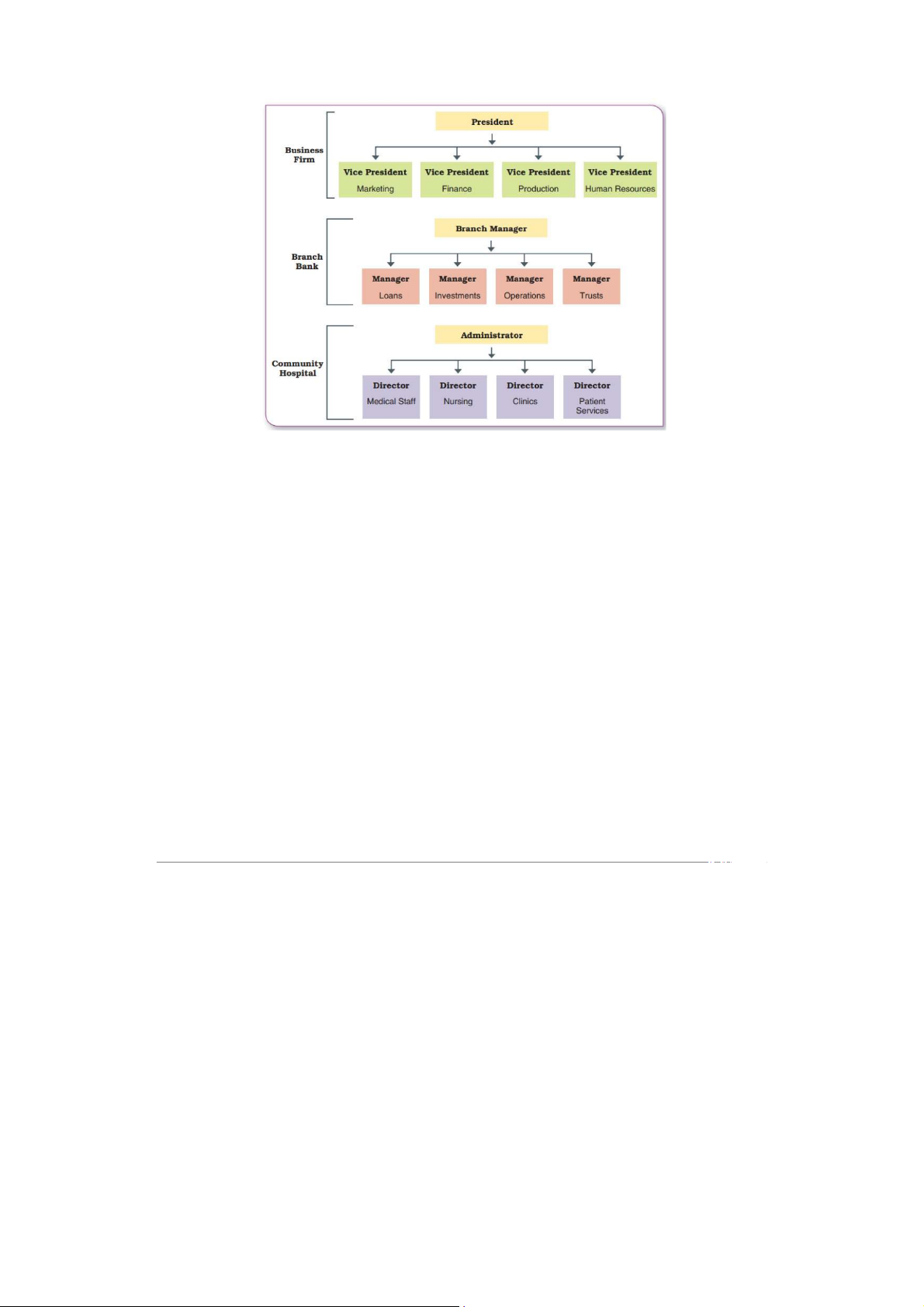
-Organization structure is a system of tasks, reporting relationships, and communication linkages.
-Formal structure is the official structure of the organization. →
Organizational chart shows the formal structure, or how the organization is
intended to function. It describes the arrangement of work positions within an organization.
Ex: Ví dụ sếp với nhân viên sẽ có title rõ ràng level rõ ràng
-Informal structure is the set of unofficial relationships among an
organization’s members. We know who talks and interacts with whom,
regardless of their formal titles and relationships. → Informal structure
impacts an individual’s job satisfaction. The motivation for coming to work is
because of the social interaction with colleagues and managers
Ex1: Chẳng hạn 2 bạn đều là nhân viên như nhau, nhưng vì một lý do
nào đó ví dụ do cơ ba bạn kia to, bạn kia perform tốt hơn,... vô hình chung đã
chia levels dù các bạn đều là nhân viên như nhau,... Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
Ex2: Dù CEO là vị trí cao nhất của công ty theo Formal, tuy nhiên kế
toán trưởng nhiều khi còn chi phối được CEO vì họ nắm được những sai phạm
của CEO (trốn thuế, hối lộ,...)
-> Các bạn có thể tìm organizational chart của 1 công ty ở website của công ty đó
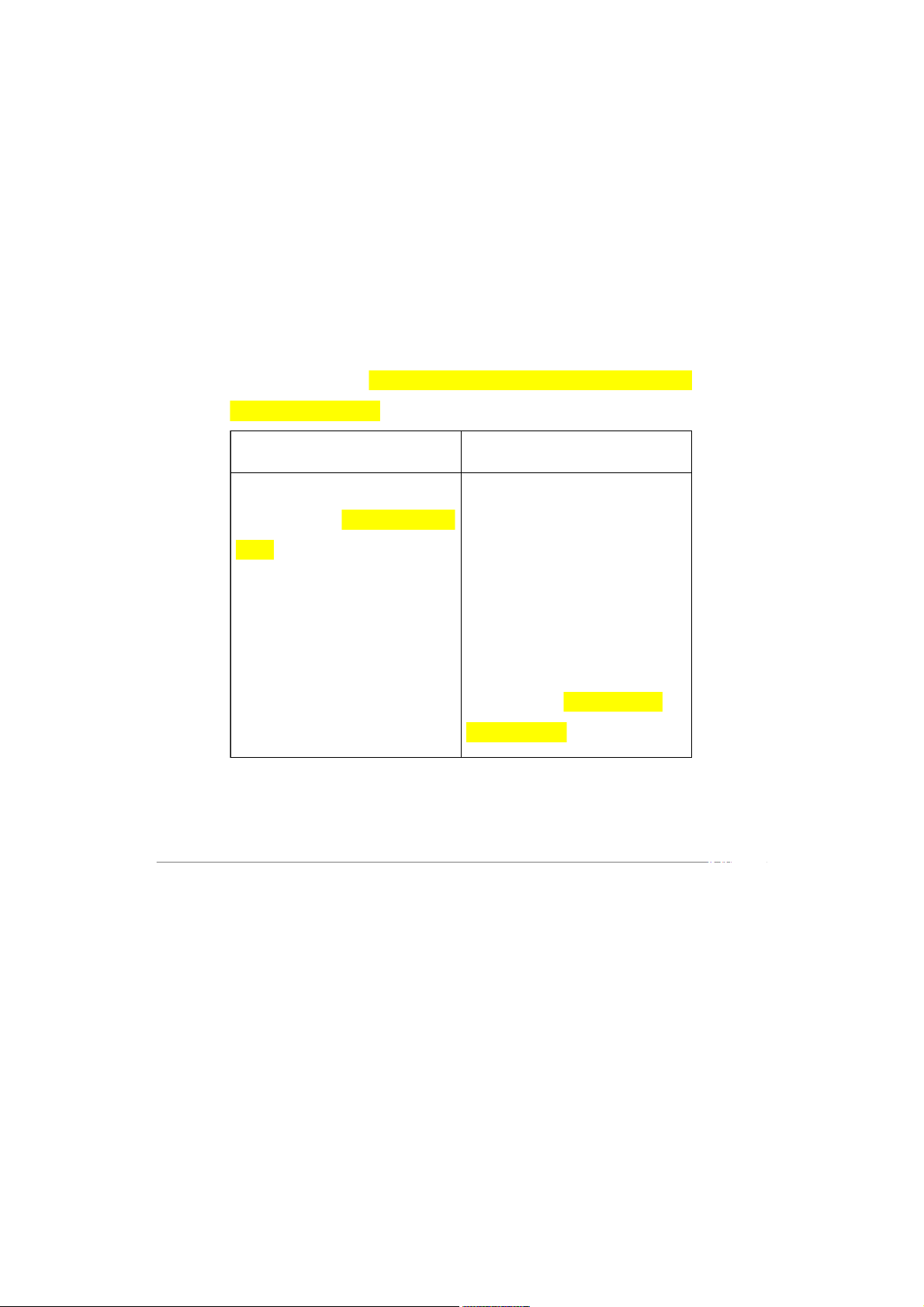
II. Traditional Organization Structures 2.1 Functional structure
- A functional structure groups together people with similar skills who
perform similar tasks. (Gộp những người có chuyên môn giống nhau để cùng nhau
làm những tasks giống nhau) Advantage Disadvantage
- Economies of scale with efficient
- Functional chimneys or functional
use of resources. (Sử dụng hiệu quả tài silos problem—a lack of nguyên)
communication, coordination, and
- Task assignments consistent with
problem solving across functions. expertise and training.
(Thiếu sự giao tiếp giữa cá thành
- High-quality technical problem viên các ban khác nhau) solving. - Difficulties in pinpointing - In-depth training and skill
responsibilities (Khó chỉ định được development within functions. trách nhiệm cụ thể) Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
- Clear career paths within functions. Ex: Ví dụ doanh thu của sản phẩm
không tăng → Do Marketing không tốt
hay là do sales không tốt, hay do team
Phát triển sản phẩm không tốt?
- Sense of cooperation and common purpose break down
- The narrow view of performance
objectives. (Thiếu đi cái nhìn bao quát
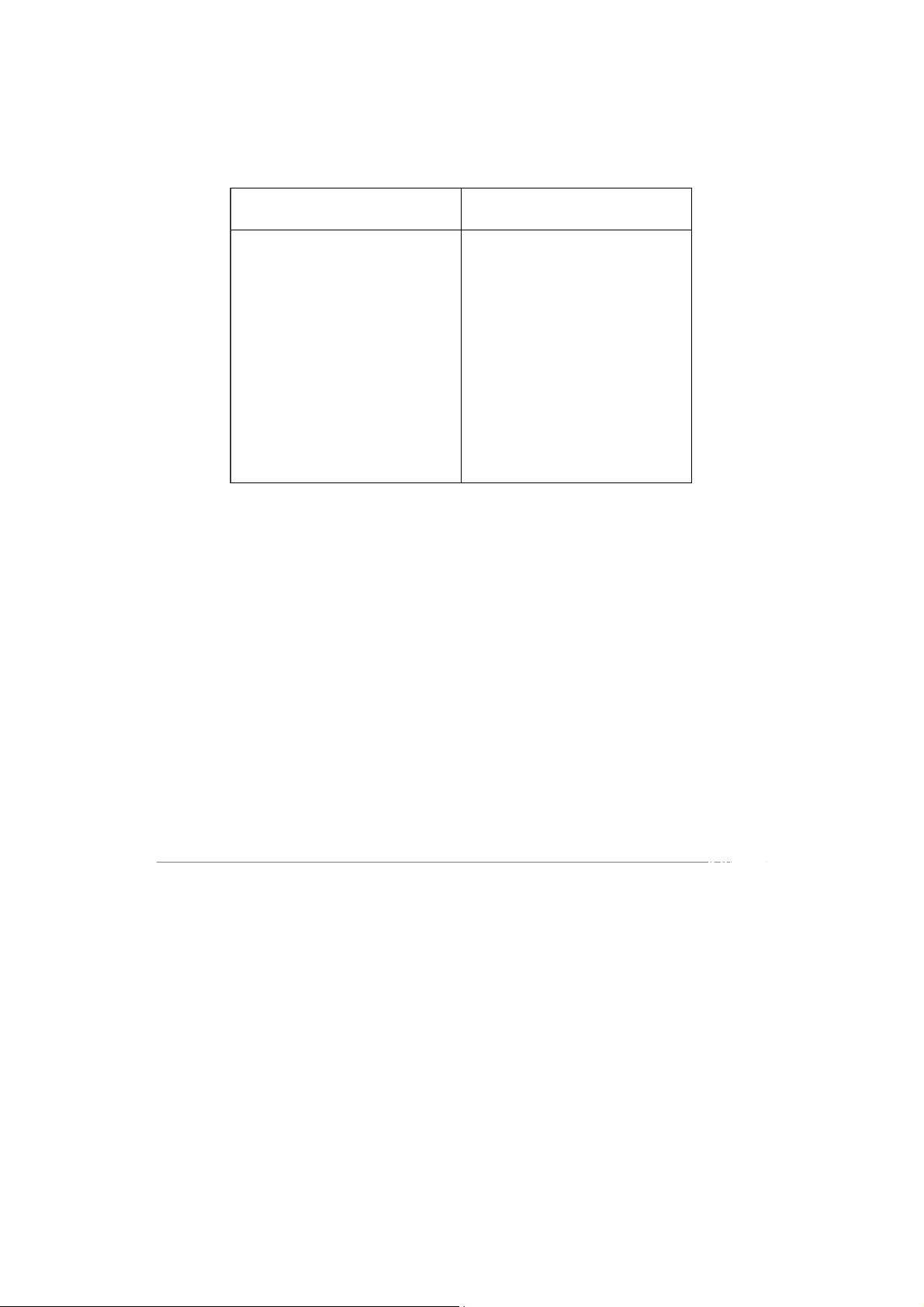
về mục tiêu chung, mỗi ban chỉ hiểu nhiệm vụ của mình) Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 2.2 Divisional structure
- A divisional structure groups together people working on the same product,
in the same area, with similar customers, or on the same processes.
+A geographical structure groups together people and jobs performed in the same location.
+A product structure groups together people and jobs focused on a single product or service.
+A customer structure groups together people and jobs that serve the same customers or clients Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
+A process structure groups jobs and activities that are part of the same processes Advantage Disadvantage
- More flexibility in responding to
- Duplication of resources and efforts environmental changes across divisions
- Competition and poor coordination - Improved coordination across divisions
- Clear points of responsibility
- Emphasis on divisional goals at
- Expertise focused on specific
expense of organizational goals
customers, products, and regions
- Greater ease in restructuring Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 2.3 Matrix structure
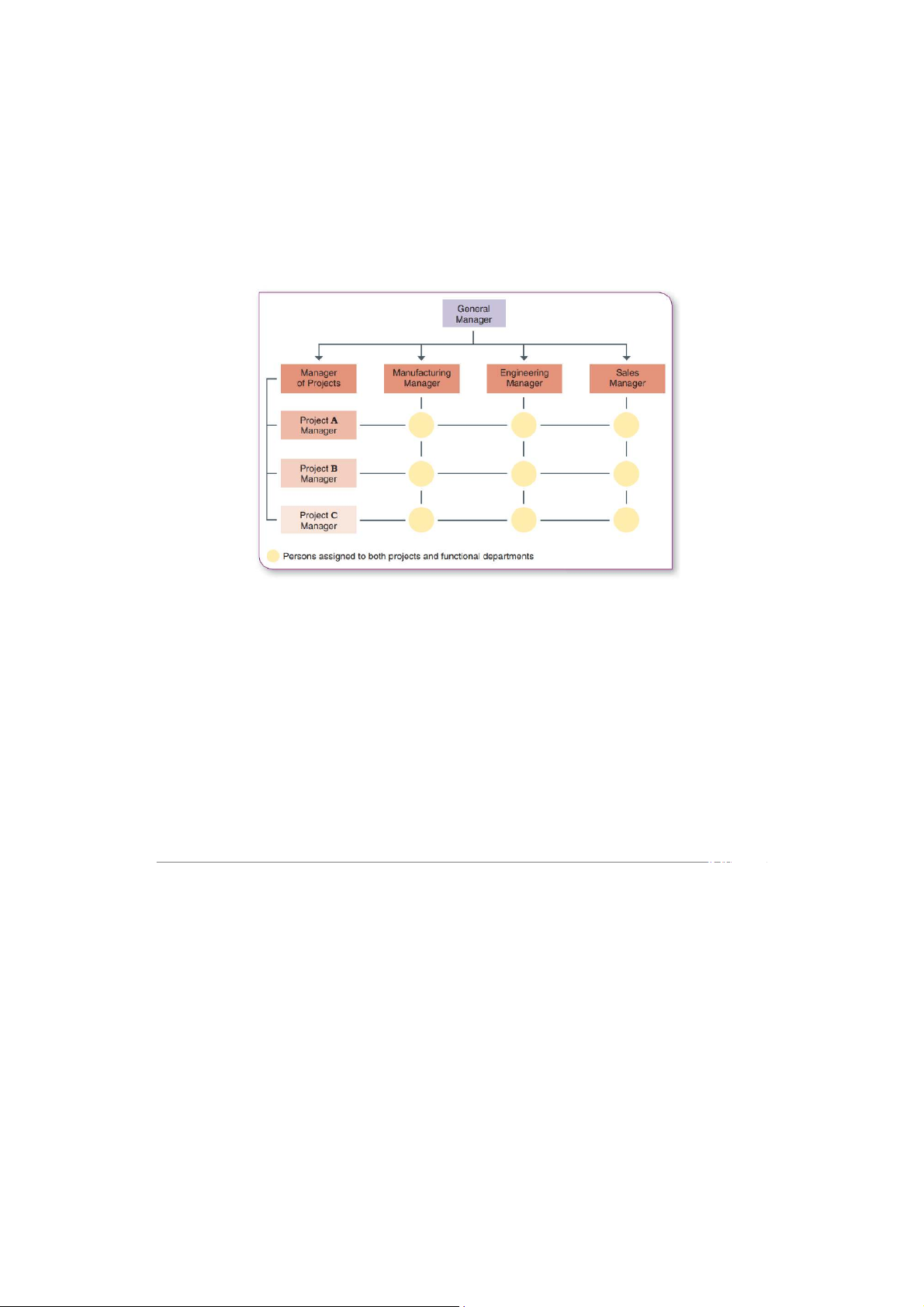
The matrix structure, oen called the matrix organization, combines the
functional and divisional structures
+ This is accomplished by creating permanent teams that cut across
functions to support specific products, projects, or programs.
+ Used in: multinational corporations, manufacturing (e.g., aerospace,
electronics, pharmaceuticals), service industries (e.g., banking,
brokerage, retailing), professional fields (e.g., accounting, advertising,
law), and the nonprofit sector (e.g., city, state, and federal agencies, hospitals, universities). Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
+ For example: Imagine you work in an advertising agency as a video
producer. You will probably have to report to the media department
manager, your functional chain of command boss – the head of your
department. However, you will probably also have to report to somebody
who is in charge of a specific project for a client – the project manager –
he or she is your boss in the project chain of command. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 Advantage Disadvantage
– Better cooperation across functions - Two-boss system is susceptible to power struggles – Improved decision making
- Two-boss system can create task – Increased flexibility in
confusion and conflict in work restructuring priorities – Better customer service
- Team meetings are time consuming
– Better performance accountability
- Team may develop “groupitis”
- Increased costs due to adding team
– Improved strategic management leaders to structure III. Horizontal Structures
-A team structure uses permanent and temporary cross-functional teams to improve lateral relations.
- A cross-functional team brings together members from different functional
departments (opposite to matrix organization)
- A network structure uses information technologies to link with networks of
outside suppliers and service contractors. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
- A boundaryless organization eliminates internal boundaries among
subsystems and external boundaries with the external environment. → The
virtual organization takes the boundaryless concept to the extreme. A virtual
organization uses IT and the Internet to engage a shiing network of strategic alliances
IV. Trends in organizational design
- Bureaucracy (không thấy thầy nhắc) Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
- A mechanistic design is centralized, with many rules and procedures, a
clear-cut division of labor, narrow spans of control, and formal coordination. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
Mở rộng kiến thức: Compare between the traditional structure and the modern one Traditional Modern Authority
- centralize authority: decision- - decentralize authority: making authority is maintained decision-making authority is at the top level of management
delegated to lower level managers
more familiar with local conditions - bureaucratic than headquarters management could be. - democratic Stability
stable in business activities and more dynamic with multiple progress
business strategies, which need
multiple processes to deal with constant changes. hierarchy (thứ Tall Hierarchy:
Flat Hierarchy: networking together bậc) and collaborating - power flows vertically and upward, the higher level of management, the more power they have
- the flat chain of command with few
- the vertical chain of command layers with many layers Employee Morale - pressure, inflexible,
more freedom and flexibility to uncomfortable fulfill their works Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 Management - conservative - do modification such as policy rescheduling, flexible entity - follow traditional rules and management, dynamic business regulation strategy
- make static workflow model to maintain business strategy Technology - centralized and backward to - more technology based and accept advanced technology boundaryless. So the number of
employee or the office compartment doesn’t matter Span of control:
- a small span of control because
A broad span of control because the optimal the top management rarely
directors can directly manage their number of directly manage their lowest employees subordinates a level. manager supervises or should supervise Report From the lowest level to the Many ways to report highest one - fast - slow, waste time Organizational - line organization
- cross-functional self-managed model teams - line and staff organization - virtual organization - matrix organization Formal organization Informal organization




